Integrated Optics III
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
218 Terms
The basic parts of a frame are
the frame front
the temples
when connected by a solid bridge of any kind (metal or plastic), the frame front is the combination of
eyewires, bridge, and endpieces
the eyewire is
the rim of the frame that goes around the lenses.
the bridge is
the part between the two eyewires

What type of bridge is this?
(Plastic) Saddle Bridge - the weight is evenly distributed over the sides and crest of the nose
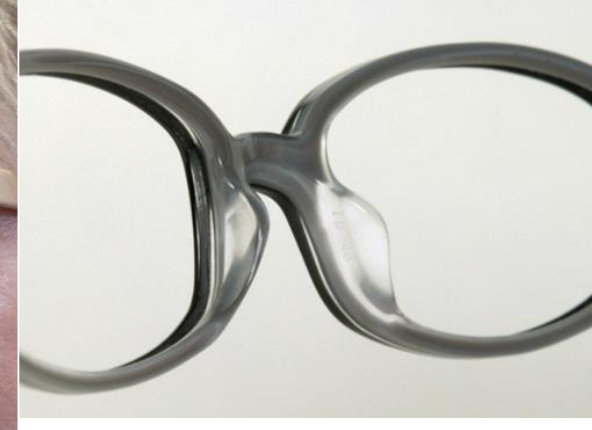

What type of bridge is this?
(Plastic) Modified Saddle Bridge - nose pads are added to help carry some of the weight of the frame
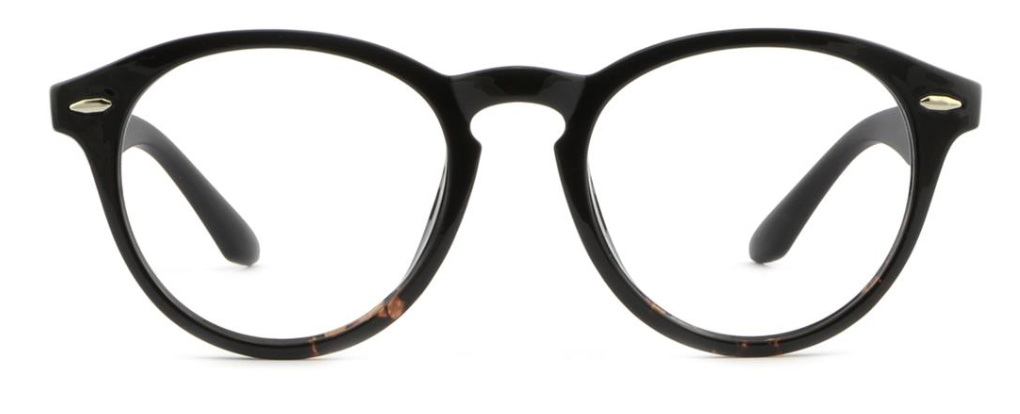

What time of bridge is this?
(Plastic) Keyhole Bridge - the bridge rests on the sides of the nose and not the crest of the nose
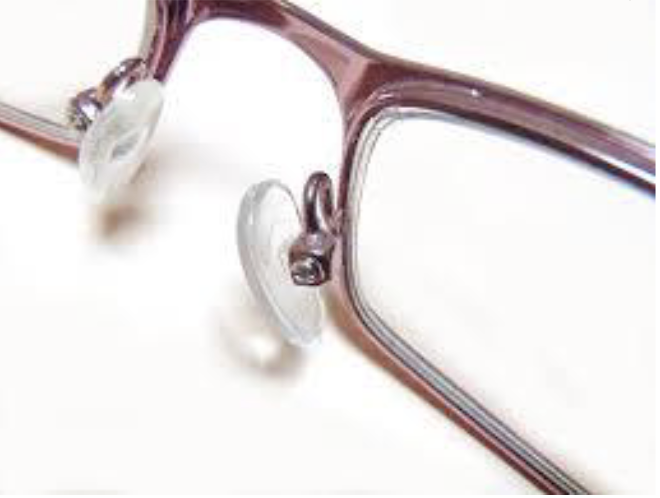
What type of bridge is this?
(Metal) Nose Pad Bridge - the pads support the weight of the glasses
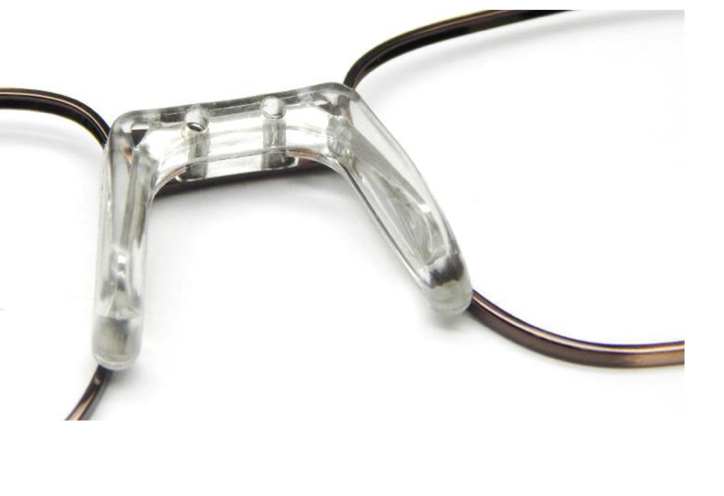

What type of bridge is this?
(Metal) Comfort Bridge - clear plastic saddle added with screws or snapped into a metal frame
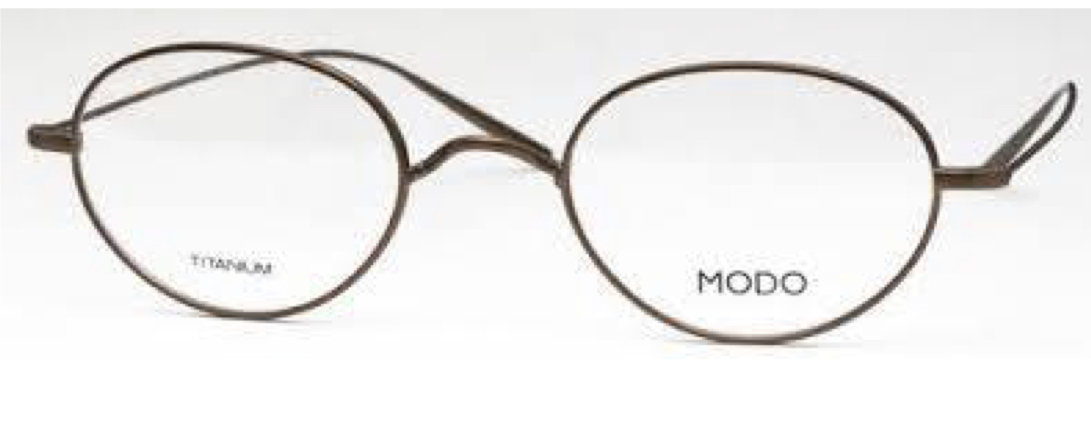

What type of bridge is this?
Metal Saddle Bridge - no nose pads or comfort bridge; can cause irritation
Nose pads are designed to
contact the nose, hold the frame up off the nose, and away from the face. they support the eright of the glasses.
Guard arms are
the small wire arm that holds the nose pad in place.
The endpiece is
one of the two outer areas of the frame front to the extreme left and right where the temples attach to the frame front
Hinges:
part where the temple is connected to the frame front, and allows the temple to fold in and out to the frame front and usually hed in place by a screw
Spring Hinge:
allow frames to stay in adjustment for a longer period of time
prevents stress on the temple that comes from constantly taking off glasses
they can freeze, break, and add weight to the frame
they don’t improve the fit
Temples:
the pieces that hold the frame front to the head and ears
run from the endpiece on the frame front back to behind the ear

What Temple style is this?
Skull - the most common temple style
bends down behind the ear and follows the contour of the skull
the bent-down portion is narrower at the top of the ear and widens towards the end

What temple style is this?
Riding Bow temple - plastic material
similar to comfort cable, seen on children’s frames
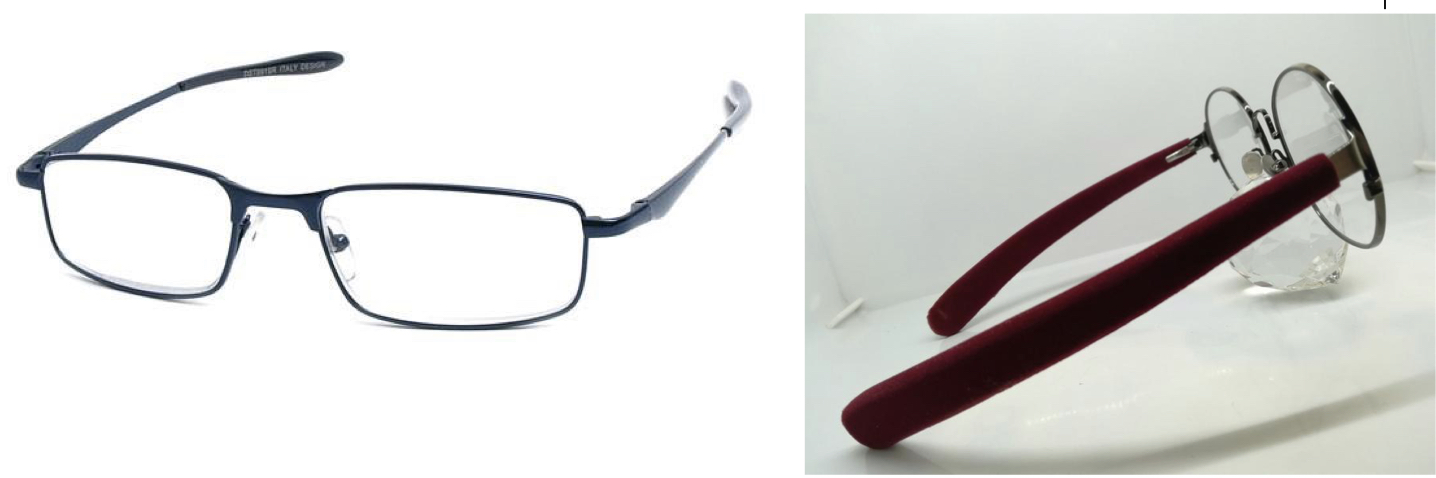

What Temple style is this?
Library - straight back
hold glasses on by pressure against the side of the head
originally popular for reading glasses
some sports glasses use this (it fits under helmet)

What Temple style is this?
Convertible Temple - versatile: can switch between skull and library

What Temple style is this?
Comfort Cable - metal material
wrap around the entire ear to hold glasses firmly in place
found on some safety glasses and shooting glasses
Temple Tips:
usually, removable plastic sleeves that slip over the ends of the metal temples to provide comfort for the wearer
the part of the temple on a plastic frame that goes behind the ear
Full Frame (Metal):
the metal frame has a solid metal eyewire that surrounds the entire lens
Full Frame (Plastic):
characterized by a plastic eyewire around the entire lens
Bevel:
how the lenses are held in place in most full frames
Cold Insert:
no heat to insert lenses
Semi-Rimless:
semi-rimless mounting/ groove mount/ logo
half an eyewire of metal or plastic with attached nylon fishing cord
can also be drill mounted
Combination Frame:
metal chassis and plastic top rims or frames with some major parts plastic and some of metal
3-Piece, Rimless, Drill Mount:
created by attaching two temples independently, then attaching a bridge directly to the lenses through holes that have been drilled through them
only polycarbonate or higher index lenses MUST be used (CR-39 or mid-index lenses will crack/break)
modern mountings are assembled using plastic sleeves and pressure fittings instead of screws.
Numont (Antique Design)
one point of attachment per lens (nasal edge)
Balgrip (Antique Design)
notches in lenses; held by clips
Universal Fit (Asian Fit)
helps with individuals who have flatter/lower nosebridges
higher nosepad height for better fit
flared nose pad design for improved stability
narrower distance between lenses for added comfort for a narrower bridge
less frame front curvature easier to fit a wider range of faces
Occipital Wrap:
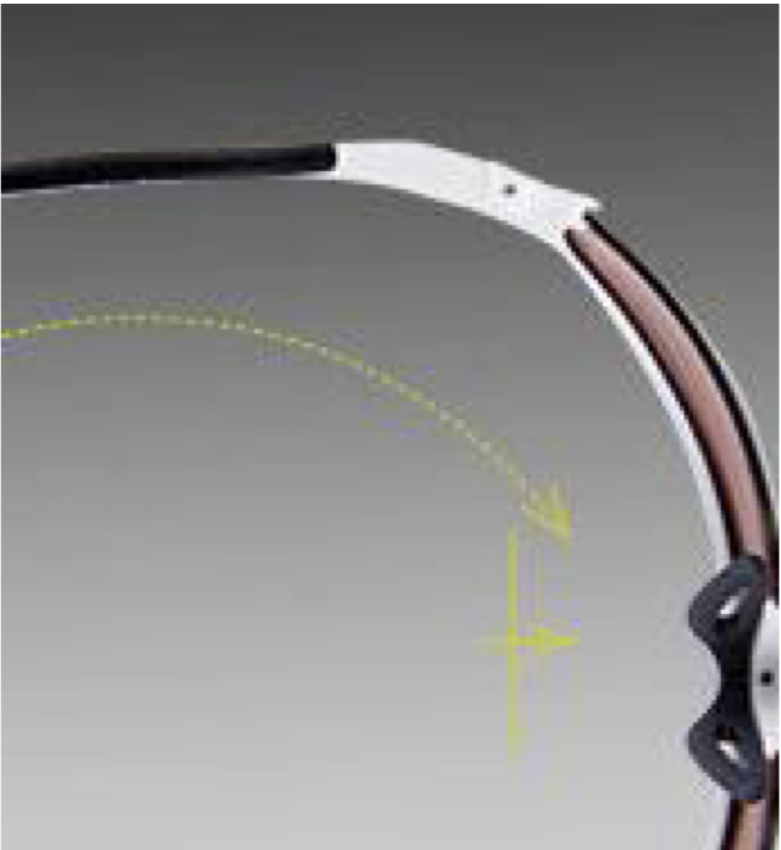

highly extended endpiece, seen on sports eyewear and others
Plastic Frame Materials: Zyl
Cellulose Acetate (“zyl”) makes up the majority of plastic frames on the market
What are the advantages of Zyl?
light in weight
huge range of colors/patterns
string
fairly easy to adjust
can be molded in any shape and size
What are the disadvantages of Zyl?
can lose shape and even be ruined by high heat
will discolor over time
will dry out and become brittle over time
will stretch out and lose fit in hot weather
Plastic Frame Material: Cellulose Nitrate
“zylonite”; flammable
Plastic Frame Material: Propionate
lighter weight than zyl; inexpensive but color can fade easily
manufactured by injection molding
Plastic Frame Material: Optyl
stronger and lighter than zyl
epoxy resin with thermo-elastic (“memory”)
hypoallergenic
manufactured by injection molding
Plastic Frame Material: Nylon/Polyamide
lightweight, flexible, durable, translucent (in color and design)
hypoallergenic, chemical resistant
manufactured by injection molding
Plastic Frame Material: Carbon Fiber
combined with nylon: thin, light, strong
Plastic Frame Material: Polycarbonate
sports, safety purposes
Plastic Frame Material: Kevlar
combined with nylon: strong and lightweight
Plastic Frame Material: Rubber
sports eyewear/ sunglass frames/ swim goggles
What Plastic Frame Materials are NOT adjustable?
carbon fiber, polycarbonate, kevlar, rubber
Metal Frame Material: Monel
nickel-based metal with copper and iron: ~65% nickel
makes up the majority of all low and mid-range metal frames made today
What are the advantages of Monel?
easy to adjust
holds adjustments well
very strong
relatively light in weight
can have a wide range of colors and plating
economical
can be repaired with solder
What are the disadvantages of Monel?
outermost plating can wear off resulting in skin allergies or reaction to nickel
prone to breaking after repeated bending
once plating is worn away, metal may erode quickly and create abrasive areas and sharp edges
the heaviest of metal frame materials
Metal Frame Material: Stainless Steel
used in many mid-range to high-end frames
very thin: may be just a little thicker than a paper clip
most stainless-steel frames are marked on the demo lens and/or inside the temple “Stainless” or “Stainless Steel”
What are the advantages of using Stainless Steel?
light in weight/strong
corrosion resistant
doesn’t contain nickel so less chance of allergic reactions (not truly hypoallergenic material)
holds color well
attractive appearance
springiness/flexibility
What are the disadvantages of using Stainless Steel?
limited range of colors
colors tend to have a matte finish
larger frames can become heavy
temples are rarely made in any other shape other than “paper clip”; very thin temple
Metal Frame Material: Titanium
used in many mid-range to high-end frames
versatile and abundant
Vision Council of America est voluntary marking guidlines for frames containing titanium
certified 100% titanium: at least 90% of frame is titanium with no nickel
certified “beta titanium”: at least 70% titanium and no nickel
What are the advantages of using Titanium?
hypo-allergenic: lacks nickel material
extremely lightweight (almost ½ weight of other metals)
100% corrosion, rust, and tarnish proof (will last long time)
extremely durable - can last for years
very strong so frames can be made thin and hold their shape, so fewer adjustments needed
What are the disadvantages of using Titanium?
not as easy to manufacture so it’s more expensive
special soldering (brazing) required
adjustments can can tricky - if not made well, it can break easily at solder points
discourages repeat sales due to its durability
Metal Frame Material: Memory Metals (mix of titanium and other metals)
generally high-end
popular for kids frames - they bend, not break
not all are created equal
difficult to adjust
not hypoallergenic
Metal Frame Material: Aluminium
strong, lightweight, no flexibility
wide variety of colors, no corrosion
Sustainable Materials:
historic airplane material
vinyl from recods
buffalo horn
skateboards
private jet interiors
wood
lightweight
reclaimed
unique
biodegradable
Sustainable materials are virtually impossible
to adjust
What are hypoallergenic choices for material allergies?
optyl**
polyamide
titanium**
stainless steel
What is the first thing to do when doing bench adjustment?
tighten the screws: tight scres create resistance - this is needed to bend a frame properly
What are some Bench adjustment tools?
frame warmer
salt pan
optical screwdriver
wise jaw angling pliers
flat round nylon jaw pliers
case angle pliers
needle nose pliers
european nose pad pliers
use heat when adjusting
plastic
do NOT use heat when adjusting
metal
What is the single most important factor in determining proper heat setting?
the thinness of the frame material
the enemy of all frame materials is
excessive heat
after using the frame warmer, the frame is ready when it
is pliable. don’t wait until it actually softens
What are tips to remember when using the frame warmer?
heat only the part of the frame that you’re working on
make sure the material can handle the heat
be mindful of lenses with A/R coating
use it to insert (mount) lenses or remove lenses
Where should you start when doing Bench adjustment?
always start at the bridge, work your way towards the endpieces and then the temples
Alignment of Frame Front:
is all about the bridge! there is both a horizontal and vertical alignment component
Horizontal Alignment of Frame Front:
skewing: a bridge misalignment when one lens appears higher than the other.
How to correct skewing:
heat the bridge and force one side up and the other side down.
How do your check Vertical alignment:
four-point touch
What is face form/wrap around?
when the frame front is slightly rounded to the form of the face
the bridge sits slightly more forward than the end pieces
What purpose does face form/wrap around serve?
cosmetic purpose: improving frame appearance
optical purpose: aligning the lens with the patient’s line of sight
What is X-ing (or propeller)?
the frame front is twisted forming an “x” when viewed from the side
How do you correct x-ing?
heat the bridge and bend in opposite directions (like wringing out a cloth)
What is the variant plane assess?
the lenses are parallel - one lens may be further forward than the other
Angles formed between the temple and frame front should be
between ~90-95 degrees and equal on both sides
Temple Parallelism: the two temples must be
parallel to one another when viewed from the side
What is used to check for temple parallelism?
the flat surface touch test or ‘wobble test’
The ‘wobble test’ helps to assess
if pantoscopic tilt is even on both sides
What is pantoscopic tilt?
the angle between the plane of the frame front and a plane perpendicular to the temple when viewing frames from the side
the amount of inward tilt of the frame front, away from the vertical
frames should have slight pantoscopic tilt, ~10-12 degrees
How do you adjust pantoscopic tilt on frames?
use a wide jaw angling plier to increase/decrease panto tilt at the hinge
What is the proper bench adjustment for skull temples?
1 ½" from end of temple
bent down equally, about 45 degrees
turned inward slightly, about 5 degrees
*should be heated first! in a metal frame, heat the plastic portion only
Temple Fold Angle:
also called Case Angle; it is the temples in closed position
What do you use to adjust the Case Angle?
case angle pliers
When do you not use heat to adjust plastic frames?
when changing pantoscopic tilt. do NOT heat the hinge of the frame
What is the EXCEPTION to heating metal frames?
when bending end of temple with a plastic covering
otherwise, DO NOT heat metal frames
Adjusting nosepads can
adjust frame height
adjust vertex distance
move the frame left/right
Guard Arm types:
“domestic”: question-mark style
“european”: inverted U-shaped
What are the different types of nose pads adjustments?
frontal angle
splay angle
vertical angle
pad spacing/pad height
Pad Adjustment: Frontal Angle
the vertical position of pads when viewed from the front
chicken flapping its wings
Pad Adjustment: Splay Angle
the angle created by the face of pad when viewed from above
beauty pageant wave
Pad Adjustment: Vertical Angle
the angle the longitudinal axis of the nosepad make when viewed from the side
flight attendant wave
Pad Adjustment: Pad Space and Pad Height
pushing the entire guard arm closer or further away from each other
pads should be:
equidistant from eyewire
about 1mm closer to nose than eyewire
at the same height - occupying the same horizontal plane
Overview of Adjusting the Frame on the Patient:
temple spread
equality of vertex distance
pantoscopic tilt
level of eyewires
temple fit
Frame Fitting Theory: Fitting Triangle
the temples should leave the frame front and go straight back and only touch the face where the temples meet the ears
frame should fit like a triangle: points of contact at crest of nose and tops of ears
A frame with some face form maximizes
a close fit for optimum vision
neutral or negative face form allows light to reflect off the back surface of the lens
What is the first component to consider in frame selection?
width - most important factor in the fit of a frame, some frames come is several eyesizes
Temples should NOT
put pressure on the sides of head