MOD 07 - Gypsum (Type III)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Dental Stone
Type III, Alpha form (Caso4.1/2h2o)
high strength stone
calcined by 30% calcium chloride solution
construction of casts, fabrication of full dentures to fit soft tissues
stronger and more expensive than plaster
more uniform, dense, prismatic shape in the form of
mold and prism
if mixed with water, dental stone sets harder mass
Dental stone is produced in two methods which are:
Heated 125 degrees under steam pressure in autoclave (more regular and less poroud)
Boiled in colution of salt Cacl2 (less porosity, produced by autoclaving)
Dental stone is used for
making cast
diagnostic purpose
cast for rpd & cd
processing dentures
Wet calcination of dental stone
aLpha calcium sulfate hemihydrate is formed smaller, regularly shaped, crystalline particles in form of rods and prism
type iii dental stone or hydrocal or clas 1 stone
wp ratio of dental stone
0.28-0.30
water ratio for dental stone
29-35
powder ratio for dental stone
100
advantages and disadvantages of dental stone
Advantages is greater strength and surface hardness while the disadvantage is it is more expensive than plaster
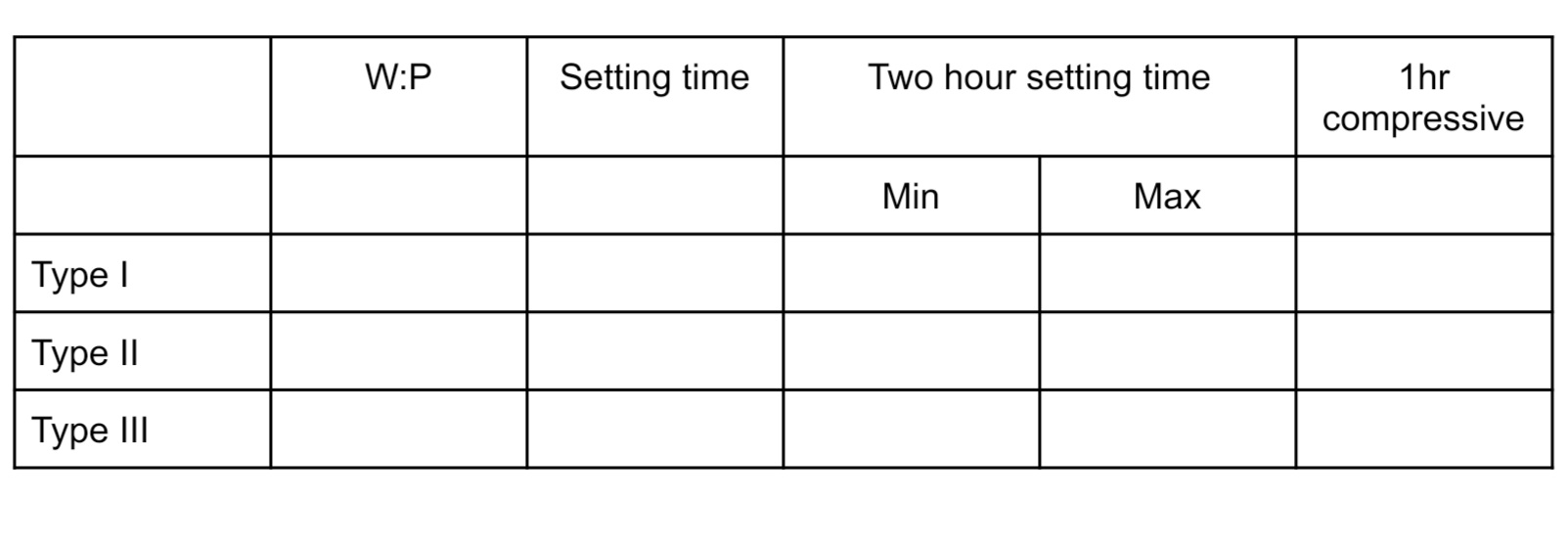
Fill out the property requirements for each gypsum products
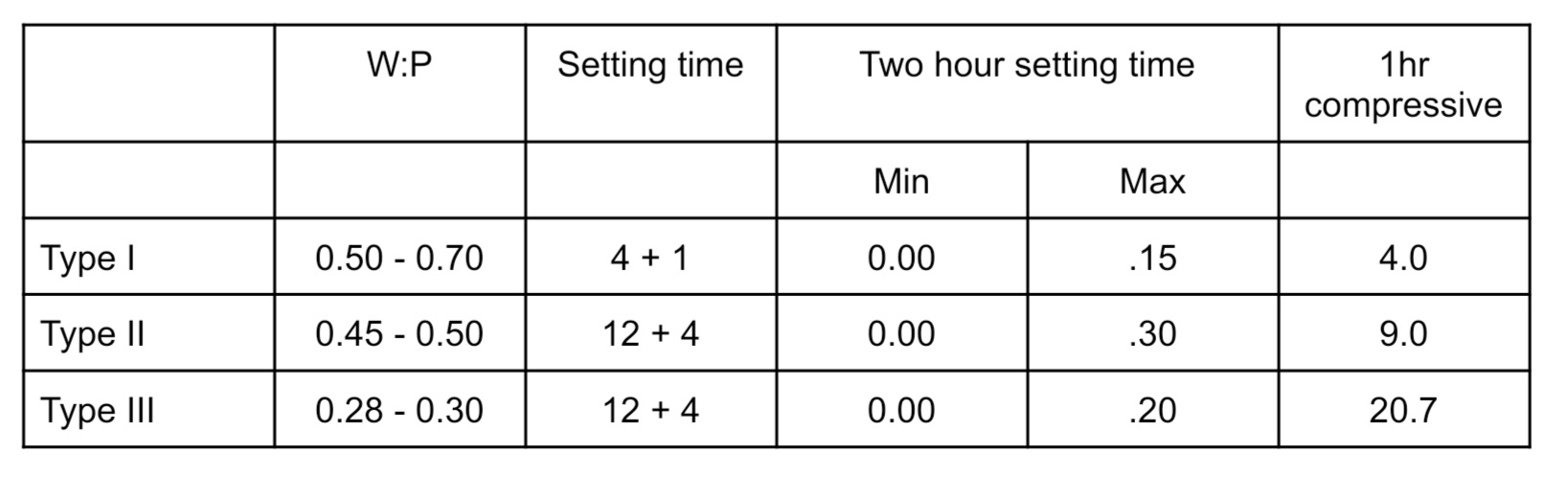

Fill out the setting time for each gypsum products


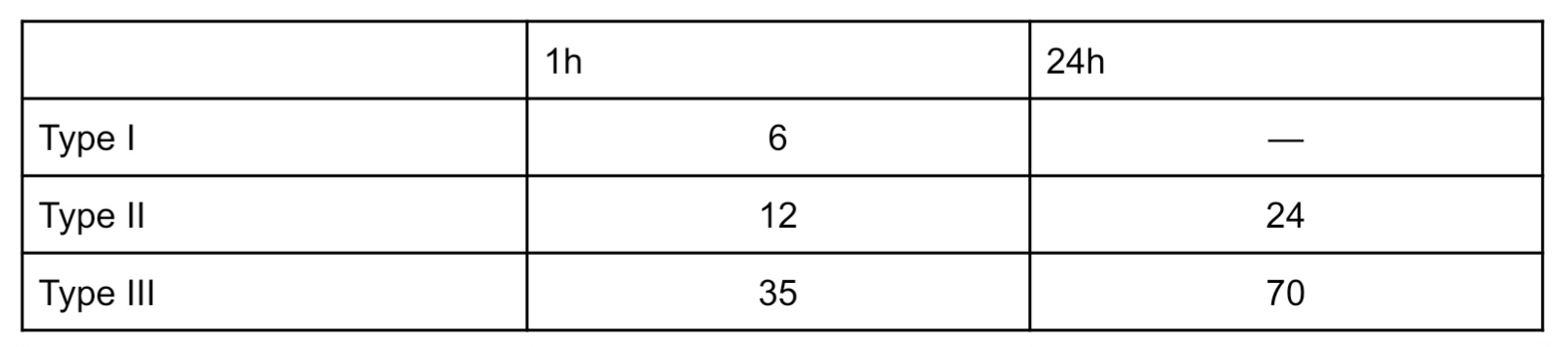
Fill out the compressive strength for each gypsum products
Factos controlling setting time
Factors under manufacturers
Factors under control of the operator
Factors under manufacturers
Concentration of nucleating agents in hemihydrate powder. more nucleating = more crystallization
Addition of chemical accelerators or retarders to dental stone
Factors under control of operators
Temperature
Increasing W:P
Increasing mixing time
Setting expansion of Type I, II, III
Type I - 0-0.15
Type II - 0-0.30
Type III - 0-0.20
To produce an accurate model or die, you should maintain
setting expansion at low value
Compressive strength
Depends on porosity, time which material allowed to dry out
Flexural strength
Stone is less fragile but must be treated with care
likely to fracture if droped
Flexural strength of Types I, II, III
Type I - 1
Type II - 1
Type III - 15
Detail reproduction
Reproduce surface detail of hard and soft tissue either directly or from impression
Strength, hardness, accuracy requires dental stone
stone are most likely to be damaged during laying down & caring of wax pattern & give optimal dimensional accuracy
Detail reproduction of types I, II, III, IV, V
Type I - 75
Type II - 75
Type III - 50
Type IV - 50
Type V - 50
What number of detail reproduction is capable of greater fine details
Type III, IV, V