Neuro Lecture 9 (pt. 1): Brainstem, Cranial Nerves, CN V & VII
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What 3 structures does the brainstem consist of?
- Midbrain
- Pons
- Medulla
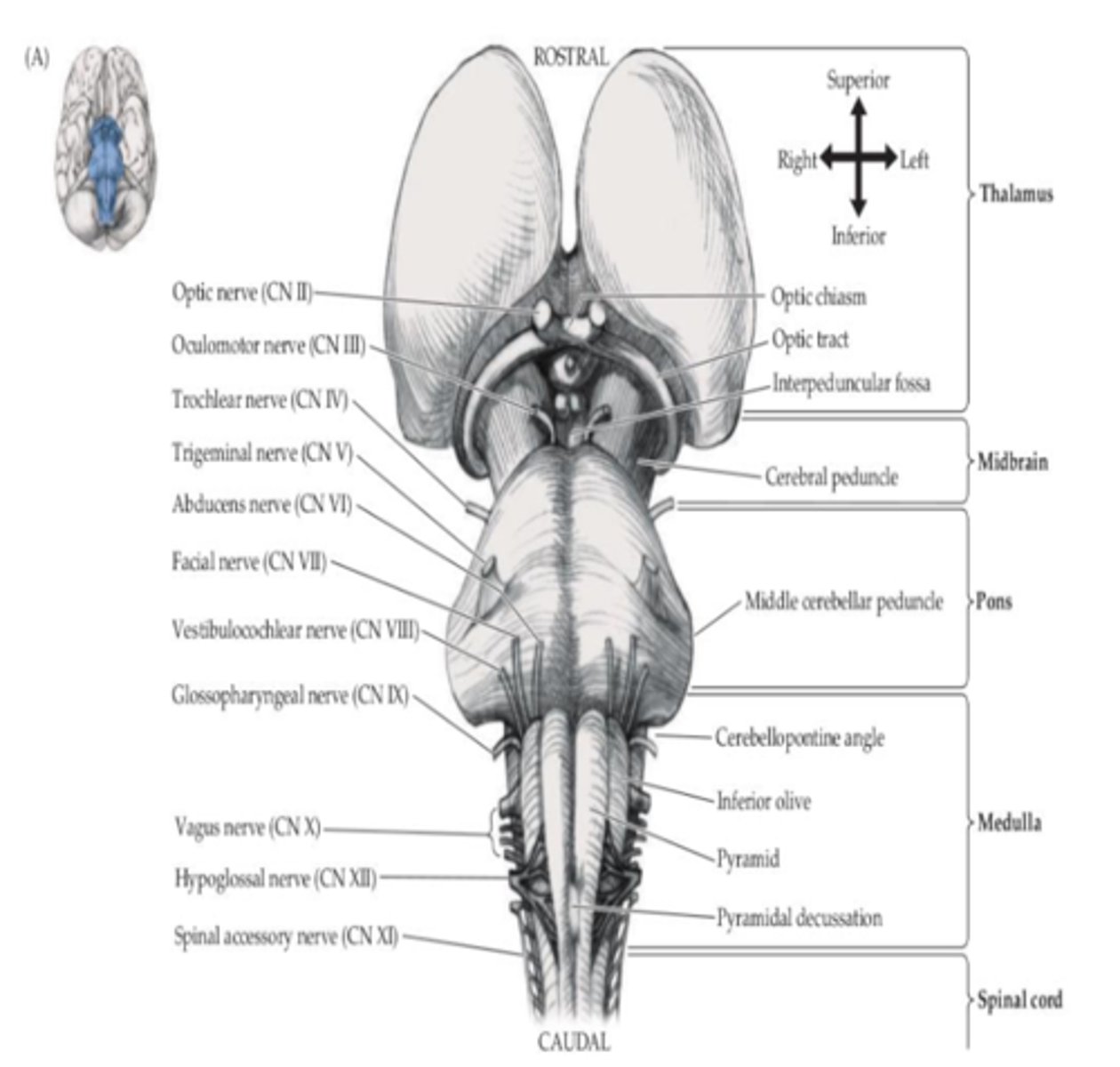
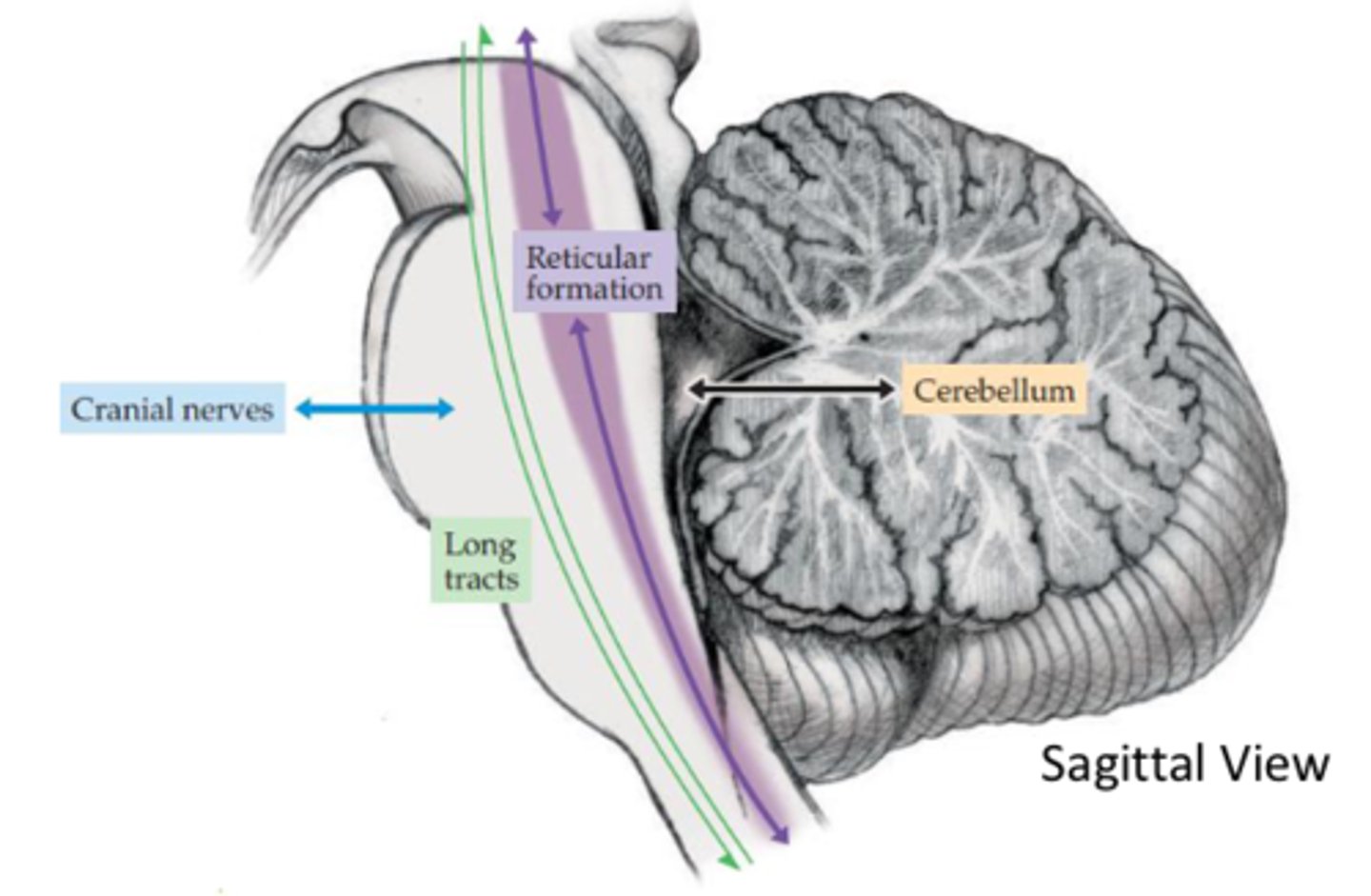
What are the main components of the brainstem (5)?
- Corridor between brain and body
- Long tracts
- Reticular formation
- Cerebellar circuits
- CN nuclei and related structures
What are the dorsal long tracts running in the brainstem?
- DCML
- Anterolateral spinothalamic tract
What are the ventral long tracts running in the brainstem?
Lateral corticospinal tract
What is the only cranial nerve to exit on the dorsal side?
CN IV (trochlear)
What is the main blood supply to the midbrain?
Posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
What is the main blood supply to the pons?
- Basilar artery
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)
What is the main blood supply to the medulla?
Vertebral artery
What is a neuron?
A single sensory or motor cell
What is a nerve?
A bundle of neurons (neuronal fibers)
How are cranial nerves defined?
A bundle of neurons that consist of a combination of motor/sensory neurons
How many types of sensory neurons are there?
3
How many types of motor neurons are there?
3
What is a ganglion?
Nerve cell bodies in PNS, with a few exceptions (ex. basal root ganglion in CNS)
What is a nuclei?
Collection of nerve cell bodies in the CNS
What are the 3 types of sensory neurons?
- General
- Special
- Visceral
What information are general sensory neurons responsible for?
- Touch
- Pain
- Temperature
Which cranial nerves carry general sensory information (4)?
- CNV
- CN VII
- CN IX
- CN X
What information are special sensory neurons responsible for?
- Smell
- Vision
- Hearing
- Equilibrium
- Taste
Which cranial nerves carry special sensory information (5)?
- CN I
- CN II
- CN VIII
- CN VII
- CN IX
What information are visceral sensory neurons responsible for?
- Viscera
- GI tract
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Lungs
- Heart
Which cranial nerves carry visceral sensory information (2)?
- CN IX
- CN X
What are the 3 types of motor neurons?
- Somatic
- Branchial
- Visceral
What do somatic motor neurons innervate?
Skeletal muscles
Which cranial nerves carry somatic motor information (4)?
- CN III
- CN IV
- CN VI
- CN XII
What do branchial motor neurons innervate?
- Muscles derived from branchial arches
- Muscles of mastication, facial expression, palate, pharynx, larynx, traps, SCM
Which cranial nerves carry branchial motor information (6)?
- CN V
- CN VII
- CN IX
- CN X
- CN XI
What do visceral motor neurons innervate?
Involuntary (smooth) muscle or glands and parasympathetic pathways
CN I is also known as...
Olfactory nerve
What is the function of CN I?
Olfaction
CN II is also known as...
Optic nerve
What is the function of CN II?
Vision
CN III is also known as...
Oculomotor nerve
What is the function of CN III?
- Eye movements
- Pupil constriction
CN IV is also known as...
Trochlear nerve
What is the function of CN IV?
Eye movements
CN V is also known as...
Trigeminal nerve
What is the function of CN V?
- Facial sensation
- Muscles of mastication
CN VI is also known as...
Abducens nerve
What is the function of CN VI?
Eye movements
CN VII is also known as...
Facial nerve
What is the function of CN VII?
- Muscles of facial expression
- Taste
- Lacrimation
- Salivation
CN VIII is also known as...
Vestibulocochlear nerve
What is the function of CN VIII?
- Hearing
- Equilibrium sense
CN IX is also known as...
Glossopharyngeal nerve
What is the function of CN IX?
- Pharyngeal muscles
- Carotid body reflexes
- Salivation
- Taste
CN X is also known as...
Vagus nerve
What is the function of CN X?
- Parasympathetics to most organs
- Laryngeal muscles (voice)
CN XI is also known as...
Spinal accessory nerve
What is the function of CN XI?
- Head turning
- Trapezius and SCM
CN XII is also known as...
Hypoglossal nerve
What is the function of CN XII?
Tongue movement
What detects odors (CN I)?
- Chemoreceptors
- Located in nasal epithelium
Where do short olfactory nerves exit (CN I)?
- Bipolar
- Cribriform plate
How many short olfactory nerves are there (CN I)?
- 9-15 nerves
- Unmyelinated
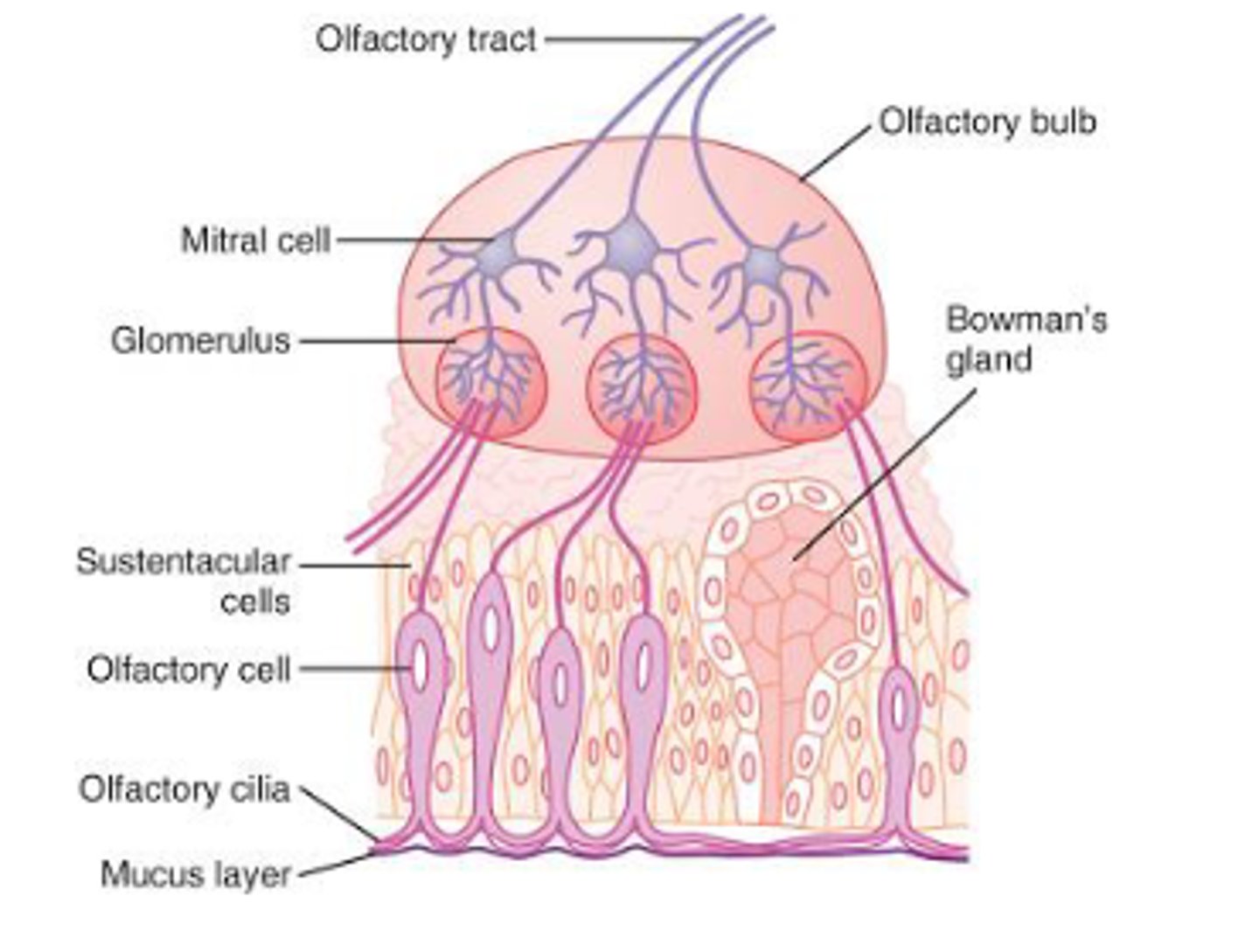
What is the first step in the pathway of the olfactory nerve (CN I)?
Synapse in olfactory bulb
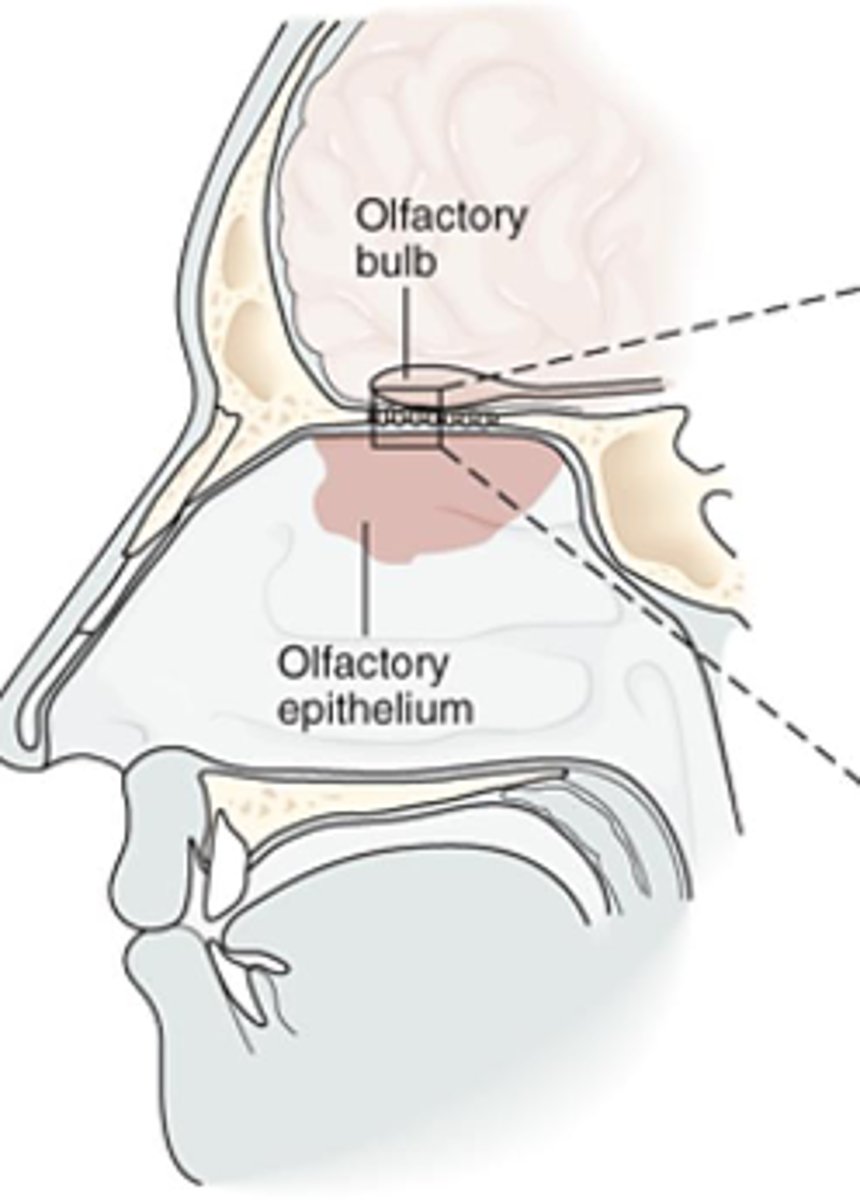
What is the second step in the pathway of the olfactory nerve (CN I)?
- Travel in olfactory tract
- Reach olfactory processing centers
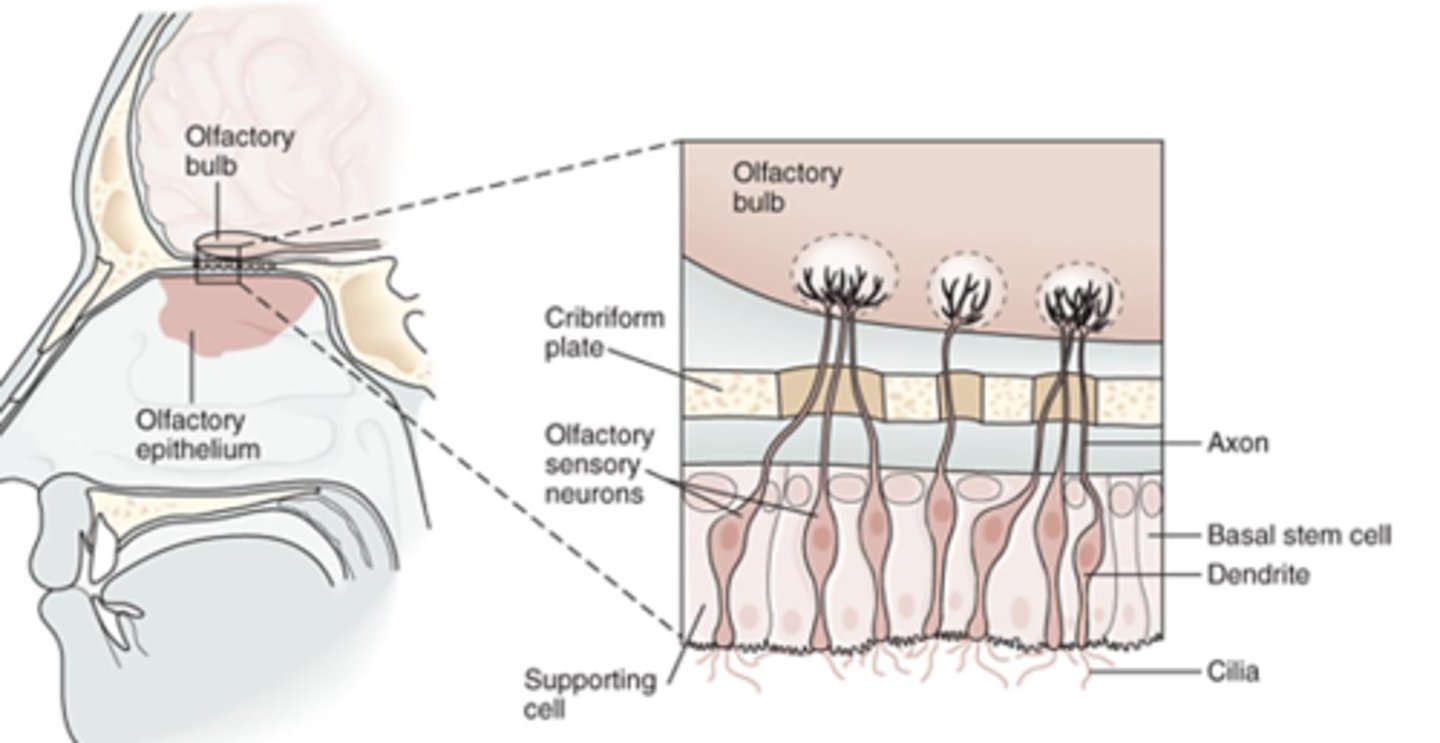
What is the third step in the pathway of the olfactory nerve (CN I)?
Anterior olfactory nuclei
What is orthonasal smell responsible for (CN I)?
Normal olfaction
What is retronasal smell responsible for (CN I)?
Odors from food and drink
What are lateral olfactory striae responsible for (CN I)?
- Perceive olfactory stimuli
- Perceptions of smell and memory
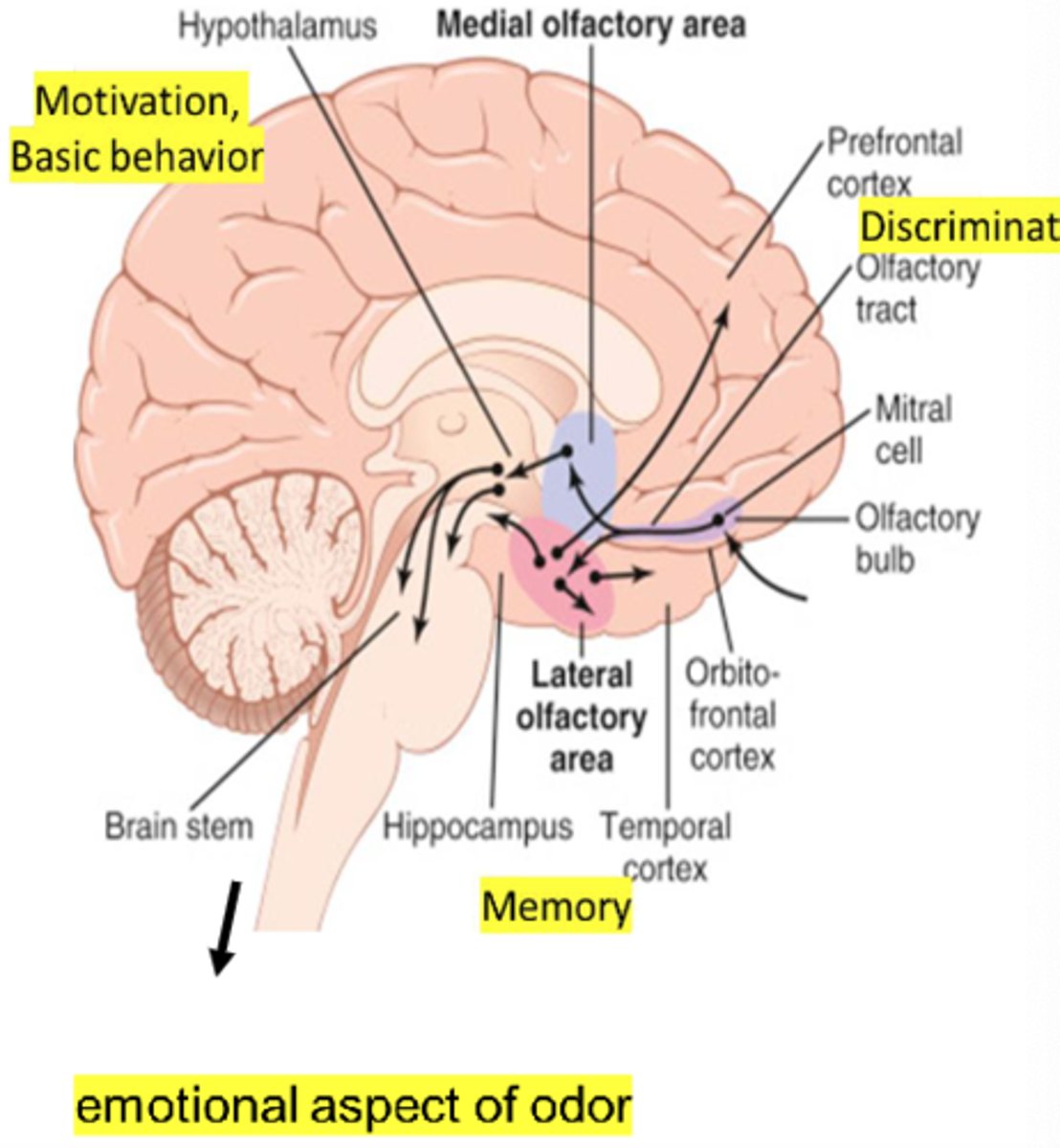
What are medial olfactory striae responsible for (CN I)?
- Connect with limbic system
- Emotional responses to smell
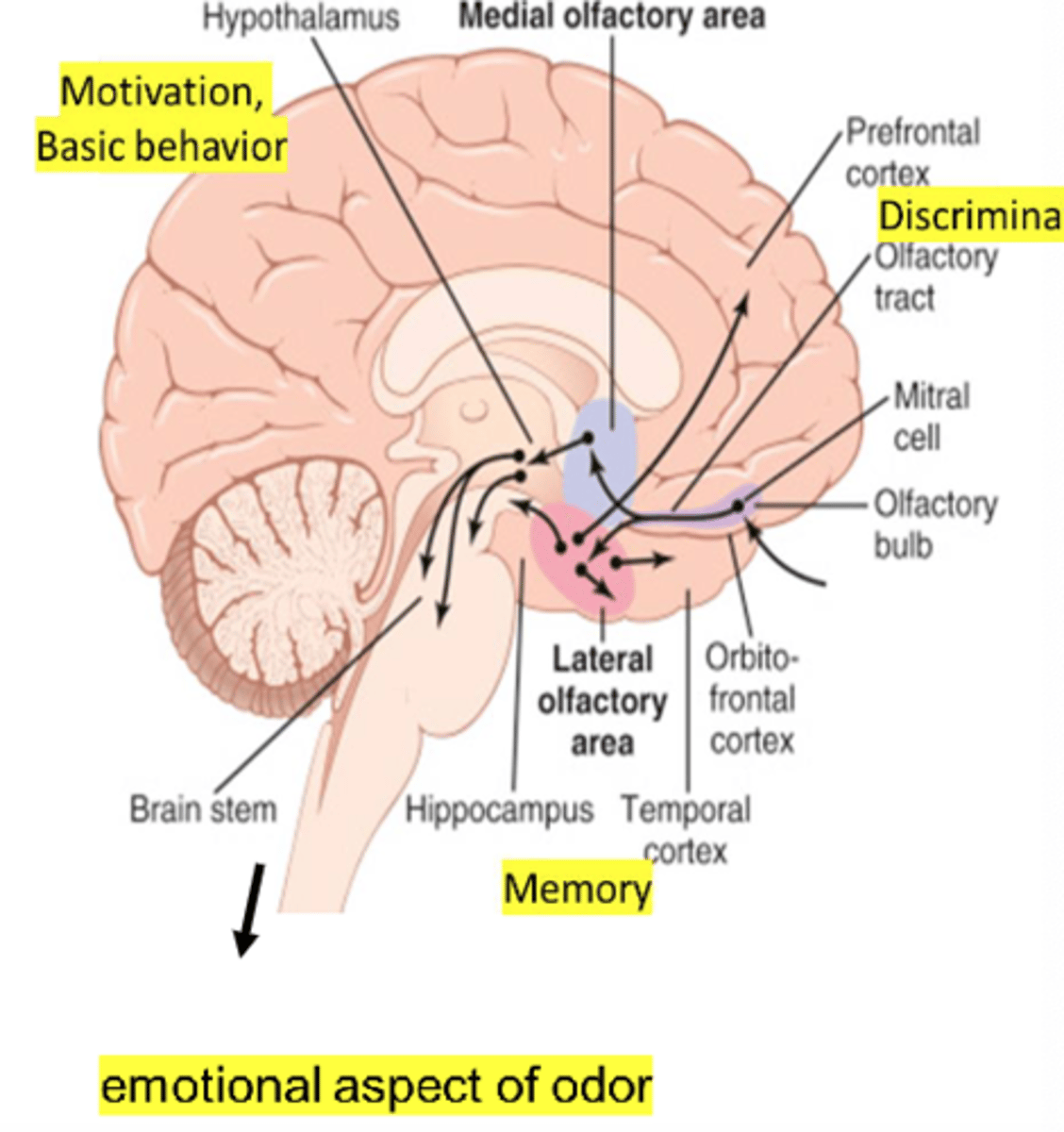
What are other functions of olfaction (CN I)?
- Safety
- Pleasure finding mates
- QOL
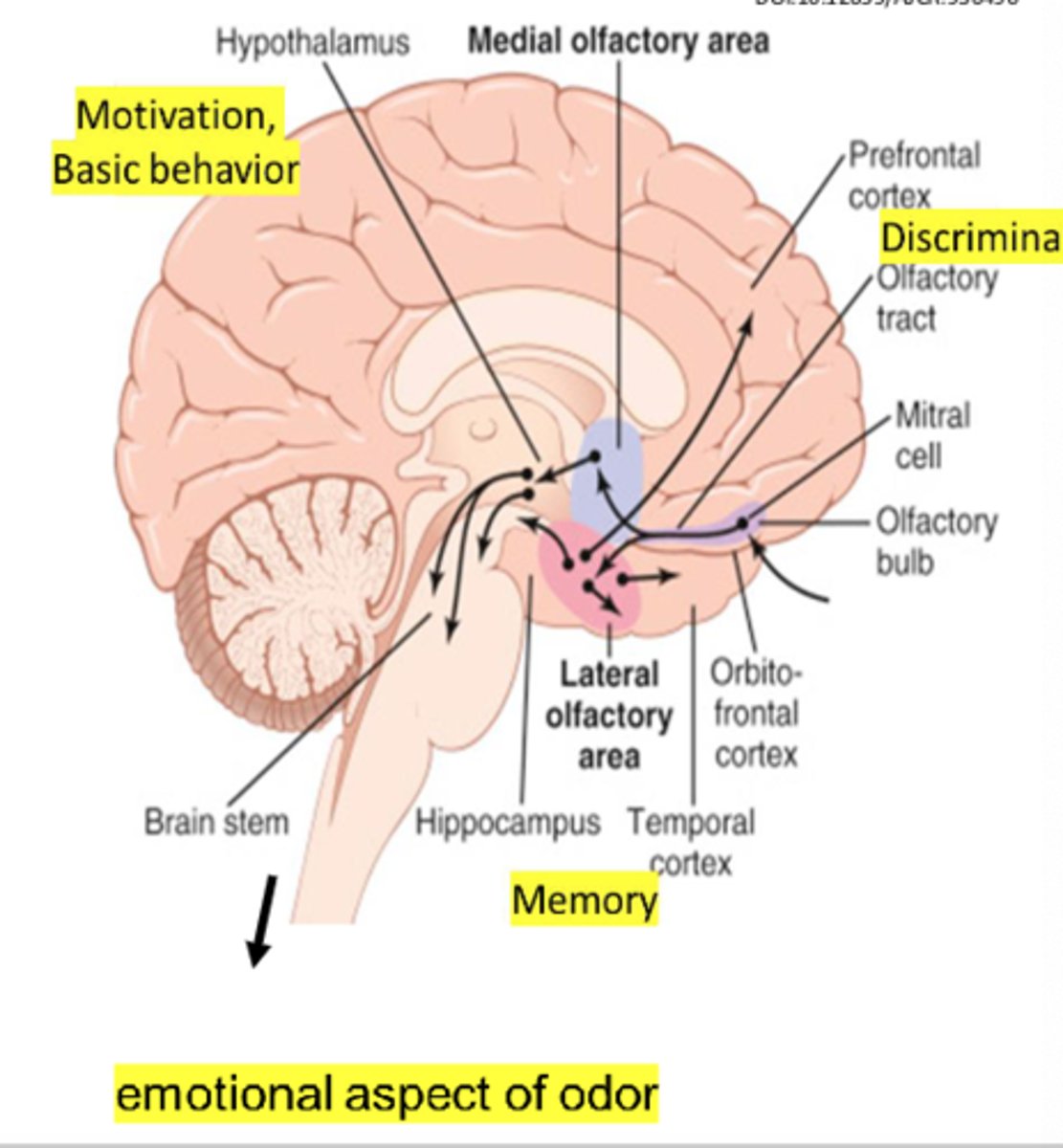
What is anosmia (CN I)?
Inability to smell
What can cause anosmia (CN I)? (8)
- Nasal congestion
- Polyps
- Viral infections
- Head trauma
- Aging
- Parkinson's and Alzheimer's
- Cocaine abuse
- Medications
What is hyperosmia (CN I)?
Enhanced olfactory sensitivity (ex. pregnancy)
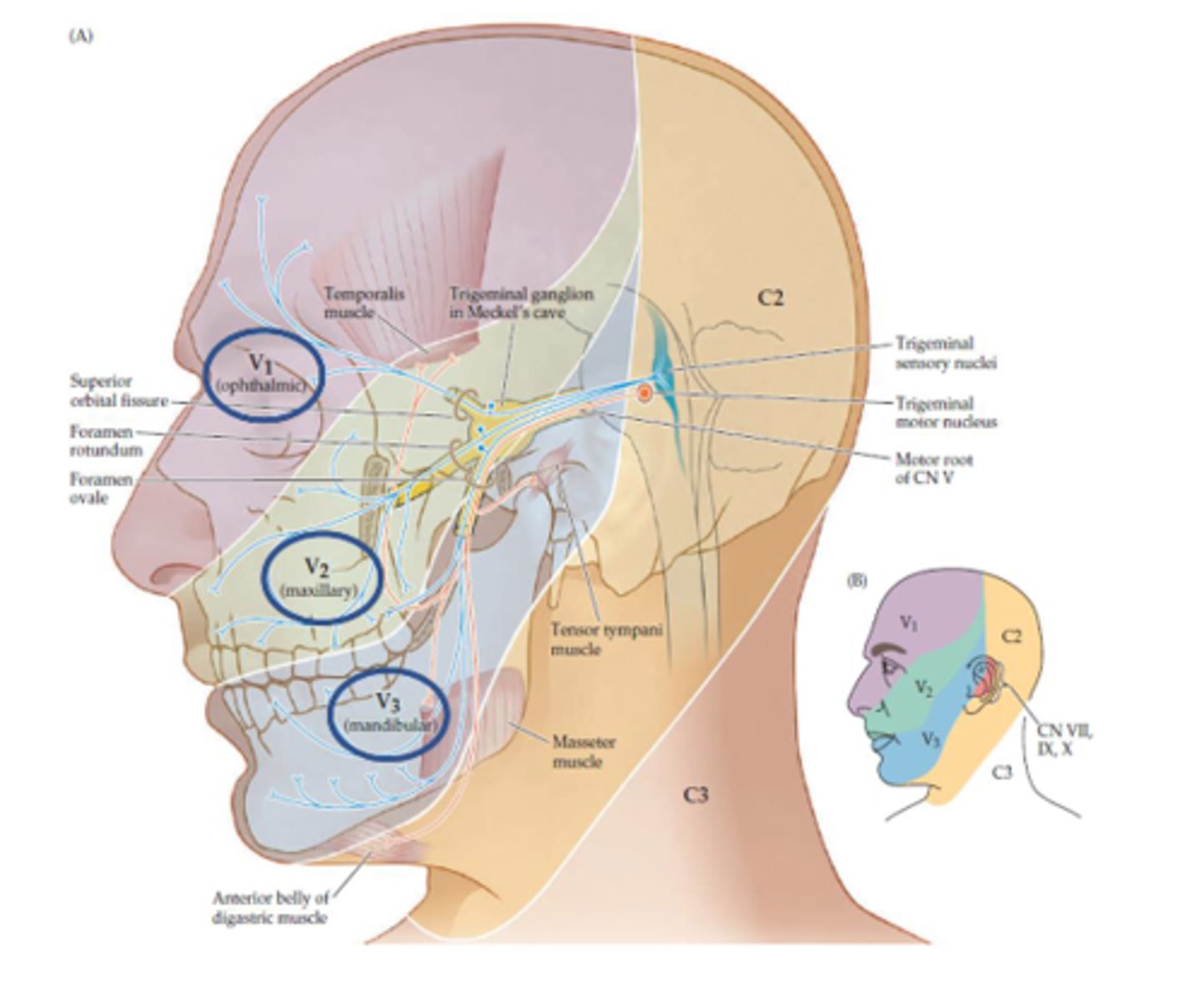
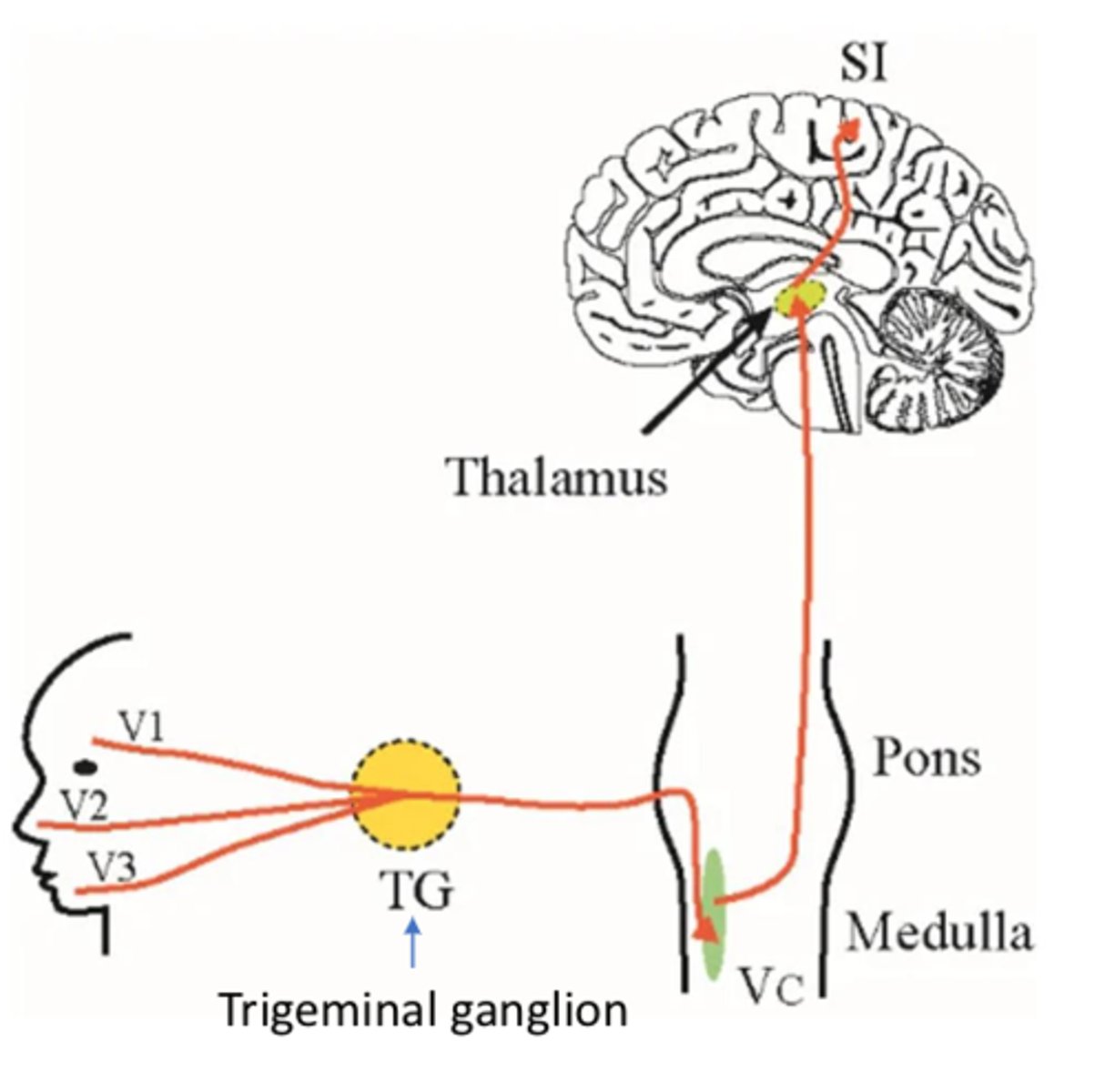
What are 3 major divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)?
- V1 Ophthalmic division
- V2 Maxillary division
- V3 Mandibular division
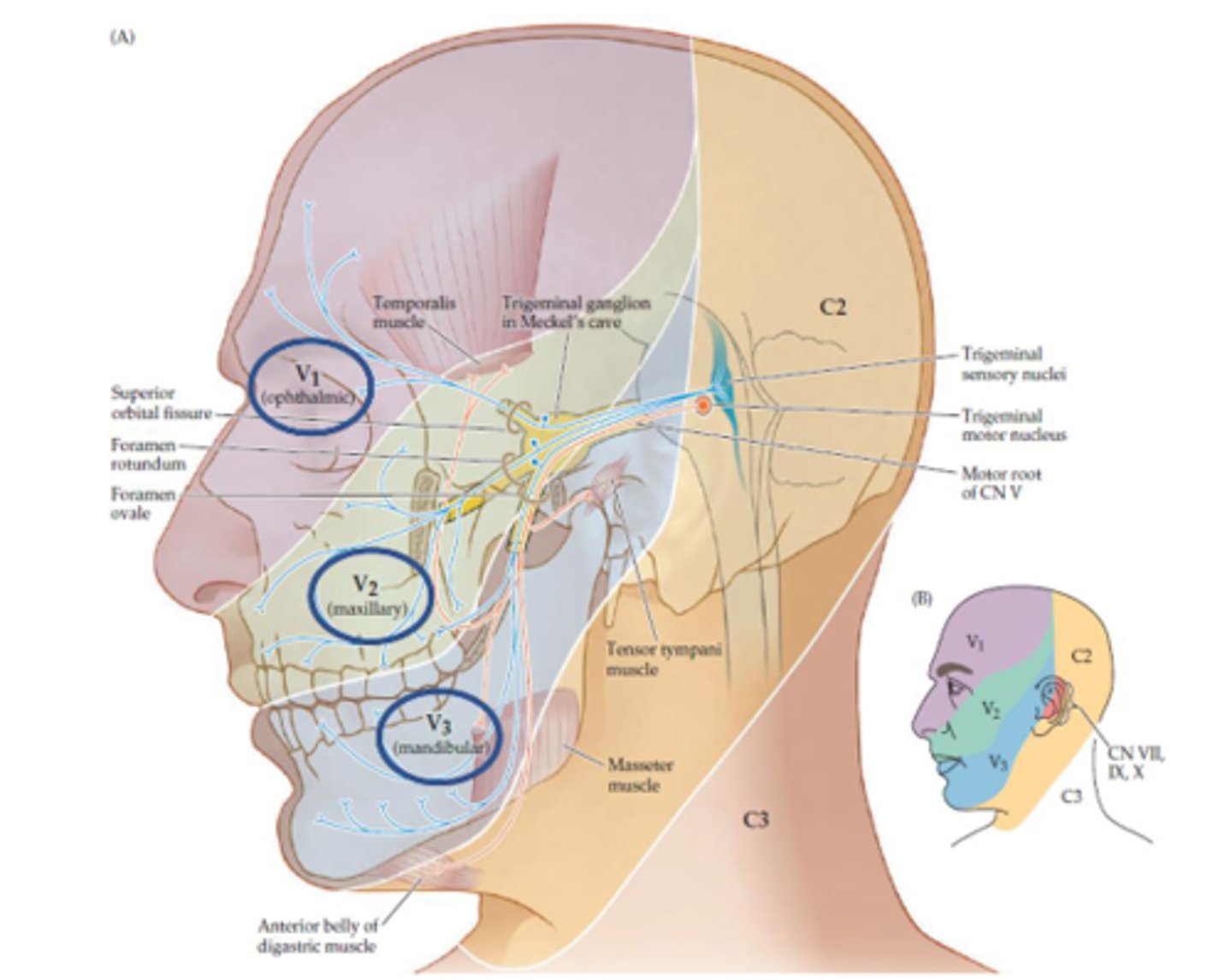
Is the V1 ophthalmic division sensory or motor (CN V)?
Sensory
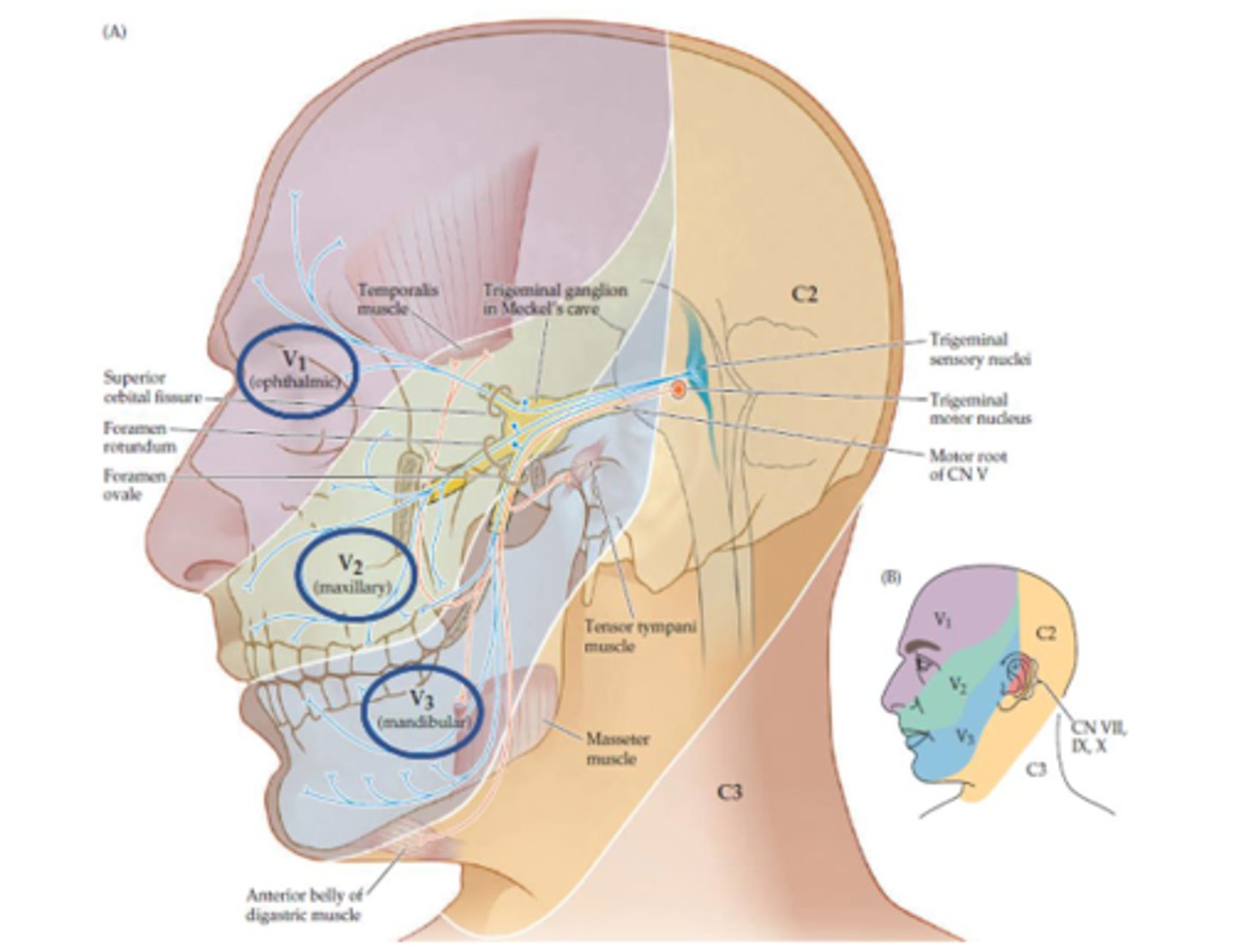
Is the V2 maxillary division sensory or motor (CN V)?
Sensory
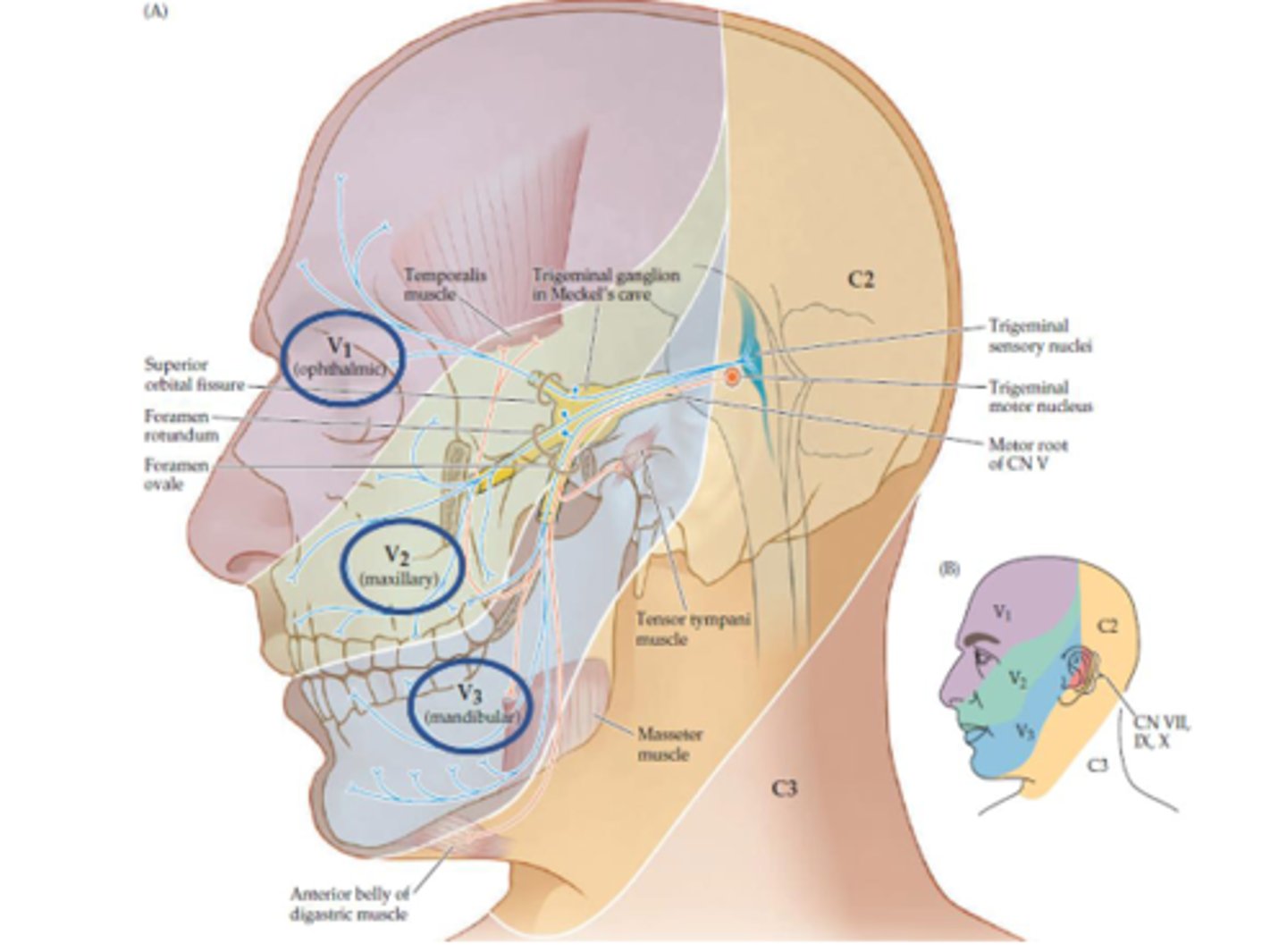
Is the V3 mandibular division sensory or motor (CN V)?
- Sensory to face
- Anterior 2/3 of tongue (general sensory)
- Small motor rootlet for muscles of mastication/tensor tympani muscle
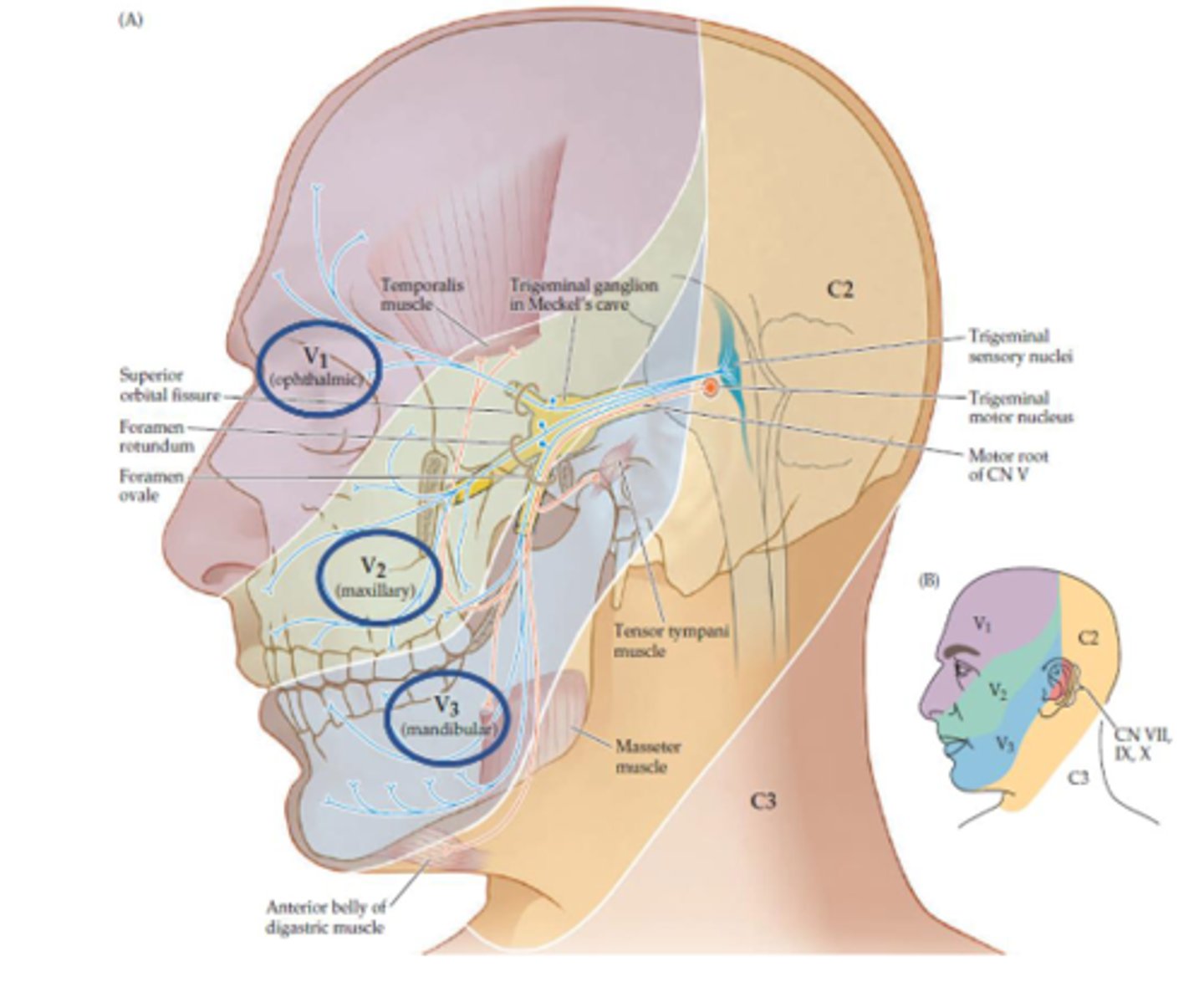
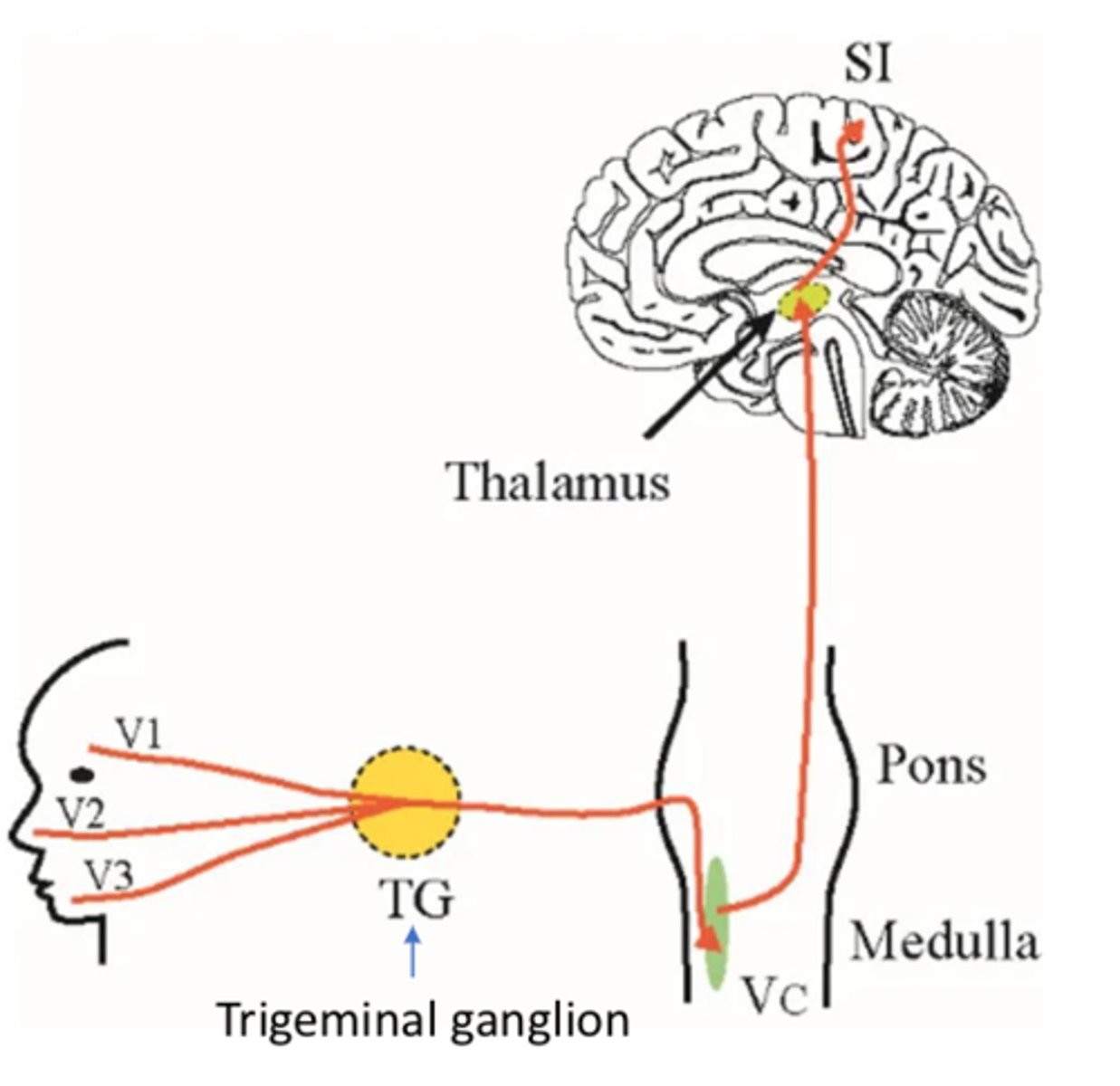
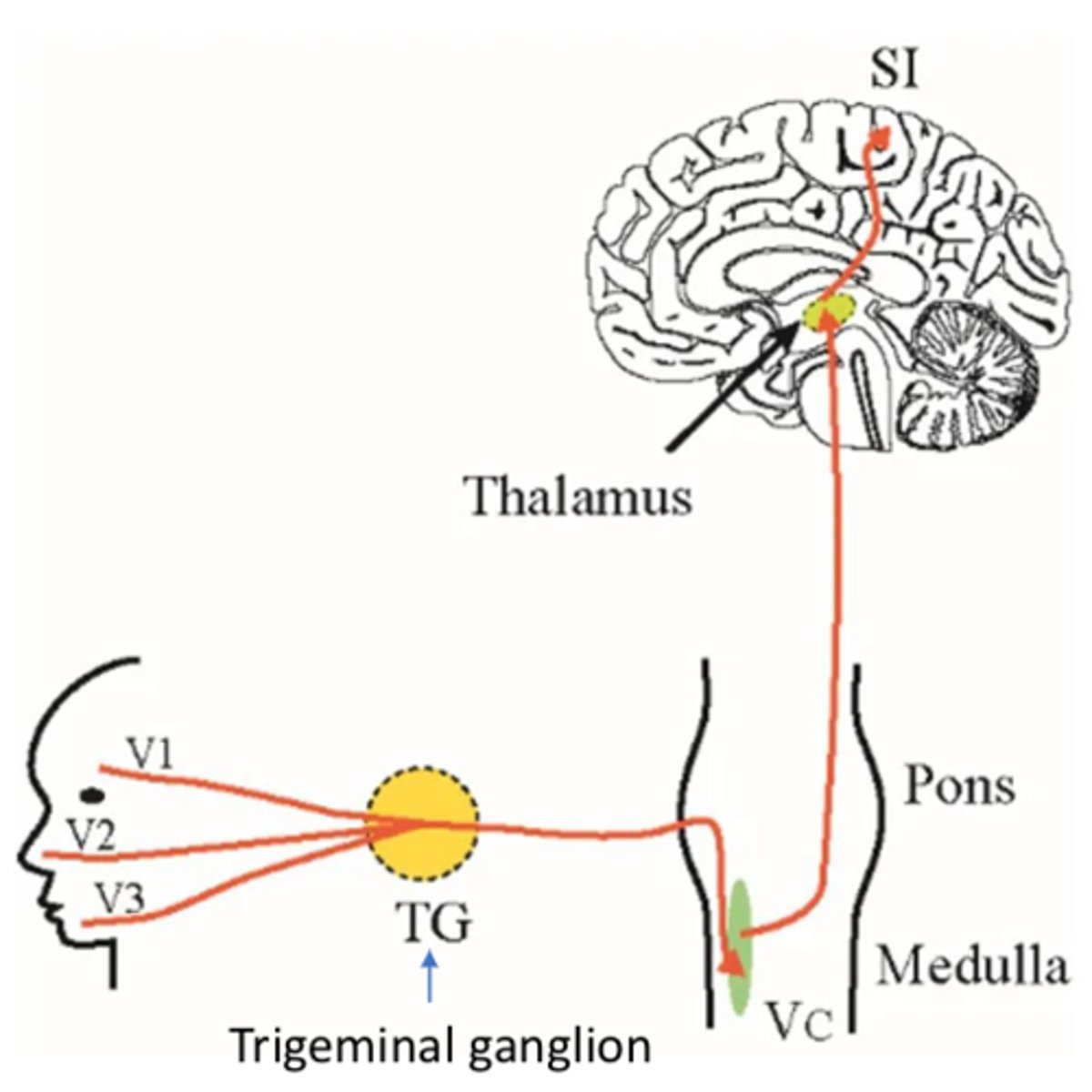
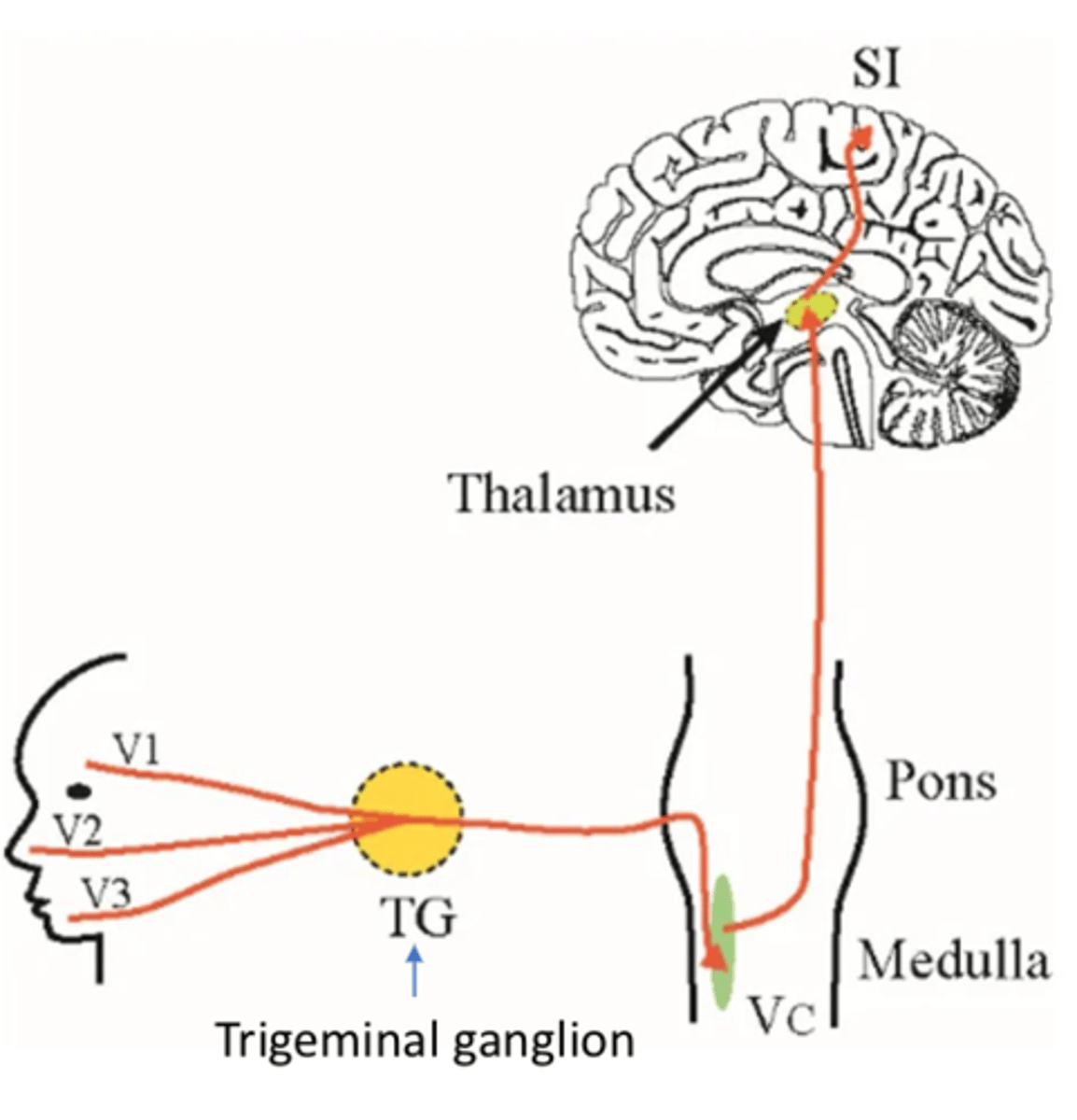
What does a lesion to the trigeminal nerve result in (CN V)?
- Ipsilateral sensory loss
- Synapses in trigeminal nucleus THEN crosses over
What is trigeminal neuralgia also known as (CN V)?
Tic douloureux
What causes trigeminal neuralgia (CN V)?
- Usually unknown
- Prevalent with MS
What triggers trigeminal neuralgia (CN V)?
- Irritation of trigger zones
- Chewing, shaving, touch, etc.
What are signs of trigeminal neuralgia (CN V)?
- Brief recurring episodes of severe pain
- Lasting seconds to minutes in V2/V3
How does trigeminal neuralgia affect facial sensation (CN V)?
- Normal
- Ipsilateral, usually unilateral involvement
What are 2 components of the facial nerve (CN VII)?
- Facial nerve proper
- Nervus intermedius
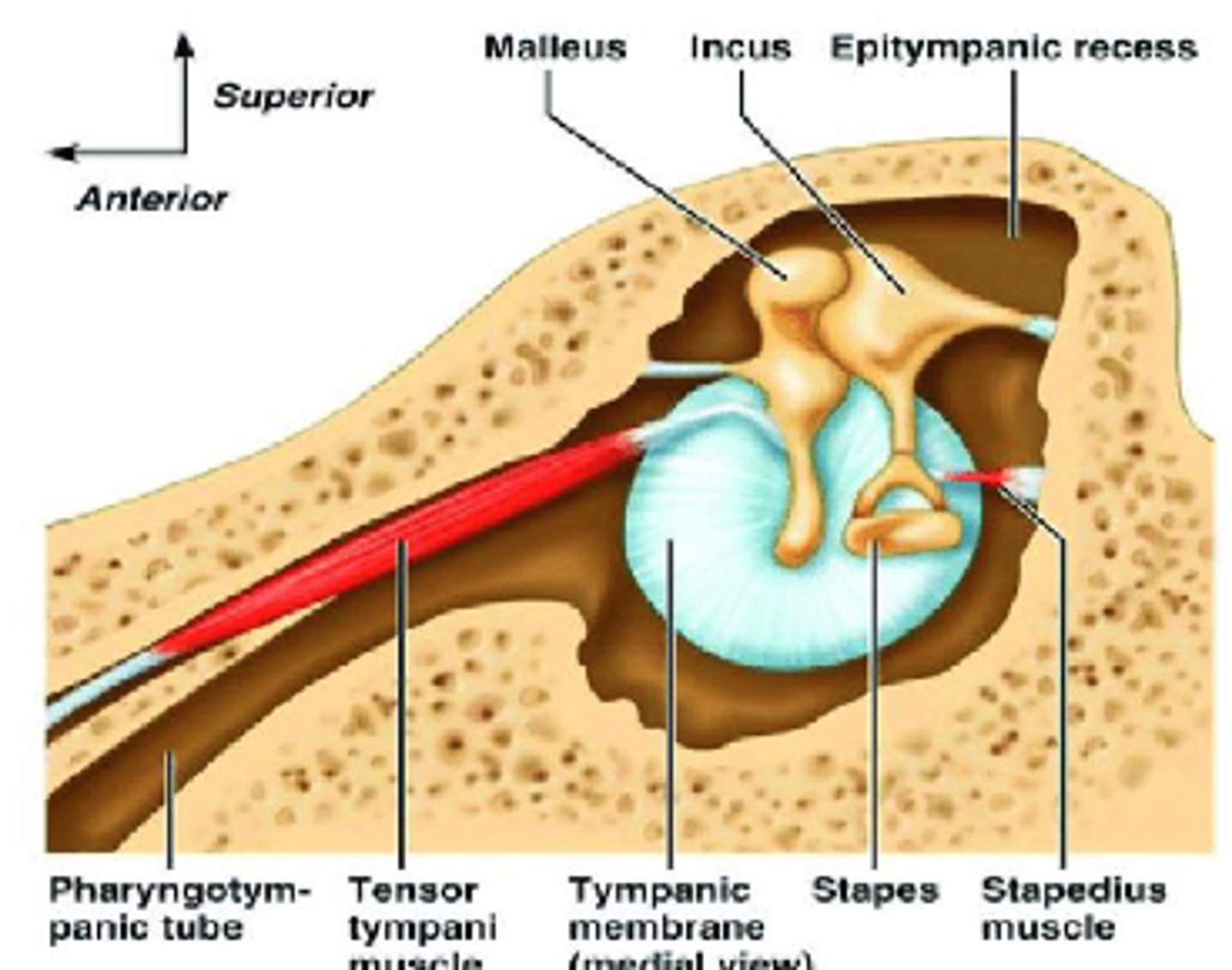
What type of nerve is facial nerve proper (CN VII)?
Branchial motor
What muscles is facial nerve proper responsible for (CN VII)?
- Facial expression
- Platysma and digastric
- Stapedius (inner ear)
What type of nerve is nervus intermedius (CN VII)?
- Parasympathetic
- Special sensory
- General somatosensory
What is the parasympathetic aspect of nervus intermedius responsible for (CN VII)?
- Lacrimal gland (tears)
- Salivary gland
What is the special sensory aspect of nervus intermedius responsible for (CN VII)?
Taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue
What is the general somatosensory aspect of nervus intermedius responsible for (CN VII)?
Sensation to external auditory meatus (ear canal)
What tests could an OT do for the facial nerve (CN VII)?
- Puff cheeks
- Smile
- Raise eyebrows
- Frown
What type of innervation does CN VII supply to the forehead?
Bilateral
What type of innervation does CN VII supply to below the eyes?
Contralateral
What does an UMN lesion to CN VII result in?
- Contralateral
- Weakness/paralysis below eyes
- Muscles of forehead unaffected (ipsilateral)
What does a LMN lesion to CN VII result in?
- Ipsilateral
- Facial paralysis (whole side)
What causes Bell's Palsy (CN VII)?
Viral/inflammatory (unknown)
What are signs of symptoms of Bell's Palsy (CN VII)?
- Unilateral facial weakness of LMN type
- Loss of taste on ipsilateral tongue
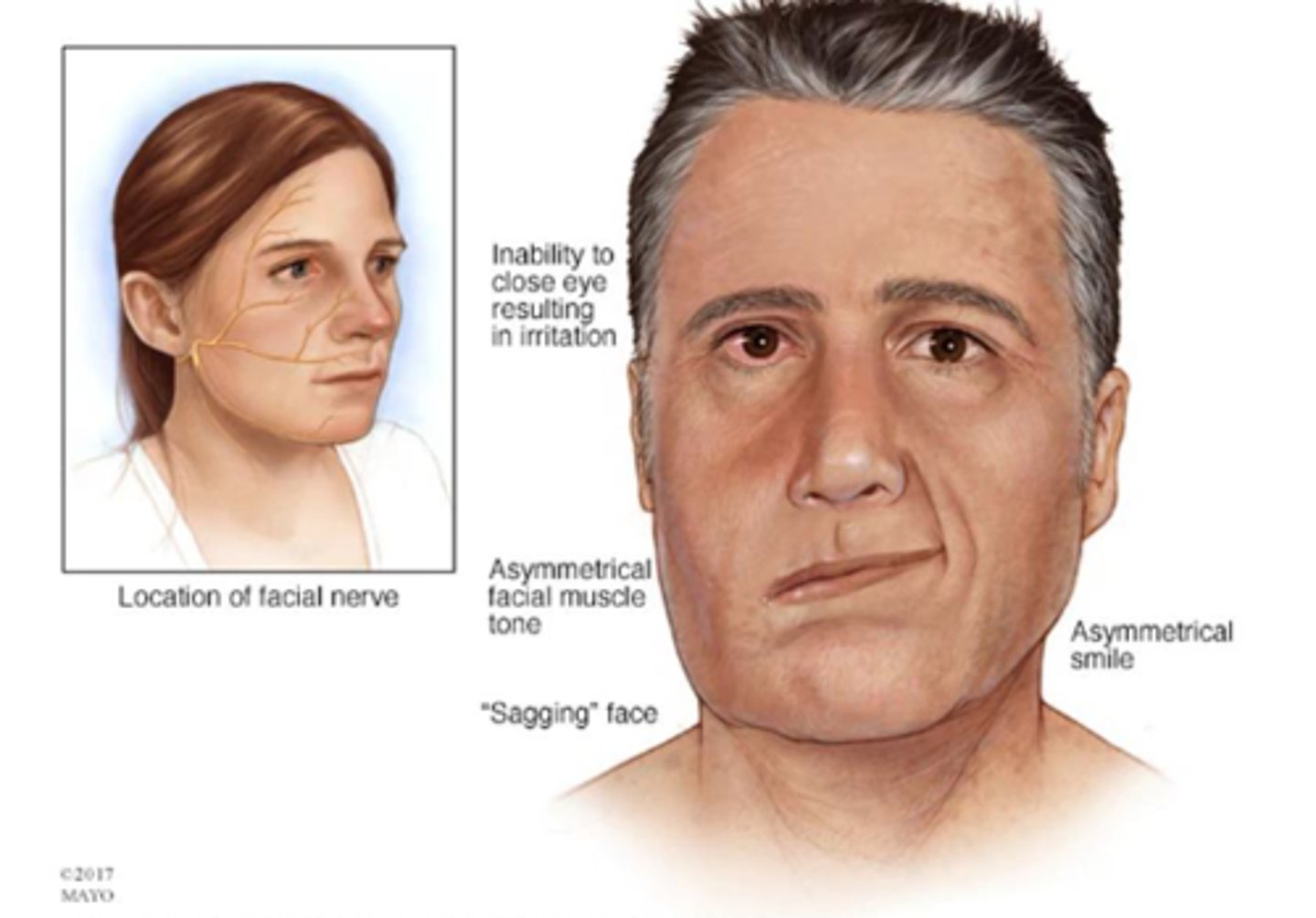
What tests could an OT do for Bell's Palsy (CN VII)?
- Smile
- Puff cheeks out
- Clench eyes tight
- Wrinkle brow
- Look for asymmetry
What signs would help you rule out Bell's Palsy (CN VII)?
- Hand weakness
- Sensory loss
- Dysarthria
- Aphasia
- UMN lesion is NOT Bell's Palsy