Signal to Noise Enhancement - Artifact Rejection, Averaging, Filtering
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
epoch
period of time around a stimulus that is pulled out for analysis
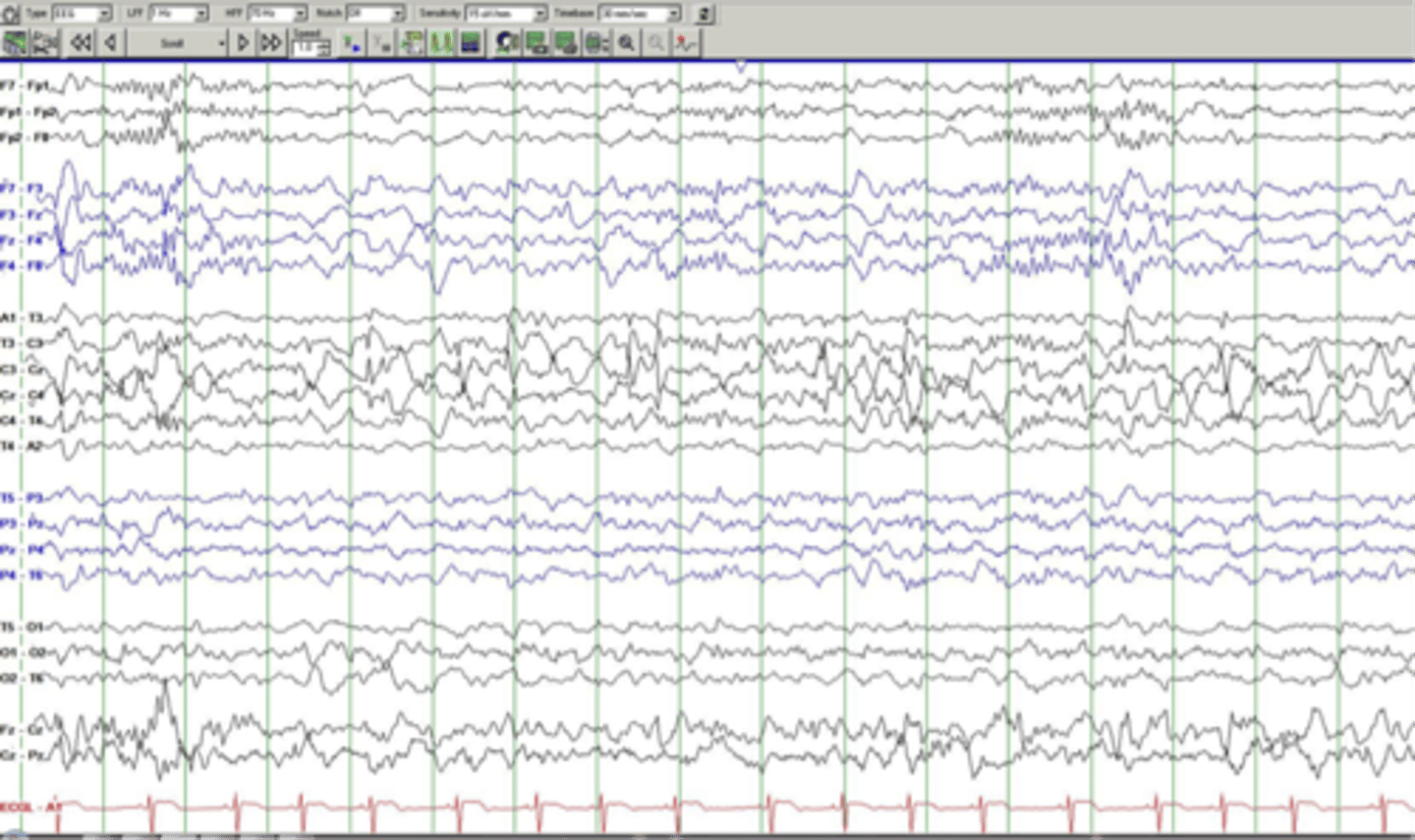
What are the assumptions of EEG averaging? Are they usually upheld? (3)
1. signal and noise linearly sum together to produce the recorded waveform, this is always true
2. the signal is the same for every repetition of the event (usually not true)
3. the noise is sufficiently irregular from event to event and thus can be considered random and statistically independent (not always true)
What are the characteristics of ideal noise? (2)
stationary (doesn't change over time), independent (random and unrelated to the stimulus of interest)
square root rule of averaging
rule stating how noise is reduced by averaging - average will reduce the ideal noise to an amount that is proportional to the magnitude of the noise and inversely proportional to the square root of the number of repetitions
What is the implication of the square root rule of averaging?
Increasing repetitions does not increase noise to the same extent - you must increase trials a very large amount to reduce noise a more modest amount. For example, to reduce the noise to 1/4 of the original, you must have 16 times the number of trials
How can the amount of residual noise in data be estimated? (2)
1. using a + - reference
2. looking at the pre-stimulus baseline (quick and dirty)
EEG signal
the portion of recorded waves coming from the brain that are time locked to the stimulus of interest
EEG noise
everything in the EEG recording that is not from the brain and time-locked to the stimulus of interest. Includes electrical influence of surroundings, non-stimulus related cerebral activity, and noncerebral physiologic potentials, and amplifier blocking/clipping (which shouldn't exist)
Ocular Artifacts (what, types, cause, where)
- drifts in EEG that occur due to eye movements (saccades) or blinks.
- saccades usually recorded from HEOG, seen in frontal electrodes too, longer shifts
- blinks seen on VEOG, and frontal channels, very large
- flutters seen if wearing contacts, frontal
- rolling seen if tired, slow, rolling shifts
How can ocular artifacts be minimized?
no contacts, don't use a totally dark room, fixation point, frequent breaks
Muscle artifact
caused by muscle contractions associated with movement and shivering, jaw clenching, forehead olympics, especially in frontal or temporal channels (T6/T7)
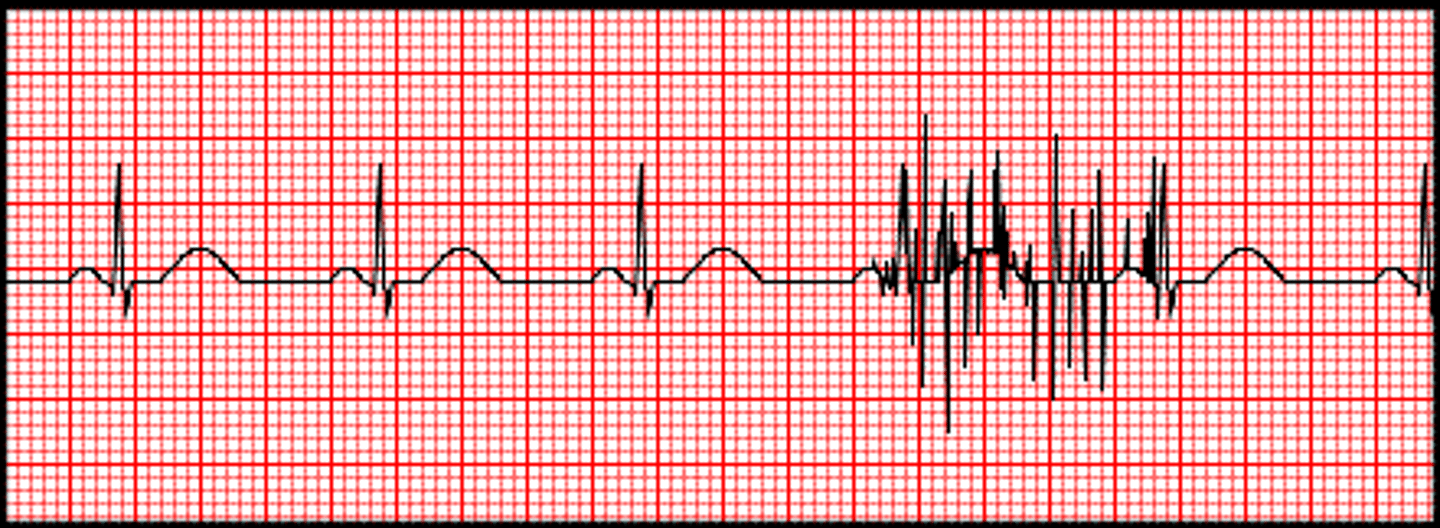
How can muscle artifacts be minimized?
instruction mostly, tell them to release jaw, gives breaks to improve comfort
main artifacts
consistent, unchanging noise in data, usually at around 60Hz, from electrical noise in surroundings, or static
How can main artifacts be reduced?
analog filtering, anti-static carpets, distance from monitor, other mechanical upgrades
How can muscle artifacts be distinguished from main artifacts and referencing errors?
A referencing error will be in all channels except HEOG, and will only be fixed if the reference is changed or a common reference is used. Muscle artifacts should disappear when people close their eyes and relax
Amplifier blocking artifact
occurs when gain is too high for the A-D board, signals get "clipped" at the top. Will notice on blinks before anything else due to their large amplitude
How can artifacts be fixed in data? (not prevented) (3)
1. Surgical - reject trials with too many artifacts, plan ahead of time to reject a certain number of trials
2. Medical - lower the weight of trials with lots of artifacts in averaging
3. Rehab - compensate for artifacts, for example by subtracting scaled EOG