Exam 3 by Branna Campbell
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:10 PM on 10/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
1
New cards
Mutualism is ________.
positive species interaction
2
New cards
Competition
-/-
3
New cards
Neutral
0
4
New cards
Commensalism
+/0
5
New cards
Amensalism
-/0
6
New cards
Predation
+/-
7
New cards
Parasitism
+/-
8
New cards
Parasatoidism
+/-
9
New cards
Coevolution
the process in which two species undergo reciprocal evolutionary change through natural selection
10
New cards
Qualitative natures of species interactions can...
Be altered if the background environment changes
11
New cards
Niche
range of physical and chemical conditions under which that species can survive and produce (ex: hydra living is a specific temperature, salinity, and pH)
12
New cards
N-dimentional hypervolume
species that coexist differ in some aspect of their niche
13
New cards
Fundamental role
The environmental conditions under which a species can survive and reproduce; sometimes called a physiological niche; the set of environmental conditions under which a species can persist
14
New cards
Realized niche
Portion of the fundamental niche that a species actually uses as a result of interactions with other species
15
New cards
Competition can restrict the...
Fundamental niche
16
New cards
What can restrict the realized niche?
-Presence of predators or pathogens
-mutualism/commensalism
-mutualism/commensalism
17
New cards
Alpha = 1
Intraspecific and interspecific are equal to each other
18
New cards
Alpha is
Competition coefficient
19
New cards
Lotka-Voltera competition model: interspecific competition
- simplest and best known two species model of competition
- provides foundation for many other ecological models
- predicts a full range of outcomes, depending on the values of K's and alpha's
- provides foundation for many other ecological models
- predicts a full range of outcomes, depending on the values of K's and alpha's
20
New cards
Competition exclusion
One species eliminates the other
21
New cards
Stable coexistence
Persist together forever
22
New cards
Unstable coexistence
Persist together until perturbed
23
New cards
Interspecific competition affects...
The populations of 2 or more species adversely (-/-)
24
New cards
Intraspecific and Interspecific competition are likely occurring
Simultaneously
25
New cards
2 forms of Interspecific competition
Exploitation and interference
26
New cards
Most types of Interspecific interactions can be classified as 1/6 types
- consumption competition
-preemption competition
-overgrowth competition
-chemical interaction competition
-territorial competition
-encounter competition
-preemption competition
-overgrowth competition
-chemical interaction competition
-territorial competition
-encounter competition
27
New cards
consumption competition
Individuals of one species inhibit individuals of another by consuming a shared resource (squirrels, birds, etc eating acorns)
28
New cards
Preemption competition
Individuals of one species prevent occupation of an area by individuals of another species (sessile organism such as barnacles and clams)
29
New cards
character displacement
increased ecological differences between species in regions where they occur together
30
New cards
ecological release
the expansion of a species niche under conditions where their competitor species is absent; niche of the competitively-inferior species expands in the absence of the competitively-superior species
31
New cards
observational competition studies
- negative correlations between species
- attributed to present or past competition ("ghost of competition past")
- cant determine cause and effect
- other factors may be involved
- attributed to present or past competition ("ghost of competition past")
- cant determine cause and effect
- other factors may be involved
32
New cards
experimental competition studies
- addition/removal studies
- manipulate presence and/or density of would-be competitors
- must account for density effects
- provides strong interference (strong evidence for or against)
- difficult to do for many species
- manipulate presence and/or density of would-be competitors
- must account for density effects
- provides strong interference (strong evidence for or against)
- difficult to do for many species
33
New cards
Connell, 1961
- determined factors regulating distribution of Cthamalus stellatus and Semibalanus balanoides
- one of the first studies to show interspecific competition through manipulative experiments
- one of the first studies to show interspecific competition through manipulative experiments
34
New cards
fundamental niche depends on...
physical (abiotic) conditions
35
New cards
realized niche depends on...
biotic and abiotic conditions
36
New cards
competitive exclusion principle
states that complete competitors cannot coexist
37
New cards
complete competitors
two distinct species that live in the same place and have exactly the same ecological requirements
38
New cards
competitive exclusion requires that...
- competitors require exactly the same resources
- environmental conditions remain constant
- environmental conditions remain constant
39
New cards
competition is influenced by
non-resource factors
40
New cards
environmental features that are not resources can...
influence the outcome of competition between species (ex: trout species)
41
New cards
temporal variation in the environment...
influences competitive interactions
42
New cards
why are there so many species?
- non-resource variability
- resources varying in time
- resources can be a variety of things, water, light, food, microhabitats
- disturbance
- resources varying in time
- resources can be a variety of things, water, light, food, microhabitats
- disturbance
43
New cards
predation
consumption of one living organisms by another
44
New cards
predators are
heterotrophs
45
New cards
carnivores
consume animal tissue
46
New cards
herbivores
consume plant or algal tissue
47
New cards
omnivores
consume plant and animal tissue
48
New cards
true predator
kills its prey immediately upon capture, more of less
49
New cards
predators consume multiple prey organisms and function as ____________ throughout their lifetimes
agents of mortality
50
New cards
lethal effects
- predators directly affect mortality rates through total combustion
- prey directly affect predator birth/death rates
- form modeled by L-V predator/prey model
- prey directly affect predator birth/death rates
- form modeled by L-V predator/prey model
51
New cards
predators may_______ affect prey birth/mortality rates through partial consumption (herbivory or parasitism)
directly
52
New cards
predators may __________ affect pre birth/ mortality rates through effects on prey behavior
indirectly
53
New cards
Lotka and Volterra on predation
- developed 2 linked equations, one for prey and one for predator
- plot results on a phase plane
- plot results on a phase plane
54
New cards
Lotka-Volterra Predator- Prey Model
predicts population cycles
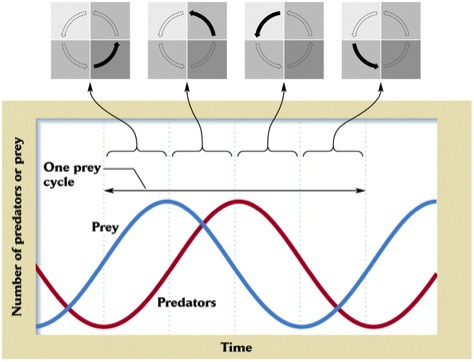
55
New cards
high latitude animals often have
population cycles
56
New cards
Optimal foraging: Type 1
- number of prey consumed is linearly related to prey population size
- more prey available, more are eaten
- more prey available, more are eaten
57
New cards
prey switching
predator doest eat the prey at low densities, relying on a different food source instead
58
New cards
apparent competition
a shared predator can make it appear that two species compete when they dont; two species that do not compete directly for resources affect each other indirectly because they share the same predator
59
New cards
competitive release
a predator can reverse competitive exclusion
60
New cards
trophic cascade
a predator of an herbivore can help a plant (the enemy of my enemy is my friend)
61
New cards
chemical defenses
Compounds released by prey to defend themselves from predators.
62
New cards
prey weapons
prey having physical defense mechanisms like hard shells or thorns to protect or fight their predators
63
New cards
plant defenses: physical and chemical
plants evolved spines, thorns, and chemical toxins, such as morphine, strychnine, and nicotine, against herbivores.
64
New cards
feigning death
faking death
65
New cards
predator swamping
a prey strategy in which the per capita predation rate is reduced at high prey density
66
New cards
schooling, flocking, group living
prey that tend to group together in order to survive (ex: prairie dogs, birds)
67
New cards
escape tactics
being fast and/or maneuverable
68
New cards
camoflauge & startling displays
an adaptation that allows an organism to blend in with its envoronment
69
New cards
symbiosis
the intimate and protracted association between two or more individuals of different species; can be positive, negative, or neutral
70
New cards
all parasitic relationships are...
symbiotic relationships
71
New cards
larger species is typically considered the...
host species
72
New cards
parasitism
- feed on the live host organism
- an intimate relationship, with the parasite living on or in the host at least part of its life cycle
- actively is harmful but generally not lethal, at least in the short term
- an intimate relationship, with the parasite living on or in the host at least part of its life cycle
- actively is harmful but generally not lethal, at least in the short term
73
New cards
parasitoids
- attack the prey indirectly by laying eggs on the host's body
- and intimate association with a single host
- the eggs hatch and the larvae feed on the host, eventually killing it
- and intimate association with a single host
- the eggs hatch and the larvae feed on the host, eventually killing it
74
New cards
parasites increase their fitness by using the host in a close, prolonged association for
food, habitat, & dispersal; usually dont kill the host
75
New cards
Host fitness is often decreased by the parasite through
- stunted growth
- emaciation
- behavior modification
- sterility
- emaciation
- behavior modification
- sterility
76
New cards
parasites generally
- are much smaller than the host
- are highly specialized
- reproduce more quickly and in larger numbers than the host
- are highly specialized
- reproduce more quickly and in larger numbers than the host
77
New cards
parasites are found in many groups such as
- viruses
- bacteria
- protists
- fungi
- plants
- invertebrates
- vertebrates
- bacteria
- protists
- fungi
- plants
- invertebrates
- vertebrates
78
New cards
facultative symbiosis
species can survive individually when separated
79
New cards
obligate symbiosis
species can not survive without the relationship
80
New cards
generalist symbiosis
interaction can be among many different species
81
New cards
specialist symbiosis
interactions can only be among a small set of species
82
New cards
invasive species
a non-native species that can sores on its own and does harm to the environment
83
New cards
species interactions help determine invasion success through
- lack of competition
- release from predators
- mutualism
- release from predators
- mutualism
84
New cards
species composition
Biological structure of a community
85
New cards
absolute abundance
number of individuals of each species in a community can be counted or estimated
86
New cards
relative abundance
the proportion of each species relative to the total number of individuals of all species living in the community
87
New cards
relative abundance equation
pi = ni/N
pi = proportion of individuals of species I
ni = number of individuals of species I
N = total number of individuals of all species
pi = proportion of individuals of species I
ni = number of individuals of species I
N = total number of individuals of all species
88
New cards
rank abundance diagram
plots rank abundance (x-axis) against corresponding relative abundance (y-axis)
89
New cards
species richness
the number of species in the community (long curve)
90
New cards
species evenness
how equally individuals are distributed among the species (flat curve)
91
New cards
species dominance
when a single or few species predominant within a community and therefore have a large impact on the functioning of the ecosystem
92
New cards
diversity
multiple indices that incorporate both evenness and richness into one number
93
New cards
Alpha > 1
interspecific competition > interspecific competition
94
New cards
Alpha < 1
interspecific < infraspecific competition
95
New cards
overgrowth competition
individuals of one species grow over individuals of other species, inhibiting access to a resource (taller plants shading shorter plants)
96
New cards
chemical interaction competition
individuals of one species release growth inhibitors or toxins that inhibits or kills other species (allelopathy in plants- secretion of chemicals that inhibit germination of other species)
97
New cards
territorial competition
behavior of one species that excludes another species from a specific location that is defended as a territory ( a bird keeping other birds from nesting in its territory)
98
New cards
encounter competition
non-territorial encounters of individuals of different species affect one or more of the species involved (scavengers fighting over a dead animal carcass)
99
New cards
intraspecific competition: logistic growth rate equation
(dN1/dt) = rN1 (1-N1/K1)
100
New cards
dN1/dt =
population growth over time