Chapter 9 - Enthalpy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
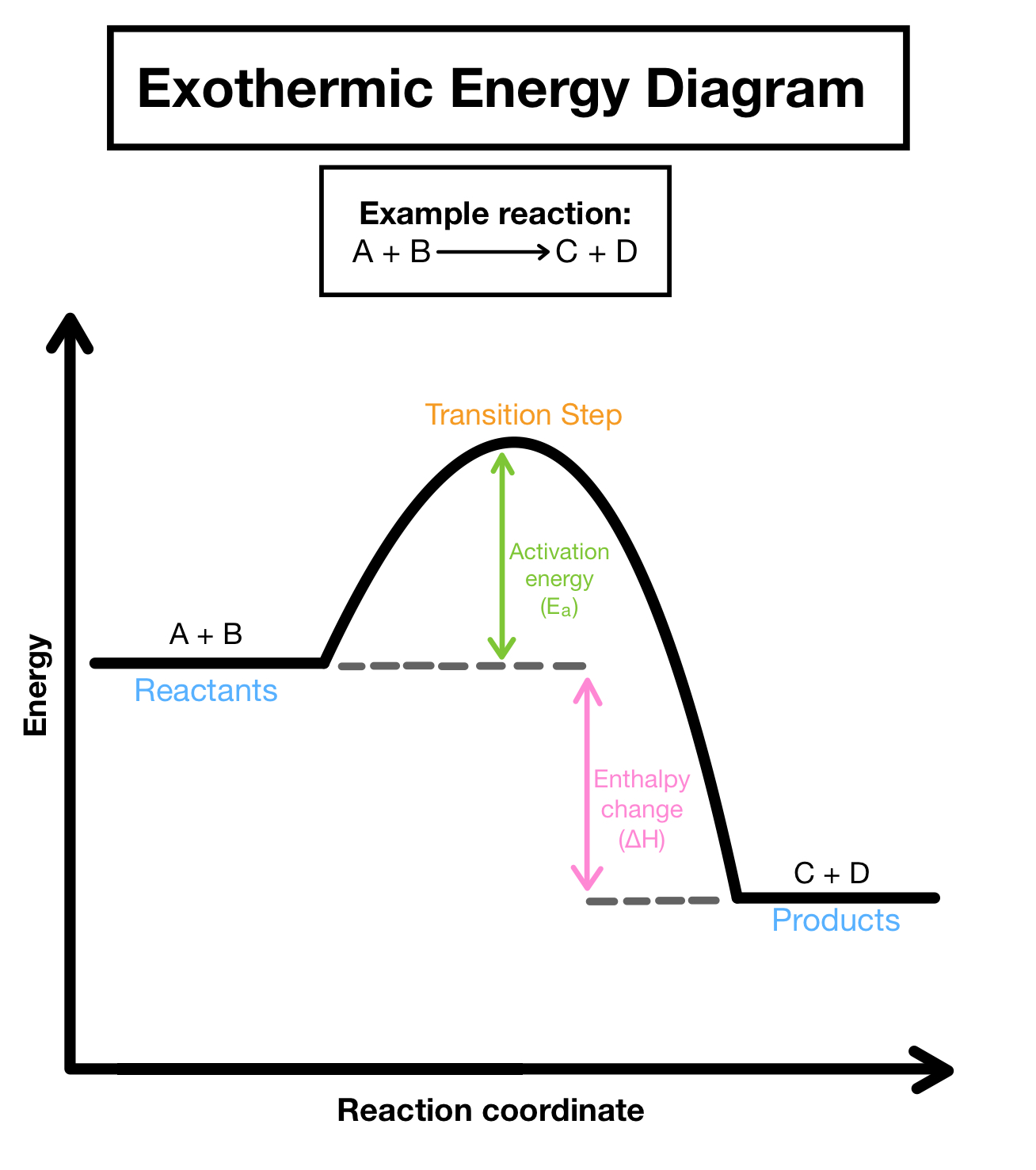
exothermic
-bonds are made
-energy is released
-temperature increases
-products have less energy
-enthalpy change is negative
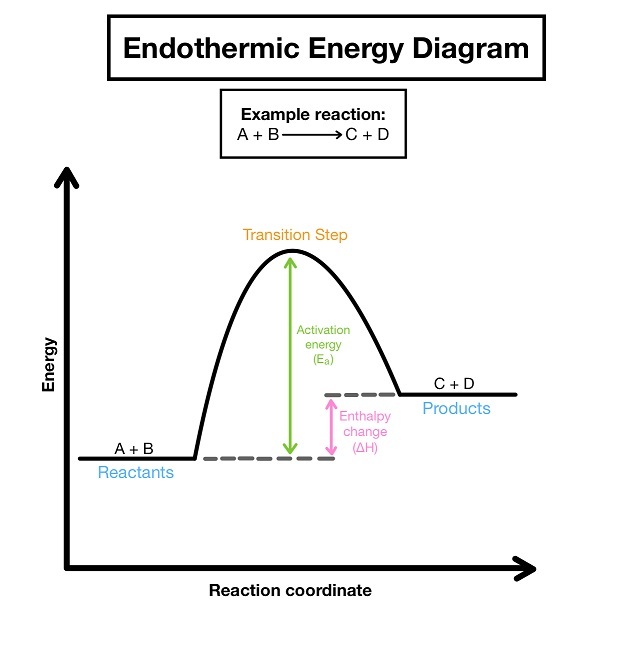
endothermic
-bonds are broken
-energy is taken in
-temperature decreases
-products have more energy
-enthalpy change is positive
average bond enthalpy
the enthalpy change when breaking one mole of covalent bonds in gaseous molecules
breaking - making (reactants - products)
‘Explain in terms of bond energies why the reaction is exothermic’
more energy is released during bond making than is taken in during bond breaking
specific heat capacity equation
Q = m x c x change in T
REASONS for differences in calculated + data values
-heat loss to the surroundings
-incomplete combustion
-evaporation of water/alcohol
-non-standard conditions
standard conditions
pressure = 100kPa
temperature = 298K
concentration = 1 moldm-3
state = physical state
standard enthalpy change of reaction
the energy change in a given reaction in molar quantities in a chemical equation under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of formation
the energy change that takes place when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of combustion
the energy change when one mole of a substance completely reacts with oxygen under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of neutralisation
the energy change that takes place when one mole of water is formed from a neutralisation reaction
why is calculating enthalpy change not always possible?
-slow reaction rate
-high activation energy
-alternative products formed
Hess’ Law
direct pathway = A
indirect pathway = B + C
A = B + C
enthalpy change of combustion -EQUATION
-arrows face down
-intermediate = CO2 + H2O
A = B - C
enthalpy change of formation -EQUATION
-arrows face up
-intermediate = elements
A = C - B
MULTIPLE equations in Hess’ Law
-match up the equations to main equation using arrows
-then use A=B+C