chemical reactions
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
what is the 1st law of thermodynamics?
energy cant be created
what is Hess’ law?
enthalpy of a reaction is equal to sum of enthalpies of reactions into which it may be divided, enthalpy is independent of route taken
what is the 2nd law of thermodynamics?
not possible to convert heat into mechanical work completely
what is the equation with: dH, dQ, dW, since its to energy-which part is the heat part, work part
dH= dQ (heat) + dW (work)
how can energy content be exchanged?
via heat or work
what is the equation that connects p, V, n, R, T
since its to do w energy- what is the work part and heat part
pV (work part)= nRT (heat part)
how can energy be described?
pressure, temperature, volume, amount (n)
what is the equation for gibbs free energy?
dG= dH-TdS
even if dG<1, activation energy is still needed, what controls the reaction if:
EA is provided at norm level,
EA is not provided at norm levell
if EA provided at norm level- thermodynamic control
if EA not provided at norm level- kinetic control
what is the Arrhenious equation?
k= Z x e-EA /RT
Z=orientation influence
e=reflects EA influence (EA /RT smaller= k is bigger)
what controls the reaction if k<1 or k>1
if k>1= thermodynamic control
if k<1= kinetic control
how does order of reaction correlate to rate?
rate= k[ ]order
what is a Bronsted-Lowry acid and base?
acid- proton donor, base- proton acceptor
what is mass action law?
in a reversible reaction- the products and reactants have a ratio - represented by k
k= [C] [D]/ [A] [B]
what is the equation for speed of the forward reaction?
vfor = Kfor [A] [B]
what is le Chatelier principle?
when a stress is imposed on an equilibrium the reaction will shift to relieve the stress
what equation connects log[H+ ] and log[OH]
-log[H+] - log[OH]= 14
pH + pOH =14
what equation correlates Ka and Kb and Kw
Ka Kb =Kw
what does a big Ka mean?
strong acid
what is an ampholyte?
weak acid +weak base
what is the Henderson Hasselbach equation?
pH= pKa + log [A- ]/ [HA]
how do you decide what half equation runs first? (when calculating dE)
more negative E runs first (electron flow goes from most negative cell to least) (dE)
what are the 2 types of electrode?
-metal rod in metal ion
-Hg, Hg2 Cl2, KCl paste, KCl solution, Pt wire (inert)
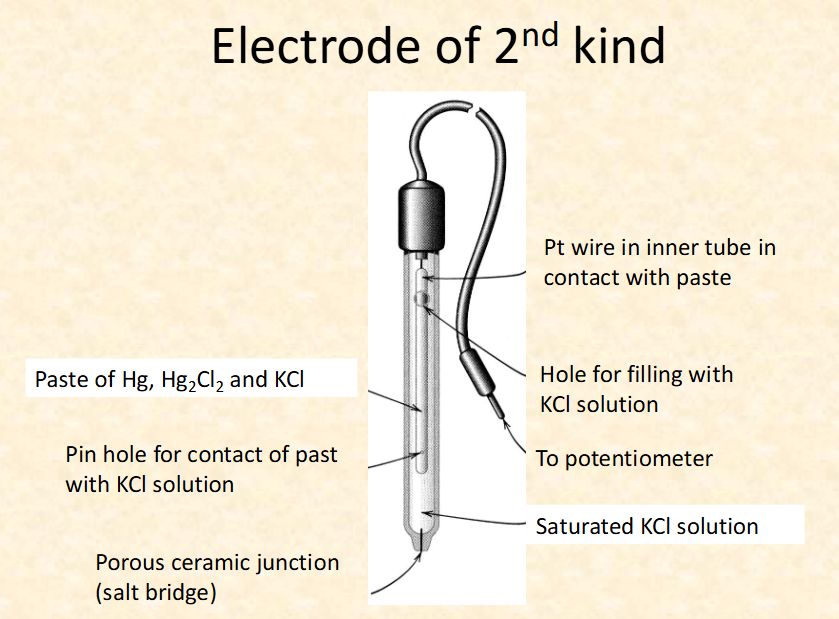
what are the limitation of pH electrodes?
if pH<1 as [H+ ] does not equal aH
if pH>12 as [Na] interferes
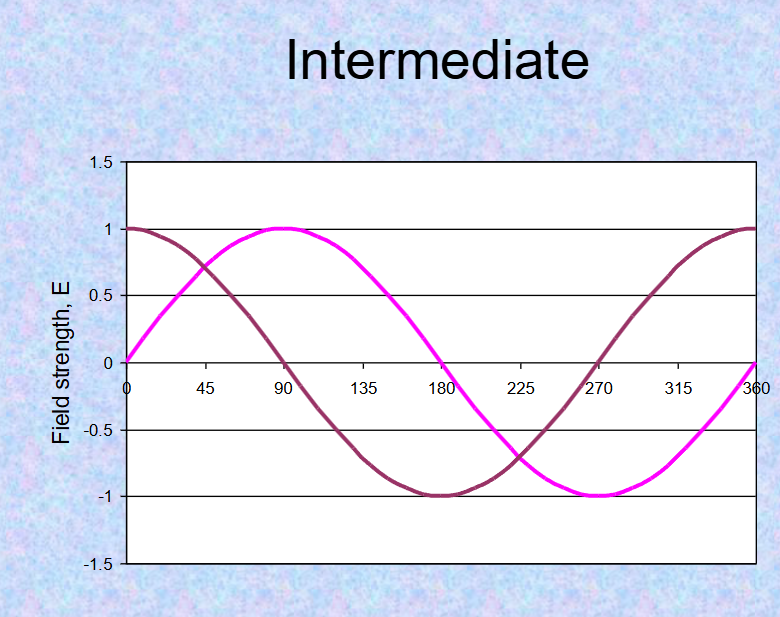
light is polarised, allowing for interactions between light waves: what are constructive, destructive and intermediate interference
constructive- additive (crests and troughs align)
destructive-cancel out (crests align with troughs)
intermediate-no effect (crests or each wave 90degrees apart)
what equation shows the quantum mechanics of energy (of a photon?)
E=hv (h=planck’s constant)
(v=frequency) (e=energy)
what are the 3 ways of energy transfer?
translation, rotation, oscillation
what is the equation connecting translation energy, rotation energy, vibration energy, electronic excitation of energy?
total E= Etrans +Erot +Evib +Eelec
what is the order of the sizes of energies? (trans, rot, vib, elec) and what uses each kind of energy transfer?
dEtrans<dErot (microwaves)<dEvib (infra-red)<dEelec (Uv visible)
what is the equation for absorbed and transmitted radiation
absorbed= -log i/ i0 (i= transmitted radiation, i0=incident radiation)
transmitted= i/i0
what is the beer’s law equation?
A= 3 x c x d
A= absorbance in given wavelength
3=molar absorptivity L/mol.cm
c=conc. mol/L
d=path length cm
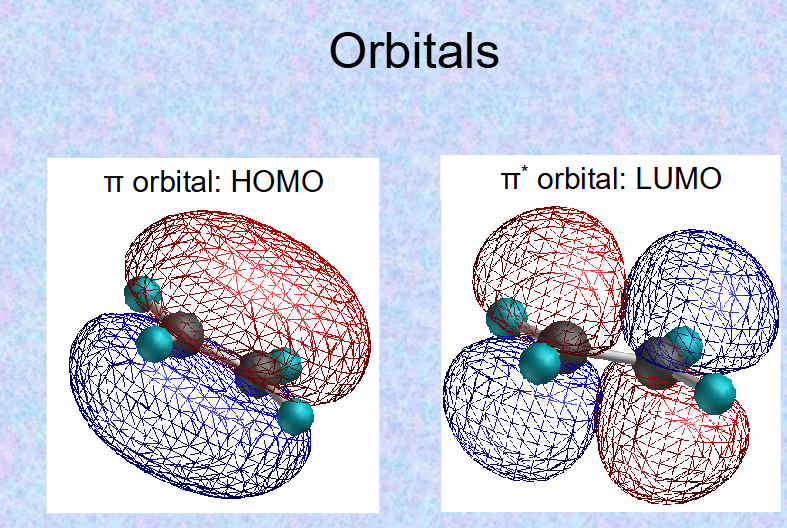
what is the difference between π and π*?
π* is higher energy (π absorbs energy→ π*)
HOMO=highest occupied molecular orbital
LUMO=lowest unoccupied molecular orbital)
what do HOMO and LUMO arrangements look like?
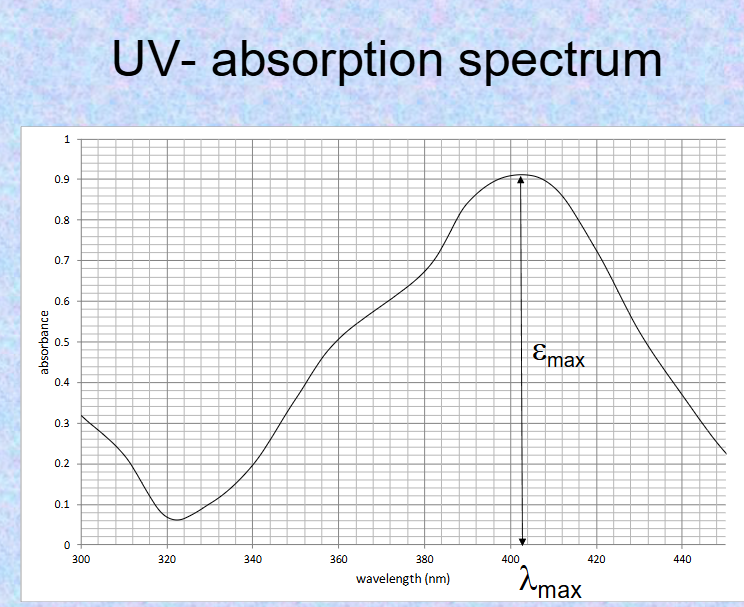
what is Max absorbance characterized by?
3Max and ymax (absorbance Max and wavelength Max)
what is the Nernst equation
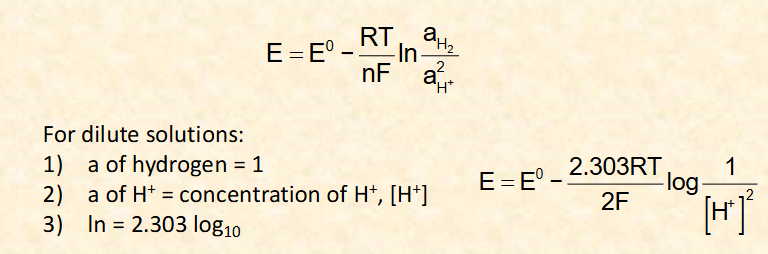
how do double bonds affect 3Max and ymax?
multiple double bonds- shift in 3max ONLY
how does co-planar molecules & conjugated double bonds affect 3max & ymax?
increases both
how is colour vision facilitated?
double bond systems
what is a bathochromic shift, hypsochromic shift?
bathochromic- red shift towards a longer wavelength, hypsochromic-blue shift toward a shorter wavelength
what is a hyperchromic, hypochromic shift?
hyper-intensity of absorption 3Max increases, hypo- the opposite
what is the order of autochromes increasing wavelength (and generally decreasing in absorption intensity)
NR2 > -NHR > -NH2 > -OH > - Halogen > -OCH3
what are the two methods of ionising a molecule?
electron impact,
chemical ionisation (uses reagent gas ions) (has less fragmentation)
electrospray ionisation (uses strong electric fields)
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation- (uses laser beam)
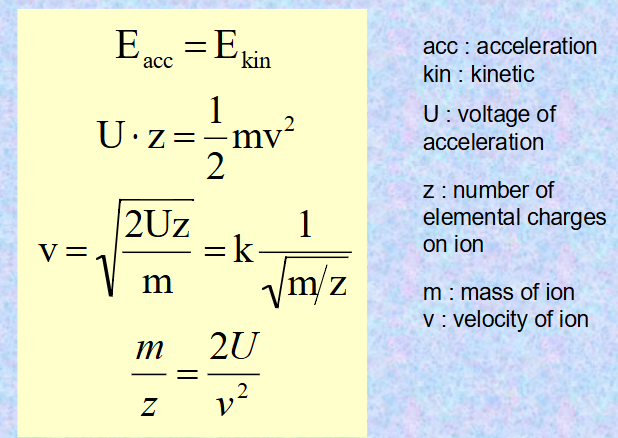
how are energy of acceleration and kinetics connected?