IB ESS Topics 2.2, 2.3 & 1.3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Last updated 10:09 PM on 4/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
Species
A group of organisms that are capable of interbreeding
and have fertile offspring
and have fertile offspring
2
New cards
Population
A group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time
3
New cards
Community
A group of populations living and interacting with each other in a common habitat. It involves biotic interactions only
4
New cards
Ecosystem
A community of interdependent organisms and the physical environment they inhabit. It includes the interactions of communities with the abiotic habitat
5
New cards
Biosphere
The part of the Earth inhabited by organisms. It extends from the atmosphere to the Earth's crust
6
New cards
Producers
Make their own food from compounds found in environment. All other organisms depend one way or another on biomass that was assimilated by producers.
7
New cards
Consumers
Consists of herbivores (primary consumers), carnivores (secondary or higher level consumers) and omnivores (plant and meat eaters). Consumers either directly or indirectly (several steps removed) gain energy from the producer level. About 10% of the energy from one trophic level is passed on to the next level
8
New cards
Decomposers/Detritivores
Organisms that feed off of dead and decomposing organic material. They recycle organic matter by biodegrading detritus to get their nutrients. They then release simple inorganics into the environment for use by producers
9
New cards
Assimilation
Process by which living organisms integrate nutrients from external resources to their body
10
New cards
Biomass
Total mass of living organisms in a given area
11
New cards
Carnivore
Consumers that eat other animals
12
New cards
Omnivore
Consumers that eat both plants and animals
13
New cards
Herbivore
Consumers that eat only plants
14
New cards
Abiotic factors required to do photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll, and light
15
New cards
Respiration
Sugars gained through photosynthesis or feeding are used to provide energy during respiration
16
New cards
Anaerboic Respiration
Process of cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen, leading to the breakdown of glucose into energy and producing lactic acid or ethanol as a byproduct
\
The break down of organic material in a landfill relies on anaerobic respiration
\
The break down of organic material in a landfill relies on anaerobic respiration
17
New cards
Productivity
The rate at which energy is added to the bodies of a group of organisms in the form of biomass
18
New cards
Primary Productivity
The rate at which solar energy (sunlight) is converted into organic compounds via photosynthesis (producers). Measured in units of energy per unit area per unit time.
19
New cards
Gross productivity
The total gain in energy; total biomass produced
20
New cards
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
the gross productivity specifically of producers. It is the total rate of photosynthesis in a given area.
21
New cards
Factors that affect GPP
Amount of light, CO2 and H2O available, nutrient availability, temperature, and herbivory
22
New cards
GPP can be measured through
the rate of oxygen production, CO2 consumption rate & glucose production rate
23
New cards
Net Primary Production
the rate of energy storage by photosynthesizers in a given area after subtracting the energy lost to respiration
24
New cards
NPP formula
NPP = Photosynthesis (GPP) - Respiration (R)
25
New cards
What does negative NPP mean?
Loss in biomass
26
New cards
What does positive NPP mean?
Growth, gain in biomass
27
New cards
What does zero NPP mean?
No change
28
New cards
Methods to measure NPP
* CO2 Assimilation (use probe to measure GP and to measure the amount of CO2 released during R)
* O2 production
* O2 production
29
New cards
The gross primary productivity of a meadow in southeastern Kansas is found to be **40,000 kcal/m²**. Respiration, which is measured by the amount of CO₂ released, is **15,000 kcal/m²**, what is the net primary productivity for this ecosystem, in kcal/m² per year?
\
1. 25,000 kcal/m2/yr
2. 55,000 kcal/m2/yr
3. -25,000 kcal/m2/yr
4. -55,000 cal/m2/yr
1. 25,000 kcal/m2/yr
2. 55,000 kcal/m2/yr
3. -25,000 kcal/m2/yr
4. -55,000 cal/m2/yr
30
New cards
The net annual primary productivity of a particular wetland ecosystem is found to be 6,000 kcal/m² per year. If respiration by the aquatic producers is 12,000 kcal/m² per year, **what is the gross annual primary productivity** for this ecosystem, in kcal/m² per year?
\
1. 6,000 kcal/m2/yr
2. 18,000 kcal/m2/yr
3. -6,000 kcal/m2/yr
4. 12,000 kcal/m2/yr
1. 6,000 kcal/m2/yr
2. 18,000 kcal/m2/yr
3. -6,000 kcal/m2/yr
4. 12,000 kcal/m2/yr
31
New cards
Gross Productivity of a consumer
equal to the NP of the trophic group before it
* Producer: GPP - R = NPP
* Producer: GPP - R = NPP
32
New cards
Gross Secondary Productivity
GSP is the total energy or biomass assimilated by consumers
33
New cards
GSP formula
GSP = food eaten - fecal loss
34
New cards
Net Secondary Productivity
NSP = GSP - R
35
New cards

Bottle Method
36
New cards
Food Webs
Show the feeding relationships with multiple species per trophic level and multiple energy pathways (multiple arrows).
37
New cards
Food Chains
Show one feeding interaction that depicts how one species per trophic level gets energy from the previous level. It depicts one energy arrow per trophic level.
38
New cards
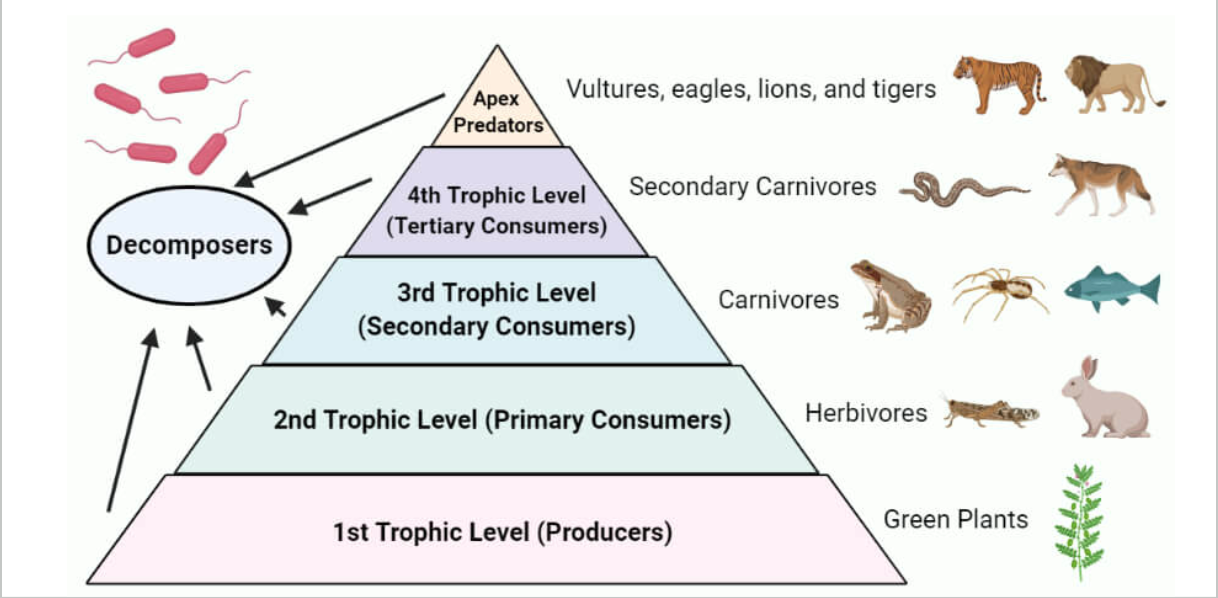
Trophic Level
Is the position an organism occupies in a food chain. In a food web, omnivores may occupy more than one trophic level.
39
New cards
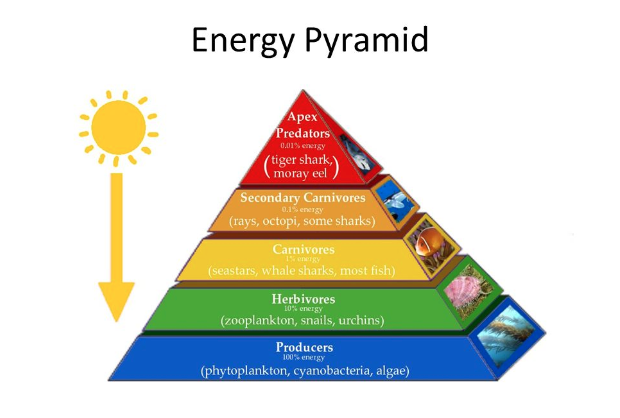
Ecological Pyramids
Is the position an organism occupies in a food chain. In a food web, omnivores may occupy more than one trophic level.
40
New cards
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed but it may be changed to other forms.
41
New cards
\
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Energy is always degraded (lost to an unwanted form) during a transfer of energy. This means the entropy of the universe is always increasing.
42
New cards
Pyramid of numbers
Compares the number of organisms at each trophic level
43
New cards
Pyramid of biomass
Compares the mass of biological material at each trophic level
44
New cards
Pyramid of energy/productivity
Compares the amount of energy passing through each trophic level over a period of time
45
New cards
Inverted Pyramids - why?
\
1. **Producer is large in size**--Leads to inverted pyramid of numbers
1. Ex. 1 tree may support many small primary consumers
2. **Seasonal Changes**
1. **Ex. After a seasonal fire, a grassland has less biomass in the producer level**
3. **Reproduction/Migration/Feeding Habits**
1. Ex. When a meadow blooms it attracts a large number of pollinators who may not always stay in that area
1. **Producer is large in size**--Leads to inverted pyramid of numbers
1. Ex. 1 tree may support many small primary consumers
2. **Seasonal Changes**
1. **Ex. After a seasonal fire, a grassland has less biomass in the producer level**
3. **Reproduction/Migration/Feeding Habits**
1. Ex. When a meadow blooms it attracts a large number of pollinators who may not always stay in that area
46
New cards
Bioaccumulation
the process in which a non-biodegradable toxin that has been released into the environment ends up stored in the body tissue of an organism
47
New cards
Biomagnification
the process in which a non-biodegradable toxin becomes more concentrated in higher trophic level organisms.
48
New cards
Why are DDT and mercury bad?
*In the environment, insects would encounter DDT and absorb some of it into their bodies. Often, they would receive a sub-lethal dose, enough to impair them but perhaps not kill them. In any event, it stands to reason that insects either dying or merely slowed down by pesticide intake would become easy targets for birds. Upon ingestion, the DDT in the insect bodies is released and makes its way into the tissues of the bird's body, particularly the fat deposits. Because an individual bird eats many insects, and because the DDT does not leave the bird's body, and because DDT resists breaking down (either in the environment or the body), it accumulates to higher levels in the bird's tissues. In other words, the DDT that was spread out over, say 1,000 crickets will be concentrated in one bird.*