Nervous system
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the basic order of the nervous system?
receptor —> sensory neurone —> synapse —> relay neurone —> synapse —> motor neurone —> effector (muscle glands)
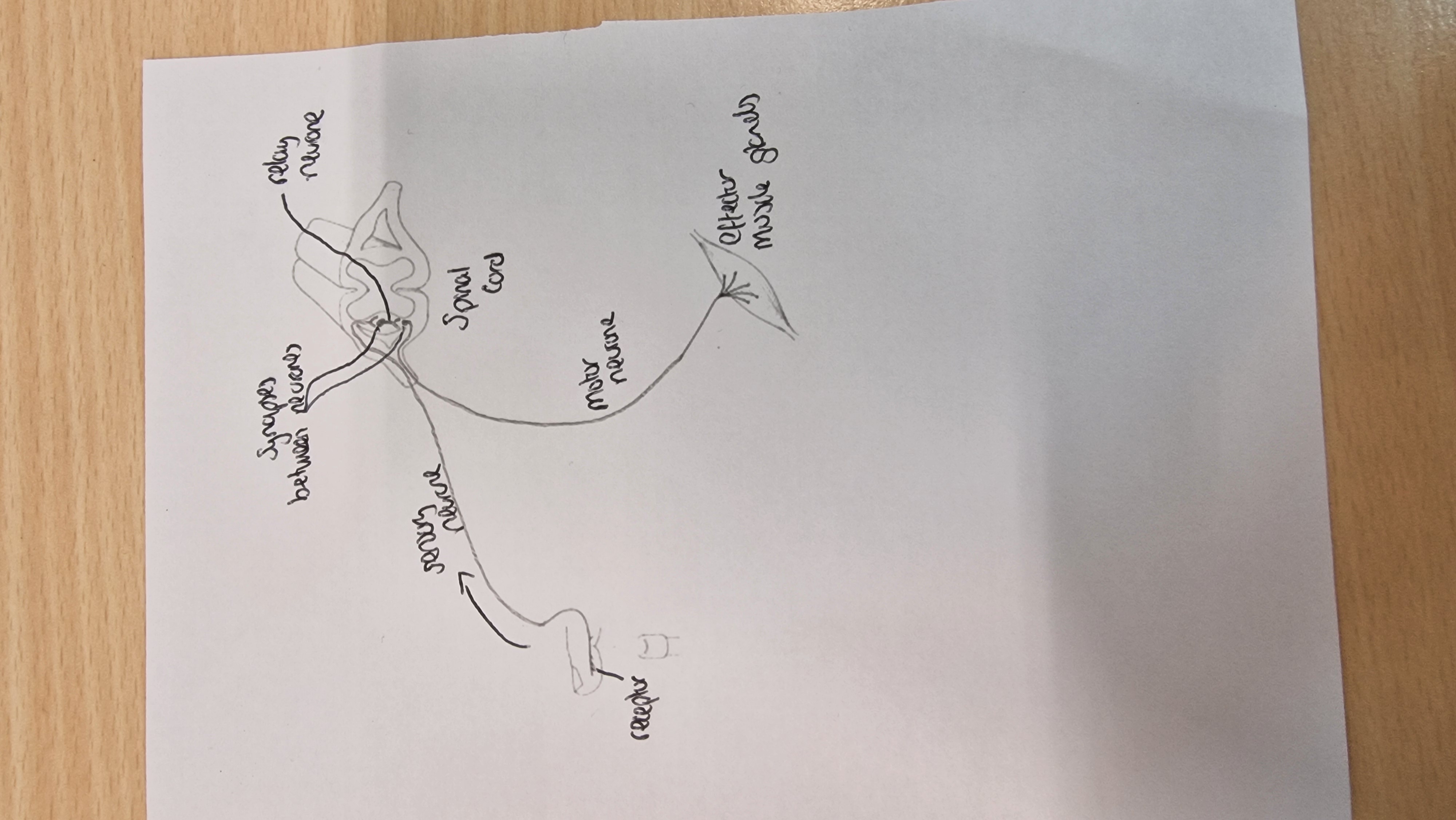
What components are in the spinal cord?
synapse and relay neurone be between the sensory neurone and motor neurone
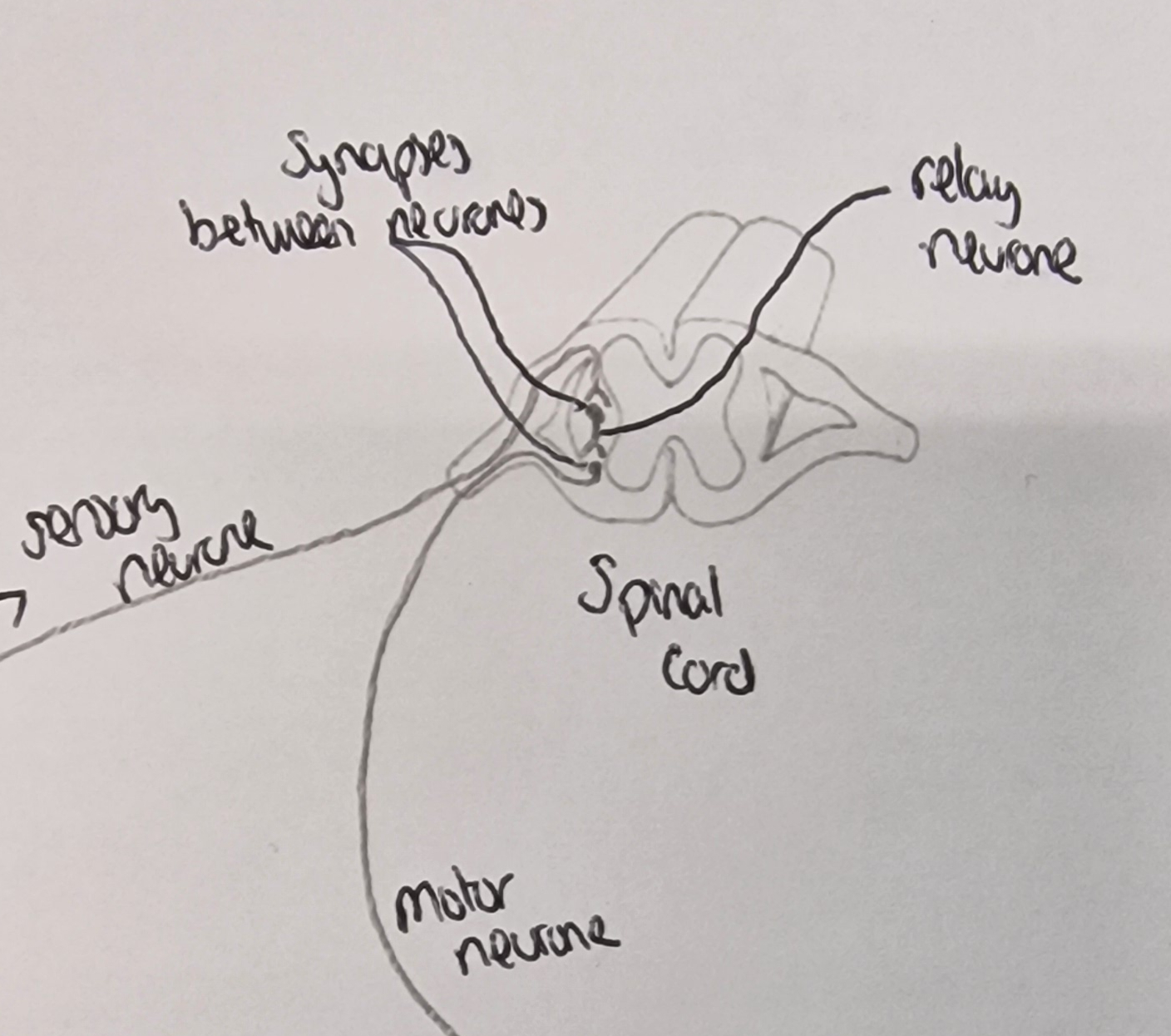
What side does the sensory neurone and motor neurone come out of the spinal cord?
same side (as the impulse reacting is on the same side of the body, e.g. otherwise, if left hand touches something hot, right arm would raise which is wrong, so impulse runs on the same side of the spinal cord to make the correct effect)
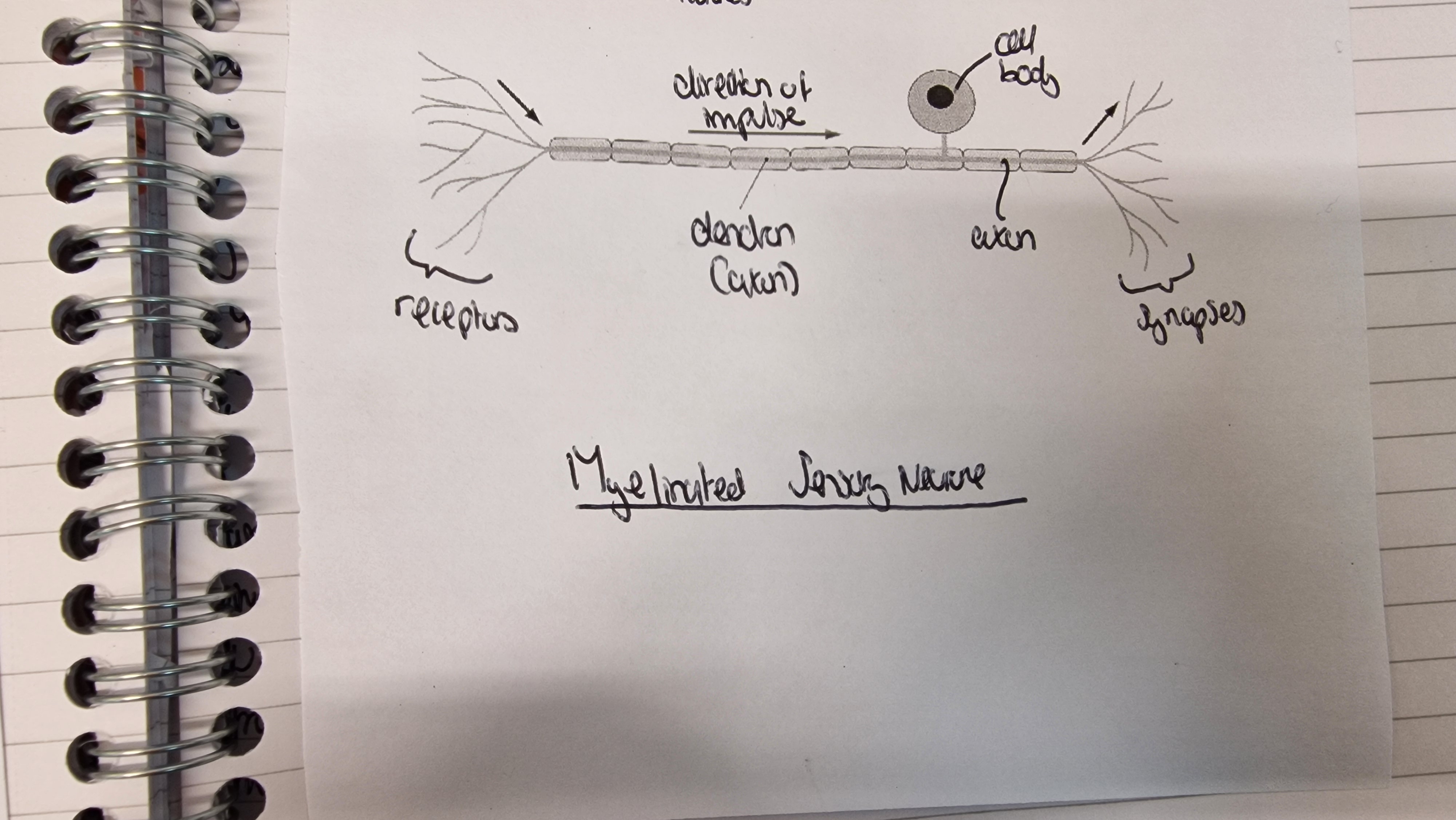
myelinated sensory neurone
contains receptors, dendrons (axons) and cell body and synapses. The direction of impulse is from receptors to the synapse
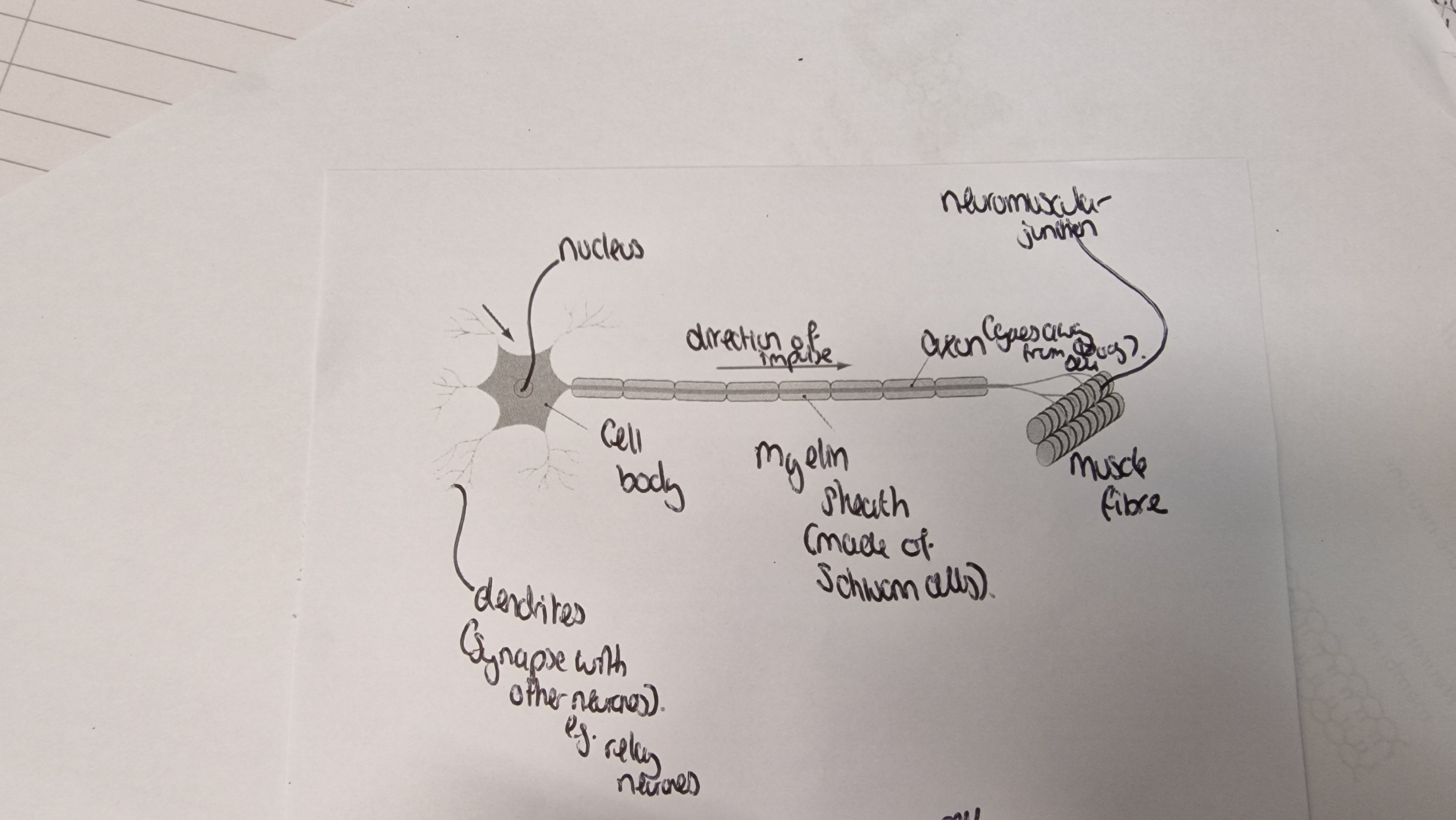
Myelinated motor neurone
contains the cell body, myelin sheath, axon neuromuscular junction and muscle fibre. The direction of the impulse is from the cell body to the muscle fibre
Key features and advantages of reflexes
do not have to be learnt/ automatic/ involuntary
rapid - only 3 neurones involved
protect against damage to body tissues
prevents injury/named injury
help escape from predators
finding food/mates/suitable conditions
enable homeostatic control
Resting membrane potential
NA+/K+ pump actively transports using ATP 3NA+ OUT of the neurone and 2K+ IN
SO
a higher concentration of NA+ OUTSIDE
a higher concentration of K+ INSIDE
Differential permeability of the membrane
More permeability to K+ than NA+ (as K+ protein channel gates are open and Na+ channel gates are closed)
More K+ ions diffuse out than Na+ diffuse in (one K+ ion is able to diffuse in but one NA+ ion can’t diffuse out)
The membrane has a potential of -70 mV, this is the resting potential

The action potential
Resting potential (-70mV). High concentration of Na+ ions outside. High concentration of K+ inside. The membrane is polarised
Some Na+ channels in the membrane open. (e.g. stimulus). Diffusion Na+ move in by facilitated diffusion. Membrane starts to become less negative. start to depolarise the membrane
If enough Na+ ions diffuse in to reach threshold potential (-55mV) voltage gated sodium ion channels open, leading to a rapid influx of Na+ (diffusion in of Na+ ions)
The membrane becomes depolarised (more positive inside than outside) reading a membrane potential +40mV. This is the action potential (+inside and - outside).
Na+ channels close. K+ channels open.
K+ ions diffuse out - so membrane repolarises
The membrane becomes hyperpolarised
The Na+/K+ pump restores resting potential
Pacinian corpuscle
detects pressure
features of a Pacinian Corpuscle
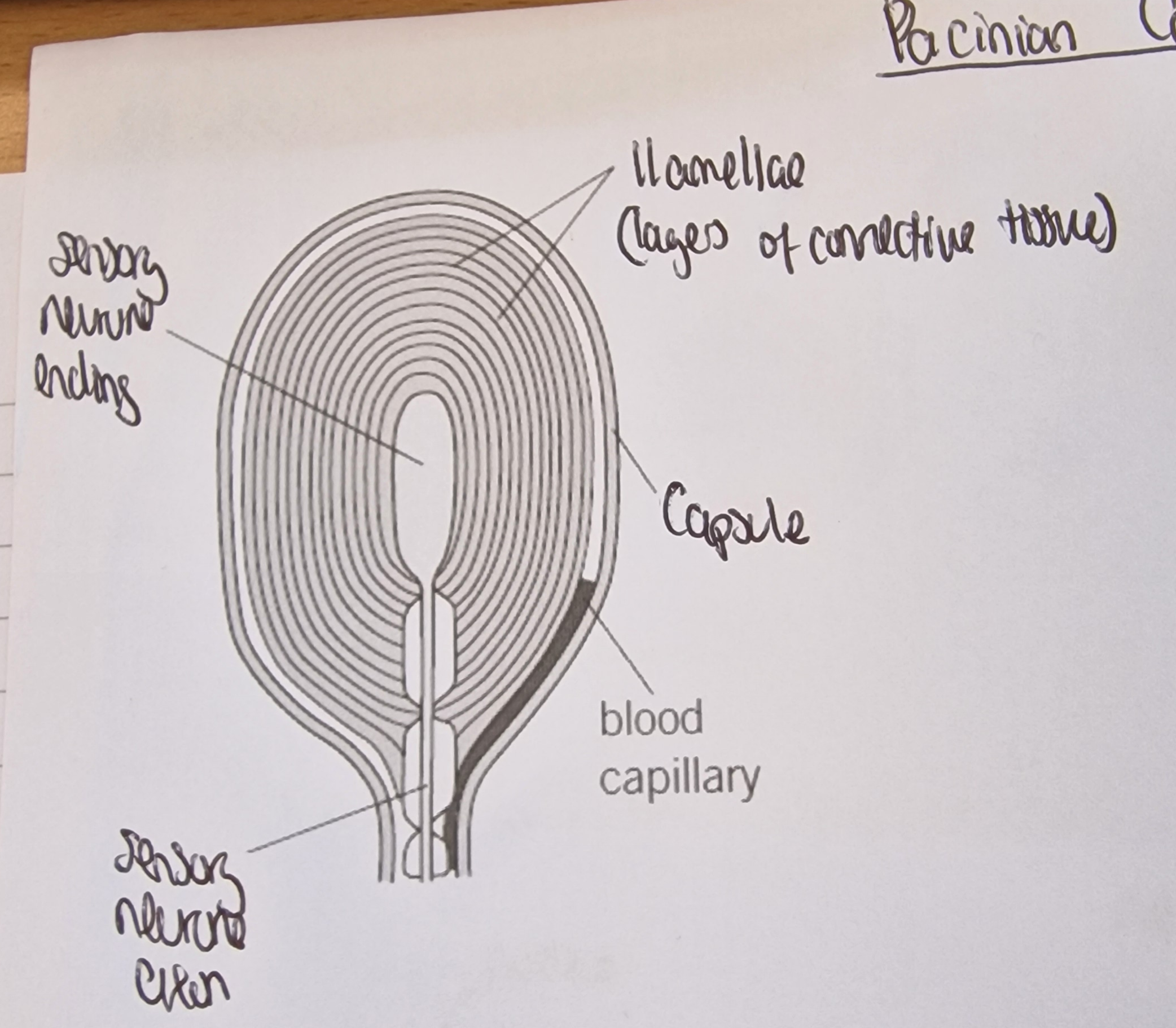
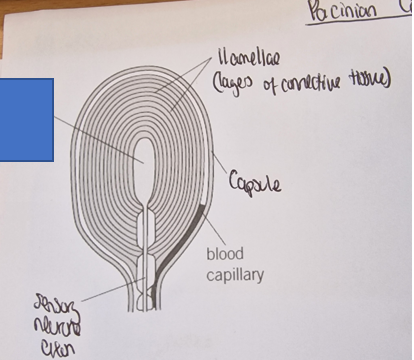
What part of the Pacinian corpuscle is this
Sensory neurone ending
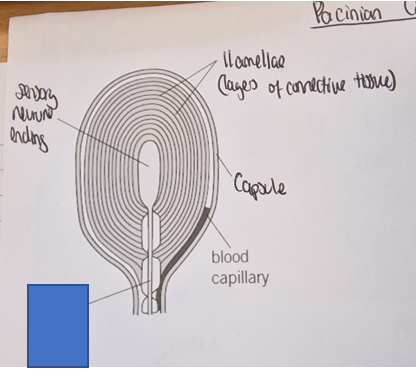
What part of the Pacinian corpuscle is this
Sensory neurone ending
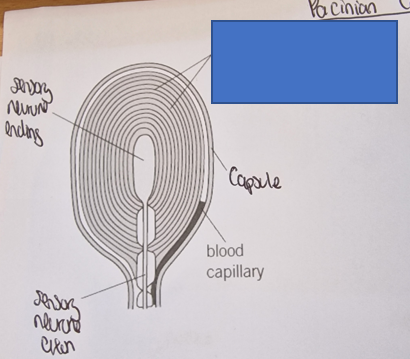
What part of the Pacinian corpuscle is this
lamellae (layers of connective tissue)
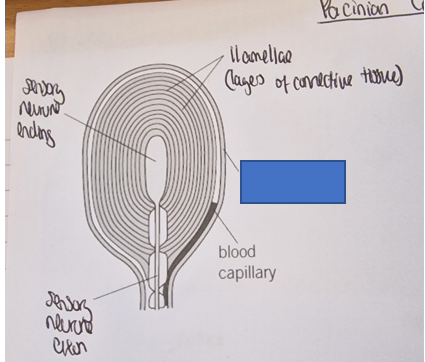
What part of the Pacinian corpuscle is this
capsule
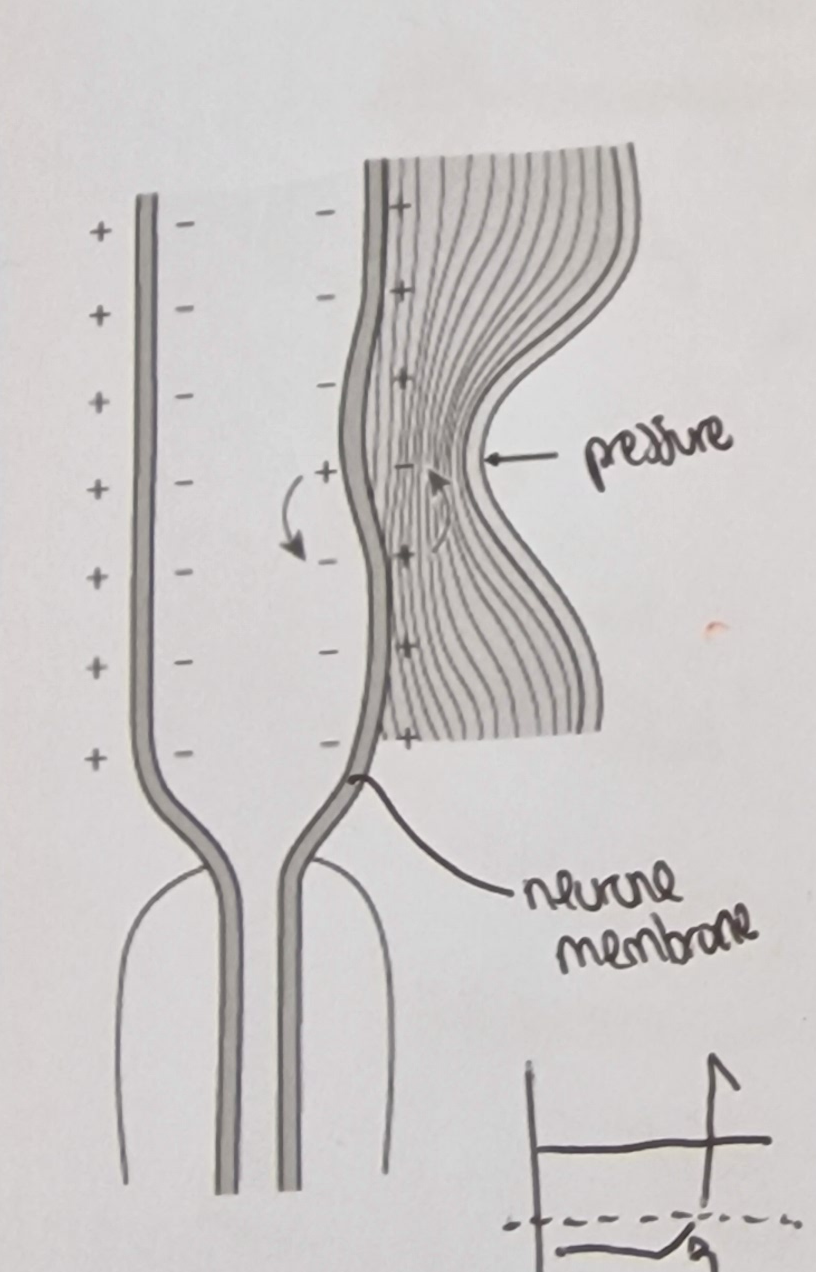
What happens if there’s pressure detected from the Pacinian Corpuscle?
Stretch mediated sodium ion channels in the membrane
Increased pressure:
deforms the lamella and the membrane
deforms the sodium ion channels
Na+ ion channels open
Na+ diffuse in
Depolarisation of the membrane leading to a generator potential
If a generator potential reaches threshold potential, an action potential will be produced
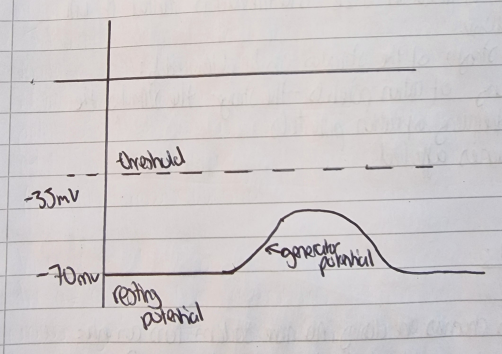
Low pressure exerted
Not enough Na+ channels open, generator potential doesn’t reach threshold so no action potential
deforms lamellae and membrane
some stretch mediated channels open
Na+ diffuse in (depolarisation) generator potential
High pressure exerted
more Na+ channels open, more depolarisation, generator potential reaches threshold —> action potential
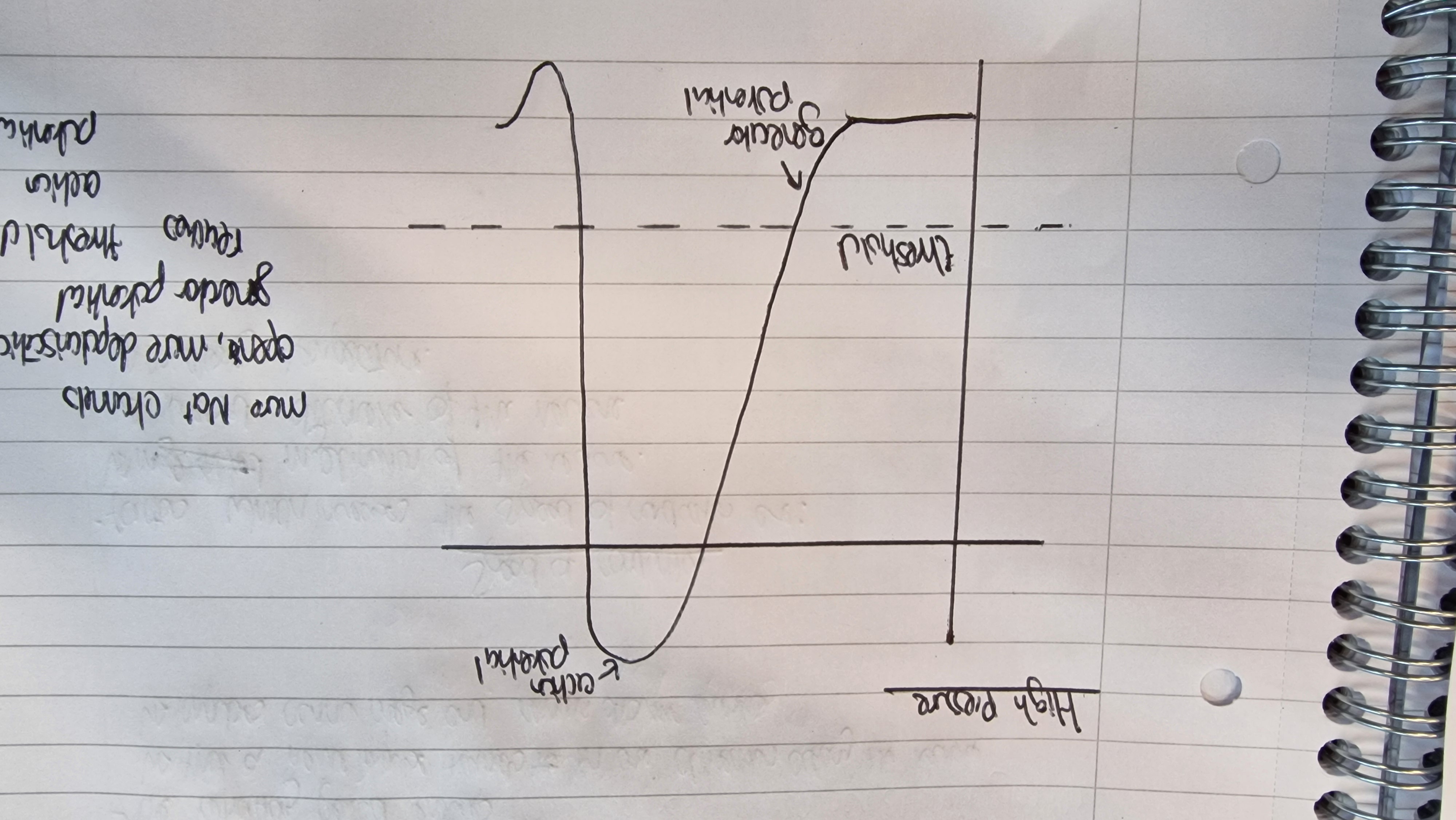
‘All or nothing’ reponse
an action potential is only generated when threshold is reached
If threshold is not reached, there is no action potential
Action potential is fixed in size - once threshold is reached it will always be +40mv
The strength of the stimulus can be determined by:
‘ frequency of action potentials- the stronger the stimulus, the greater the frequency of action potentials.
‘ number of neurones affected
Refractory period
When the sodium channels are closing, no more sodium ions can enter
The neurone cannot be stimulated (at that point of the membrane) and an action potential cannot be generated
The refractory period ensures that:
‘ a nerve impulse travels in one direction along the neurone,
‘ impulses cannot merge and become discrete events
Transmission of Action Potential
Factors that affect speed of conduction
myelination of neurone
increased diameter of neurone
increasing temperature
What occurs in a relaxed muscle
tropomyosin blocks the myosin binding sites on the actin filament
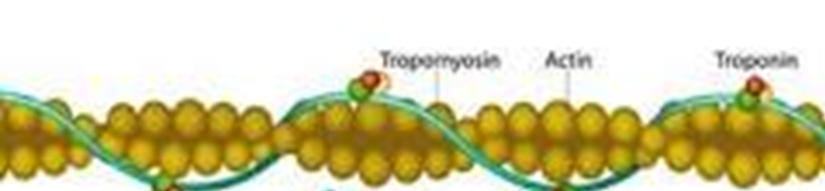
(don’t need to know about troponin)
Process of muscle contraction