CHE2A EXAM 1 REVIEW (ch1-4)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
1
New cards
Scientific method
A logical, systematic approach to the solution of a scientific problem

2
New cards
Natural law
explains what happens
3
New cards
theory
explains WHY something happens
4
New cards
Density =
mass/volume
5
New cards
Kelvin =
273 + C

6
New cards
Farenheit =
9/5(C) + 32
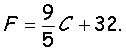
7
New cards
Celcius =
(F-32) x 5/9
8
New cards
Common Conversions
0°C = 273.15 K
1 in = 2.54 cm
1 mL = 1 cm^3
1 bar = 100 kPa
1 atm = 101.325 kPa
760 torr = 1 atm
1 mol = 6.022 x 10^23 particles
1 in = 2.54 cm
1 mL = 1 cm^3
1 bar = 100 kPa
1 atm = 101.325 kPa
760 torr = 1 atm
1 mol = 6.022 x 10^23 particles
9
New cards
Rules for sig figs (multiplication/division)
use number of sig figs of least sig fig number
ex. *1.4* x 5.376 = 7.5
ex. *1.4* x 5.376 = 7.5
10
New cards
Rules for sig figs (addition/subtraction)
use number of decimal places as number w/ least decimal places
ex. 1.30 x *2.7* = 3.5
ex. 1.30 x *2.7* = 3.5
11
New cards
law of conservation of mass
total mass of substances present after a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass of substances before the reaction
12
New cards
law of definite proportions
(law of constant composition)
all samples of a compound have the same composition
all samples of a compound have the same composition
13
New cards
law of multiple proportions
If 2 elements combine to form different compounds, the ratio of masses of the second element that react with a fixed mass of the first element will be a simple, whole-number ratio
14
New cards
isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
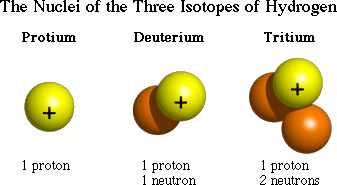
15
New cards
number of protons defines ...
the element (atomic number)
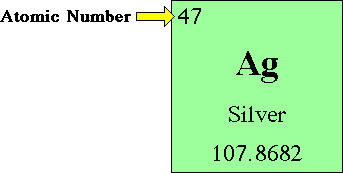
16
New cards
number of neutrons defines ...
isotopes, mass of element (protons + neutrons)
17
New cards
number of electrons defines ...
charge of element

18
New cards
molecular formula
shows the types and numbers of atoms combined in a single molecule of a molecular compound
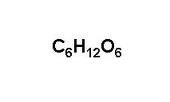
19
New cards
empirical formula
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
20
New cards
Where are *alkali metals* located on the periodic table?
Column 1
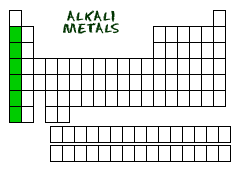
21
New cards
Where are *alkaline earth metals* located on the periodic table?
Column 2
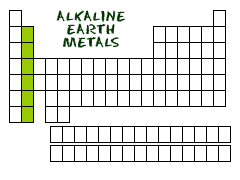
22
New cards
Where are *transition metals* located on the periodic table?
Columns 3-12
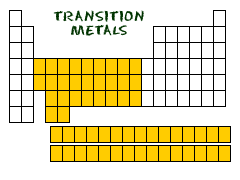
23
New cards
Where are *chalcogens* located on the periodic table?
Column 16
24
New cards
Where are *halogens* located on the periodic table?
Column 17
25
New cards
Where are *noble gases* located on the periodic table?
Column 18
26
New cards
Where are *the main groups* located on the periodic table?
Column 1, 2, 13-18
27
New cards
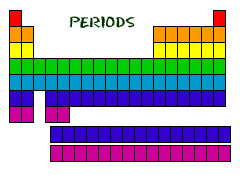
What are *periods* on the periodic table?
horizontal rows
28
New cards
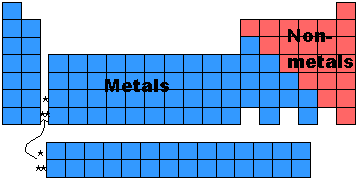
Where are *nonmetals* located on the periodic table?
Metals = left of staircase
Nonmetals = right of staircase
Nonmetals = right of staircase
29
New cards
9 transition metals with uncertain charges
*+2 or +3 charges*
Cr (Chromium)
Fe (Iron)
Co (Cobalt)
*+1 or +2 charges*
Cu (Copper)
Ag (Silver)
Au (Gold)
Hg (Mercury)
*+2 or +4 charges*
Sn (Tin)
Pb (Lead)
Cr (Chromium)
Fe (Iron)
Co (Cobalt)
*+1 or +2 charges*
Cu (Copper)
Ag (Silver)
Au (Gold)
Hg (Mercury)
*+2 or +4 charges*
Sn (Tin)
Pb (Lead)
30
New cards
Oxygen common oxidation state
-2
31
New cards
Hydrogen common oxidation state
+1
32
New cards
Fluorine common oxidation state
-1
33
New cards
Naming *covalent compounds*
between 2 nonmetals
= PREFIXES
ex. SF10 = Sulfur decafluoride
= PREFIXES
ex. SF10 = Sulfur decafluoride
34
New cards
Covalent compound prefixes
1: mono
2: di
3: tri
4: tetra
5: penta
6: hexa
7: hepta
8: octa
9: nona
10: deca
2: di
3: tri
4: tetra
5: penta
6: hexa
7: hepta
8: octa
9: nona
10: deca

35
New cards
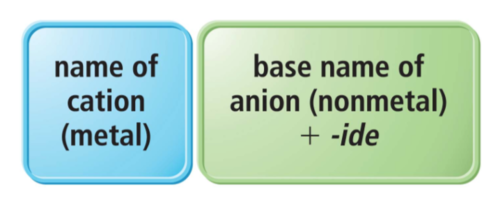
Naming *binary ionic compounds (type 1)*
with a metal with specified charge
= full name cation, anion +ide
ex. CsF = Cesium Fluoride
= full name cation, anion +ide
ex. CsF = Cesium Fluoride
36
New cards
Naming *binary ionic compounds (type 2)*
with a metal with UNspecified charge
= ROMAN NUMERALS
ex. FeO3 = Iron (III) Oxide
= ROMAN NUMERALS
ex. FeO3 = Iron (III) Oxide

37
New cards
Naming *acids (with NO oxygen)*
add hydro- and -ic
ex. HF = hydrofluoric acid
ex. HF = hydrofluoric acid

38
New cards
Naming *acids (with oxygen)*
*for -ate endings*
= add - ic
ex. HClO3 = chloric acid
*for -ite endings*
= add -ous
ex. HClO2 = chlorous acid
= add - ic
ex. HClO3 = chloric acid
*for -ite endings*
= add -ous
ex. HClO2 = chlorous acid
39
New cards
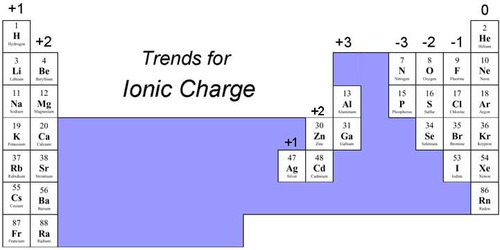
Charges of periodic table
40
New cards
Common polyatomic ions (MEMORIZE)
*NH4+ = ammonium*
NH3+ = ammonia
NO2- = nitrite
*NO3- = nitrate*
SO3 = sulfite (2- charge)
*SO4 = sulfate (2- charge)*
*OH- = hydroxide*
CN- = cyanide
*PO4 = phosphate (3- charge)*
*CO3 = carbonate (2- charge)*
C2H3O2- = acetate
MnO4- = permanganate
*CrO4 = chromate (2- charge)*
O2 = peroxide (2- charge)
ClO2- = chlorite
*ClO3- = chlorate*
NH3+ = ammonia
NO2- = nitrite
*NO3- = nitrate*
SO3 = sulfite (2- charge)
*SO4 = sulfate (2- charge)*
*OH- = hydroxide*
CN- = cyanide
*PO4 = phosphate (3- charge)*
*CO3 = carbonate (2- charge)*
C2H3O2- = acetate
MnO4- = permanganate
*CrO4 = chromate (2- charge)*
O2 = peroxide (2- charge)
ClO2- = chlorite
*ClO3- = chlorate*
41
New cards
Polyatomic ion prefixes
per- = +1
-ate = __
-ite = -1
hypo- = -2
-ate = __
-ite = -1
hypo- = -2

42
New cards
Atomis Mass =
*sum of [(isotopic masses) x (fractional abundance)]*
ex. 99.630% N-14 and .37% N-15 = (.99630)(14)+(.0037)(15) = 14.0037 u
ex. 99.630% N-14 and .37% N-15 = (.99630)(14)+(.0037)(15) = 14.0037 u
43
New cards
Molar Mass =
*sum of amount of grams per element in compound*
ex. Na2SO4 = 2(Na) + S + 4(O) = 2(22.99) + 32.07 + 4(16) = 142.05 g/mol
ex. Na2SO4 = 2(Na) + S + 4(O) = 2(22.99) + 32.07 + 4(16) = 142.05 g/mol
44
New cards
Percent Mass =
*(mass of element ÷ mass of compound) x 100*
ex (using formula). CoCl2 x 6H2O find mass % of water
6(2.016+16) ÷ 237.93 g/mol x 100 = 45.44%
ex (using grams). 87.28 g P, 112.72 g O, 200g total compound
87.28 g P ÷ 200 g x 100= 43.64% P
112.72 g O ÷ 200 g x 100 = 56.36% O
ex (using formula). CoCl2 x 6H2O find mass % of water
6(2.016+16) ÷ 237.93 g/mol x 100 = 45.44%
ex (using grams). 87.28 g P, 112.72 g O, 200g total compound
87.28 g P ÷ 200 g x 100= 43.64% P
112.72 g O ÷ 200 g x 100 = 56.36% O
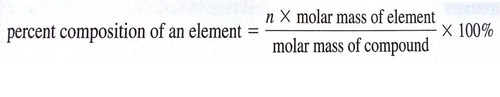
45
New cards
Combustion reaction
reaction where an organic compound (contains C, H, and sometimes others) reacts with O2 to create CO2 + H2O
46
New cards
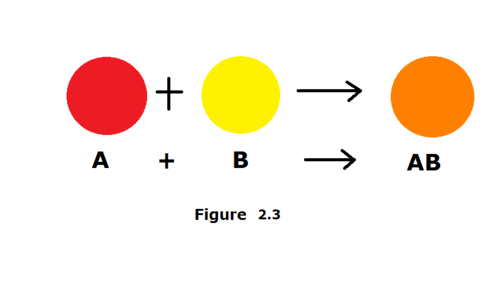
Combination reaction (synthesis)
2 or more species combine to form compound
*A + B --> AB*
*A + B --> AB*
47
New cards
Decomposition reaction
compound decomposes into 2 or more species
*AB --> A + B*
*AB --> A + B*
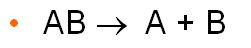
48
New cards
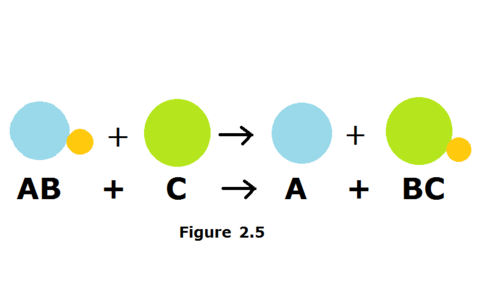
Single Replacement reaction
a chemical change in which one element replaces a second element in a compound
*AB + C --> A + BC*
*AB + C --> A + BC*
49
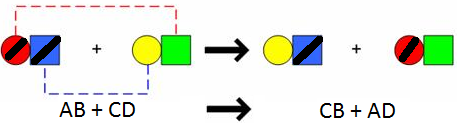
New cards
Double Replacement reaction
a chemical change that involves an exchange of positive ions between two compounds
*AB + CD --> AD +BC*
*AB + CD --> AD +BC*
50
New cards
Redox reaction
A chemical reaction involving the transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another; also called oxidation-reduction reaction

51
New cards
Limiting Reactant steps
1. Balance equation
2. Calculate moles or mass of reactants
3. Calculate moles/mass of opposite reactant that is produced from using each reactant
4. Smaller production = limiting reagant
5. Use moles/mass of limiting reagant to calculate product
6. To find excess: subtract available moles/mass of excess with used moles/mass of excess
2. Calculate moles or mass of reactants
3. Calculate moles/mass of opposite reactant that is produced from using each reactant
4. Smaller production = limiting reagant
5. Use moles/mass of limiting reagant to calculate product
6. To find excess: subtract available moles/mass of excess with used moles/mass of excess

52
New cards
Percent Yield =
*actual yield ÷ theoretical yield x 100*
aka. given amount ÷ calculated amount x 100
aka. given amount ÷ calculated amount x 100
53
New cards
Molarity =
*moles of solute ÷ volume in liters*

54
New cards
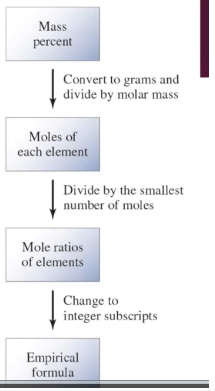
Empirical Formula steps (from mass %)
1. base mass % out of 100 g of compound (each % = g)
2. Determine moles of each element
3. Divide each mole by smallest mole value
4. Whole number values = subscripts of each element in compound
2. Determine moles of each element
3. Divide each mole by smallest mole value
4. Whole number values = subscripts of each element in compound
55
New cards
Molecular Formula steps (from empirical formula)
*molar mass ÷ empirical formula mass* = factor to multiply subscripts by
56
New cards
Dilution =
*Molarity (M1) x Volume (V1) = Molarity (M2) x Volume (V2)*
ex. 1 L of 11.75 M HCl reacts with 2 L NaOH, find molarity NaOH
(11.75 M)(1 L) = (M2)(2 L) = M2 = 5.9 M NaOH
ex. 1 L of 11.75 M HCl reacts with 2 L NaOH, find molarity NaOH
(11.75 M)(1 L) = (M2)(2 L) = M2 = 5.9 M NaOH

57
New cards
Titration =
(molarity of subject) (volume of subject) = (molarity of titrant) (volume of titrant)
58
New cards
Strong electrolytes
completely dissociate into ions when dissolved in water
- strong acids (aq)
- strong bases (aq)
- ionic compounds (aq)
- salts (aq)
- strong acids (aq)
- strong bases (aq)
- ionic compounds (aq)
- salts (aq)
59
New cards
Weak electrolytes
don't completely disassociate in water
- weak acids
- weak bases
- molecular compounds
- organic compounds
- liquids
- solids
- gases
- weak acids
- weak bases
- molecular compounds
- organic compounds
- liquids
- solids
- gases
60
New cards
Precipitate reactions
reactions that result in the formation of an insoluble product (precipitate)
molecular formula:
ex. AgNO3 (aq) + KCl (aq) --> AgCl (s) + KNO3 (aq)
molecular formula:
ex. AgNO3 (aq) + KCl (aq) --> AgCl (s) + KNO3 (aq)
61
New cards
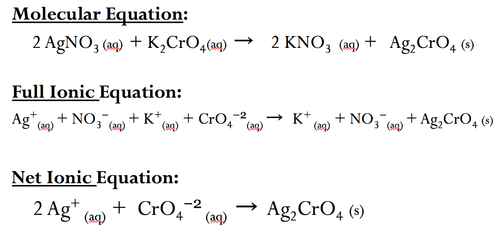
Precipitate reactions: Net ionic equation
ionic equations that include only the particles that participate in the reaction (no spectator ions)
ex. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) --> NaCl(aq) + H2O (l)
full ionic equation:
H+ + Cl- + Na+ + OH- --> 2H+ + Cl- + Na+ + OH-
net ionic equation:
*H+(aq) + OH-(aq) --> H2O(l)*
ex. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) --> NaCl(aq) + H2O (l)
full ionic equation:
H+ + Cl- + Na+ + OH- --> 2H+ + Cl- + Na+ + OH-
net ionic equation:
*H+(aq) + OH-(aq) --> H2O(l)*
62
New cards
What is an acid?
compound that provides H+
63
New cards
What is a base?
compound that provides OH-
- NOT including compounds that do not contain a metal in addition to OH- (not CH3OH, not MeOH)
- NOT including compounds that do not contain a metal in addition to OH- (not CH3OH, not MeOH)
64
New cards
Strong Acids (MEMORIZE)
- HCl
- HBr
- HI
- HClO4
- HClO3
- HNO3
- H2SO4
- HBr
- HI
- HClO4
- HClO3
- HNO3
- H2SO4

65
New cards
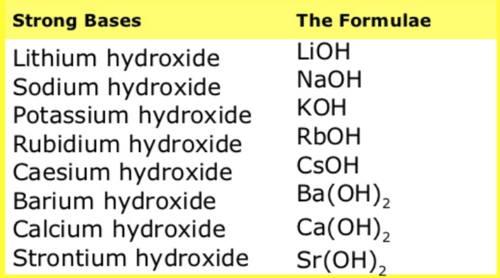
Strong Bases (MEMORIZE)
- LiOH
- NaOH
- KOH
- RbOH
- CsOH
- Ca(OH)2
- Mg(OH)2
- Sr(OH)2
- Ba(OH)2
- NaOH
- KOH
- RbOH
- CsOH
- Ca(OH)2
- Mg(OH)2
- Sr(OH)2
- Ba(OH)2
66
New cards
redox reactions (oxidation-reduction reactions)
chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants
- oxidized = loses electrons (reducing agent - electron donor)
- reduced = gains electrons (oxidizing agent - electron acceptor)
- oxidized = loses electrons (reducing agent - electron donor)
- reduced = gains electrons (oxidizing agent - electron acceptor)
67
New cards
remember OIL RIG
*O*xidation *I*s *L*osing electrons
*R*eduction *I*s *G*aining electrons
*R*eduction *I*s *G*aining electrons
68
New cards
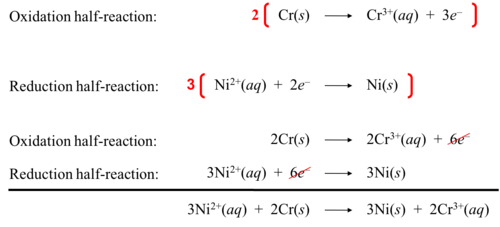
Half reactions
equations that show either oxidation or reduction alone
69
New cards
Half reaction balancing steps
1. elements (not H2O)
2. oxygen (use H2O)
3. hydrogen (use H+)
4. charge (use electrons)
2. oxygen (use H2O)
3. hydrogen (use H+)
4. charge (use electrons)
70
New cards
Half reactions: reduction
ex. SO2 + Cr2O7 (-2) ---> SO4 (-2) + Cr (+3) + H2O
1. reduction equation: Cr2O7 (-2) ---> 2Cr(+3)
ox states: Cr went from +6 to +3 (gained 3 electrons - reduced)
2. balance oxygen
Cr2*O7* (-2) ---> 2Cr(+3) + *7H2O*
3. balance hydrogen
Cr2O7 (-2) + *14H+*---> 2Cr(+3) + *7H2*O
4. balance charges
Cr2O7 (-2) + 14H+---> 2Cr(+3) + 7H2O
(Cr2 = +12 to 2Cr(+3) = +6) 12-6 = add 6 electrons to left
Cr2O7 (-2) + 14H+ + *6e* ---> 2Cr(+3) + 7H2O
1. reduction equation: Cr2O7 (-2) ---> 2Cr(+3)
ox states: Cr went from +6 to +3 (gained 3 electrons - reduced)
2. balance oxygen
Cr2*O7* (-2) ---> 2Cr(+3) + *7H2O*
3. balance hydrogen
Cr2O7 (-2) + *14H+*---> 2Cr(+3) + *7H2*O
4. balance charges
Cr2O7 (-2) + 14H+---> 2Cr(+3) + 7H2O
(Cr2 = +12 to 2Cr(+3) = +6) 12-6 = add 6 electrons to left
Cr2O7 (-2) + 14H+ + *6e* ---> 2Cr(+3) + 7H2O
71
New cards
Half reactions: oxidation
ex. SO2 + Cr2O7 (-2) ---> SO4 (-2) + Cr (+3) + H2O
1. oxidation equation: SO2 ---> SO4(-2)
ox states: S went from +4 to +6 (lost 2 electrons - oxidized)
2. balance oxygen
SO2 + *2H2O* ---> S*O4*(-2)
3. balance H+
SO2 + *2H2*O ---> SO4(-2) + *4H+*
4. balance charge
SO2 + 2H2O ---> SO4(-2) + 4H+
(S=+4 to S=+6) so, 4-6 = add 2 electrons to right
SO2 + 2H2O ---> SO4(-2) + 4H+ + *2e*
1. oxidation equation: SO2 ---> SO4(-2)
ox states: S went from +4 to +6 (lost 2 electrons - oxidized)
2. balance oxygen
SO2 + *2H2O* ---> S*O4*(-2)
3. balance H+
SO2 + *2H2*O ---> SO4(-2) + *4H+*
4. balance charge
SO2 + 2H2O ---> SO4(-2) + 4H+
(S=+4 to S=+6) so, 4-6 = add 2 electrons to right
SO2 + 2H2O ---> SO4(-2) + 4H+ + *2e*
72
New cards
Half reactions: adding reduction and oxidation
reduction: Cr2O7 (-2) + 14H+ + 6e ---> 2Cr(+3) + 7H2O
oxidation: SO2 + 2H2O ---> SO4(-2) + 4H+ + 2e
Cr2O7 (-2) + 14H+ + 6e + SO2 + 2H2O ---> 2Cr(+3) + 7H2O + SO4(-2) + 4H+ + 2e
14H+/4H+ cancels, 6e/2e cancels, 7H2O/2H2O cancels
*Cr2O7 (-2) + 10H+ + 4e + SO2 ---> 2Cr(+3) + 5H2O + SO4(-2)*
oxidation: SO2 + 2H2O ---> SO4(-2) + 4H+ + 2e
Cr2O7 (-2) + 14H+ + 6e + SO2 + 2H2O ---> 2Cr(+3) + 7H2O + SO4(-2) + 4H+ + 2e
14H+/4H+ cancels, 6e/2e cancels, 7H2O/2H2O cancels
*Cr2O7 (-2) + 10H+ + 4e + SO2 ---> 2Cr(+3) + 5H2O + SO4(-2)*