B&B - Class 8: Attention and Conciousness
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is attention on a psychological level?
Preferential allocation of processing resources to specific environmental stimuli
What is attention on a neural level?
Alternations in the selectivity, intensity, duration of neuronal responses to those stimuli
What are the four common “types” of attention
Alertness
Selective Attention
Vigilance
Divided Attention
What is top-down processes of attention also known as?
“Brain-first” processes
Top-down processes works by doing what?
Using ideas, models, expectations to interpret sensory info
Bottom-up processes works by doing what?
Taking sensory info and assembling and integrating it
When it comes to attention, its not a matter of which brain regions are involved so much as _____ and _____.
when, what direction
True or false? Top-down and bottom attention CANNOT influence each other.
False. They can influence each other.
Knowt won’t let me delete this on mobile
Poop
What is vigilance?
Ability to sustain attention in the face of distractors
“Sustained attention for social media” was an example for which type of vigilance?
Stimulus
“Kids with ADHD have a challenging time remaining vigiland in the face of any distractors” was an example for which type of vigilance?
Person-specific
“Anxious individuals show greater vigilance for anxiety-provoking stimuli” was an example for which type of vigilance?
Personal-stimulus
What is divided attention?
Ability to split attention towards multiple stimuli at the same time.
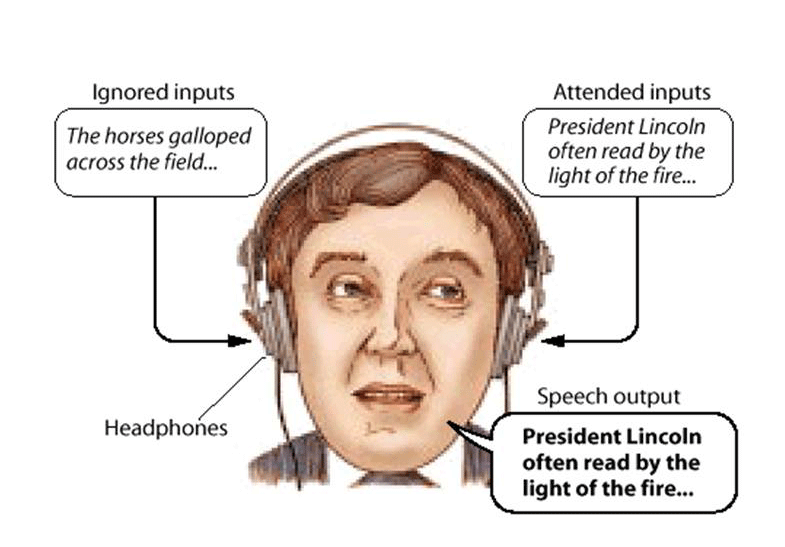
What is this task called and what ability does it show?
Dichotic listening. Our ability to divide attention
(Dichotic listening tasks are often used to evaluate divided attention)

This is a video demonstrating “____ ____” (Hint: it starts with in-)
inattentional attention
What is blindsight?
A neurological condition where someone can perceive the location of an object despite being cortically blind.
The person cannot visually see images, but part of the unconscious brain can still perceive them and their locations in space.
Why are people with blindsight blind?
Due to extensive damage to damage to the primary visual cortex (V1)
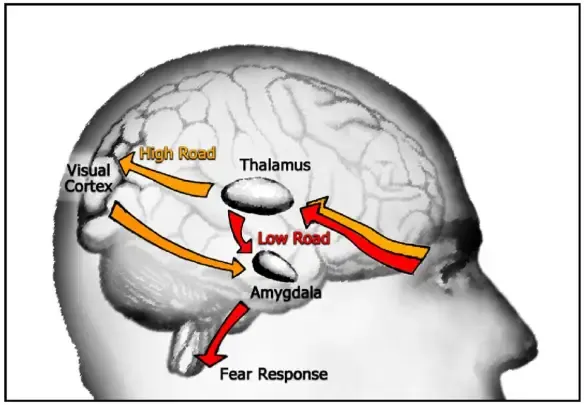
This image shows two types of our perception. What are they and what the two differences between the two. (More details in answer)
Low road perception and high road perception.
Low road = Evolutionary primitive, simple, reflexive. Reticular activating system, including amygdala
High Road = Evolutionarily newer, more complicated, less reflexive. Dorsal and ventral
Patients with blind sight have a damaged _____ perception.
high road
Somewhere between perception and experience is ____.
Conciousness
What is subliminal processing? What an example?
Stimuli that we don’t see that still “gets in”.
Blindsight
Blindsight is strong evidence that ____ and ____ are not the same thing?
attention, consciousness
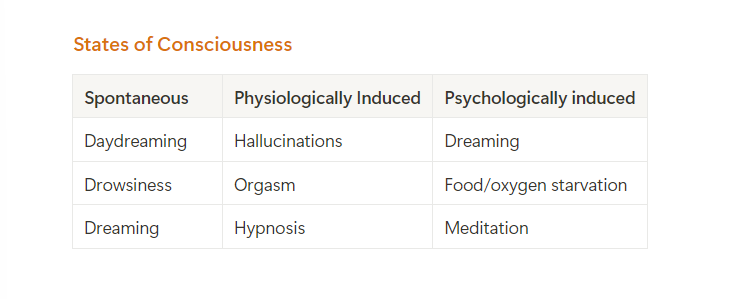
We have 3 types of states of consciousness. Give at least one example for each.
True or False? Two people, one in a coma, one not, will show similar brain activity to questions.
True
What is quality?
The objective qualities of individual stimuli
Qualia
Subjective quality of individual experience
Brainstem/Thalamus System is responsible for?
Wakefulness.
Necessary for the alert/awake component of consciousness.
Occipital/Parietal/Temporal Cortices is responsible for?
The Phenomenon of Consciousness.
Necessary for something to be experience conciously.
Frontal Cortices is responsible for?
Attention.
Necessary for guiding consciousness