Unit 5.2 - Analysing Financial Performance
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Budgets
Financial plans that forecast revenue from sales and expected costs over a time period
3 types of budget
Income
Expenditure
Profit
Income budget
Set out a businesses expected revenue from selling its product
Expenditure budget
Sets out the expected costs to be incurred by the business i.e labour, raw materials, fuel and other items
Profit budget
by combining sales revenue and expenditure budgets, it is possible to calculate expected profits.
income budget-expenditure budget
Research in constructing budgets
- Analysing the market to predict likely trends in sales and prices to help forecast revenue
- Researching costs for labour, fuel and raw materials by contacting suppliers and seeing if they can negotiate price reductions for prompt payment or ordering in bulk
- Considering government estimates for wage rises and inflation, then incorporating them into future sales revenue and expenditure budgets
Difficulties in constructing budgets
- Difficult to accurately forecast sales - tastes and preferences
- The risk of unexpected changes - external environment
- Decisions by governments and other public bodies - publishing of the budget
- Unreliable data may be used i.e market research data
Variance analysis (budgeting)
Process of investigating the difference between forecast data and actual figures
Adverse variance
difference between the figures in the budget and actual figures will lead to the firm's profits being lower than planned.
i.e Budgeted revenue = £100,000 Budgeted costs = £50,000
Actual revenue = £80,000 Actual costs = £60,000
Adverse profit variance of £50,000 - £20,000 = £30,000
Favourable variance
difference between the figures in the budget and actual figures will lead to the firms profits being higher than planned.
Causes of adverse variances
Anything that can lead to lower revenues or higher costs than expected this may include:
- Competitors introduce new products and win extra sales
- Government increases business tax rates by an unexpected amount
- Fuel prices increase as price of oil rises
Causes of favourable variances
Anything that can lead to higher revenues or lower costs then expected this may include:
- Wage rises were lower than expected
- Economic boom leads to higher than expected sales
- Rising value of the pound makes imported raw materials cheaper
Overcoming adverse variances due to low revenue
Cut prices - this will work if customers are sensitive to price.
Improve brand image /reputation.
Seek new markets.
Expand product range.
Increase advertising / promotions.
Overcoming adverse variances due to high costs
Seek cheaper raw materials.
Reduce waste.
Cut wages.
Increase labour productivity.
Benefits of budgeting
Control finance effectively
Enable managers to make informed and focused decisions
Production budgets ensures that a business doesn't overspend
Can allocate finances where needed/redirect funds
Used to motivate staff
Revenue budget used as a target
Benchmark to evaluate financial control against
Drawbacks of budgeting
- If employees are delegated responsibility then they will need to be trained, which could be costly
- Teething problems, errors or delays as employees adjust to the position of managing budget
- Allocating budgets fairly and in the best interest of the business can be difficult
- Budgets are normally within the current financial year - so may try and stay within budget which may not be in the longer term interest of the business
- Can become inflexible limiting the businesses ability to adapt
Cash flow
Movement of cash into and out of a business over a period of time
Cash flow forecasts
State the inflows and outflows of cash that the managers of a business expect over some future period
Reasons to forecast cash flow
Support applications for loans - banks and other financial lenders more likely to lend to a business that has done some financial planning which gives them more confidence the repayments will be met
Avoid unexpected cash flow issues - forecasting to see when additional cash will be needed so that solutions can be found to keep a business functioning
Possible cash inflows
- Cash sales
- Credit sales
May also include one off large inflow such as loans, sale of non-current assets, investment through equity capital
Possible cash outflows
- Raw materials
- Wages
- Utilities
- Loan repayments
- Purchase of non-current assets
- Any other costs
Opening balance
The amount of money in a business at the start of the month, this will be the same as the closing balance of the previous month
Net cash flow (monthly)
Total inflow - Total outflows
Closing balance
What a business has left at the end of the month
Formula: Opening balance + Net cash flow
Simple cash flow forecast example (table)

Payables
the amount of time taken by a business to pay its suppliers and other creditors i.e a supplier may give trade credit of 50 days
Receivables
the amount of time taken by debtors (businesses customers) to pay for the products that has been supplied i.e a business may offer trade credit to a customer of 50 days
Relationship between tradables and receivables
Large impact on cash flow, if receivable days are higher than payables this means a business is paying for suppliers before receiving payment from customers. Therefore outflows occur before inflow possibly leading to cash shortage
Causes of cash flow issues
Overtrading - business expands quickly without organising funds to finance the expansion
Allowing too much trade credit
Poor credit control - getting customers to pay on time
Inaccurate cash flow forecasting
Fixing cash flow issues
Offer less trade credit
Arrange short term borrowing
Negotiate improved terms for trade credit
Debt factoring
Sale and leaseback
Break-even
a level of output which the sales of products generate just enough revenue to cover all costs of production.
- Break even output: total revenue = total costs
- The business makes neither a loss nor a profit
- Always given in units
- Always round up
Break even formula
Fixed costs/contribution per unit
Contribution per unit
Selling price - variable cost per unit
Total contribution
The difference between the total sales revenue and the total variable costs.
Two ways to calculate:
1) Total revenue - total variable costs
2) Contribution per unit x units sold
Fixed costs (break-even chart)
Costs that do not vary with the quantity of output produced
on a break even diagram this is a horizontal flat line starting at value of the fixed costs
Variable costs (break-even chart)
costs that vary with the quantity of output produced
On a break even diagram this will start at 0 (as anything time 0 is 0) and slope upwards - the higher the variable cost per unit the steeper the line will be
Total costs (break-even chart)
fixed costs + total variable costs
This line will start at the same point as the fixed cost line because even if no units have sold there will be at least these costs for the business to cover. It will then slope upwards parallel to the variable cost line as they both increase at the same rate per unit
Revenue (break even chart)
Selling price x units sold
THis will start at 0 as if nothing is sold no revenue can be made. It will then slope upwards, the higher the selling price the steeper the gradient. Where this line intersects total cost line is break-even level of output
Margin of safety
difference between your actual output and break-even level of output
Actual output - break-even output
Break-even chart (diagram)
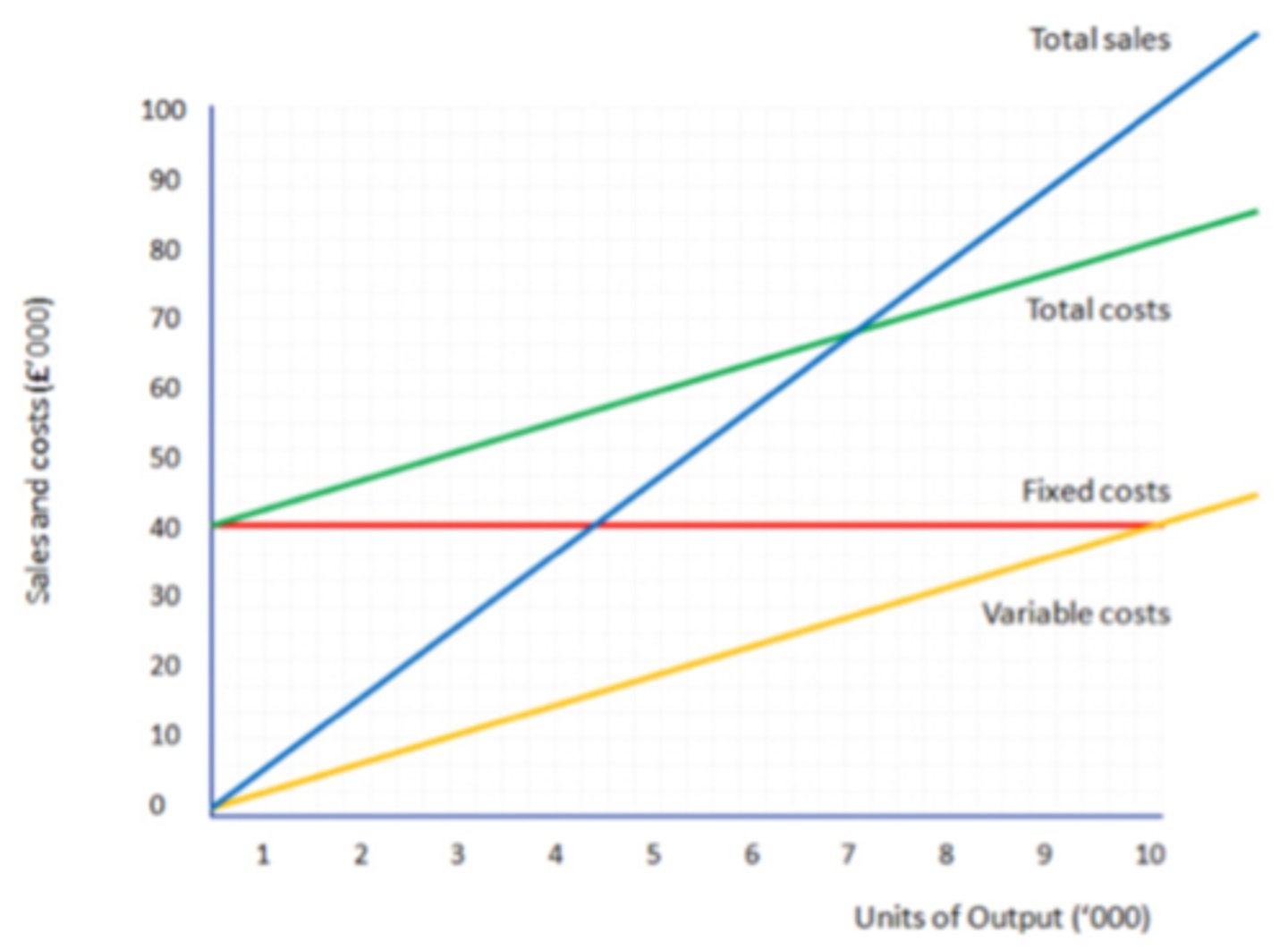
Why managers use break-even
- Help to decide whether a business idea is profitable or not
- Help to decide the necessary level of output to generate a profit
- The results can be used to support an application for a loan
- Used to assess the impact of changes in the level of production on profits
- Used to assess the effects of prices / costs on potential profits
Benefits of break-even analysis
- Forecast the effect of varying numbers of customers on revenue, costs and profit
- Implications of changes in price or costs on profitability
- Simple technique - particularly suitable for start up businesses and businesses that produce a single product
- Quick
- Used to gain additional finance - financial planning
Drawbacks of break even analysis
- A prediction - information may be inaccurate
- Simplification of what happens - businesses don't usually stick to a single price
- More difficult if a business sells numerous products
- Costs do not rise as steadily as suggested - economies of scale
Impact of changing variable costs on break even
Increase:
- Variable and Total cost line pivots upwards (gets steeper)
- Increase in break-even output required
- Greater revenue through more customers and sales needed to break even
Decrease:
- Variable and Total cost line pivots downwards (gets flatter)
- Decrease in break-even output required
- Each sales incurs lower cost so less revenue and customer needed to reach break even
Impact of changing fixed costs on break-even
Increase:
- Fixed cost and total cost line shift up (Start at higher £s)
- Increase in break-output required
- Incur more cost before even earning revenue, more sales required to cover this
Decrease:
- Fixed and total cost lines shift down (Start at lower £s)
- Decrease in break-even output required
- Overall costs will be lower so lower sales required
Impact of changing selling price on break even
Increase:
- Revenue line pivots upwards (gets steeper)
- Decrease in break even output required
- Each sale provided greater contribution per unit, therefore less sales are needed
Decrease:
- Revenue line pivots downwards (gets flatter)
- Increase in break-even output required
- Each sale provided less contribution per unit so more sales needed to break even
Profitability
Measure of financial performance that compares a businesses profits to some other factors such as revenue
Profit margin
Ratio that expresses a business's profit as a percentage of its revenues over some trading period
Can sometime just be the gap between unit and costs and selling price
Gross profit
Sales revenue - direct costs
Operating profit
Gross Profit - indirect costs
Net profit
Operating profit - tax and interest
Gross profit margin
Gross profit/sales revenue x 100
Shows us how much was spent on direct costs such as raw materials and direct wages to generate each £ of revenue.
Limited value due to not including all costs but can be useful to compare and identify where the business is being inefficient with costs
Operating profit margin
Operating profit / sales revenue x 100
Considered the best measure for financial performance as it considered all costs that are incurred in generating revenue
Net profit margin (profit for the year)
Net profit/sales revenue x 100
Will take into account interest payments or could show an improvement in debt financing, may be important indicator to show whether increasing dividends can be paid
Value of profitability analysis using margins
- Compare financial performance in a more nuanced way i.e comparing the cost of making revenue may reveal a business that is smaller or spends less on investments is actually more efficient with their resources
- Compare changes in margins overtime to improve performance
- Compare the different margins to target areas of cost that most damaging i.e if gross margin seems to be increasing or too close to operating margin suggest direct costs are too high
- Make better quality judgments on financial performance
Use of data in financial decision making and planning
- Can now analyse huge amounts of data (big data) in a more efficient and cost effective way
- Used to plan future activities (cash flow, budgets, break even)
- Measure future viability of business or investment
- Gain finance from banks i.e loans
- Decide on prices (break-even)
- Predict what-if scenarios and contiengies (variances)
- Compare investments against each other
- Forecast timescales for getting returns on investments and implication on cash flow