Understanding Distribution Channels in Business
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Place
Location and distribution channel for products.
Distribution
Process of delivering products to the market.
Distribution Channels
Routes products take from producers to customers.
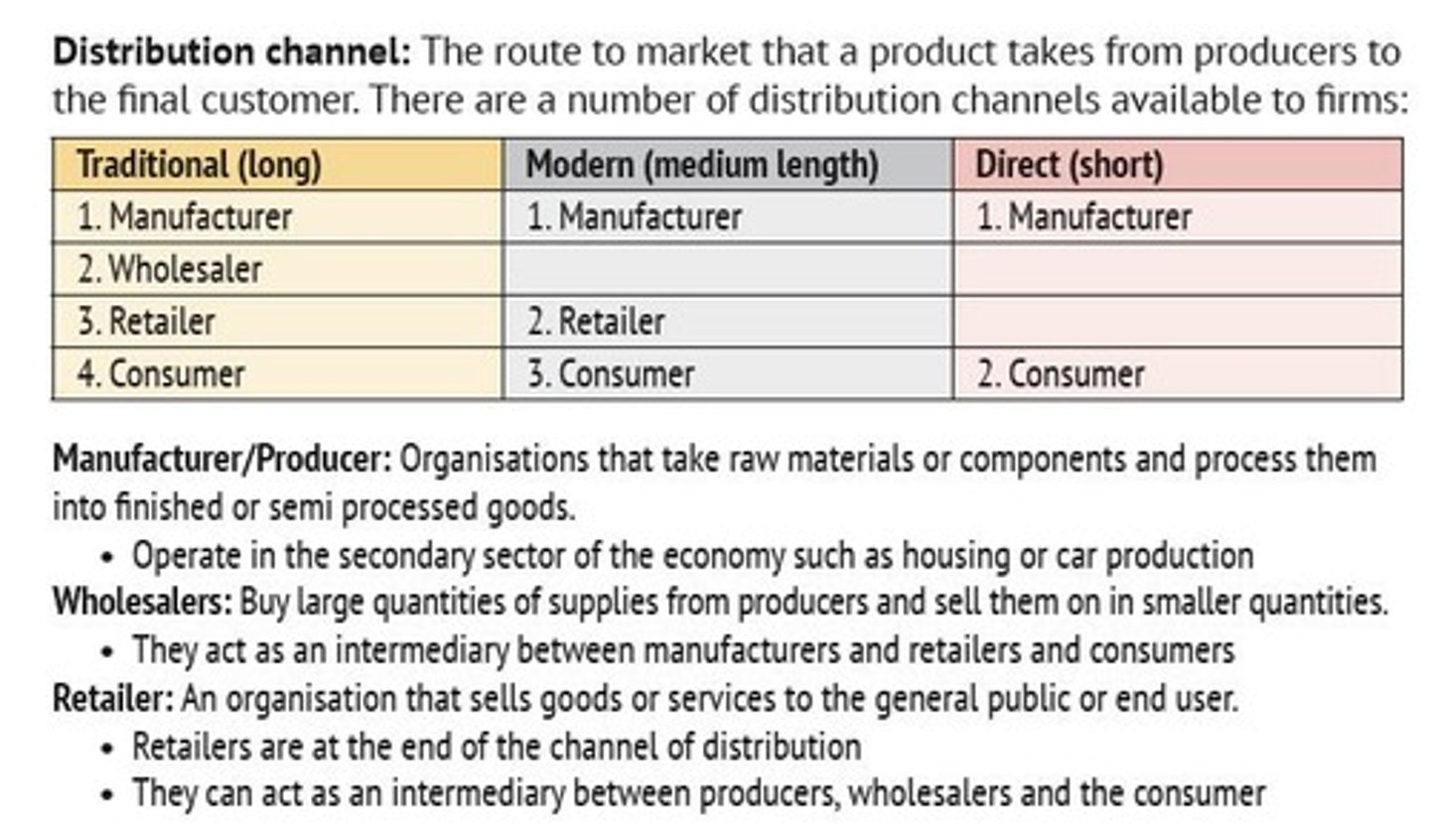
Short Distribution Channels
Direct sales from producer to customer or retailer.
Long Distribution Channels
Involves multiple intermediaries between producer and customer.
Direct Selling
Producers sell directly to final consumers.
Retailers
Businesses selling products to the general public.
Wholesalers
Buy large quantities and sell in smaller amounts.
E-commerce
Selling products online via the internet.
Multi-channel Distribution
Combination of various distribution methods used.
Distribution Decisions
Factors influencing how products are distributed.
Type of Product
Characteristics of a product affecting distribution choice.
Market Access
Ensuring customers can easily reach products.
Geographical Location
Distance of target market from the firm.
Cost of Distribution
Expense impacting a firm's profit margin.
Quantity and Frequency
Delivery volume affecting distribution efficiency.
Physical Market
Location where buyers and sellers meet face-to-face.
Virtual Location
Online spaces for product availability.
Impact of Distribution Channels
Effects on business and stakeholders from choices made.
Food Trucks Trend
Growing popularity in Asia and India markets.
Brand Image
Perception of a brand affected by availability.
Coca Cola Distribution
Syrup shipped to UK, product made locally.
High Street Accessibility
Importance of transport access for customer shopping.
Cost Effectiveness
Method must minimize expenses while achieving goals.
Degree of Control
Businesses limit product spread to protect brand.
Distribution Channels
Paths through which products reach consumers.
Marketing Mix
Combination of product, price, promotion, and place.
Target Market
Specific group businesses aim to reach.
Competitive Advantage
Edge over competitors in the market.
Social Trends
Current societal behaviors influencing consumer choices.
Technological Trends
Advancements affecting distribution methods and efficiency.
Multi-Channel Distribution
Using multiple methods to sell products.
Intermediaries
Entities between manufacturer and consumer in distribution.
Distribution Decisions
Factors influencing how products are delivered.
Place Definition
Location and method of selling products.
Marketplace
Where buyers and sellers exchange goods.
Brand Identity
Image and perception of a brand in consumers' minds.
Super-Premium Brand
High-end product positioned for affluent consumers.
Prime Selling Space
Desirable retail locations for product placement.
Direct Selling
Selling products directly to consumers without intermediaries.
Wholesaler
Middleman purchasing in bulk to sell to retailers.
Retailer
Business selling products directly to consumers.
Consumer
End user of products or services.
Vending Machines
Automated machines selling products in various locations.
Stock Ordering Methods
Processes for retailers to manage inventory efficiently.
Discounts for Retailers
Price reductions offered to encourage product placement.
Direct supply relationship
Manufacturer sells directly to retailers, reducing costs.
Wholesaler
Intermediary buying in bulk, selling smaller quantities.
Breaking bulk
Wholesaler divides large quantities for retailers.
Purchasing economy of scale
Cost savings from buying in large quantities.
Direct selling
Manufacturer sells directly to consumers, bypassing retailers.
B2C (Business to Consumer)
Direct sales from businesses to end consumers.
E-commerce
Online selling platform for businesses and consumers.
Click and collect
Online purchase with in-store pickup option.
Internet marketing
Promoting products through online channels.
Multi-channel distribution
Using various channels to reach consumers.
EPOS systems
Electronic Point of Sale for inventory management.
Online sales growth
Significant increase in internet sales annually.
Direct manufacturer profits
Higher profits from selling directly to consumers.
Retailer dominance
Large retailers increasingly control market distribution.
Traditional distribution chain
Manufacturer-wholesaler-retailer-consumer model.
Internet sales in UK
Over £7 billion in online sales during November 2014.
Auction sites
Platforms like eBay for selling products online.
Consumer concerns
Fraud and non-delivery issues in online shopping.
Distribution centres
Facilities for storing and distributing products.
Online music sales
More downloads sold than CDs in stores.
Small business competition
E-commerce enables small businesses to compete globally.
Brand values
Core principles guiding a company's branding strategy.