Chemistry Unit 12- Kinetics and Equilibrium
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What does an endothermic graph look like?
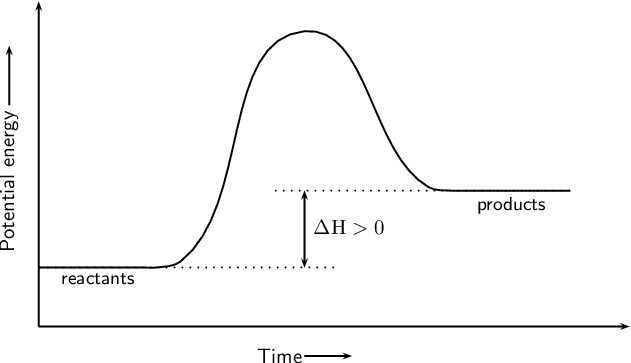
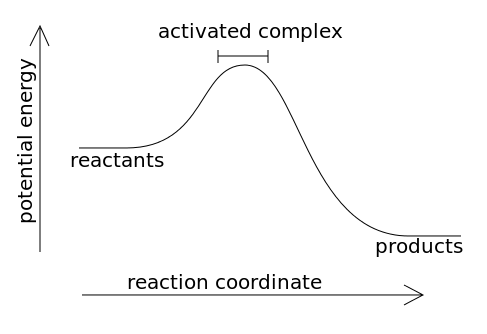
What does an exothermic graph look like?
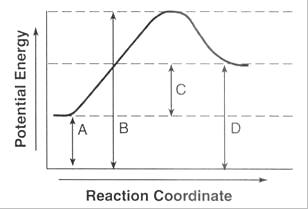
Name the numbers on the graph
A.Potential energy of the reactants
B.Activation energy
C.Heat of reaction/ delta H
D.Top of the hump: activation complex
E. Potential energy of the product
F.Always has a positive delta H!
What is needed for a reaction to take place in between atoms or molecules?
They need the proper orientation, sufficient kinetic energy, and enough speed to create collisions
What are factors that affect the rate of reaction?
Concentration
Pressure
Temperature
Surface Area
Nature of the reactants
A catalyst
How does concentration affect the rate if reaction?
Higher concentration means more particles, more collisions, and faster speed.
Lower concentration is the opposite
How does pressure affect the rate of reaction?
(Only works for gasses) higher pressure pushes particles together which causes a faster rate of speed
How does temperature affect the rate of reaction?
When the temperature increases, it also increases the rate of speed of the particles which makes them have more energy
How does surface area affect the rate of reaction?
Powder has more surface area than chunks.
More surface area means a faster rate of reaction and vice versa
How does the nature of reactants affect the rate of reaction?
Ionic reactants are faster, and covalent are the slowest.
Gasses are the fastest, aqueous is next, then liquid, then solids.
How does a catalyst affect the rate of reaction?
It lowers the activation energy and creates an alternate reaction pathway
What happens to the energy in an endothermic reaction?
The energy is absorbed by the reaction
What are the three characteristics of an endothermic reaction/graph?
Positive delta H
Heat is absorbed
Potential energy of the PRODUCTS is higher than the potential energy of the reactants
On which side does the heat energy go in an exothermic reaction equation?
On the right side (products)
On which side does the heat of energy go in an endothermic reaction?
On the left side (reactants)
What are the three characteristics of an exothermic reaction/graph?
Negative delta H
Heat is released
Potential energy of REACTANTS is higher than the potential energy of the products
What are the two things that substances in nature tend to go to and tend to want?
They tend to go from low entropy to high entropy, and want to go to lower energy, making them exothermic.
What do substances in nature tend to go to in terms of entropy?
They tend to go from low entropy to high entropy
What do substances in nature tend to want to go to in terms of energy? And what type of reaction does that make them?
They want to go to lower energy, therefore making them exothermic.
In what type of system does equilibrium happen?
In a closed system
When does equilibrium happen in terms of reactions?
When the forward reactions rate is EQUAL to the rate of the reerse reaction
What happens to the concentration of the reactants and products during equilibrium?
The concentration remains constant
When does solution equilibrium take place, in terms of the solution?
It will take place when the solution is saturated and contains a precipitate
What happens to the rate of the forward and reverse reactions in chemical equilibrium?
The rate for both of them is the same
What happens to the concentration of the products and reactants in chemical equilibrium?
The concentration of both of them remain constant
What is required for a reaction to occur successfully?
Particles must have enough kinetic energy, must be oriented properly, and must have sufficient speed in order to collide.
What makes a reaction spontaneous in terms of entropy and enthalpy?
Things tend to go toward more disorder which makes them have greater entropy, and tent to go to lower energy making them want to have lower energy
What happens to the products and reactants when a system shifts to the right?
All products increase and all reactants decrease
What happened to the products and reactants when a system shifts to the left?
All products decrease and all reactants increase
In what direction does a system shift when the concentration of a substance is increased?
It will shift away from the added system
In what direction does a system shift when the concentration of a substance is decreased?
It will shift towards the substance
Why does a reaction/system shift towards the decreased concentration of a substance?
Because it needs to make more of the substance that was decreased
What is temperature stress related to in a reaction?
It is related to the change of heat in a reaction
What happens when you increase the temperature in a reaction at equilibrium?
It will increase the heat of the reaction, speeding up the reverse reaction, causing the equilibrium to shift LEFT
What happens when you decrease the temperature in a reaction at equilibrium?
It will cause the equilibrium to shift RIGHT
What phase does pressure stress only affect?
Gases
When is pressure stress applied to a reaction at equilibrium?
It is only applied if a gas is involved in the reaction
What way will a system shift to when there is an increase in pressure?
It will shift to the side with the smallest number of moles.
In what way will a system shift to when there is a decrease in pressure?
It will shift to the side with more moles
What happens to the pressure stress when both the reactants and products have the same number of moles?
Pressure will have NO effect!
What impact does the catalyst effect have on a reaction in terms of Le Chateliers principle?
It has NO IMPACT on the equilibrium
What effect is the common ion effect similar to?
It has a similar effect as concentration stress
What happens to a reaction when an identical ion is added to it?
There is a shift in the equilibrium because the “concentration” is increasing it