m2 nucleotides and nucleic acids
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
describe nucleotide structure
nitrogenous base
pentose sugar
phosphate group
rna has ribose sugar
what are the purine bases
adenine
guanine
what are pyrimidine bases
thymine
cytosine
uracil
describe how nucleotides are joined
nucleotides are joined together by a condensation reaction where water is removed
phosphodiester bond is between carbon 3 and carbon 5 , known as 3 to 5 phoephodiester bond
describe structure of ATP
ribose sugar
adenine
3 phosphate groups
describe energy needed to break the phosphate groups in ATP
only small amount of energy needed to break the last phosphate group off ATP
large amount of energy is released when bonds are formed by the ‘free’ phosphate group which is involved in other reactions
describe reaction that breaks down ATP
hydrolysis reaction and involves energy required reactions
these are said to be coupled as they occur simultaneously

describe how it would be if it was opposite (ADP→ATP)
to go from ADP to ATP it would be a condensation reaction
energy supplied by respiration
describe structure of DNA
contained 2 polynucleotide strand running in opposite direction , anti parallel strands which are held tg by hydrogen bonds
3 hydrogen bonds between cytosine and guanine
2 hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine
a purine always binds to a pyrimidine
two strands of DNA twist around to form a double helix
complimentary base pairs in the middle
describe semi conservative dna replication
dna replicates during interphase
dna helicase breaks hydrogen bonds between bases , double helix unwinds and each strand acts as a template
free nucleotides from cytoplasm and assembly on the template DNA in complementary base pairs
hydrogen bonds reform between bases
dna polymerase joins nucleotides forming new sugar phosphate backbone
two identical dna molecules have been produced
define semi conservative replication
each new dna molecule contains one of the old strands and one new strand
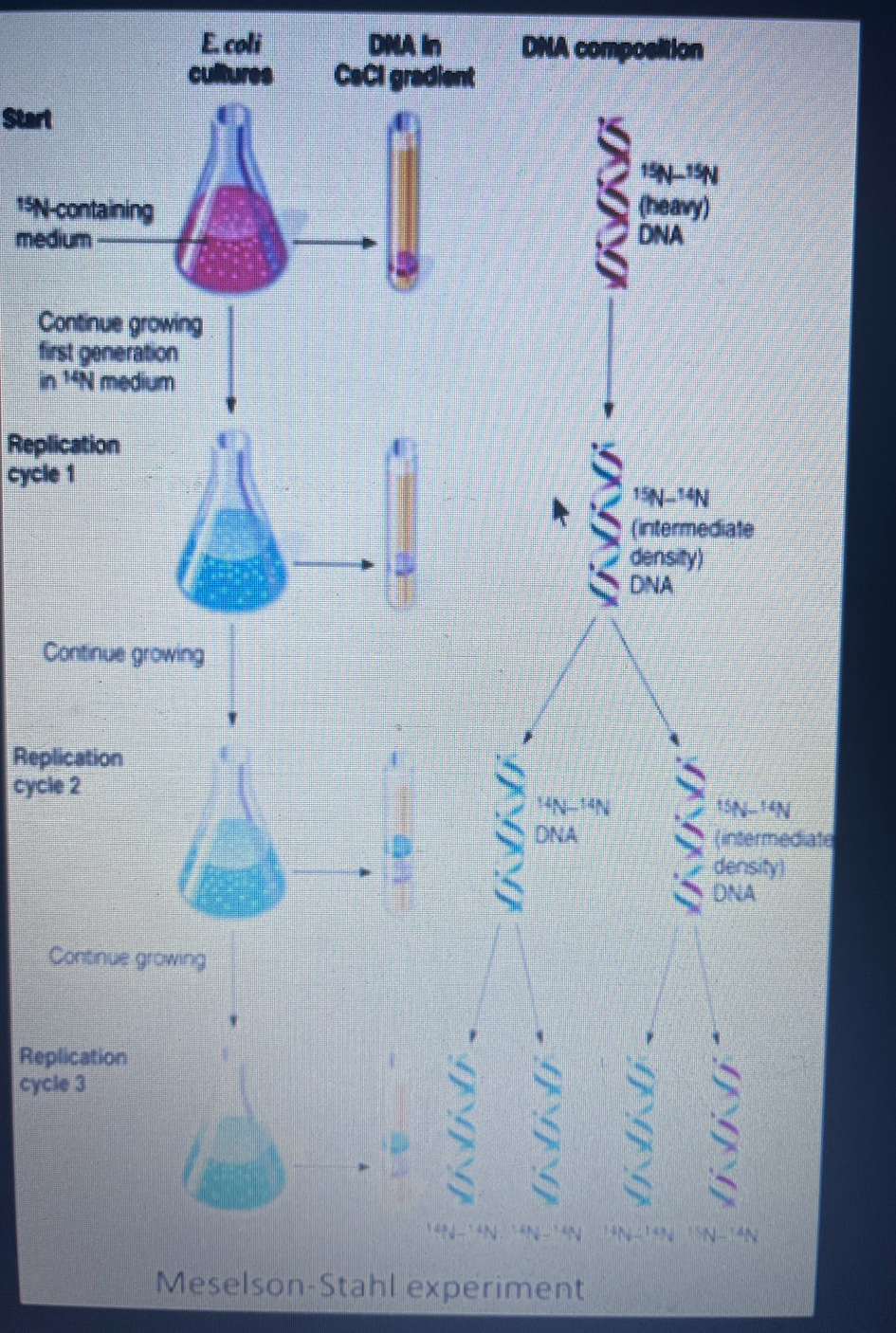
describe mehelson and stahl experiment
define gene
gene is a section of dna that codes for the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide
define alleles
different versions of a gene
describe the nature of the genetic code
dna controls protein structure by determining the amino acid sequence
the code is a triplet code
each sequence of 3 bases (codon) determines one amino acid so its non overlapping
degenerate so some amino acids have more than one triplet code
universal used across all organisms
code is always read in one direction
describe extraction of dna practical
crush sample to break down cellulose cell wall
add detergent to dissolve plasma membrane
add protease enzyme to break down histones associated with dna
filter to remove any solids
add salt to help dna clump together
pour ethanol in , dna insoluble so should float to top
precipitate formed
describe steps of transcription
hydrogen bonds between complimentary base pairs broken , dna helicase helps w this
free rna nucleotides form a complimentary strand (mRna)
RNA polymerase helps form phosphodiester bonds in between the RNA nucleotides , helps form sugar phosphate backbone
mRNA peels away from DNA and leaves nucleus through nuclear pore and DNA helix reforms
describe steps of translation
mRNA attaches to a ribosome that is made of two subunits of rRNA
anticodon on tRNA will find complimentary codon on mRNA bringing specific amino acid with it
many Trnas come
amino acids join together by peptide bonds to give a protein with specific primary stricture then go to secondary and tertiary