Chapter 23: Government Spending, Taxes, and Fiscal Policy
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
spends more than state and local governments combined
federal government
government provided insurance against bad outcomes such as unemployment, illness, disability, or outliving your savings
Social insurance programs
spending on programs that does not get determined annually
Mandatory spending
Spending that is set in law
Mandatory spending
Spending for programs like Social Security and Medicare
Mandatory spending
spending that Congress appropriates annually
Discretionary spending
Only accounts for 30% of federal government spending
Discretionary spending
provide employment and income support, education and health care
States
Provide higher education
states
Provide primary and secondary education
local governments
Provide Bus services, water, sewer lines, local parks, trash collection, police, firefighters, etc.
local governments
Total government spending is (BLANK) in the United States than in other rich countries
lower
The federal government primarily collects revenue from (BLANK) and (BLANK)
income taxes, payroll taxes
taxes on earned income
Payroll taxes
Levied as a fixed percentage of your earned income.
Payroll taxes
Funds Medicare and Social Security
Payroll taxes
(BLANK) contributes an additional amount to Medicare and Social Security along with your payroll taxes
Employer
taxes collected on all income regardless of its source
income taxes
Includes income you earned from working AND unearned income such as investment income, pensions, capital gains, and inheritance or gift income
Income taxes
is your stock of savings and assets
wealth
all the money you receive in a year
income
Income taxes are (BLANK)
progressive
The tax rate you pay increases with your income
progressive
the amount of income on that you pay taxes on
taxable income
taxable income =
total income received - deductions
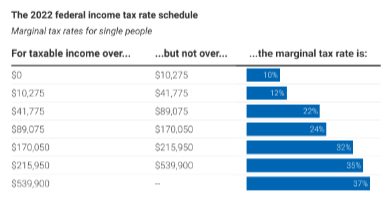
Suppose your job paid you $50,000 in 2022.
Standard deduction: $12,950
Let’s figure out how much you’ll pay in income tax this year.
$4,240.50
As taxes rise, businesses buy (BLANK) capital, which makes workers (BLANK) productive, so employers aren’t willing to pay them as much
less, less
Corporate taxes are paid by
owners of corporations and workers
collect sale, property, and income taxes
States and local governments
A tax on purchases
sales tax
Typically, a percentage of the purchase price
sales tax
a tax on a specific product, such as gas, cigarettes, or alcohol.
Excise tax
Typically, levied base on the quantity you buy, not the price you pay
excise tax
collect sale, property, and income taxes
states and local governments
is a tax on the value of property, usually real estate
property tax
is a tax where those with less income tend to pay a higher share of their income on tax
regressive tax
Sales, excise, and property taxes tend to be
regressive
special deductions, exemptions, or credits that lower your tax obligations, to encourage you to engage in certain kinds of activities
Tax expenditures
Tax expenditures have a lower
political cost
Tax expenditures encourage (BLANK) on certain goods and services
spending
encourage you to purchase health insurance, save for retirement, and buy your own home
Tax expenditures
If you pay $10,000 in interest on your mortgage, that $10,000 is (BLANK) from your taxable income
deducted
Salary $43,000, plus employer-provided health insurance. Ø You’ll have to contribute $3,000 in premium payments. How much is the taxavle income?
$40,000
Salary $45,000, but NO health insurance. How much is the taxable income?
$45,000
The value of tax exclusions and deductions is higher when your income tax rate is (BLANK)
higher
Higher-income people tend to buy (BLANK) tax-preferred goods and services
more
Most tax expenditures don’t provide much help if your income tax bill is (BLANK)
zero
Tax expenditures primarily benefit the (BLANK)
wealthy
often inefficient, poorly targeted, persistent, and rarely evaluated for
effectiveness
Tax expenditures
tries to help by providing benefits even to those who have zero taxable income
refundable tax credit
Make it so that you can get a tax refund even if you don’t pay and taxes
refundable tax credit
The American Opportunity Tax Credit gives you $1,000 to help tuition costs. This is an example of a
refundable tax credit
Government can disguise spending as
tax breaks
allows the government to require spending, while others pay the bill
regulation
Instead of Congress budgeting for this program, now employers pay (and, to some extent, workers pay)
regulation
requiring companies to pay for parental leave might lead some employers to avoid hiring workers they suspect might become parents. Regulation changes (BLANK)
incentives
The Government Sector has (BLANK) over time as the role of the government in providing social insurance and education has expanded
grown
government-provided insurance against bad outcomes such as unemployment, illness, disability, or outliving your savings
Social insurance
Spending on social insurance programs and military
federal spending
Spending on social insurance programs and education
state spending
Spending on education and community services
local spending
What is hidden government spending?
tax expenditures and government regulation
the government’s use of spending and tax policies to attempt to stabilize the economy
fiscal policy
Tries to minimize output fluctuations and keep actual GDP close to potential output
fiscal policy
Fiscal policy is (BLANK) in that it counteracts the effects of the business cycle
countercyclical
If output in the economy is weak, then the government increases spending and lowers taxes in order to boost aggregate demand for output and, thus, raise GDP
Expansionary fiscal policy
If the economy is overheating, then the government decreases spending and raises taxes in order to weaken aggregate demand for output and, thus, lower GDP
Contractionary fiscal policy
Government spending can add to GDP indirectly through
transfer payments
Transfer payments add to GDP indirectly as the boost
aggregate expenditure
describes the possibility that an initial boost in spending will set off ripple effects.
multiplier effect
Discretionary government spending can involve substantial
time lags
Fiscal policy works best when it’s
timely, targeted, and temporary
the decline in private spending—particularly investment—that follows from a rise in government spending
crowding out
Expansionary fiscal policy leads to (BLANK) real interest rates, which (BLANK) private spending
higher, reduces
fiscal policy (i.e., spending and tax programs) that adjusts as the economy expands and contracts without policymakers taking any deliberate action
automatic stabilizers
Automatic stabilizers (BLANK) output during recessions and (BLANK) output during expansions
increase, decrease
The progressive tax system helps counter both booms and busts as you change (BLANK) which changes how much you spend
tax bracket
Dropping into a lower tax bracket during a bust allows consumers to spend (BLANK)
more
Rising into a higher tax bracket during a boom allows consumers to spend (BLANK)
less
Examples of automatic stabilizers
progressive tax system and government support programs
Automatic stabilizers are
timely, targeted, and temporary
Fiscal policy is more
targeted
Fiscal policy is particularly important at the
zero lower bound
The difference between spending and revenue in a year in which spending exceeds revenue.
budget deficit
The difference between spending and revenue in a year in which revenue exceeds spending.
Budget surplus
The federal government typically runs
budget deficits
Budget deficits may reflect
short-run political incentives
Requiring the federal government to balance its budget each year would prevent the use of (BLANK) to counteract business cycles
fiscal policy
Requiring a balanced budget would make business cycles
worse
During the 2007–2009 recession, state governments that faced a balanced budget requirement saw their revenues (BLANK)
decline
helps us think about a country’s debt relative to its capacity to repay it
debt-to-GDP ratio
a commitment to incur expenses in the future without a plan to pay for them
unfunded liability
the total accumulated amount of money the government owes
gross government debt
the debt that the government owes to individuals, businesses, and other governments both here and abroad
Net government debt