The Global Environment - Unit 2 (Atmosphere)
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
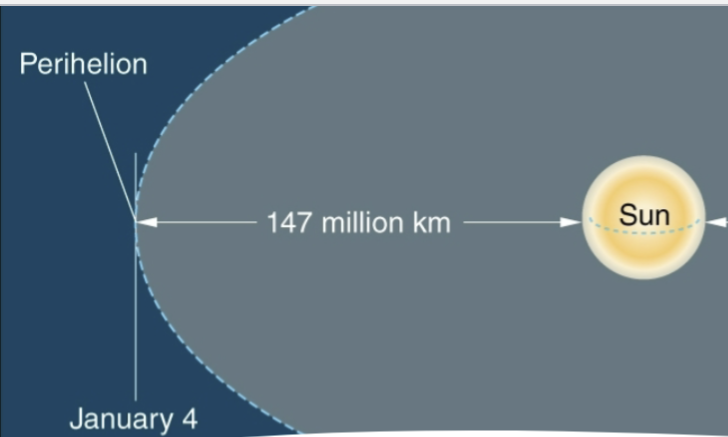
Perihelion
Closest to the sun, Northern Hemisphere: July 4
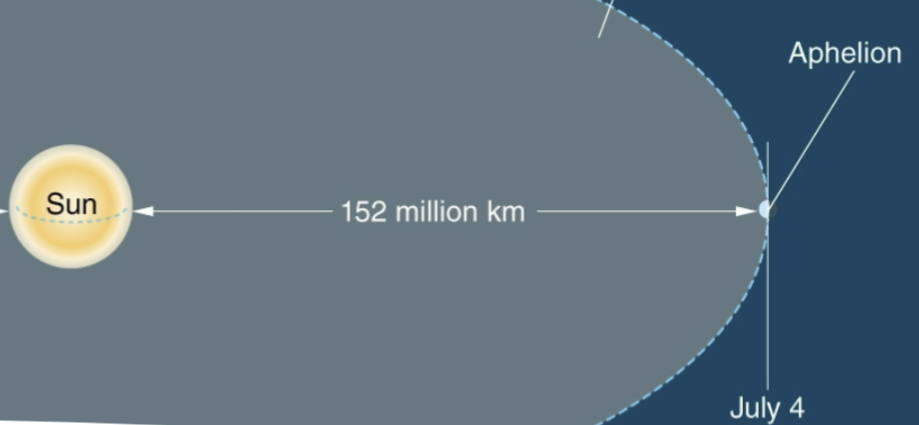
Aphelion
Farthest from the sun, Northern Hemisphere: Jan 3
Radiation
Form of energy transfer that does require mass or direct contact between bodies
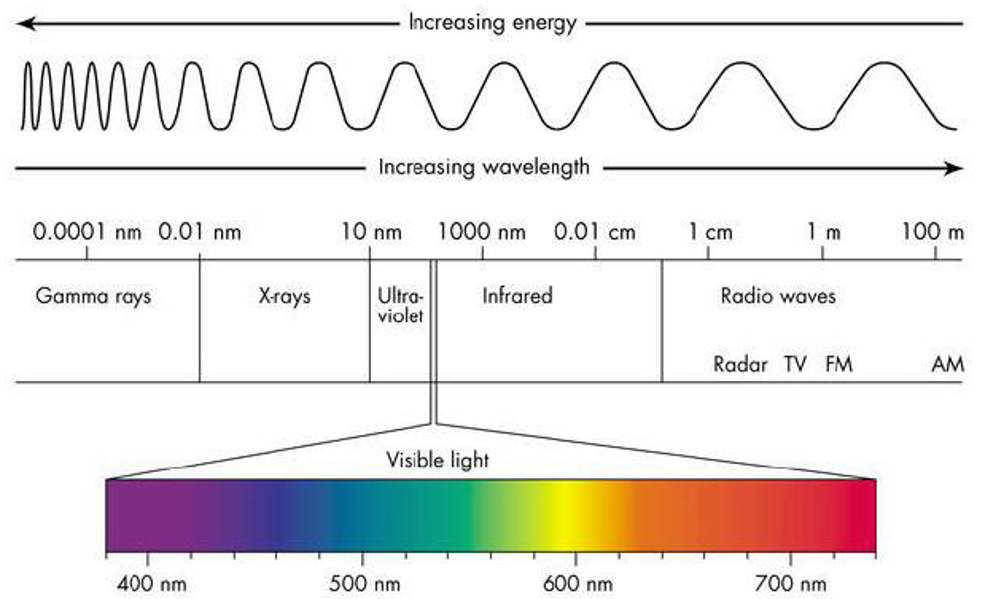
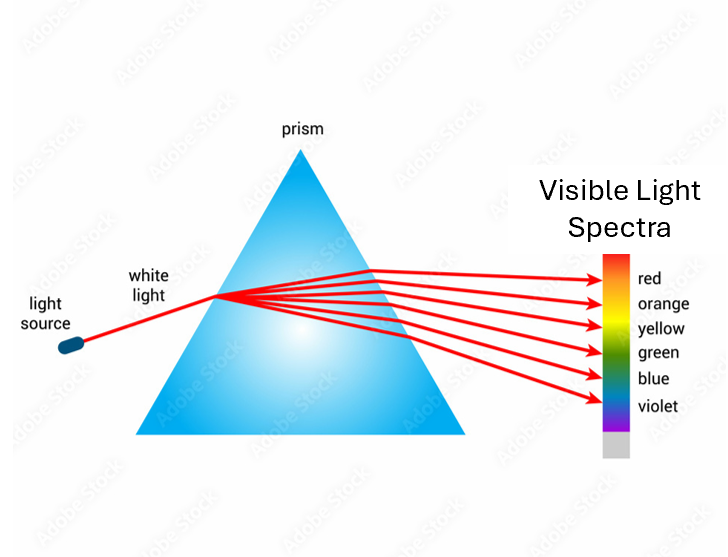
Short wavelengths
Higher frequency, higher energy (Gamma rays, x-rays, ultra-violet)
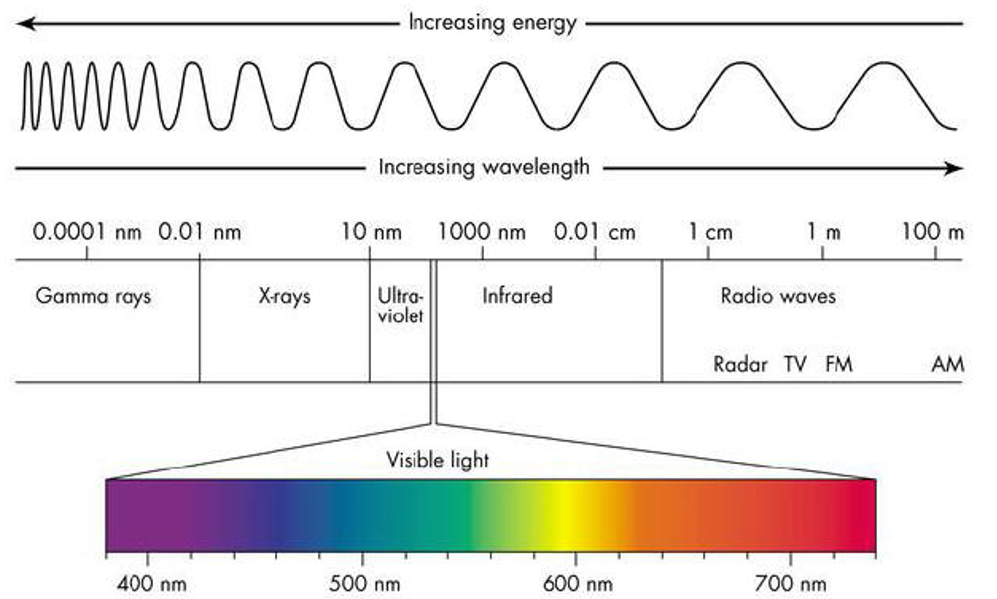
Longer wavelengths
Lower frequency, lower energy (Infrared, radio waves)
Temperature
Average measure of kinetic energy/speed of molecular movement
Hot objects
More energy, shorter wavelengths
Cold objects
Less energy, longer wavelength
Blackbody phenomena
Perfect emitters and absorbers of radiation at all wavelengths (ex: the sun)
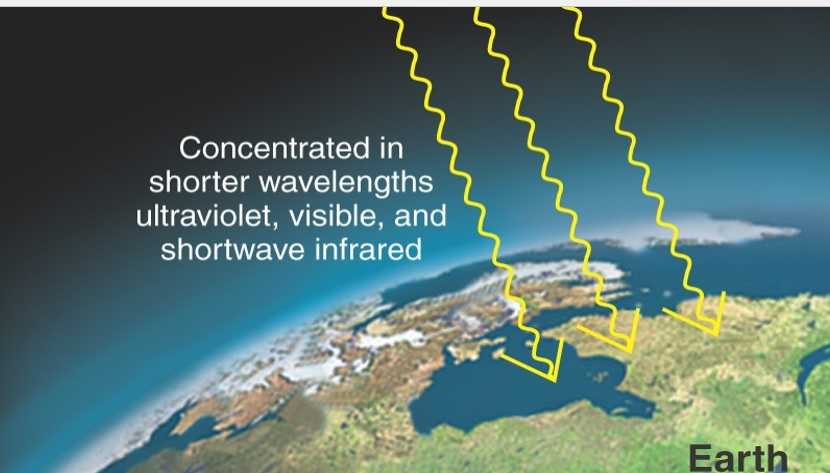
Shortwave radiation
From the sun
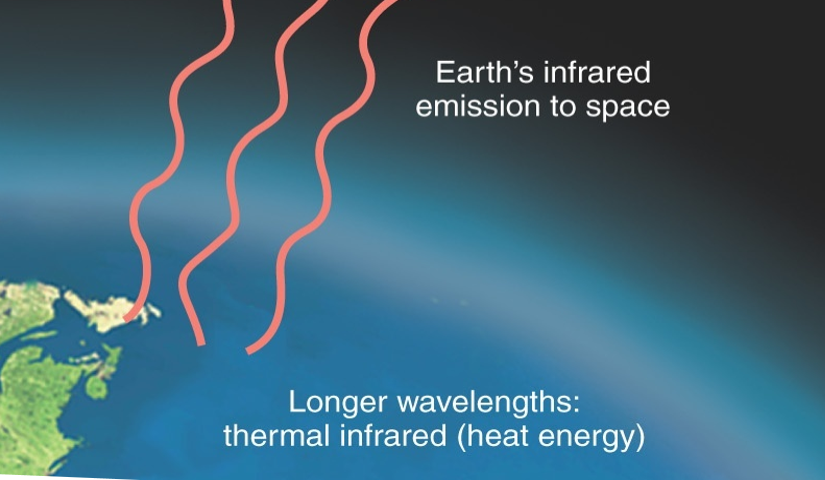
Longwave radiation
Earth’s emission into space
Law of Conservation
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or converted
Entropy
Conversion to heat is the ultimate fate of energy, heat is transferred from objects/regions with high temperature to those with low temperature
Net Radiation
The balance between incoming/outgoing energy
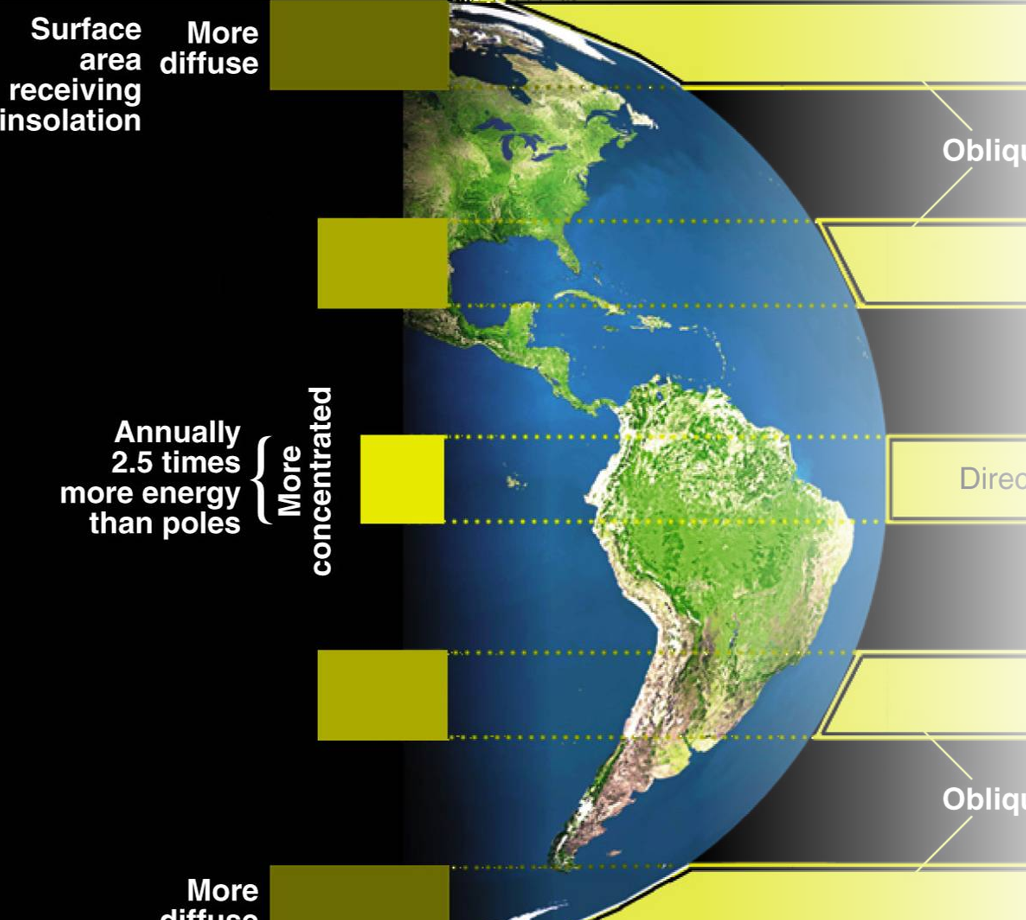
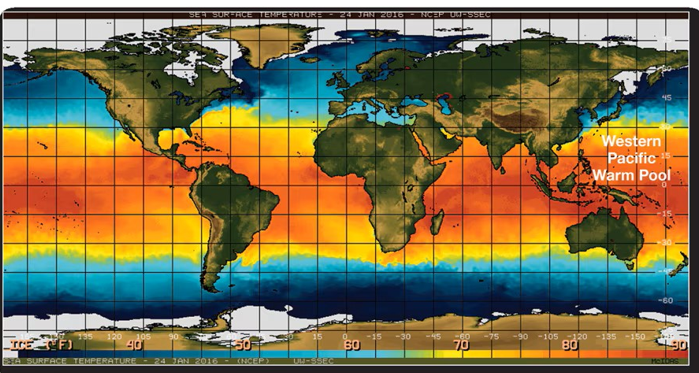
Latitudinal imbalances
Variation, uneven distribution in solar energy based on geometry, function of latitude
Net Radiation: higher latitudes
Negative net radiation
Net Radiation: tropic zones
Largest positive net radiation
Net Radiation: Antarctica
Lowest net radiation (albedo)
Insolation
Solar energy that is incoming to Earth systems
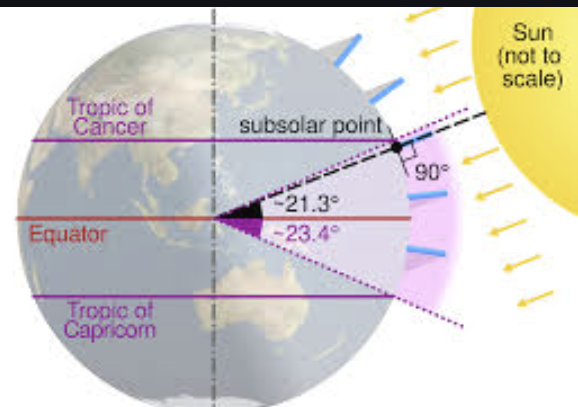
Solar Declination
The latitude that receives direct overhead insolation on a particular day
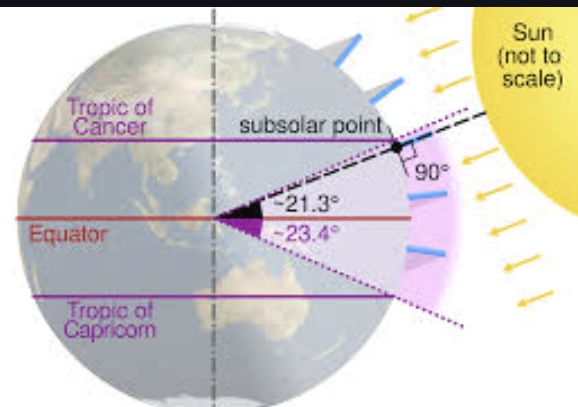
Subsolar point
The only point receiving perpendicular insolation at a given moment (the sun is directly overhead), migrates annually between Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn
Reasons for seasons
Revolution (orbit around the sun), rotation (Earth turning on its axis), tilt, axial parallelism (fixed axial alignment throughout the year), sphericity
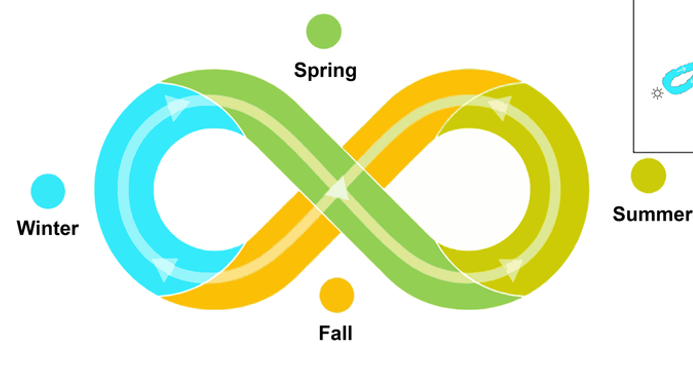
Seasonality
Fluctuations most active/present in mid-latitude regions, “expected” variability, cascading effects when thing change
Changing climate and season fluctuations
Effects timing of seasonal events (migrations, budding, etc.), duration of seasonal events (wildfires, hurricanes, etc.), variability of events (“Tornado Alley” location)
Photon
“Massless particles",” stable, no electron charge
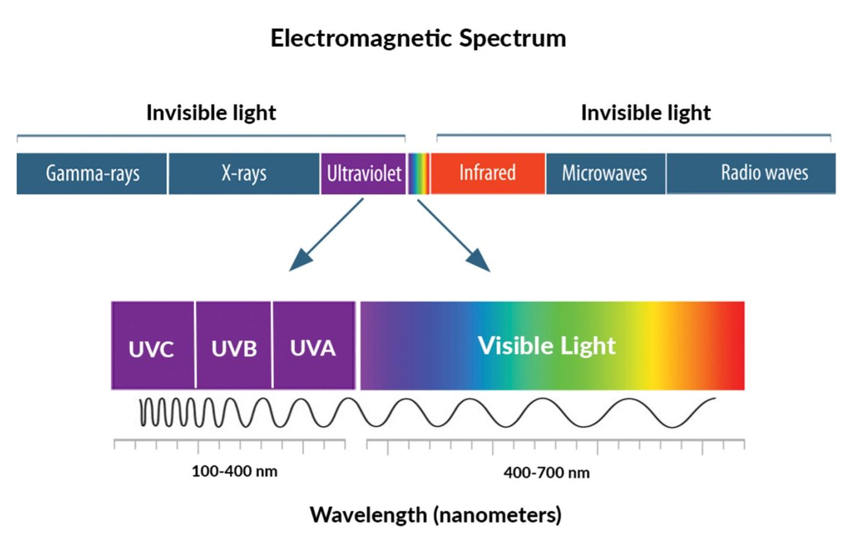
UV-A
“Longwave UV” or “BlackLight,” 95% of solar radiation we receive from the sun, responsible for signs of aging, absorbs deep into skin tissue (suntan)
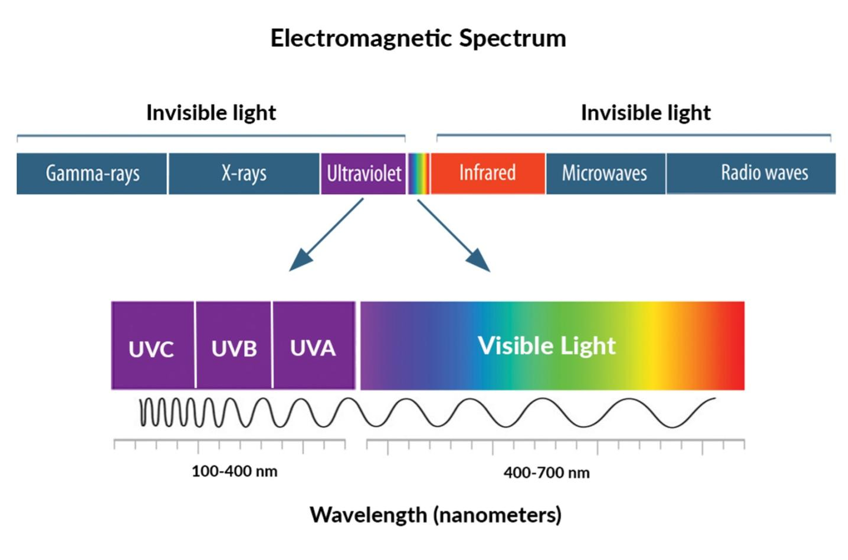
UV-B
Medium wave UV, ~5% of all solar radiation, damages skin tissue (sunburn), some absorbed by earth’s atmosphere
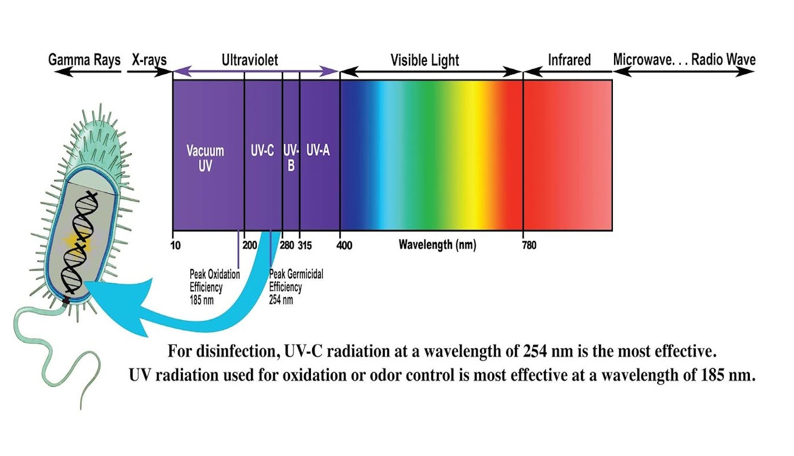
UV-C
Shorter wave UV, mostly trapped by earth’s atmosphere, anti-pathogen uses, mostly absorbed by the earth’s atmosphere
Ionizing radiation
UV-C, acute (treat cancers), chronic (cause cancers)
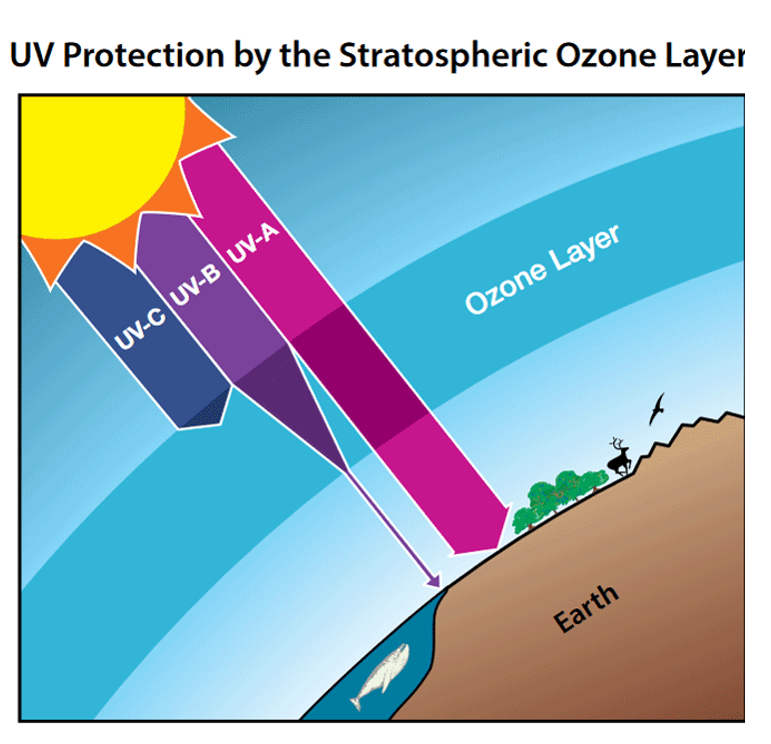
Ozonosphere
O3, naturally exists as a concentrated layer in the stratosphere, filters UV radiation entering Earth’s atmosphere
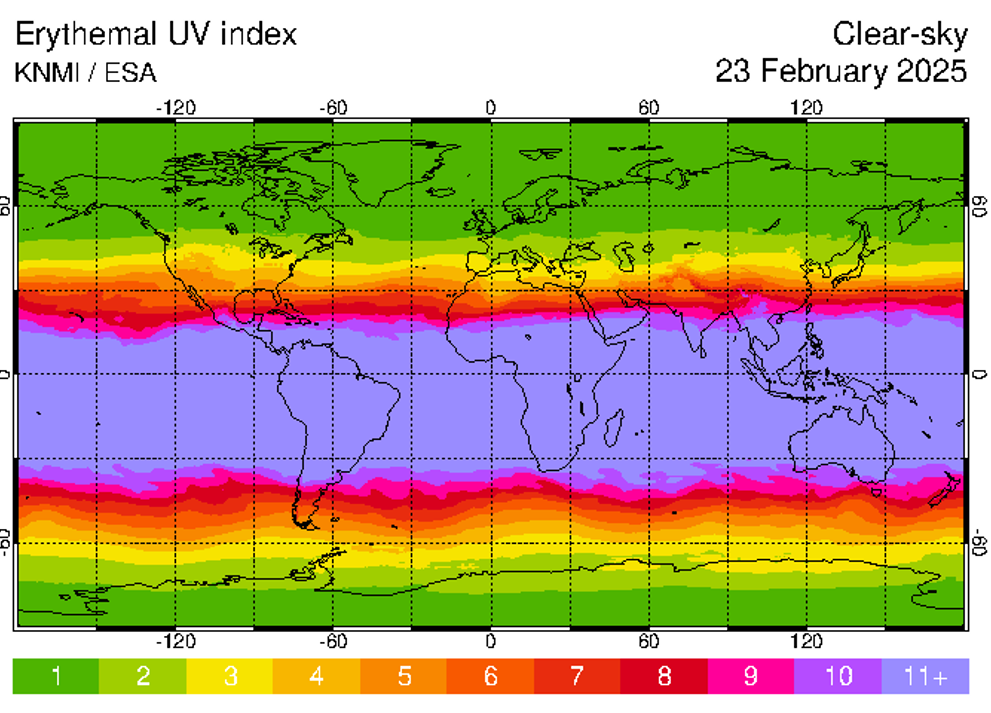
UV Index
1 to 11+ risk scale for sun exposure, 0=no risk (nighttime), determined by level of ozone present, sun angle, and cloud cover
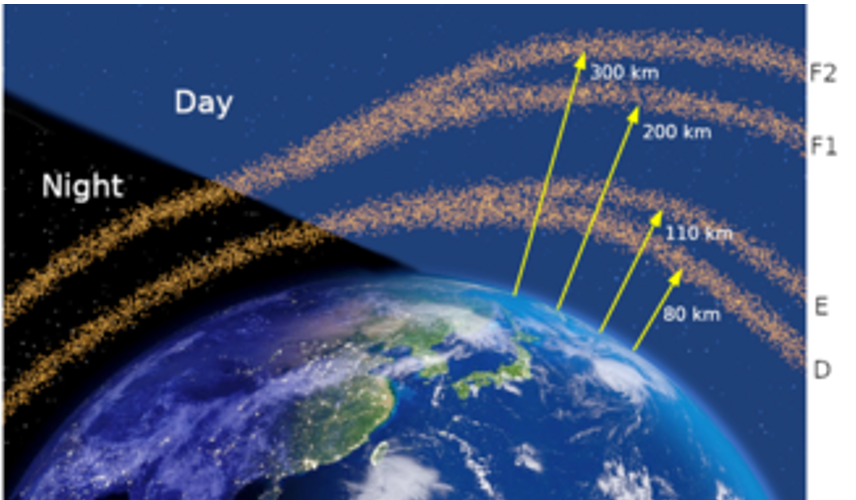
Ionosphere
Upper earth atmosphere, contains: exosphere, thermosphere, and mesosphere, influences radio and GPS signals, outer functional layer
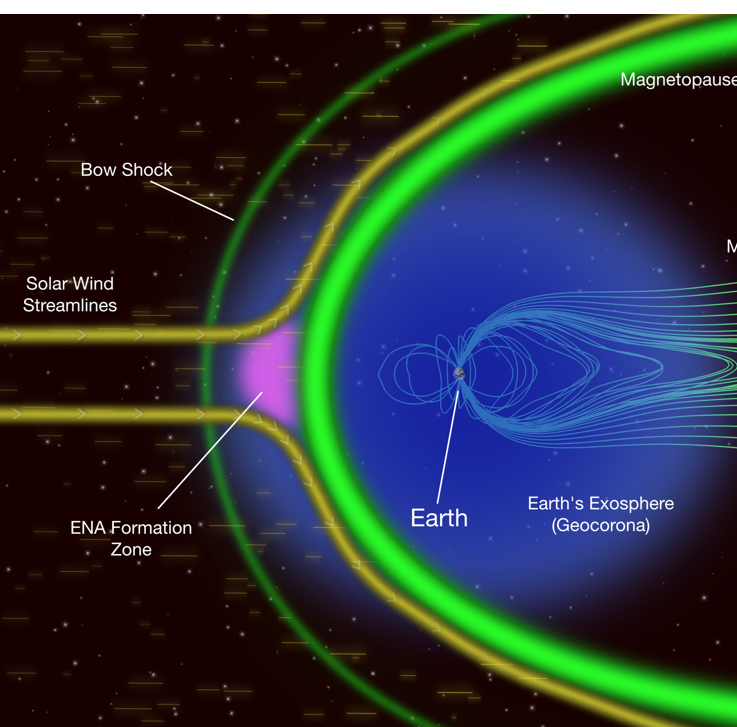
Exosphere
Protective layer, made up of hydrogen and helium atoms, highly variable temperature

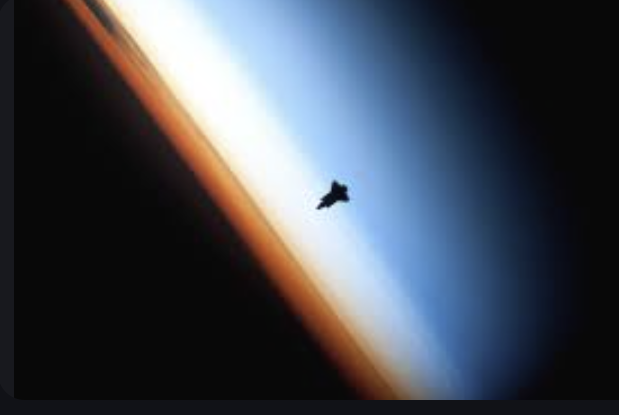
Thermosphere
Where UV absorption occurs, location of International Space Station, larger portion of the ionosphere
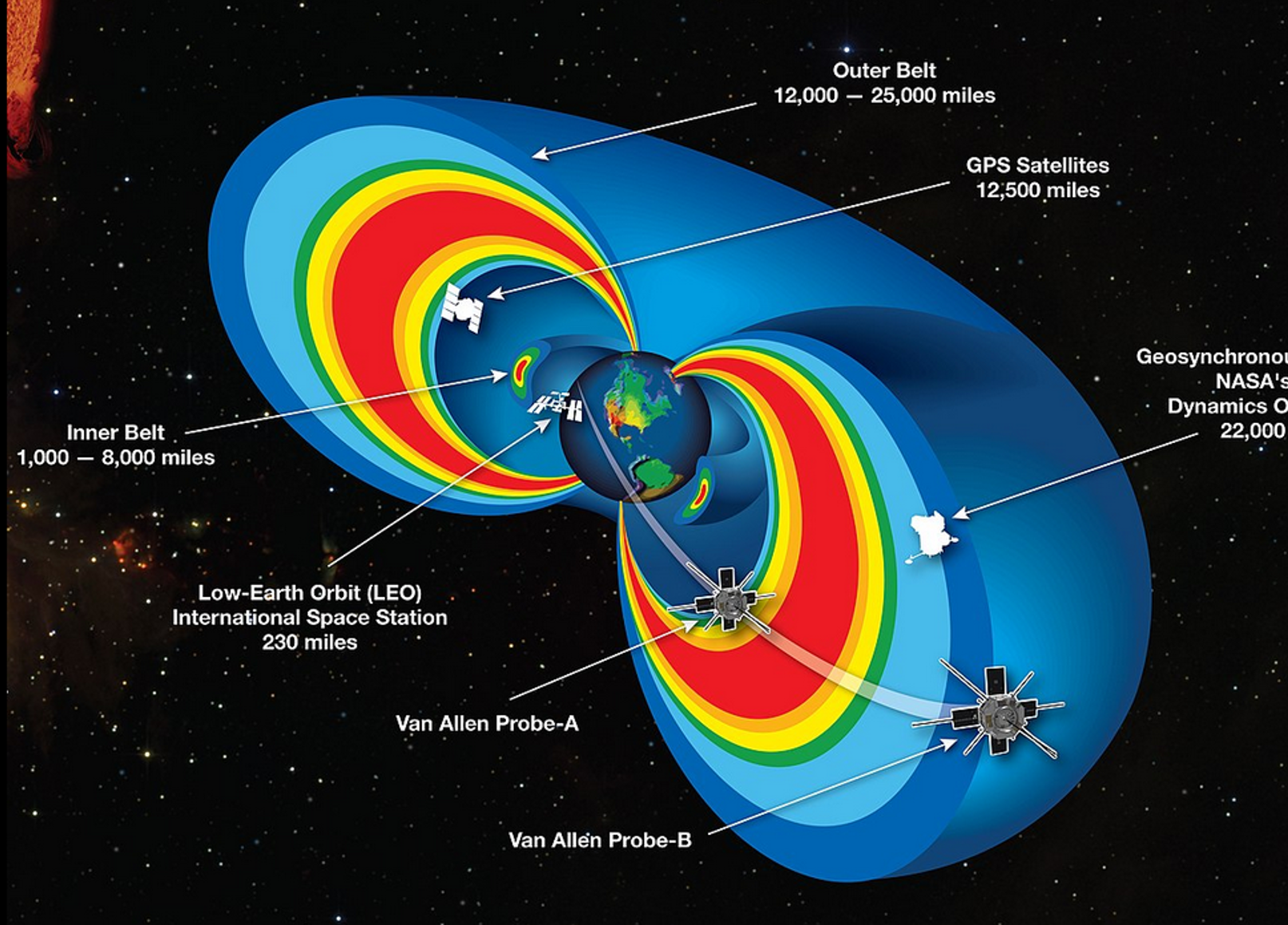
Magnetosphere
Charged particles captured and held within a planet’s atmosphere, deflects potential damages
Middle Atmosphere
Mesosphere, stratosphere, “near space”

Mesosphere
Coldest region of the atmosphere, temperature decreases as altitude increases (function of solar radiation and infrared heat trapped within)

Stratosphere
Enables oxygen exchange need for biological life, temperature stratified (warmer layers in upper atmosphere, cooler layers closer to Earth)
Troposphere
Where weather occurs and planes fly, temperature decreases with altitude, greatest variation in mid-latitudes
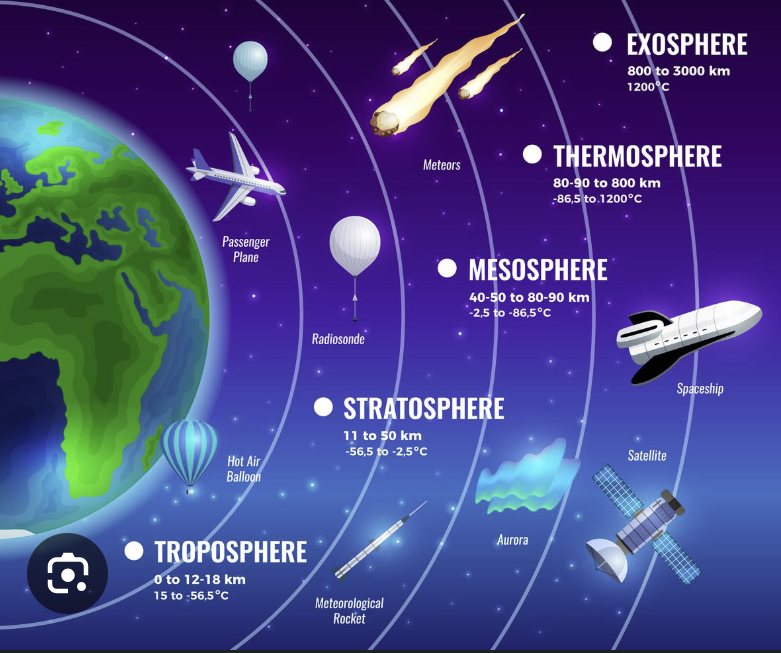
Earth’s Atmosphere
Veil of gases surrounding Earth, produce a protective boundary between outer space and the biosphere

Air pressure
Molecular activity, force exerted from colliding gas molecules on all surfaces
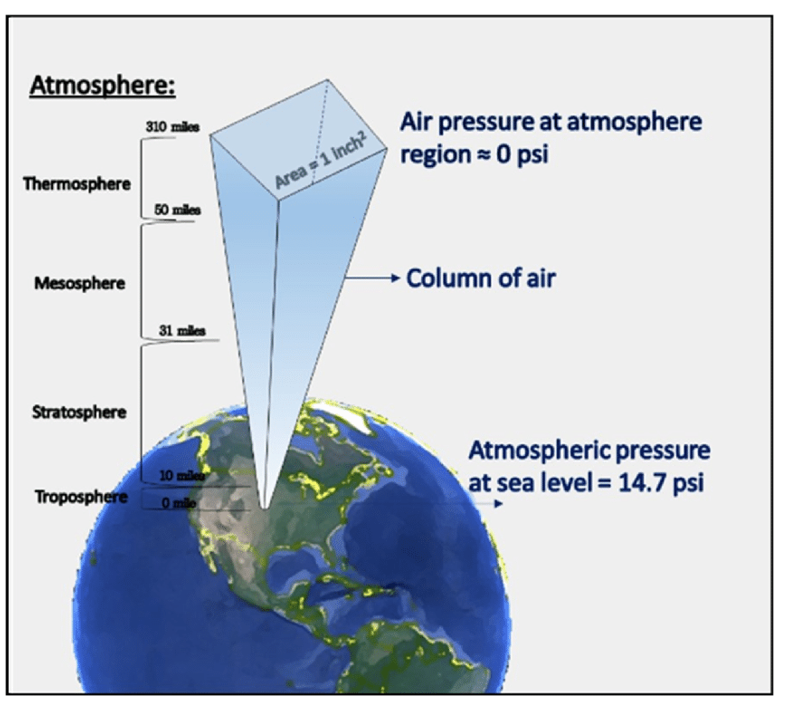
Atmospheric pressure
Pressure exerted by the weight of air present
Upper atmosphere
Less dense, fewer collisions, less pressure
Lower atmosphere
Denser, more collisions, more pressure
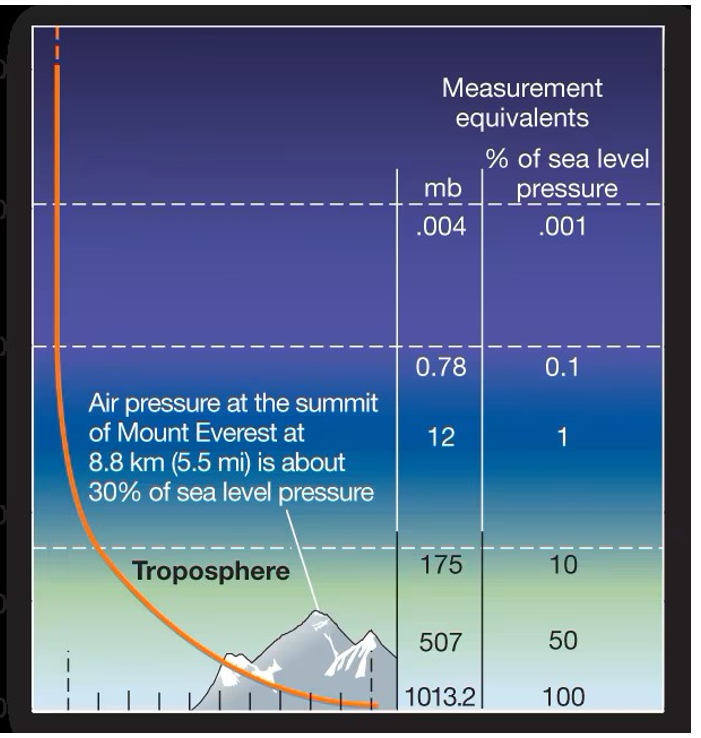
Altitude and Air Pressure
“Thinning” air in upper attitudes
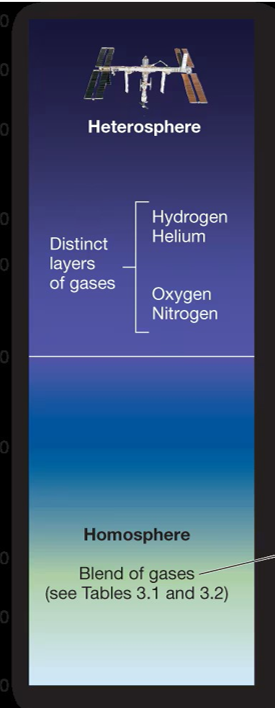
Heterosphere
Not uniform, outer atmosphere, gases not evenly mixed/distributed, layers defined by atomic weight (constant gases)
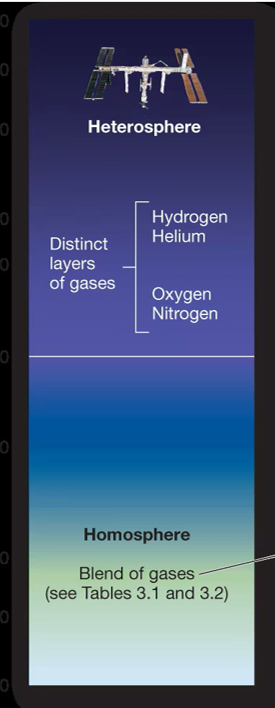
Homosphere
Uniform, gases more evenly blended, exception of the ozone layer, mix of materials (variable gases)
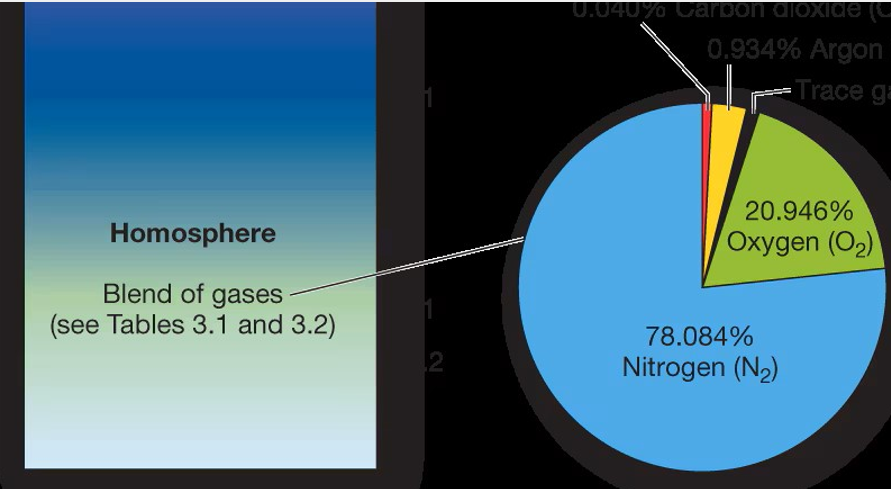
Constant gases
Nitrogen, oxygen, argon
Variable gases
Absorb/transmit radiant energy (water vapor, carbon dioxide, greenhouse gases), influence global temperatures
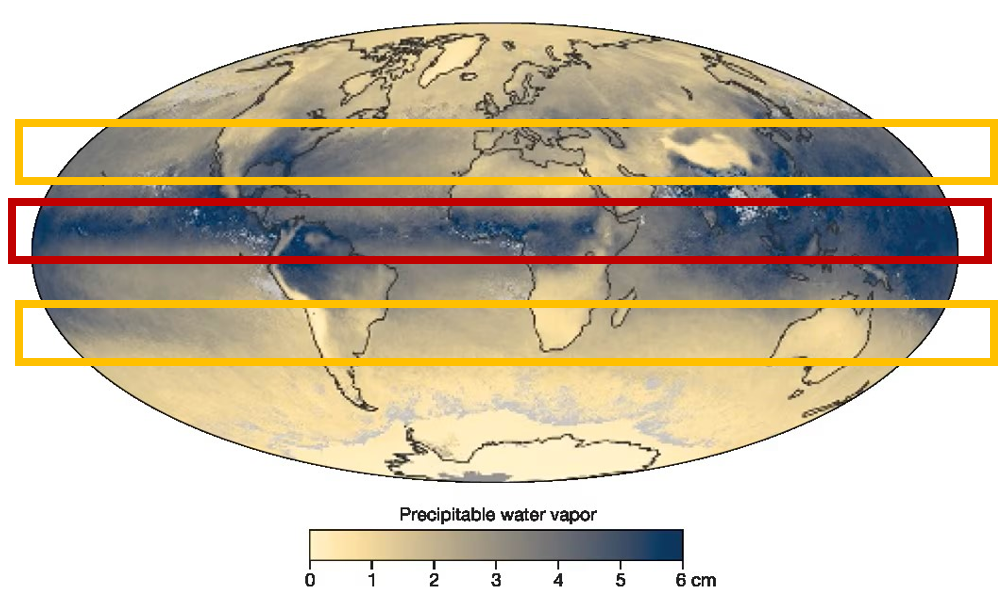
Water vapor
Earth’s most abundant variable gas, function of latitude and landforms: highest in tropical zones, lowest over deserts and dry, high latitudes
Thermopause
Outermost layer, temperature extremes

Environmental Lapse Rate
Rate of temperature decreases with altitude increase
CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons)
Aerosol propellants, fire suppressants, refrigerants. UV radiation splits CFCs, releasing chlorine that breaks down ozone molecules
Montreal Protocol
International agreement to restore the ozone layer, CFC banned
Natural factors impacting air quality
Wind direction and speed (dust transmission), local landscapes, volcanic activity (enhanced conditions (vog)), temperature inversions
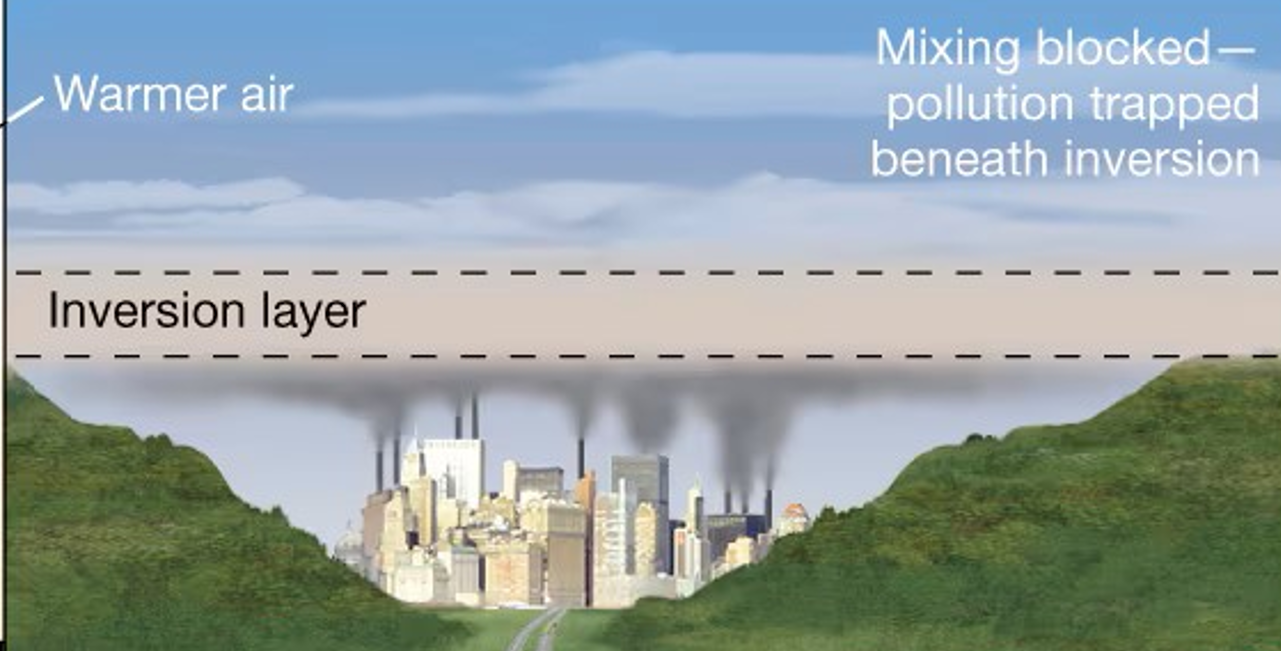
Temperature inversion
Layer of warmer air overlies cooler air (rather than temperature decreases as altitude increases), results in a layer that traps pollutants
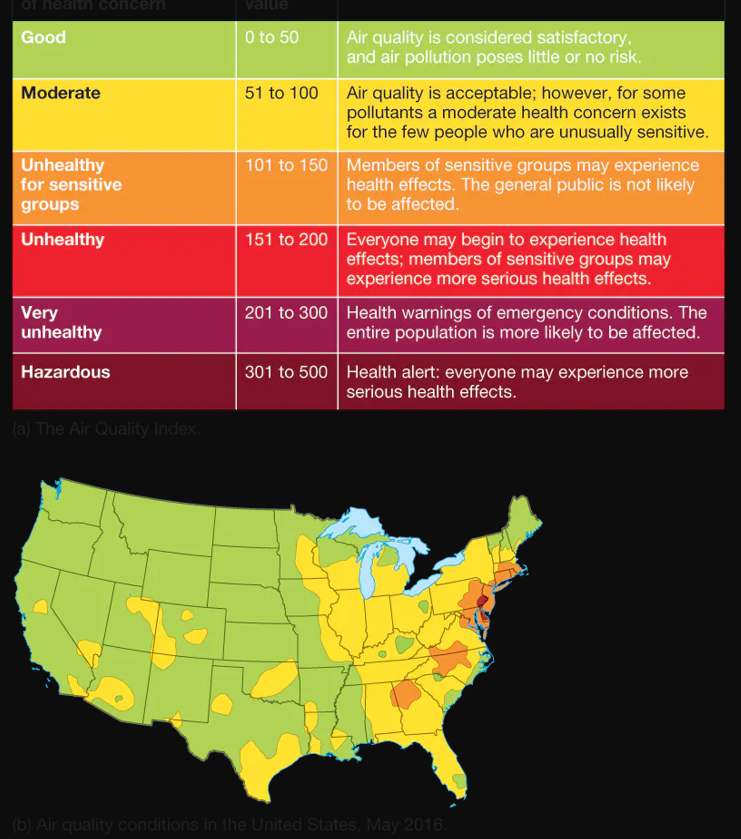
Air Quality Index (EPA)
Generalized risk exposure: 0-500, determined by carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, ground-level ozone, and particulate matter
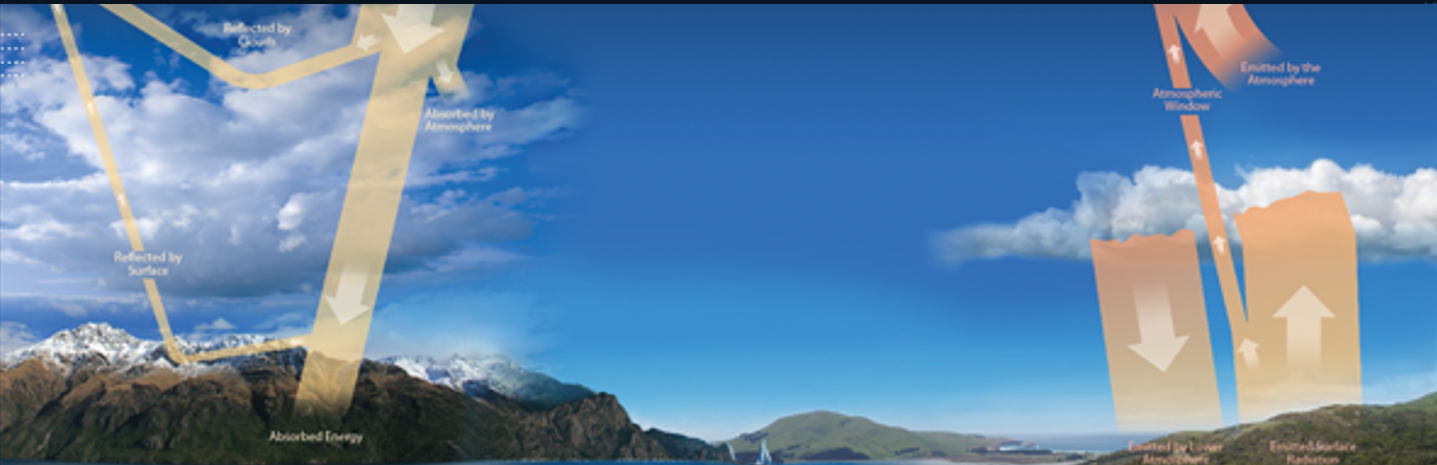

Earth’s Radiation “Budget”
Based on law of conservation of energy, balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing radiation, budget “out of balance” can affect temperature and climate
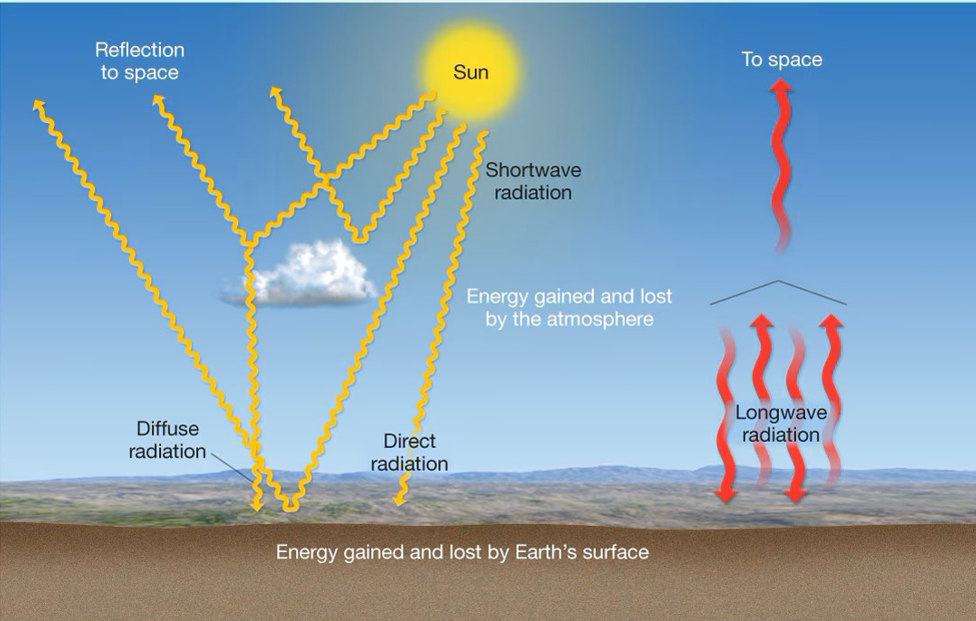
Energy Balance
Inputs: insolation (shortwave), Outputs: radiation back to space (longwave)
Scattering Radiation
Insolation/photons collide with higher concentrations of molecules as they reach Earth, interactions redirect light
Diffuse Radiation
Redirected energy waves, “shadowless light,” weaker, dispersed radiation is traveling in different directions
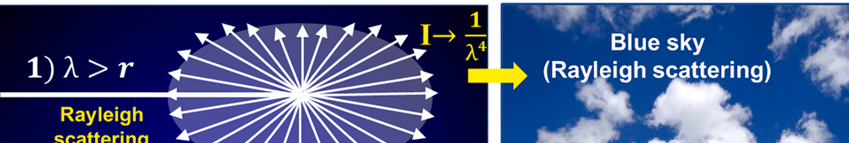
Rayleigh Scattering
Particles are smaller than the wavelength of light moving through, makes the sky blue

Mie Scattering
Atmospheric particles larger than wavelengths of light, produces white clouds, smog/haze
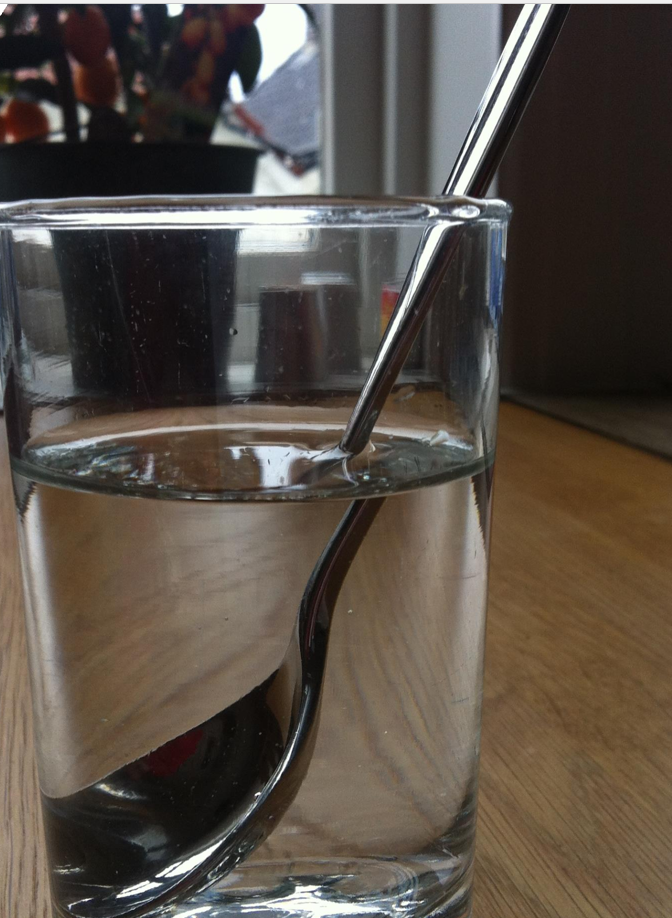

Refraction
Bending light waves, function of angles, temperature, air quality
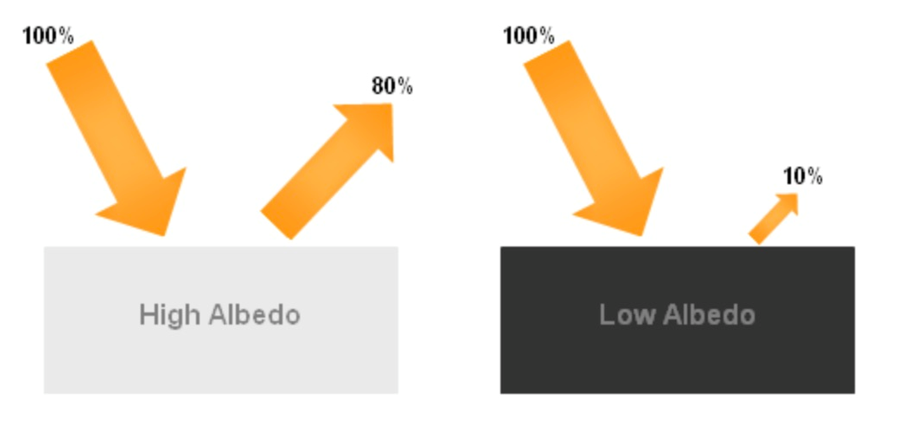
Albedo
Reflective quality, intrinsic brightness
Direct Radiation
~50% of all insolation received by the outer atmosphere makes it to the Earth surface (rest is back radiation)
Transmission
Uninterrupted passage of short and long wave energy as direct radiation (through the atmosphere and water)
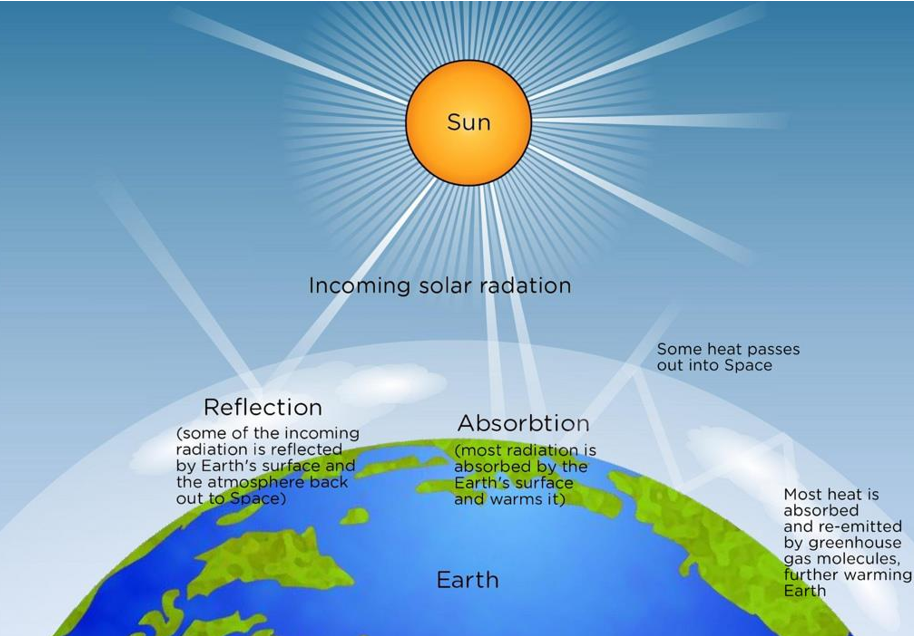
Absorption
Radiation that is converted into other energy (photosynthesis, longwave radiation (infrared heat)), produced heat energy
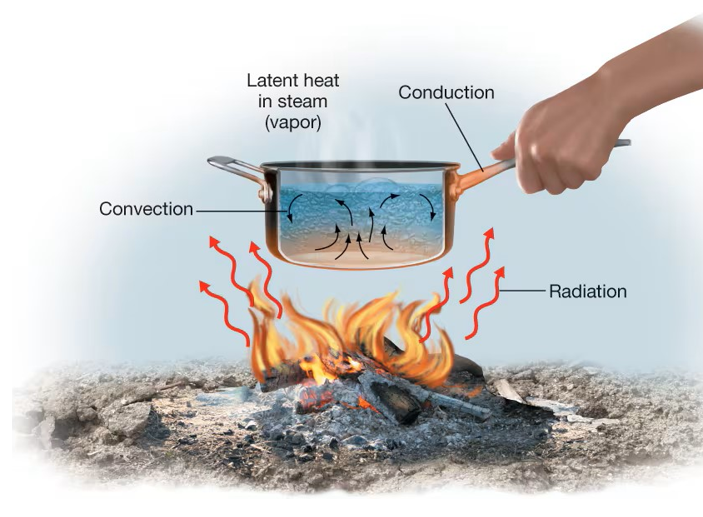
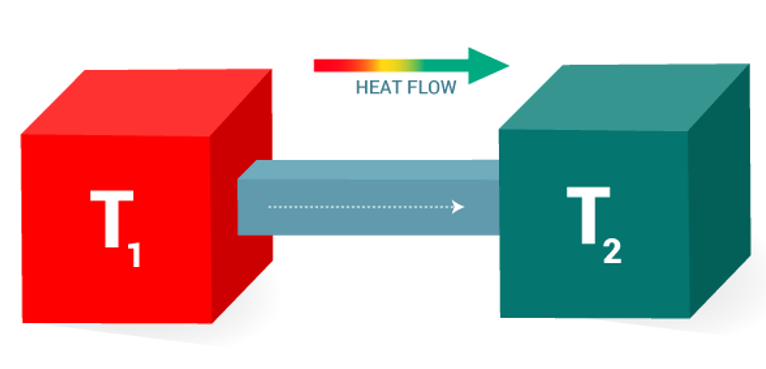
Heat
Flow of kinetic energy between molecules, from one substance to another, function of temperature difference (higher to lower)
Sensible Heat
“Sensed” by humans as temperature, function of kinetic energy
Latent Heat
“Hidden” heat energy, surrounding material experiences gains/losses, but not the substance itself; lost/gained during changes in state of matter
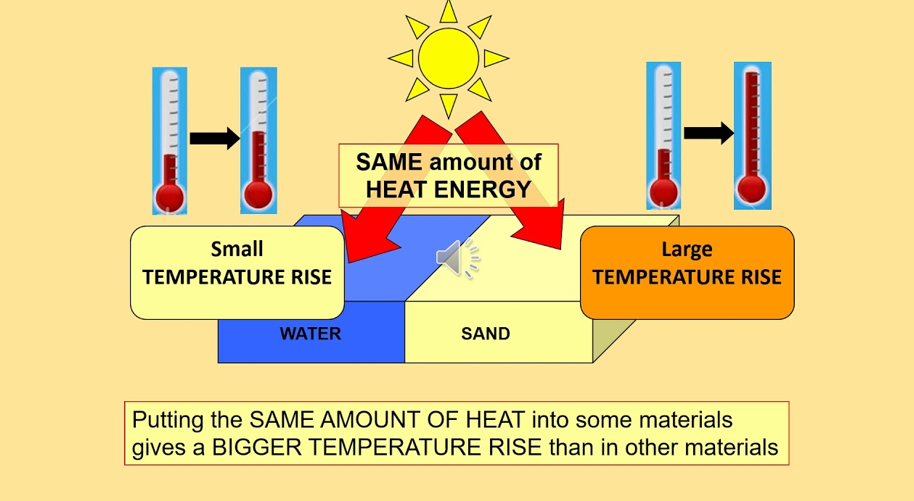
Specific Heat
The capacity for a substance to absorb heat and change temperature, how much energy is necessary to change the temperature/state of matter (water has a higher specific heat than land)
Conduction
Molecule-to-molecule transfer of energy (gas to liquid/solid)
Convection
Mixing, circulation as a means of transfer (warmer masses rise, cooler masses sink)
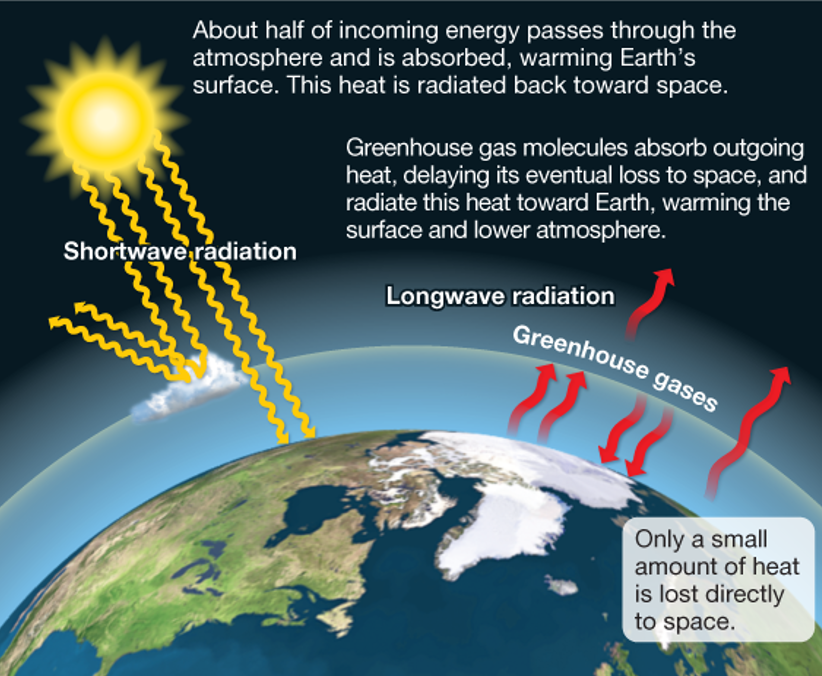
Greenhouse analogy
Earth’s atmosphere, as a result of greenhouse gases, trap and delay outgoing radiation back into space, warming the surface and lower atmosphere
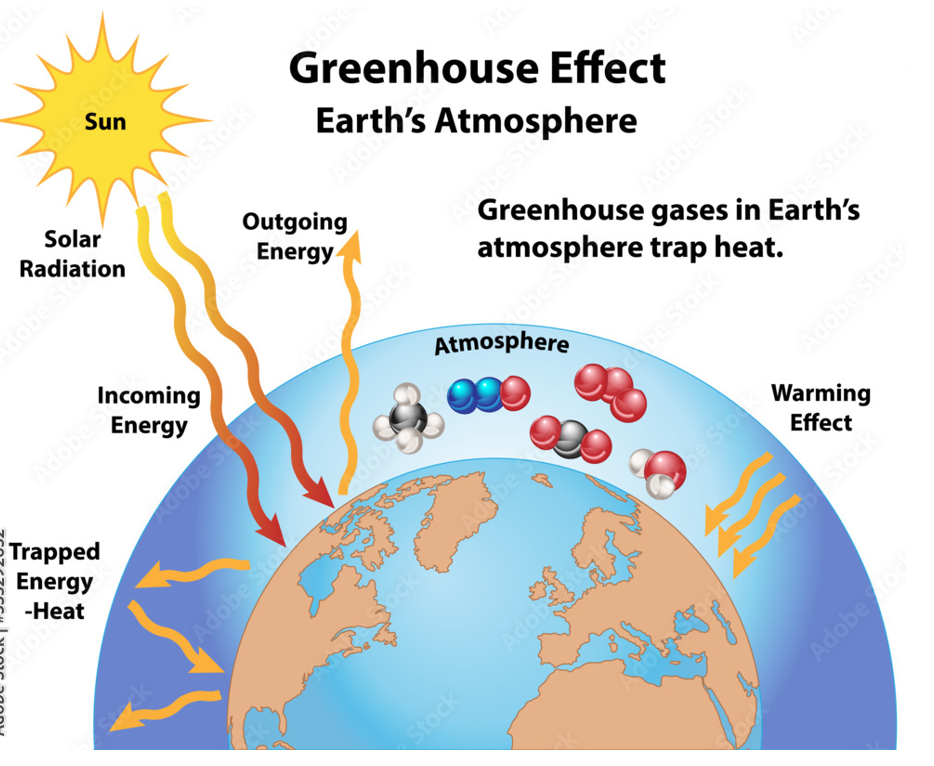
Greenhouse gases
Shortwave radiation absorbers
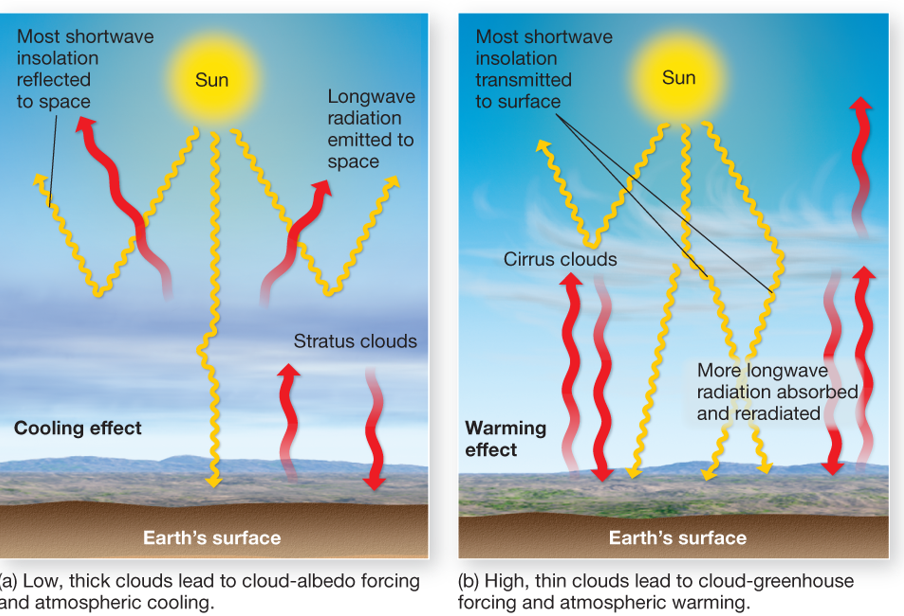
Clouds in the atmosphere
Influence heating and cooling conditions, reflect incoming short and longwave radiation
Cloud forcing
Thick clouds: reflects insolation, cooling effect if exceeds greenhouse effects. Greenhouse: reflects only 50% of insolation, warming effect when greenhouse effect exceeds
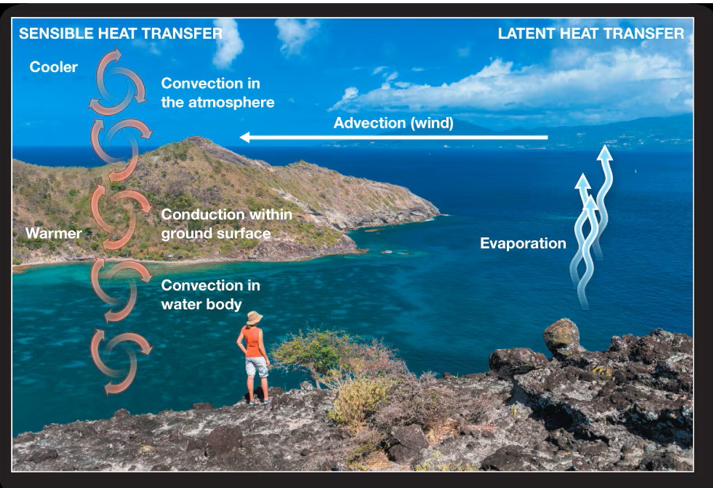
Advection
Horizontal convection motion (wind)
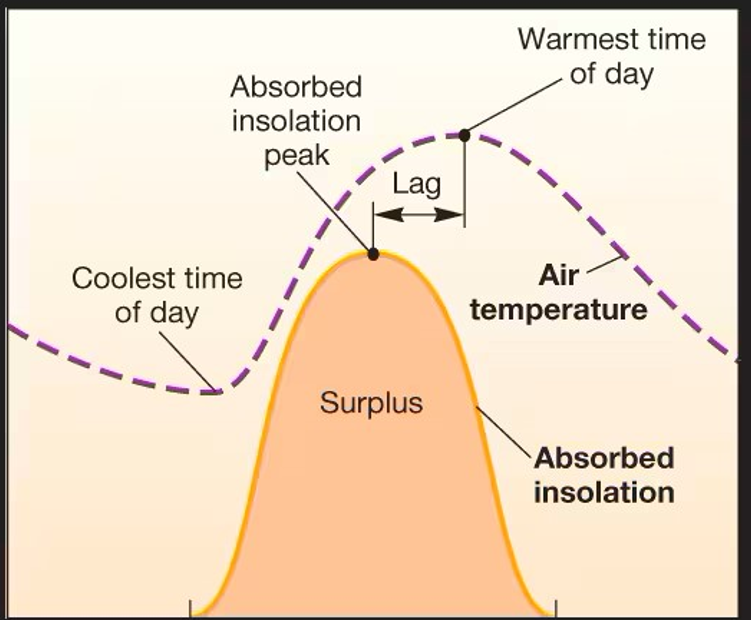
Diurnal Cycles
Daily patterns, varies with season and latitude
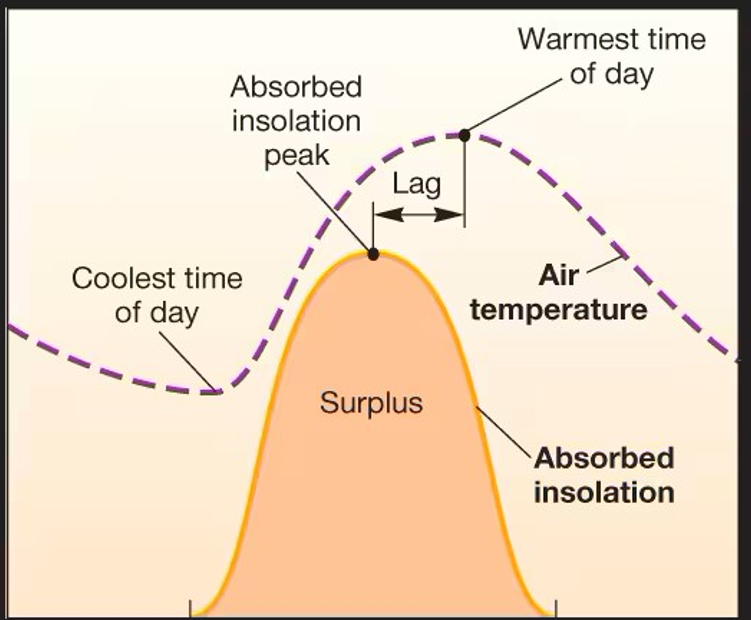
Lag time
Heat loss in atmospheric gases, both daily (after 12pm) and annually

Net Radiation: Latent heat
Energy released in a change from liquid to gas, highest in tropics and diffuses toward poles (hot, dry air meets warm ocean water)

Net Radiation: Sensible heat
Land-air heat exchange via convection and conduction, highest in subtropical latitudes (hot, dry air, waterless surfaces, cloudless skies, little vegetation)
Ground heat
Conductivity in and out of land or water, snow melt (can include ambient heat)
Microclimates
Function of latitude and elevation (why mountains have a snowline)
Cold snap
Dramatic drop in temperature over a 24 hr. period, location dependent
Heat wave
Prolonged, abnormally high temperatures, amplified by humidity, can trigger other events (wildfires)
Rising global temperatures
Influenced by delayed back radiation and urbanization
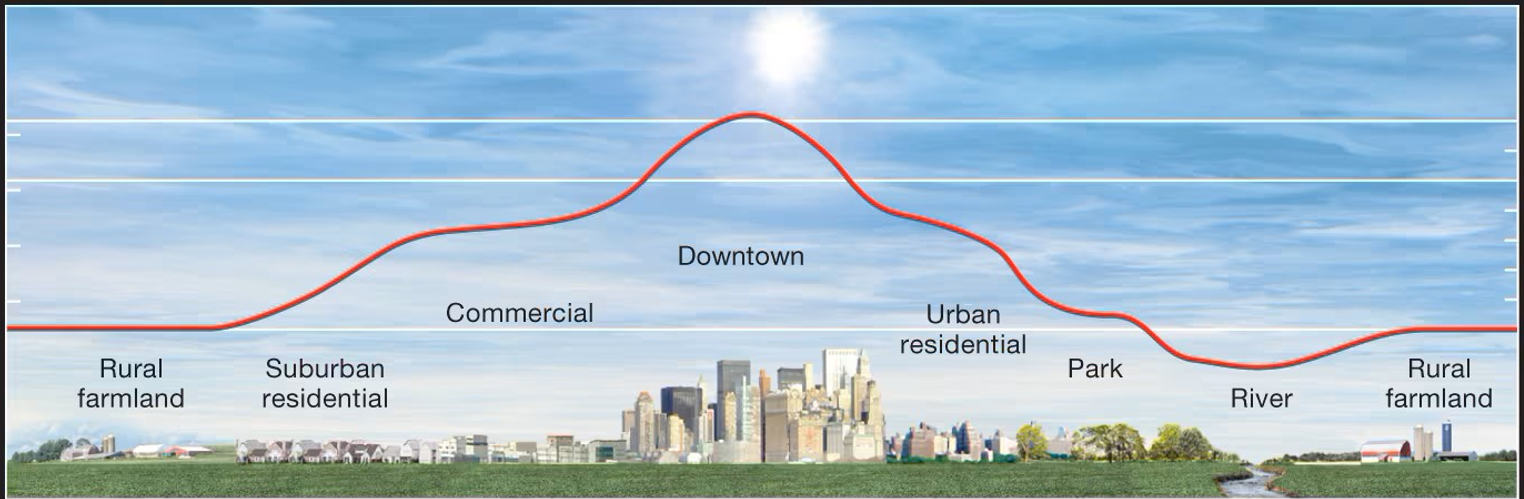
Urban Heat Island Effect
Temperature differences from suburban to rural areas, influenced by lack of shade and albedo
Atmospheric Circulation
Global energy and mass transfers driving weather patterns and ocean currents
Wind
Function of uneven heating/cooling of land, water, and atmospheric gases
Anemometer
Measures wind speed
Wind Vane
Measures wind direction
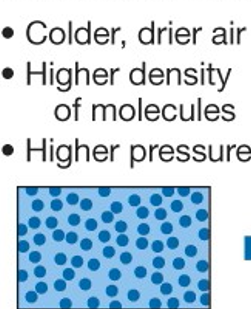
High Pressure
Colder, drier air, higher density of molecules, calm weather, clear skies
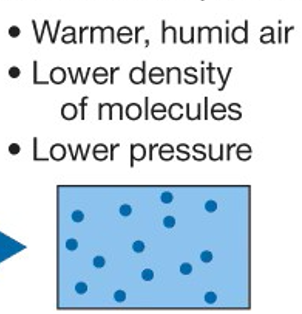
Low Pressure
Warmer, humid air, lower density of molecules, extreme weather events
Isobar
Line that connects points of equal pressure on a map. Pattern defines the extent of a pressure cell

Pressure Gradient Force
Change in pressure over a given distance, from greater density to less density. Polar regions (high pressure), equatorial (low pressure), mid-latitudes (fluctuations as a result of mixing)
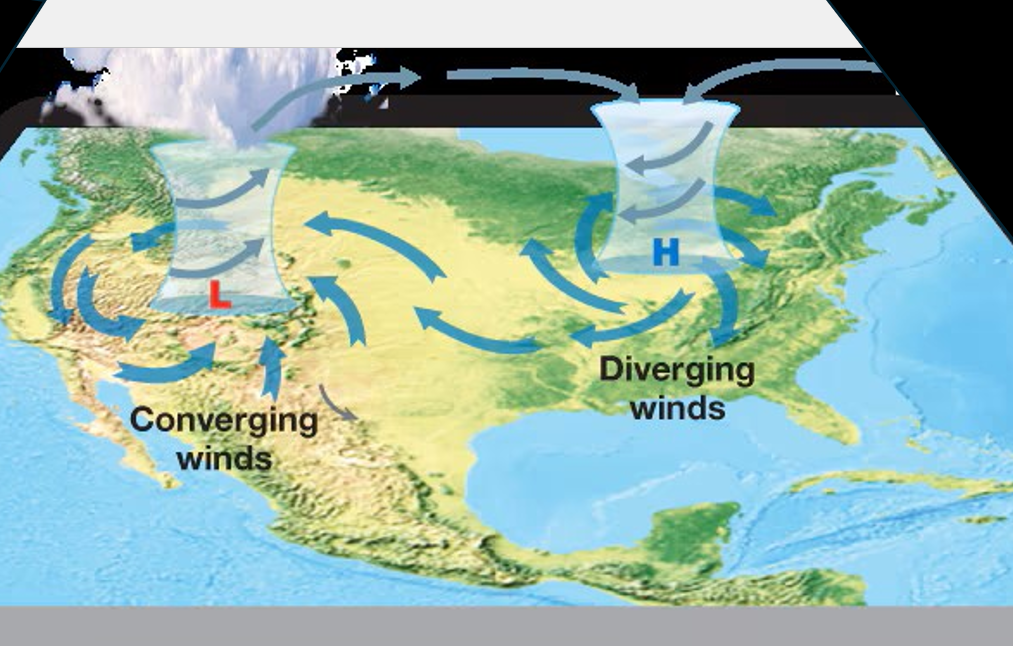
Vertical air movement: high pressure
Strongly subsiding, diverging air (upper atmosphere winds converge on lower atmospheric systems)
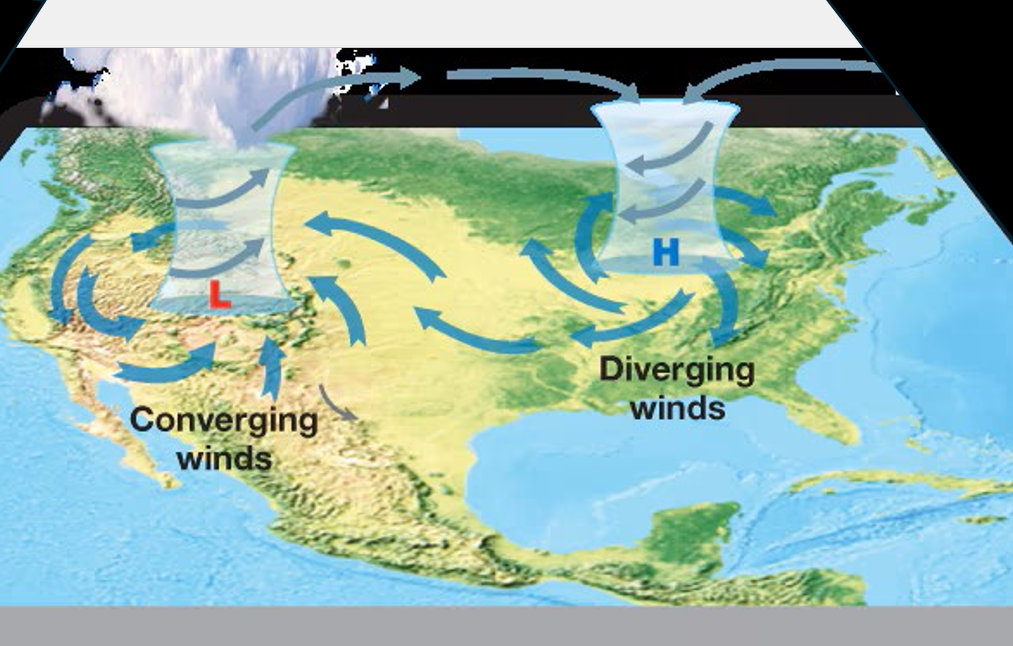
Vertical air movement: low pressure
Strongly converging, rising air (lower atmospheric gases ascend to upper atmosphere)
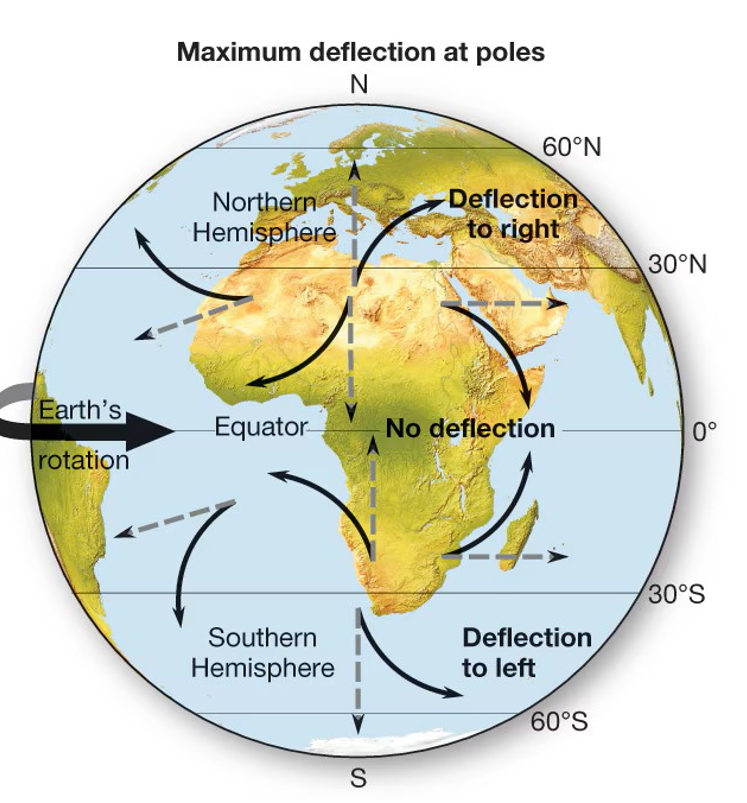
Coriolis effect
Deflection as Earth rotates, varies with latitude: polar (strongest), equatorial (weakest), mid-latitude (variable)