L11 - Motor Neurons, Corticospinal tract and Corticobrainstem tract
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
upper motor neuron (UMN)
location in spnial cord and brainstem
function
signs of inj
location
primary motor cortex or brainstem
pathways that originate from …
cortex = corticospinal tract, corticobrainstem tract
brainstem = vestibulospinal, reticulospinal, rubrospinal ,tectospinak
travel on cortico spinal tract
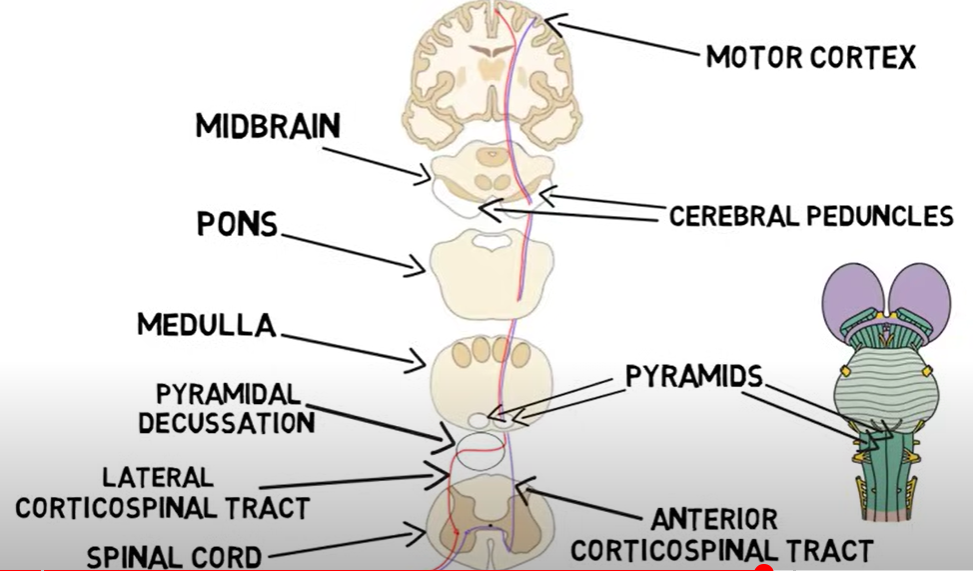
corticospinal tract
descending
1) internal capsule
2) mid-brain (cerebral peduncle)
3) pons (cerebral peduncle)
4) upper and lower medulla pyramids (cerebral peduncle)
5a) 95% cross in pyramidal decessation before spinal cord enterance (enter on opp side of body from where they originated) (lateral corticospinal tract)
5b) 10% continue into spinal cord on same side of body (anterior corticospinal tract)
5b.2) anterior corticospinal tract synapse on LMN on level of spinal cord and enter
function:
voluntary control of precise mvm of distal muscles of limbs (lateral CST)
control of less precise mvm of proximal muscles of limbs and trunk (medial CST)
corticobrainstem
descending
1) primary motor cortex
2) internal capsule
3) terminate at location of cranial nerve
function:
serves as UMN to all motor cranical nerves
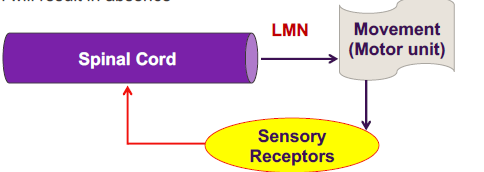
lower motor neuron (LMN)
location in spnial cord and brainstem
function
signs of inj
location
CNS
anterior horn of spinal cord (then go out through peripheral nerves)
brainstem (cranial nerves w/ motor output) (axons then go through cranial nerves)
function
convey signals to skeletal muscles
types
alpha
large cell bodies
large myelinated axons
project to extrafusal muscle fibres (muscles that do mvm)
gamma
medium sized
project to intrafusal muscle fibres in muscle spindles (regulate stretch)
Identify the function of the neurotransmitter ACH at the neuromuscular junction.
motor unit = 1 alpha LMN and all the muscle fibres it innervates
when one neuron fibres of all connected muscle cells contract due to release of Ach
Describe the structure and function of the motor unit and the relationship between cortical tissue with (i) the intricacy of movements of that part of the body and (ii) the size of motor units.
motor unit:
motor unit = 1 alpha LMN and all the muscle fibres it innervates
when one neuron fibres of all connected muscle cells contract due to release of Ach
strength of muscle contract
large motor unit = larger fibres for gross control
small motor unit = smaller fibres for precise control
inverse rel. with motor homunculus (aka less representation in cortex = greater value of feature)
larger cortical tissues (more UMN cell bodies) = smaller motor unit
smaller cortical tissue (less UMN cell bodies
Describe the systems involved in the execution of voluntary movement including speech production.
The corticobulbar tracts, originating from the motor cortex, descend via the internal capsule to brainstem motor nuclei, controlling facial, head, and neck muscles.
Describe the structure and function of the tracts controlling fractionated movements, gross and postural and movements of the face
tectospinal tract
reflexive head mvm
respond to visual or auditory input
vestibulospinal tract
arises from vestiublar nucleus to help control neck and upper back muscles
aid balance
rubrospinal tract
arise from red nucleus in midbrain
minimal cont. to upper limb extensor muscles
Apply an understanding of the function of the functioning of the primary motor and motor planning areas of the cortex to predict likely impairments, changes to activity and participation following a lesion in this area in conditions such as stroke, tumour and MS.
UMN dysfunction
decerebrate rigidity
sevre midbrain lesions
extension of limbs, trunk, internation rotatio of upper limbs and plantar flexion
decorticate rigidity
sevre lesions above midbrain
rigid flexed UL, extended neck and lower limbs and plantar flexion
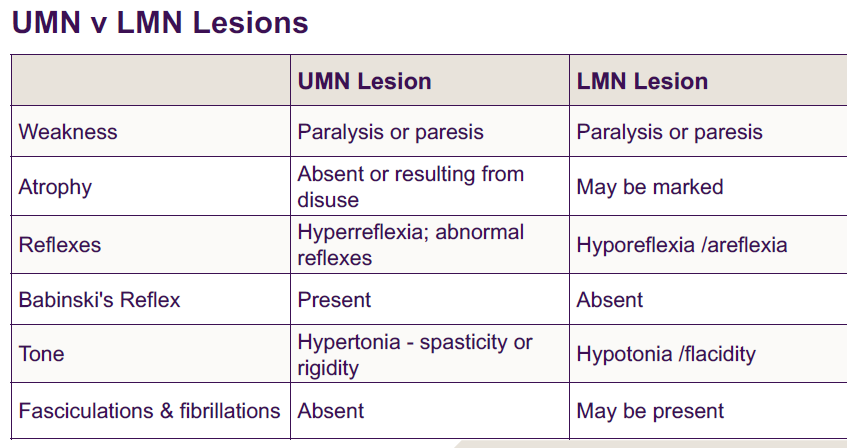
Describe reflexes and identify pathologies that would result in change to this reflex
reflex = involuntary motor response to an external stimulus
facilitated by descending pathways from cortex and brainstem
abnormal reflexes
babinki sign
extension of big toe