3.2.1.5-7 Particle classification, Quarks and Conservation Laws
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
what is the pion?
the exchange particle of the strong nuclear force, a meson
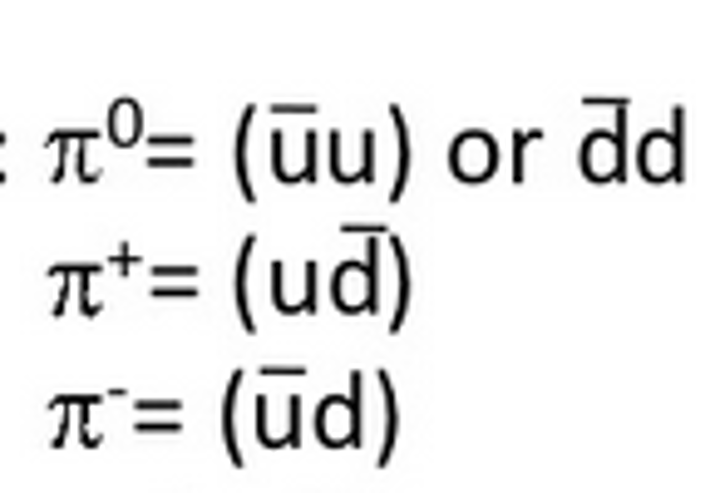
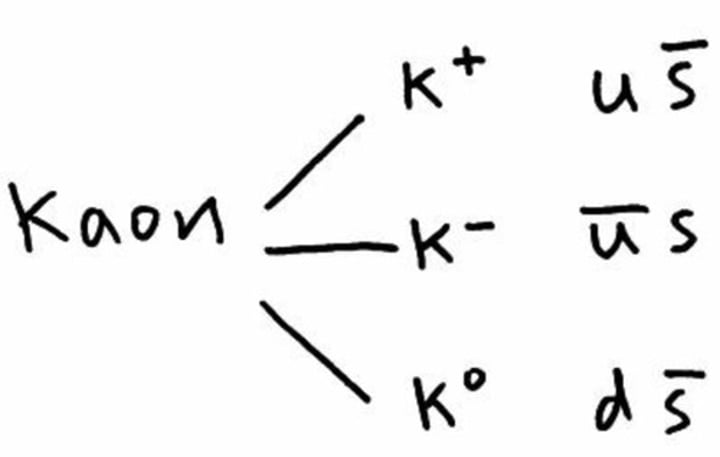
what is the kaon?
a type of meson that decays into pions
what are leptons? give examples
fundamental particles that don't feel the strong nuclear force. they only really react with other particles via weak interaction e.g. electron, muon, neutrino (e- and muon types only) and antipartcies
what is strangeness?
a quantum number that reflects the fact that strange particles are always created in pairs
what does particle physics rely on?
the collaborative efforts of large teams of scientists and engineers to validate new knowledge
what are hadrons?
anything made of quarks
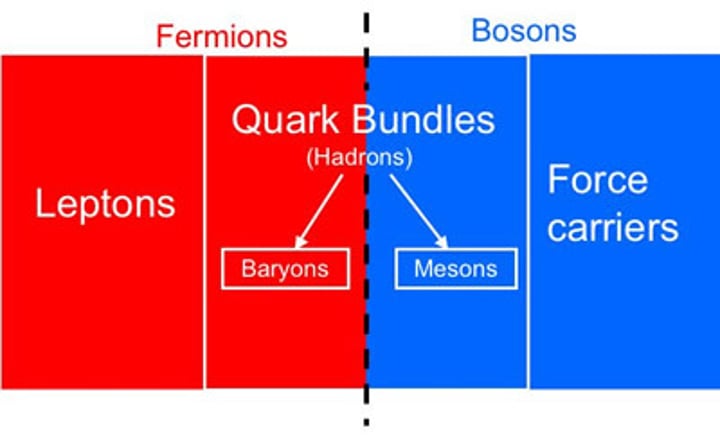
what are the 2 classes of hadrons?
baryons and mesons
what are baryons? give examples
made up of three quarks or three antiquarks (known as anti baryons) e.g. proton, neutron
what are mesons?
made up of a quark and an antiquark e.g. pion, kaon
what is baryon number?
the no. of baryons in an interaction - a quantum number that must be conserved
what is the only stable baryon?
the proton, which other baryons eventually decay into
what is the muon?
a particle that decays into an electron

what are strange particles?
contain strange quark they are produced through the strong interaction and decay through the weak interaction. e.g. kaons
what is strangeness in strong and weak interactions?
conservation in strong interactions
can change by 0/+1/-1 in weak
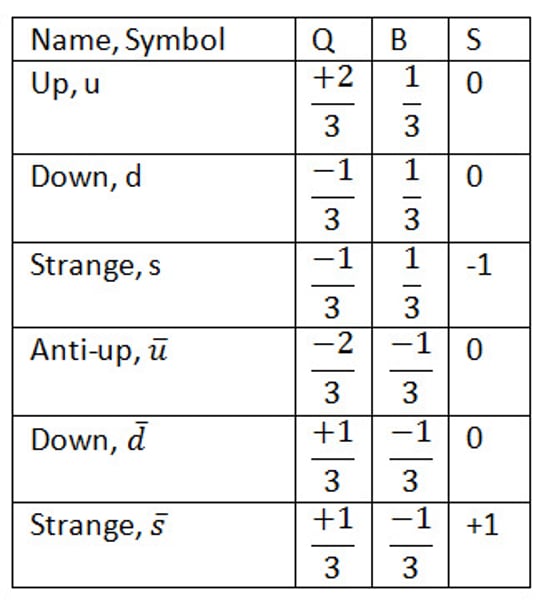
properties of quarks and antiquarks (charge, baryon no and strangeness)
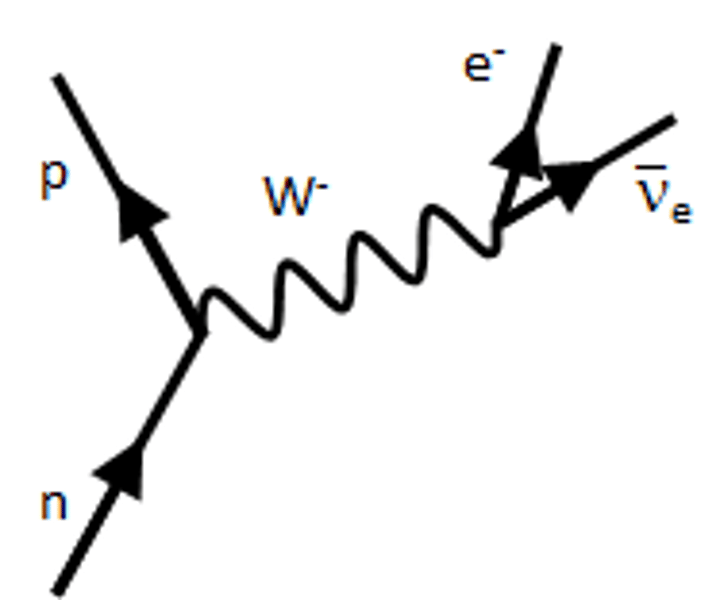
what does a neutron decay into?
a proton, an e- and an anti-neutrino
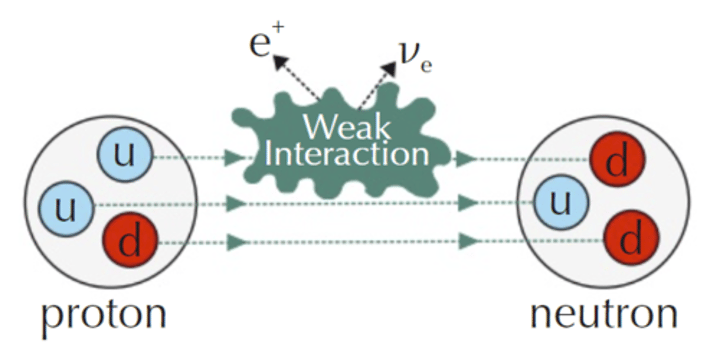
Change of quark character in β+ decay
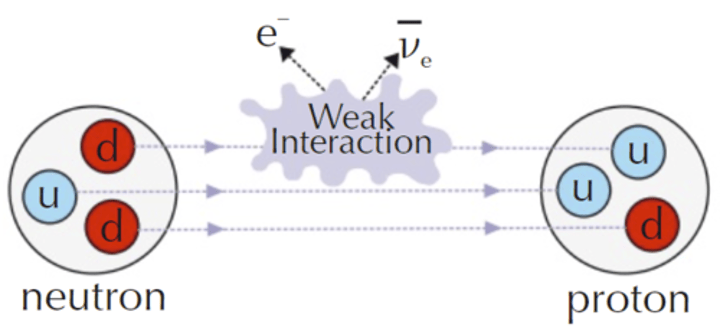
Change of quark character in β- decay
what is conserved in interactions?
energy and momentum