Affective Disorders: Antidepressants and Mood Stabilizers
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
major depressive disorder (MDD) (3)
recurring episodes of dysphoria + negative thinking → reflected in bhvr
characterized by overwhelming sadness, feelings of worthlessness, loss of interest in normally pleasurable activities
most common disabling mental disorder in adults → responsible for 50% of suicides
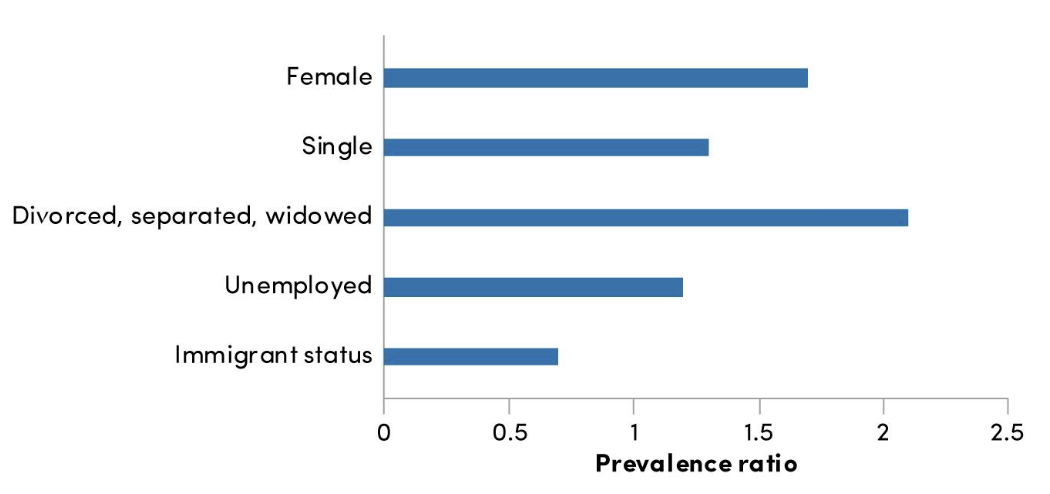
prevalence of MDD (4) country, gender, demographics
higher in high-income countries
Canada: 11% lifetime prevalence
women 2x as likely → may be under diagnosed in men
higher in young, single, unemployed, Indigenous ppl
how does MDD damage quality of life (4)
extensive overlap of depression/anxiety + alcohol dependence
comorbidity predicts more severe symptoms
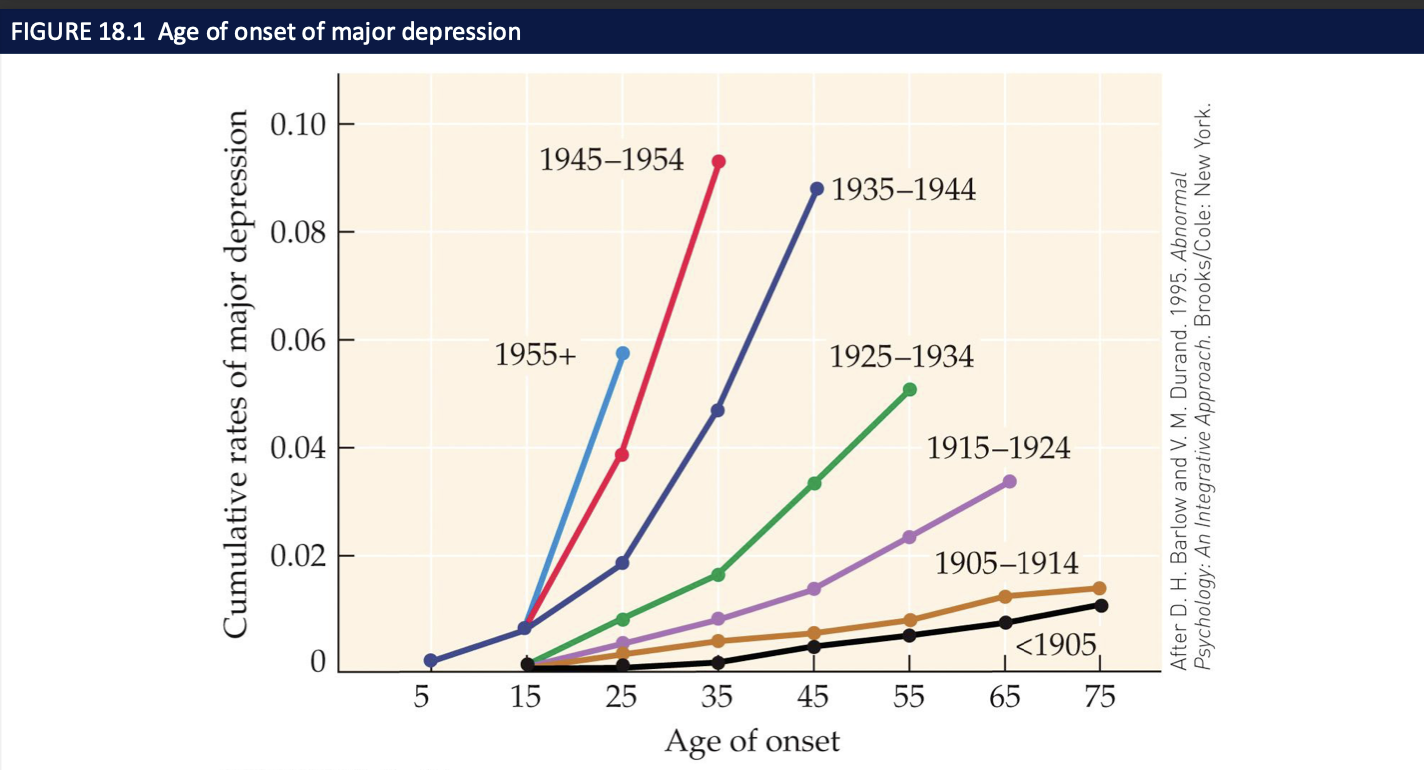
episodes recur throughout life
incidence ↑ age of onset ↓ since 1955
bipolar disorder (BPD) → describe mania (4)
cyclic mood swings from depression to mania
mania feels faultless, full of fun, talkative, energetic, need for sleep ↓
1º mood is irritability, belligerence, impatience
bhvr: reckless driving, buying sprees, foolish business deals, sexual indiscretions
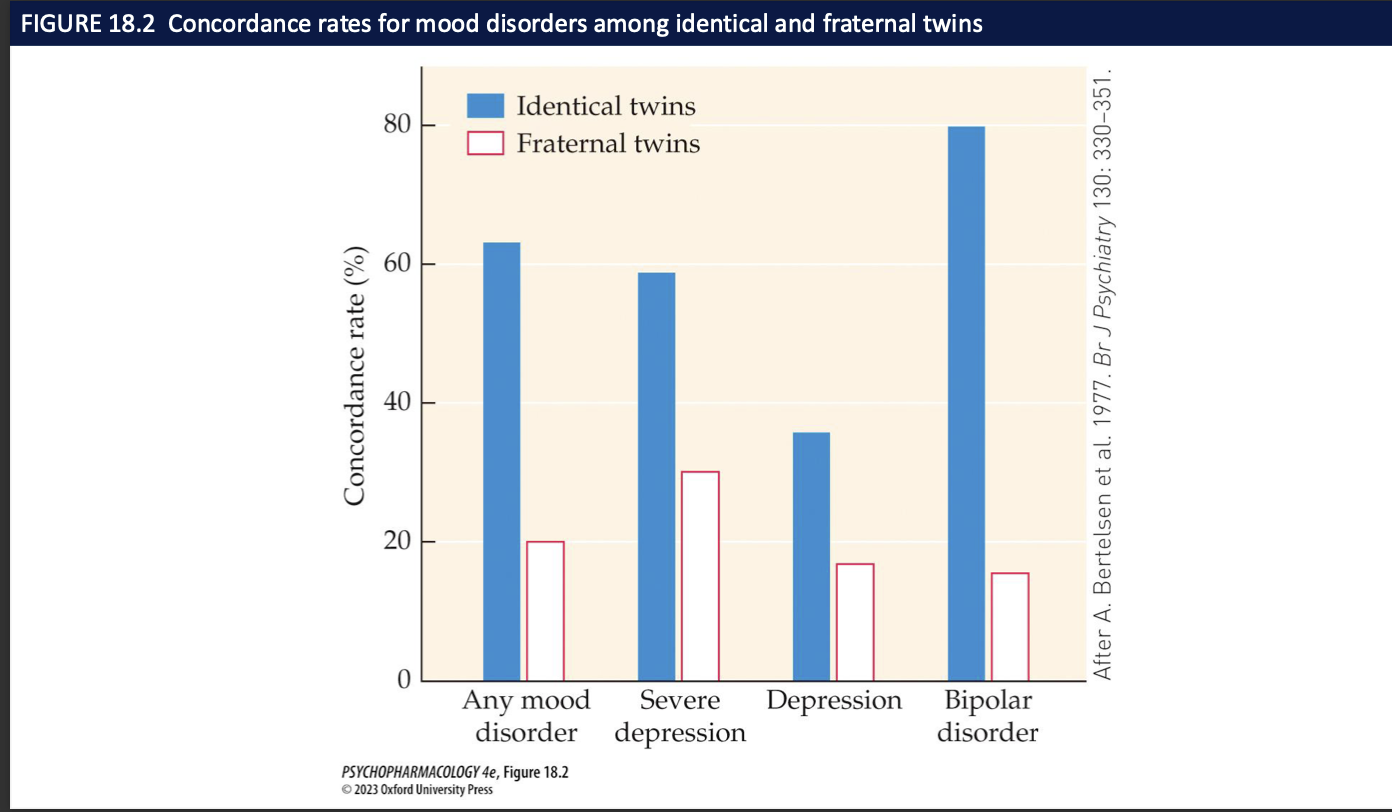
heritability of mood disorders (2)
twin studies: 65% concordance rate for identical twins → 80% for BPD
no single gene for affective disorders → vulnerability genes may contribute small amounts
risk factors for mood disorders (4)
stress: mediated by HPA axis
elevated cortisol lvls + abnormal circadian rhythm in cortisol secretion
early life stress alters HPA axis set point = permanently overly responsive
failure to respond to dexamethasone challenge
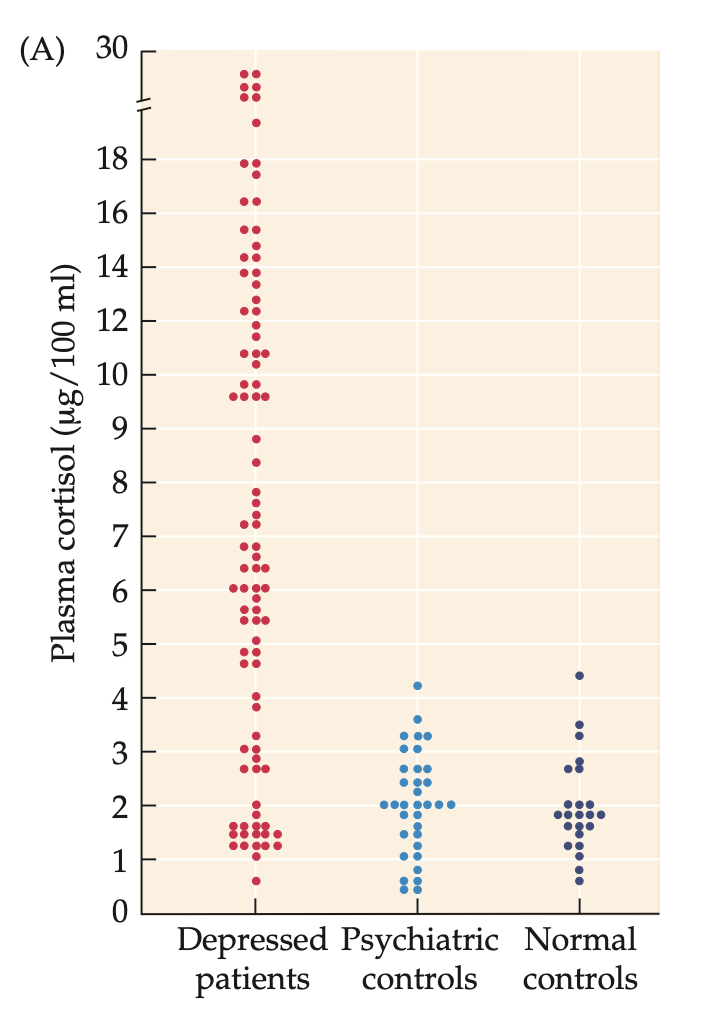
dexamethasone (3) + how do depressed individuals react to a challenge (1)
synthetic glucocorticoid
should act as a negative feedback stimulus to suppress hypothalamic release of CRF and pituitary release of ACTH,
resulting in decreased cortisol levels
Depressed individuals fail to respond with reduced cortisol levels after injection with 1 mg dexamethasone (DEX).
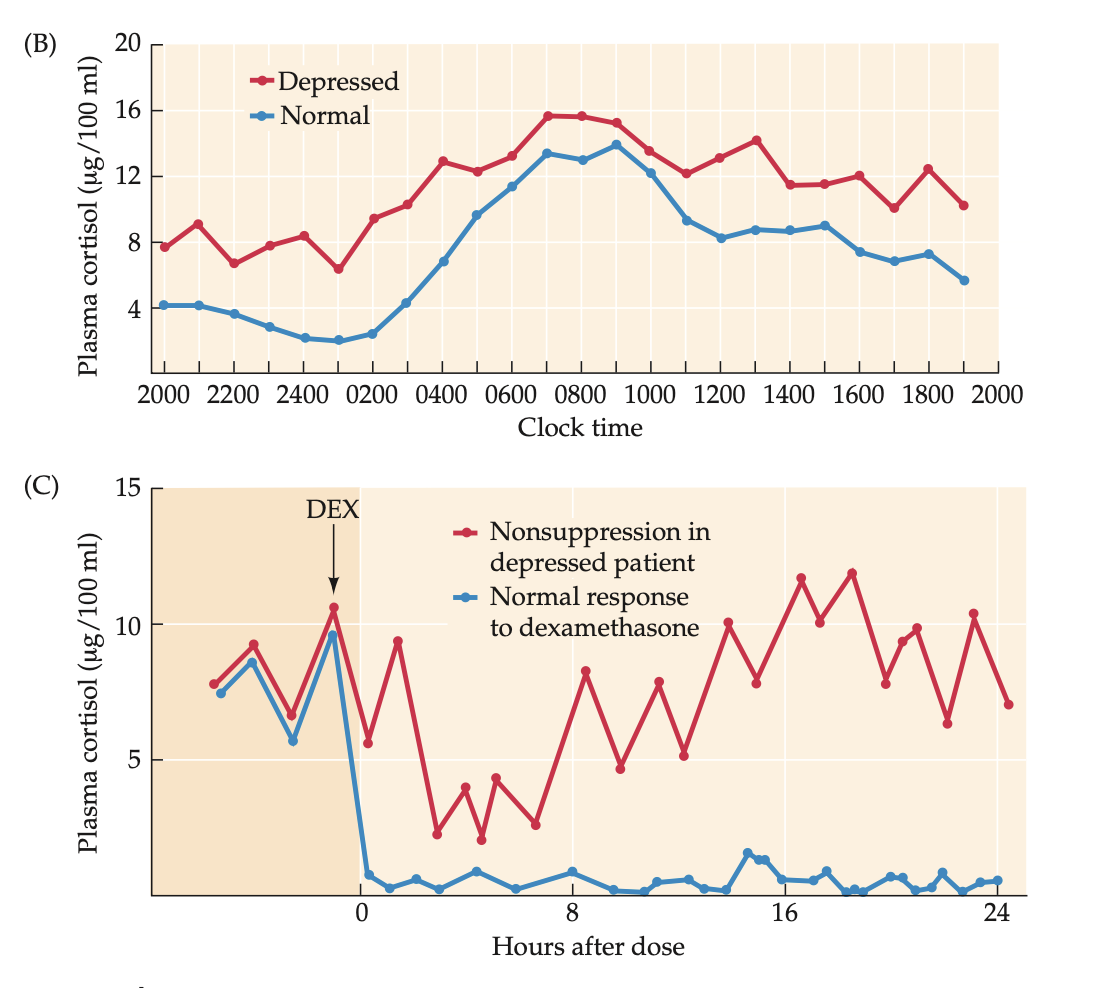
how do biological sleep rhythms ∆ in depressed individuals (4)
abnormal sleep cycles
biological clock may be phase shifted
altered sleep rhythms
BPD: sleep deprivation can trigger an episode of mania
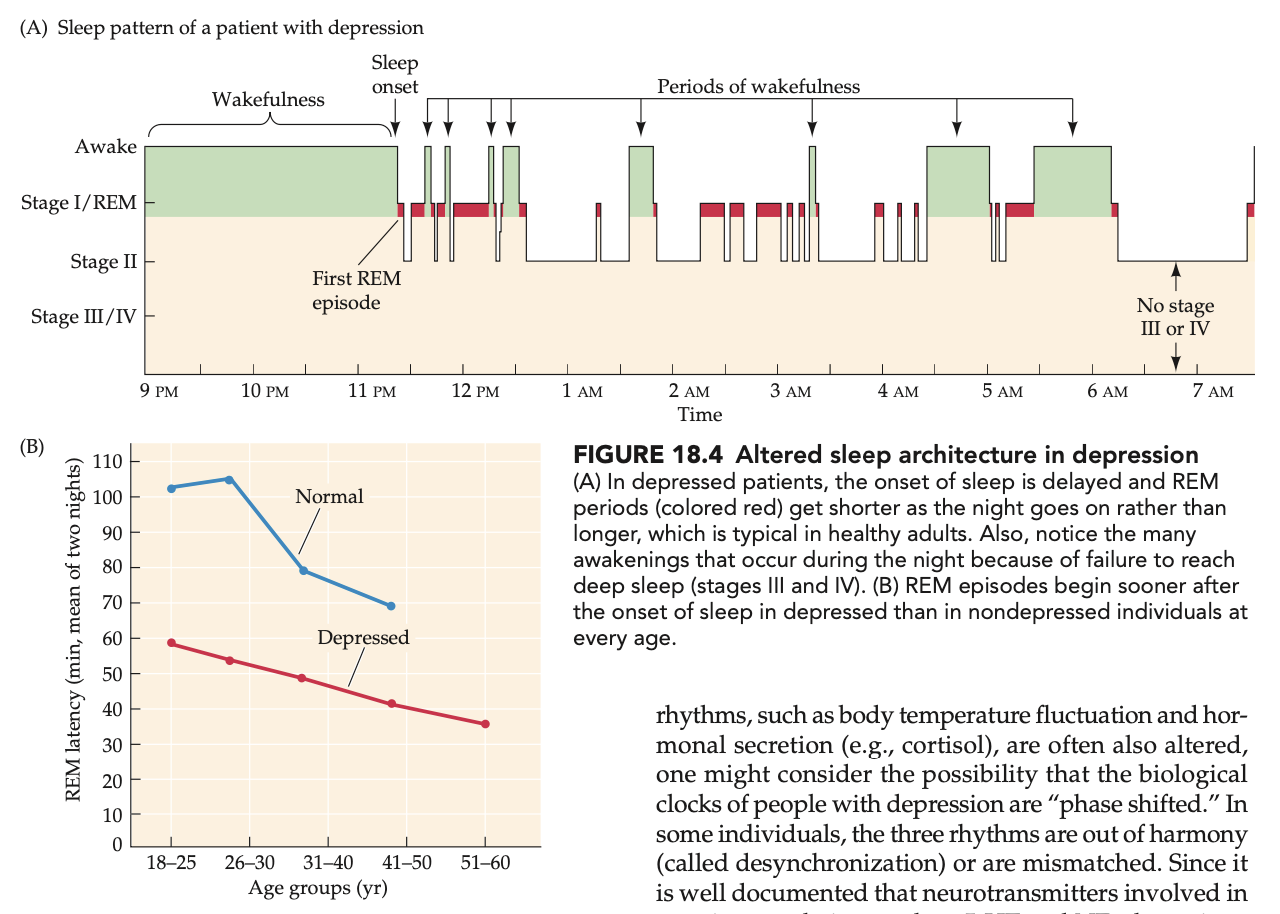
potential involvement of gut-brain axis in depression
gut bacteria can directly/indirectly impact CNS function through interaction w vagus cranial nerve
mice lacking intestinal bacteria = ↑ response to stress
different bacterial flora = variety of psychiatric symptoms
neuroanatomy ∆s of MDD (5)
smaller volumes
basal ganglia
thalamus
PFC
hippocampus
anterior cingulate cortex
psychological factors affecting mood disorders (what is the negative cognitive triad) (3)
negative cognitive triad → distorted pessimistic view of themselves, world, future
interpersonal factors: deficits in social skills/communication problems
stressful life events
social factors affecting mood disorders (7)
poverty
adverse work conditions
trauma
drug/alcohol use
lack of social support
childhood abuse
stress of prejudice
symptoms of MDD (9)
– Sadness, despair, depressed mood
– Guilt, anxiety, low self-esteem
– Lack of motivation, fatigue, loss of energy
– Loss of interest or pleasure in activities
– Diminished ability to concentrate
– Changes in appetite or weight
– Disrupted sleep patterns
– Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide attempts
– Physical symptoms such as fatigue, headache, or GI problems
diagnosis/prognosis of MDD (4)
diagnosis
at least 5+ symptoms persisting for at least 2 weeks → impair functioning
can be mild/moderate/severe
prognosis
chronic + recurrent
associated w shorter life expectancy
“How are bipolar/mania modeled in animals?” (4)
Disrupted circadian rhythms
sleep deprivation → mania-like behavior reduced by lithium
CLOCK knockout mice
glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) overexpression. → lithium targets this
monoamine theory → why is it outdated (5)
low lvls of 5HT, DA, NE in CNS responsible for depressed mood
many drugs used to MDD affect 5HT system
mania coincides w excess monoamine activity
simplistic + misguided
discrepancy in time btw rapid increase in monoamines by antidepressant drugs + slow onset of clinical effect over several weeks
how does 5HT dysfunction contributes to mood disorders (4)
Low 5-HIAA is often found in depressed people. (5HT metabolite)
If you genetically remove tryptophan hydroxylase (enzyme that makes 5-HT) or certain 5-HT receptors in mice → they show depression-like behaviours in animal tests.
tryptophan deficient diet causes depression in individuals w fam history
↑ density of 5HT receptors in post mortem brains of unmedicated depressed patients (upregulated)
the brain adding more receptors when serotonin signaling is too low (trying to compensate).
a polymorphism in the _____ gene may contribute to development of depression → short allele + ______ = _______ but studies are inconclusive
SERT
stress
greater risk of depression
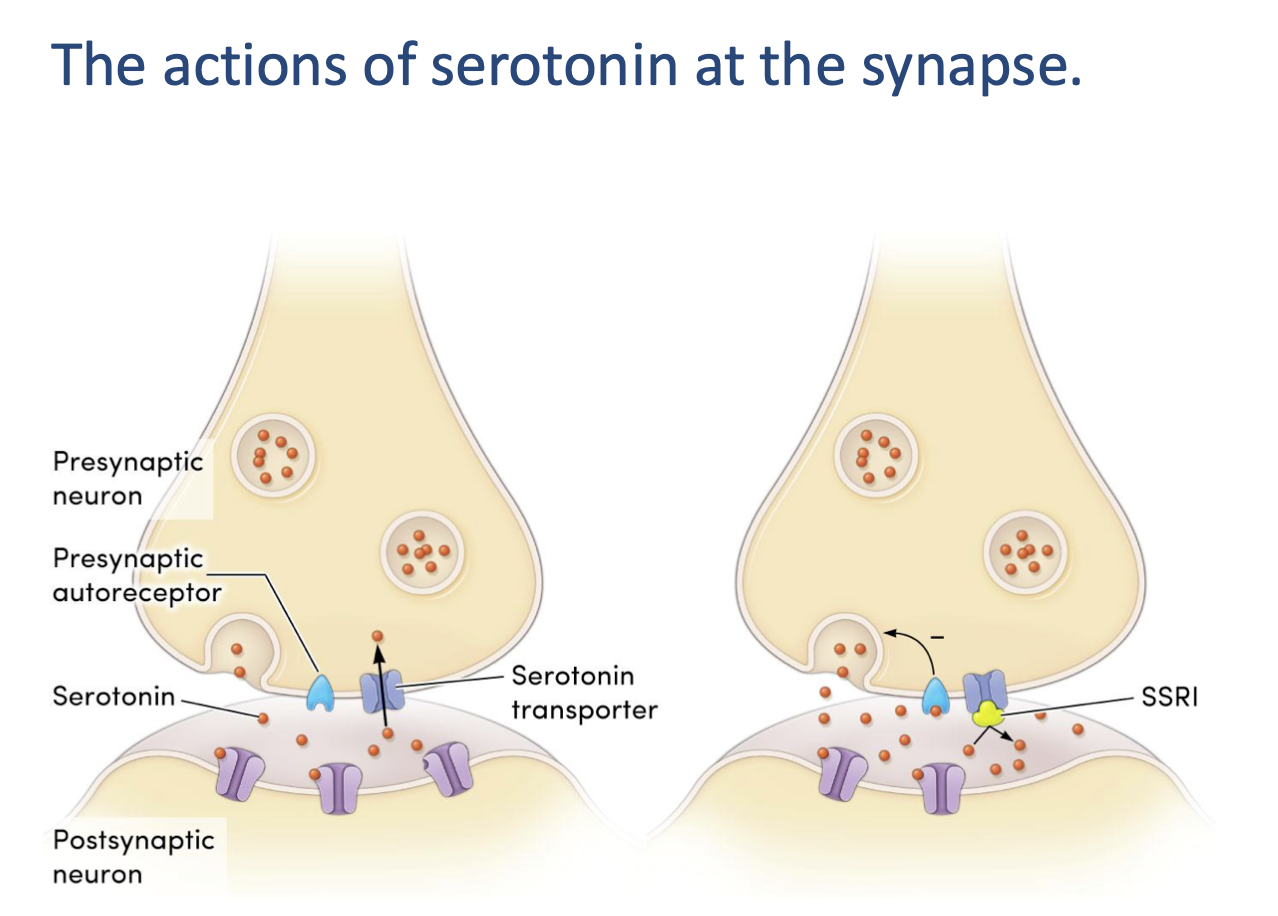
what explains the delay in therapeutic onset of SSRIs (2)
acutely: autoreceptors ↓ 5HT synthesis
chronic treatment = autoreceptor downregulation
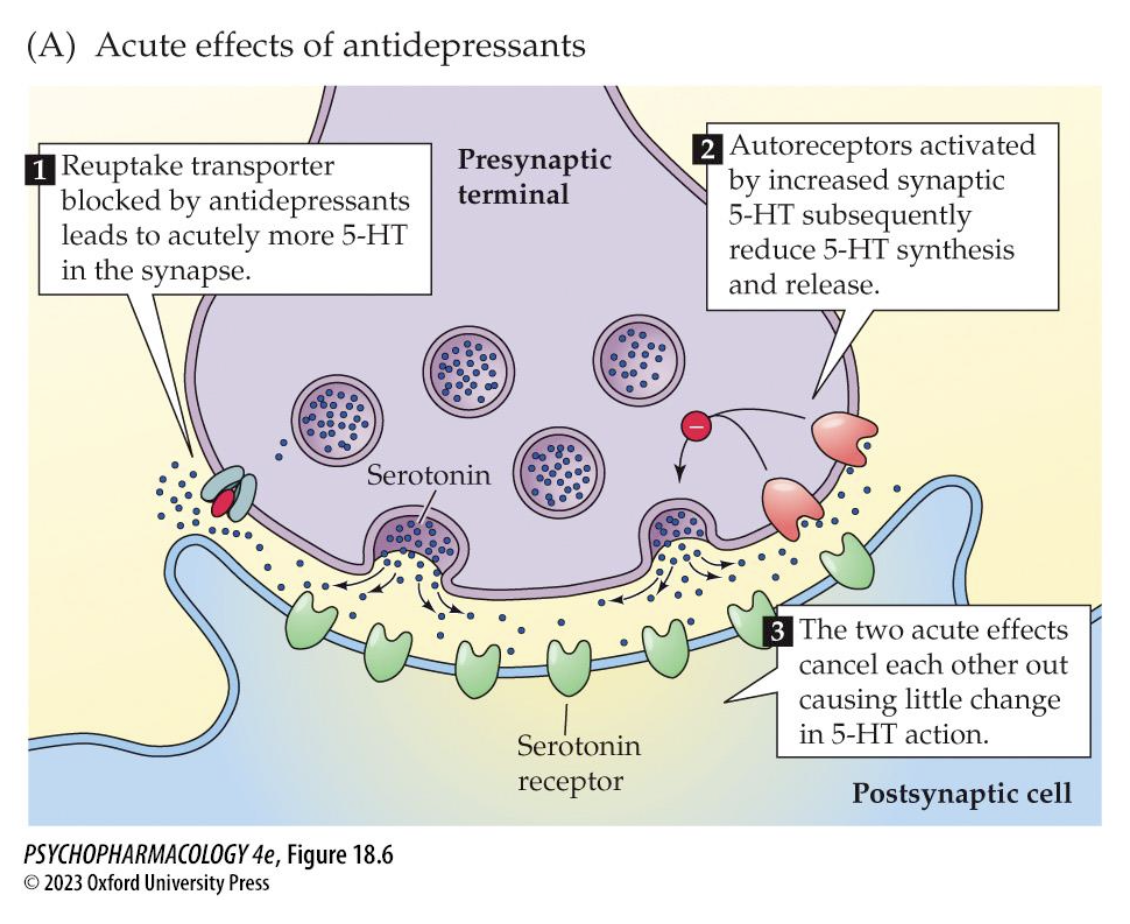
acute effects of antidepressants on 5HT cells (3)
reuptake transporter blocked by antidepressants = more 5HT at synapse
activated autoreceptors reduce 5HT synthesis + release
little ∆ in 5HT action
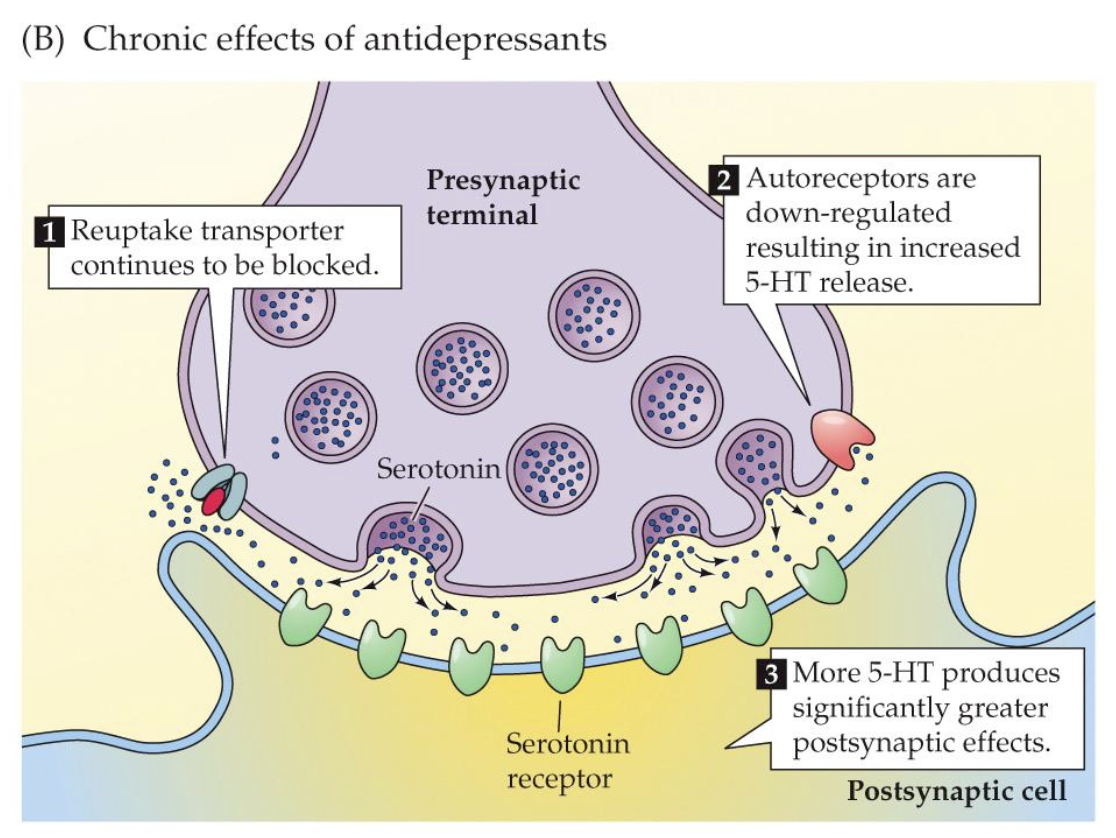
chronic effects of antidepressants of 5HT cells (3)
reuptake transporter continues to be blocked
autoreceptors downregulated = ↑5HT release
more 5HT = greater postsynaptic effects
how is NE activity altered by antidepressants (3)
down regulation of ß receptors
untreated individuals + BPD = increased density of a2 autoreceptors
More α₂-autoreceptors = stronger brake → less NE release.
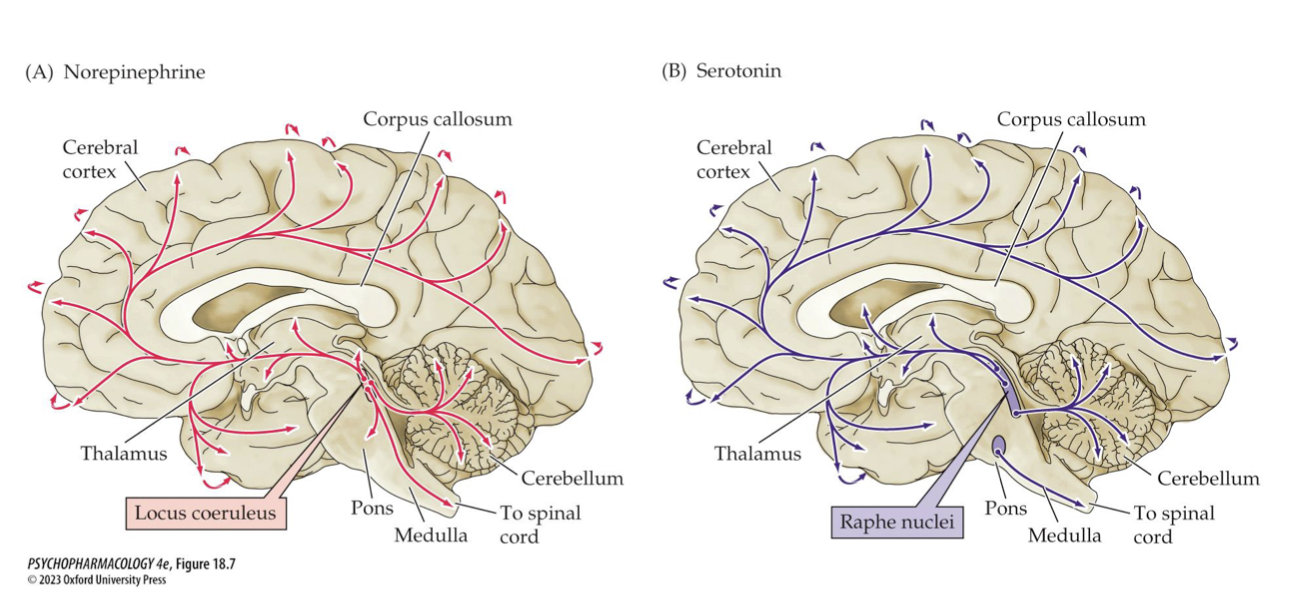
Where do NE vs 5-HT neurons originate? Modern hypothesis of modulation (2)
originate in NE: LC; 5-HT: raphe nuclei.
Modern hypothesis: depression involves both serotonin & NE, which modulate each other.
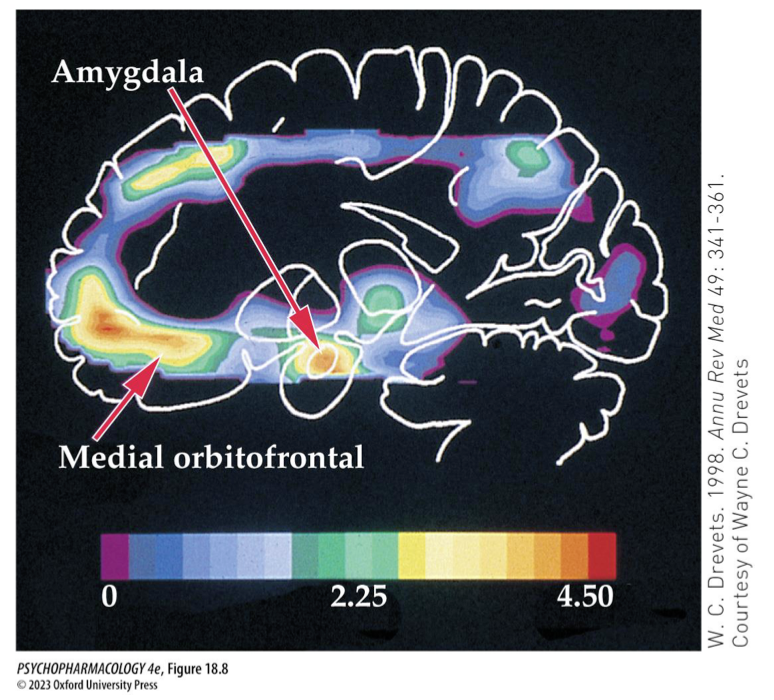
neurobiological models of depression (5) DMN vs salience networks
↓ volume of hippocampus + other brain regions
abnormal lvls of metabolic activity
highly coupled connectivity btw nodes in default-mode network (DMN) = introspective thinking
When DMN activity goes up, salience network activity tends to go down.
When the salience network ramps up (you notice something important / switch to an external task), DMN usually quiets down.
stress + prolonged hypersecretion of ___________ damages _____ branching + ____ in _____ and ____ → elevated _______ reduces the formation of ________→ neurotrophic hypothesis: these things may be due to low _____ which antidepressants prevent
CRF, ACTH, glucocorticoids
dendritic branching + spines
hippocampus + PFC
cortisol
new hippocampal cells (neurogenesis)
BDNF
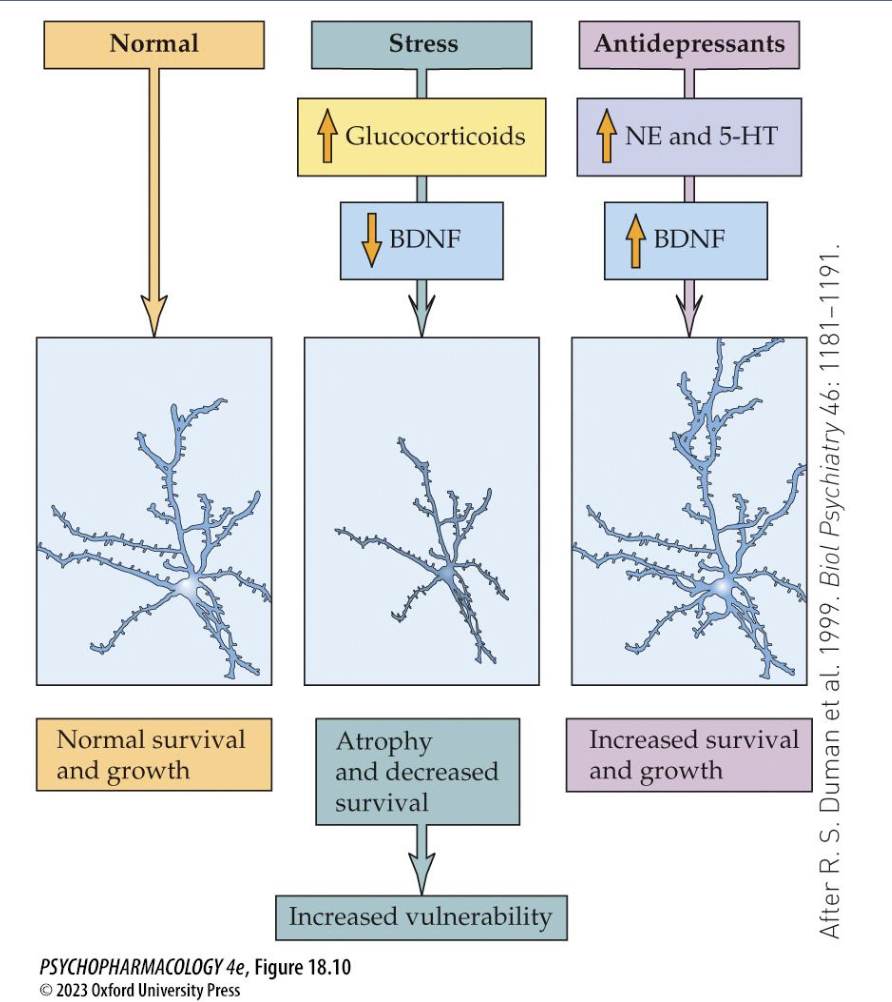
evidence for BDNF in the etiology of depression includes (3)
is low in hippocampus + PFC of depressed patients post-mortem
BDNF gene polymorphism may be associated w mood disorders
modifying gene expression in mice = depressive bhvrs
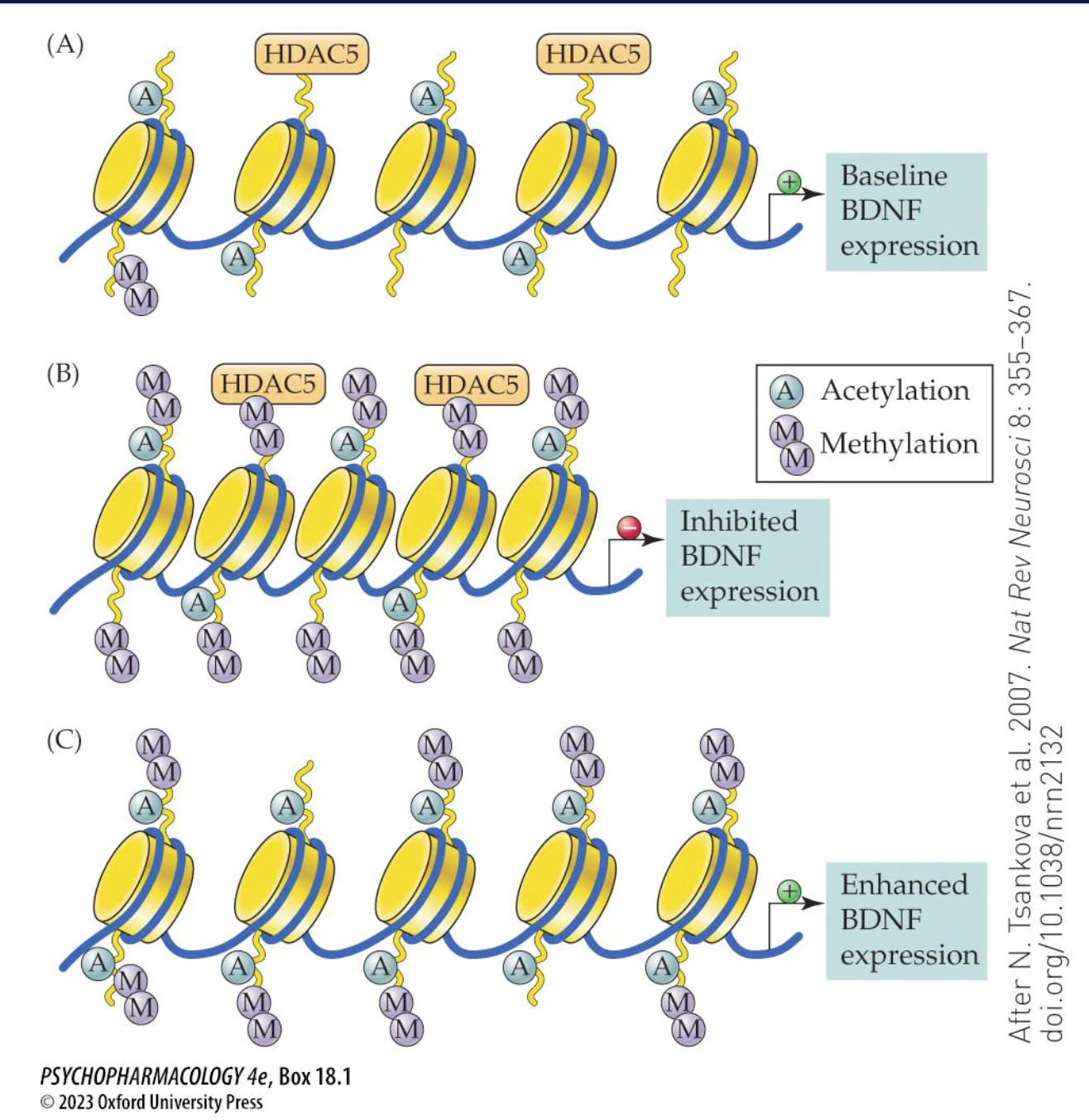
how can BDNF gene be modified (epigenetic ∆s) (3)
chromatin remodelling that affects lvls of gene expression
chronic stress = long-lasting ↓ in BDNF my ↑ histone methylation = closed chromatin state that ↓ses transcription
reversed by antidepressants
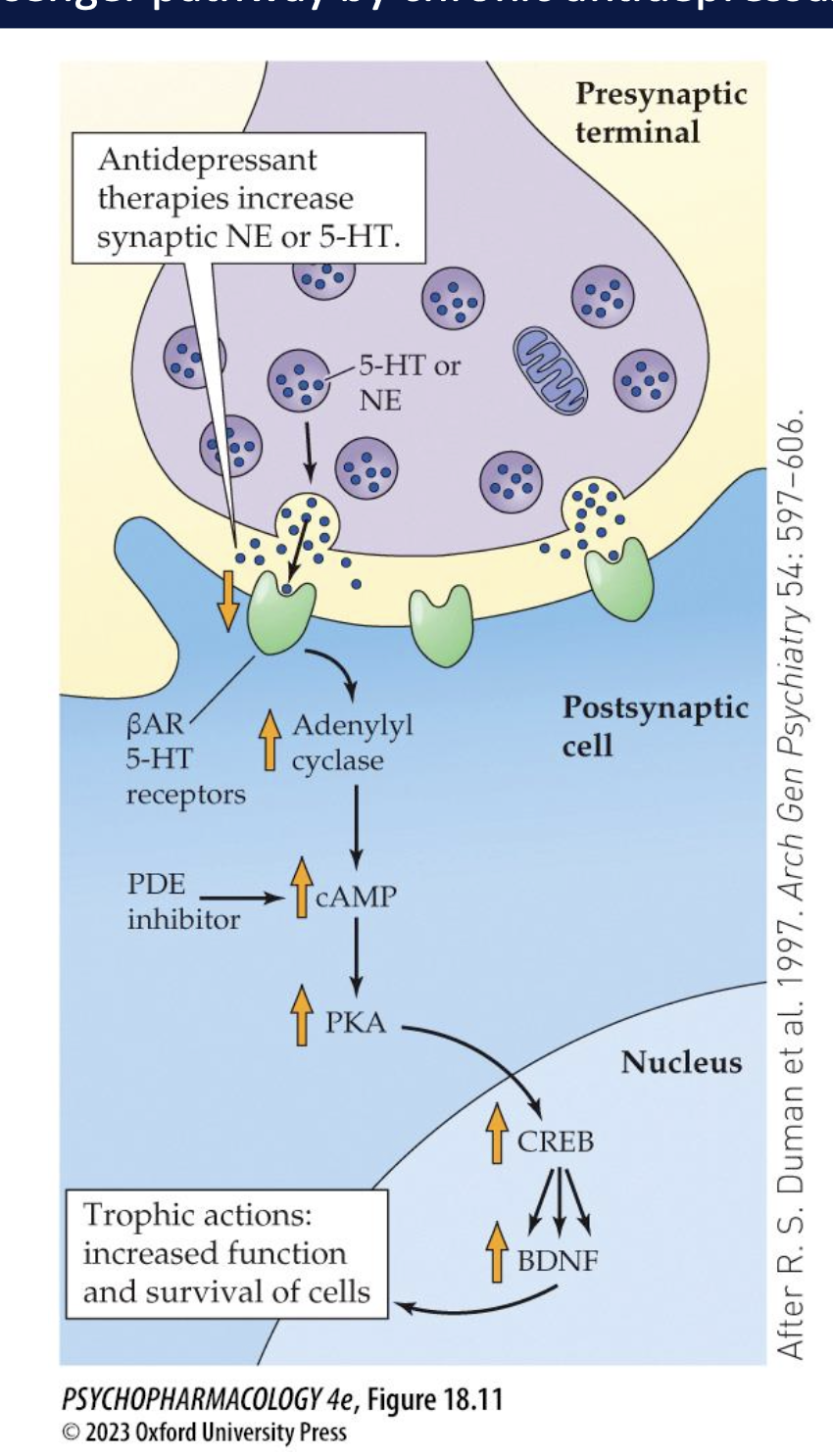
how do chronic antidepressants affect the cAMP pathway (3)
upregulate cascade despite downreg of ß-adrenergic/ 5HT receptors that are coupled to the cAMP cascade
increases phosphorylated CREB → ↑BDNF
enhances the cAMP by inhibiting PDE produced antidepressant effects
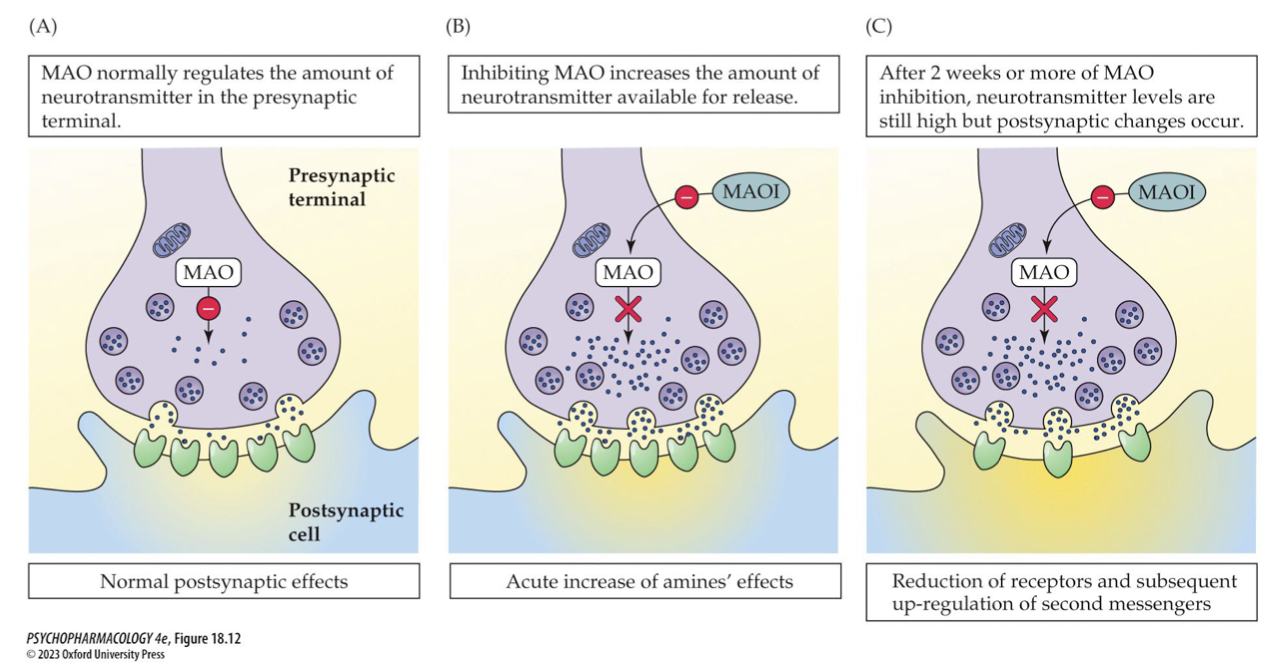
_____ are the oldest antidepressant drugs → inhibition of MAO = ____ in the amount of NT available for release BUT neuron adaptation involving ∆ in _____ or ____ function must play a role in effects → examples (3)
MAOIs
increase
receptor density
2nd messenger function
Phenelzine (Nardil), tranylcypromine (Parnate), isocarboxazid (Marplan)
side effects of MAOIs (4)
∆s in bp, sleep disturbances, overeating/weight gain
↑NE lvls intensify drugs that enhance NE function ie. cocaine, cold meds
↑lvls of tyramine releases more NE at nerve endings = ↑bp dangerously
inhibition of other liver enzymes
how do tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) block the reuptake of NE/5HT (3)
bind to presynaptic transporter protein → inhibit reuptake of NTs = pronlonged action
↓lvls of ACh, histamines
acute increase in synaptic activity in 1st step in antidepressant action → neuronal adaptation over time necessary
side effects of TCAs (4)
histamine receptor blockade = sedation
anticholinergic effects = dry mouth, constipation, dizziness
alpha 1 blockade coupled w NE reuptake blocking = potentially dangerous cardiovascular effects
OD= cardiovasc. problems, delirium, convulsions, coma, death, low therapeutic index
side effects of SSRIs (4)
↑sed 5HT at some receptors = anxiety, movement disorders, muscle rigidity, nausea, headache, insomnia, sexual dysfunction
serotonin syndrome: potentially life-threatening when combined w other 5HT agonists
can cause dependence
only good for severe depression → not moderate/mild
SNRIs (3)
modulate NE/5HT = more beneficial
mirtazapine blocks alpha2 autoreceptors = ↑ synaptic NE + a2 heteroreceptors on 5HT cells = ↑5HT
blocks only selective 5HT receptors to ↓ side effects
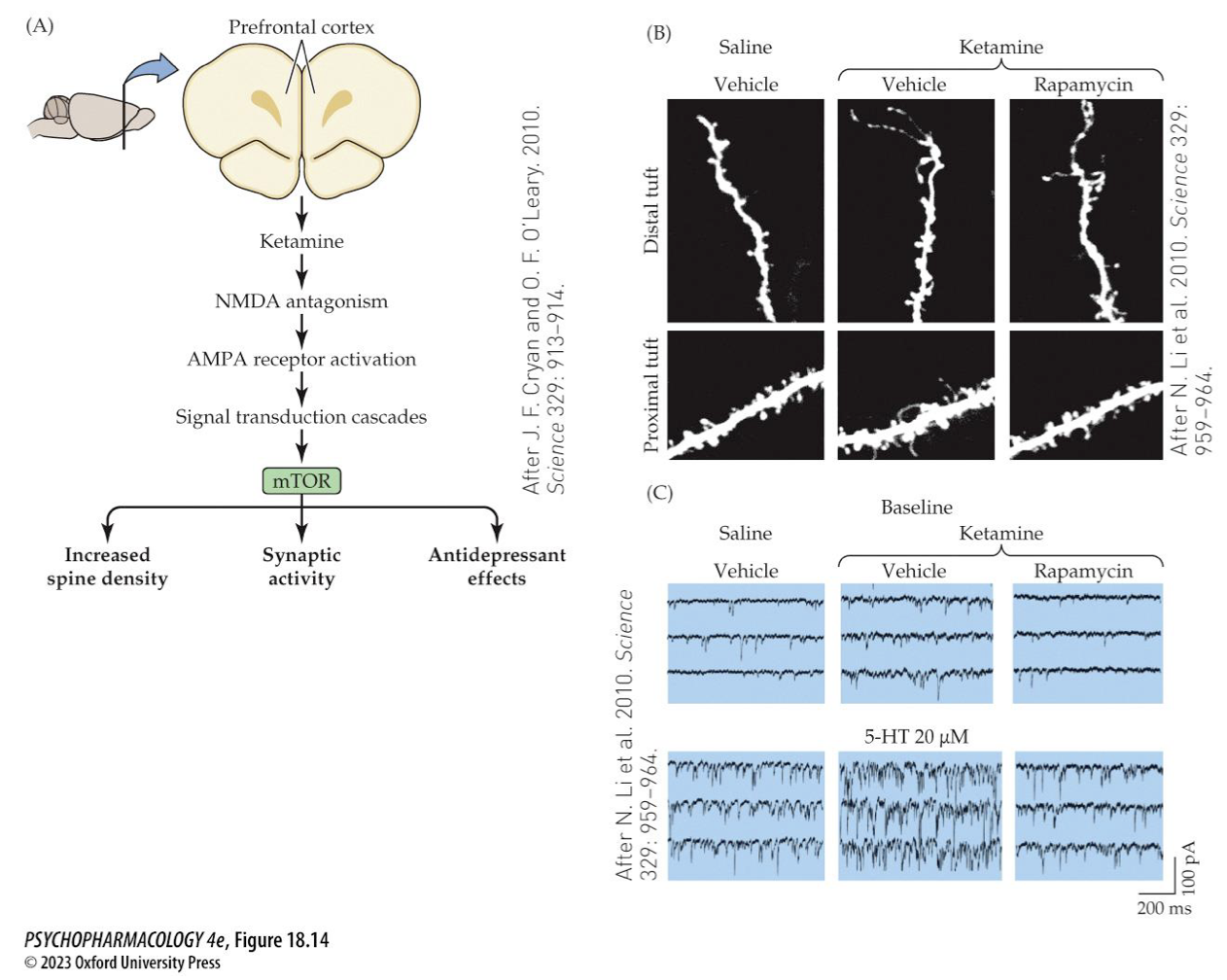
ketamine as an antidepressant
effects last longer than drug’s half life
enhances BDNF-stimulated neurogenesis + elaboration of dendritic spine growth
may be due to rapid activation of the mTOR signalling cascade
ADDs are absorbed from _____ + undergo _____ by the ____ system → they raises lvls of _______ + have serious effects if taken with ______ that also raises lvls of monoamines → stoping them abruptly may cause ________
GI tract
first-pass metabolism
cytochrome P450 system
monoamines
food/drink (ie. high in tyramine or MDMA)
antidepressant discontinuation syndrome
all ADDs affect ________ at the synapse → exert _____ effects by increasing the ______ of newly formed neurons in ________→ can also help by normalizing the lvls of _______
amount of NT
antidepressant effects
growth + survival
hippocampus
stress hormones
ADD use + pregnancy (3)
increased risk of spontaneous abortion, preterm birth, low birth weight
untreated maternal depression = same outcomes
worsen maternal care, poor nutrition, alcohol exposure, decreased bonding w infant
how does lithium for treating BPD stabilize the highs/lows (5)
lithium: most effective treatment for BPD
eliminates/reduced manic episodes w/o causing depression/producing sedation
effective in reducing suicide
mild side effects
v low theraputic index → toxic effects can be severe → needs monitoring
lithium mechanism of action (3)
enhances 5HT actions
reduces catecholamine activity
mood stabilizing due to inhibition of GSK-3 reg of circadian rhythms
other treatments include ____(4)
anticonvulsants ie.
valproate: as effective as lithium → teratogenic
increases GABA lvls by stimulating glutamic acid decarboxylase + inhibiting GABA transaminase
carbamazepine: as effective as lithium
inhibits NE reuptake = blocks + upregulates adenosine receptors