ANTIDIURETIC POSTLAB
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
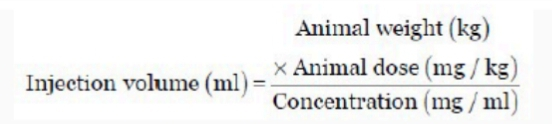
Injection volume formula

Urinary excretion formula

Diuretic index formula

Diuretic activity formula
Diuretics
Drugs that promotes elimination of excess water and sodium in the body by increasing urine production.
Natriuretic
Aquaretic
2 Classification of Diuretics
Natriuretic
Aquaretic
promote sodium excretion
promote water excretion
Natriuretics
Act by diminishing sodium reabsorption at different sites in the nephron, thereby increasing urinary sodium and water losses.
Natriuretics
This will reduce the fluid volume in the body, hence, lowers the blood pressure and relieve fluid build up or edema.
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (CAIs)
Loop Diuretics
Thiazide Diuretics
Potassium Sparing Diuretics
Classification of Natriuretics (4)
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (CAIs)
Blocks carbonic anhydrase inside the proximal convoluted tubule. It inhibits the action of carbonic anhydrase to reduce the reabsorption of bicarbonate and sodium, therefore, increasing its excretion.
Acute mountain sickness
Open-angle glaucoma
Indication of CAIs (2)
Acetazolamide
Dorzolamide
Brinzolamide
Examples of CAIs (3)
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (CAIs)
First line agent for Open-angle glaucoma
Acetazolamide
Inhibits carbonic anhydrase located intracellularly.
Acetazolamide
It decreases the production of aqueous humor and reduces intraocular pressure in patients with chronic open-angle glaucoma.
Acetazolamide
Used in the prophylaxis of symptoms of altitude sickness.
Potassium depletion
Renal stone formation
Drowsiness
Paresthesia
Adverse effects of Acetazolamide (4)
Dorzolamide
Reduces the production of aqueous humor
Ocular irritation
Blurred vision
Systemic effects (rare)
Adverse effects of Dorzolamide (3)
Brinzolamide
Treat intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
Ocular irritation
Blurred vision
Systemic effects (rare)
Adverse effects of Brinzolamide (3)
Loop Diuretics
Inhibit the co-transport of Na+/K+/2Cl− in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle.
Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter
Facilitates the transport of sodium, potassium, and chloride ions inside the cell.
Anion overdose
Edema
Indication for Loop Diuretics (2)
Bumetanide
Torsemide
Furosemide
Ethacrynic acid
Example of Loop Diuretics (4)
Bumetanide
This drug is more potent than Furosemide and has a relatively shorter duration of action compared to Torsemide.
Torsemide
This drug has a longer half-life compared to Furosemide and used to treat high blood pressure, especially in patients who have concurrent fluid retention.
Furosemide
This drug prevents the reabsorption of sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), and chloride (Cl−) back into the bloodstream.
Furosemide
Drug of choice for pulmonary edema
Ethacrynic acid
This drug is rarely used but is an alternative in patients who have a hypersensitivity reaction to a typical loop diuretic.
Has a relatively higher risk of causing hearing loss or tinnitus (ototoxicity).
Adverse effect of Ethacrynic acid (1)
Ethacrynic acid
Due to its ototoxicity that can cause permanent hearing impairment, it is only used if the px is allergic to loop diuretics.
Allergic reactions (with exception with ethacrynic acid)
Electrolyte imbalance
Adverse effects of Loop Diuretics (2)
Loop Diuretics
Sulfonamide
____ _________ such as furosemide contains sulfonamide group that can cause hypersensitivity reactions
Ethacrynic acid does not contain this ___________ group, hence, it does not exhibit allergic reactions.
Thiazide Diuretics
Inhibits Na+/Cl− cotransporter in the distal convoluted tubule.
Na+/Cl− cotransporter
Facilitates the reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the body.
Hypertension
Idiopathic hypercalciuria
Indication of Thiazides (2)
Thiazides
First line of tx for Hypertension
Idiopathic hypercalciuria
There is a loss of too much calcium in the urine without specific reason.
Benzothiadiazides
Chlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide
Thiazide-like
Chlorthalidone
Indapamide
Metolazone
Examples of Thiazides (2)
Chlorothiazide
First orally active thiazide and available in both oral and intravenous forms.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Treatment of peripheral edema related to heart failure.
Chlorthalidone
Approximately twice as potent as hydrochlorothiazide and considered a preferred option for hypertension (has long duration of action).
Metolazone
More potent than thiazides and usually used in combination with other diuretics, such as loop diuretics if there is a severe fluid.
retention and diuretics alone are not
working
Aldosterone antagonists: direct antagonism of mineralocorticoid receptors.
ENaC Inhibitors: inhibition of Na + influx through ion channels in the luminal membrane.
MOA of Potassium-Sparing Diuretics (2)
Hyperaldosteronism
Resistant hypertension
Heart failure
Ascites
Indication of Potassium-Sparing Diuretics (4)
Spironolactone
Eplerenone
Examples of Aldosterone Antagonists (2)
Spirinolactone
Eplerenone
Direct antagonist of aldosterone; prevents salt retention.
Competitive antagonist of aldosterone at mineralocorticoid receptors.
Hyperkalemia
Gynecomastia (spironolactone, not eplerenone)
Adverse effects of Aldosterone Antagonists (2)
Amiloride
Triamterene
Examples of ENaC Inhibitors (2)
Amiloride
Triamterene
Blocks epithelial sodium channels in collecting tubules.
Also blocks epithelial sodium channels in collecting tubules, much less potent, more toxic.
Spirinolactone and Eplerenone
Amiloride and Triamterene
Uses
CHF; HTN Aldosteronism
Reduces lithium-induced polyuria
Hyperkalemic metabolic acidosis
Adverse effect of ENaC Inhibitors (1)
Osmotic Diuretics
Physical osmotic effect on tissue water distribution because it is retained in the vascular compartment.
Increased intracranial pressure
Glaucoma
Indication of Osmotic Diuretics (2)
Intravenously
Mannitol is given
Hyponatremia
Dehydration
Hyperkalemia
Hypernatremia
Adverse effects of Mannitol (4)
ADH Agonist
Selective vasopressin V2 receptor agonist.
Pituitary diabetes insipidus
V2 receptor
Indication of ADH Agonist
Receptor that is responsible for water reabsorption.
Vasopressin
Desmopressin
Examples of ADH Agonist (2)
Vasopressin
Desmopressin
Hyponatremia and GI Disturbances
ADH AGONIST
Used for pediatric primary hyponatremia; GI Disturbances enuresis • hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease. It can also be used for coagulation disorders.
Sometimes used to control bleeding from esophageal varices.
ADE of ADH Agonist (2)
ADH Antagonist
V1a and/or V2 receptor antagonist.
Hyponatremia
Heart failure
Indication of ADH Antagonist (2)
Tolvaptan
Conivaptan
Examples of ADH Antagonist (2)
Conivaptan
Tolvaptan
Infusion site reactions
Antagonist of V1a and V2 receptor
Selective V2 receptor antagonist
ADE of ADH Antagonist
Hydrochlorothiazide
Directly inhibits the sodium chloride cotransporter located on the apical membrane of the distal convoluted tubules in the kidney.
Abacavir - Hydrochlorothiazide may slow down the body’s process of eliminating abacavir, an antiviral medication. This can lead to higher levels of abacavir in the blood, which may increase the risk of side effects.
Acebutolol - When used together with acebutolol, a beta-blocker, hydrochlorothiazide may increase the effectiveness of acebutolol, potentially enhancing blood pressure reduction.
Hydrochlorothiazide Possible Drug Interactions (2)
Spirinolactone
Works by increasing the excretion of sodium and water while retaining potassium. This dual effect makes it useful as both a diuretic (helping to remove excess fluid) and an antihypertensive (helping to lower blood pressure).
Salbutamol: When used with Spironolactone, Salbutamol’s effectiveness may decrease, potentially reducing its therapeutic impact.
Acetaminophen: Spironolactone may cause Acetaminophen to be excreted more quickly, lowering its levels in the blood and possibly reducing its effectiveness.
Spirinolactone Possible Drug Interactions (2)
Furosemide
Promotes the excretion of sodium and water by blocking their reabsorption in the kidney’s proximal and distal tubules, as well as the loop of Henle. This results in a strong diuretic effect, helping to reduce fluid buildup and lower blood pressure.
Acebutolol: Furosemide may enhance the blood pressure-lowering effects of Acebutolol, which can increase its effectiveness as an antihypertensive.
Abaloparatide: Using Furosemide with Abaloparatide can raise the risk or severity of side effects.
Furosemide Possible Drug Interactions (2)