Unit 1: Never trust an atom
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
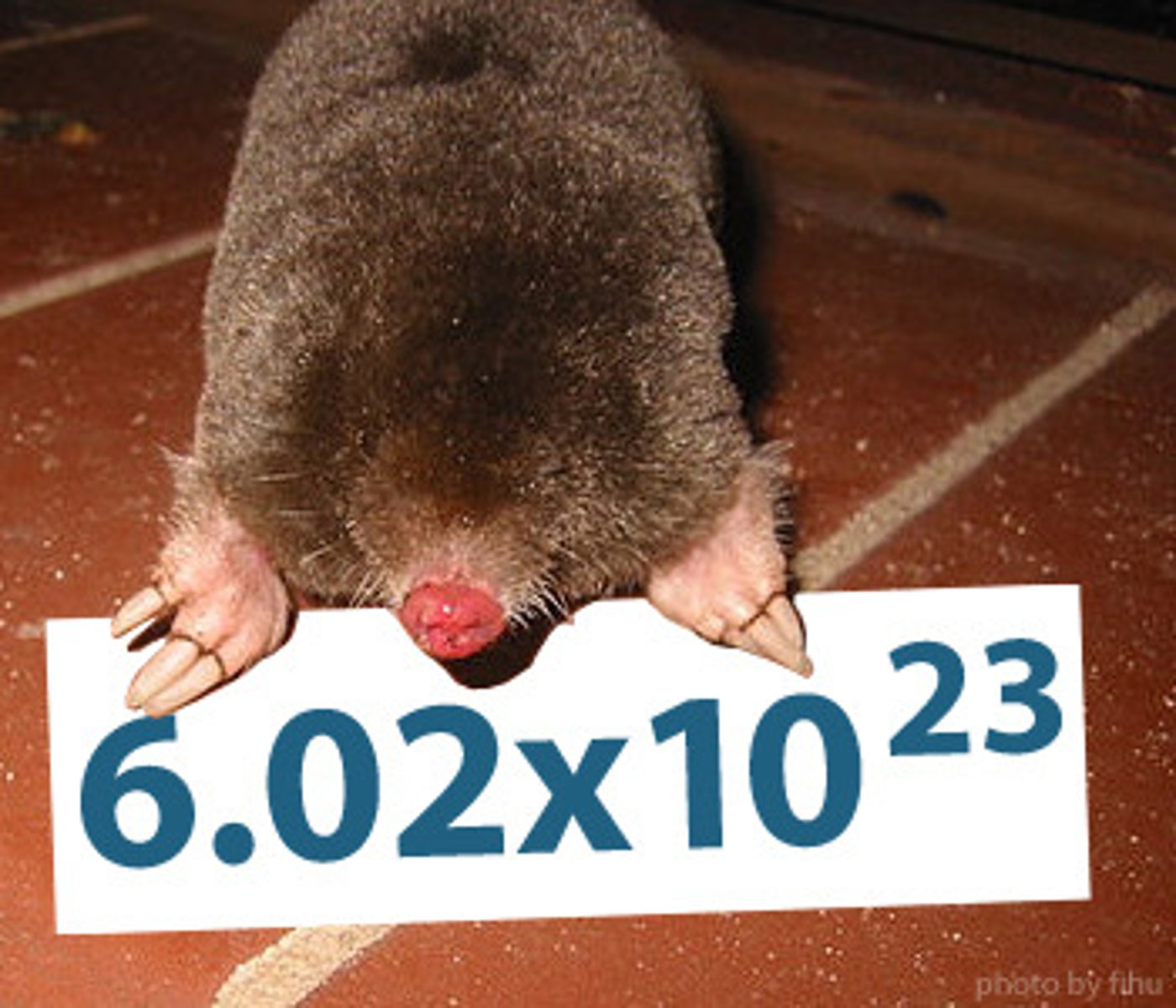
Avogadro's number
number of representative particles in a mole, 6.02 X 10^23
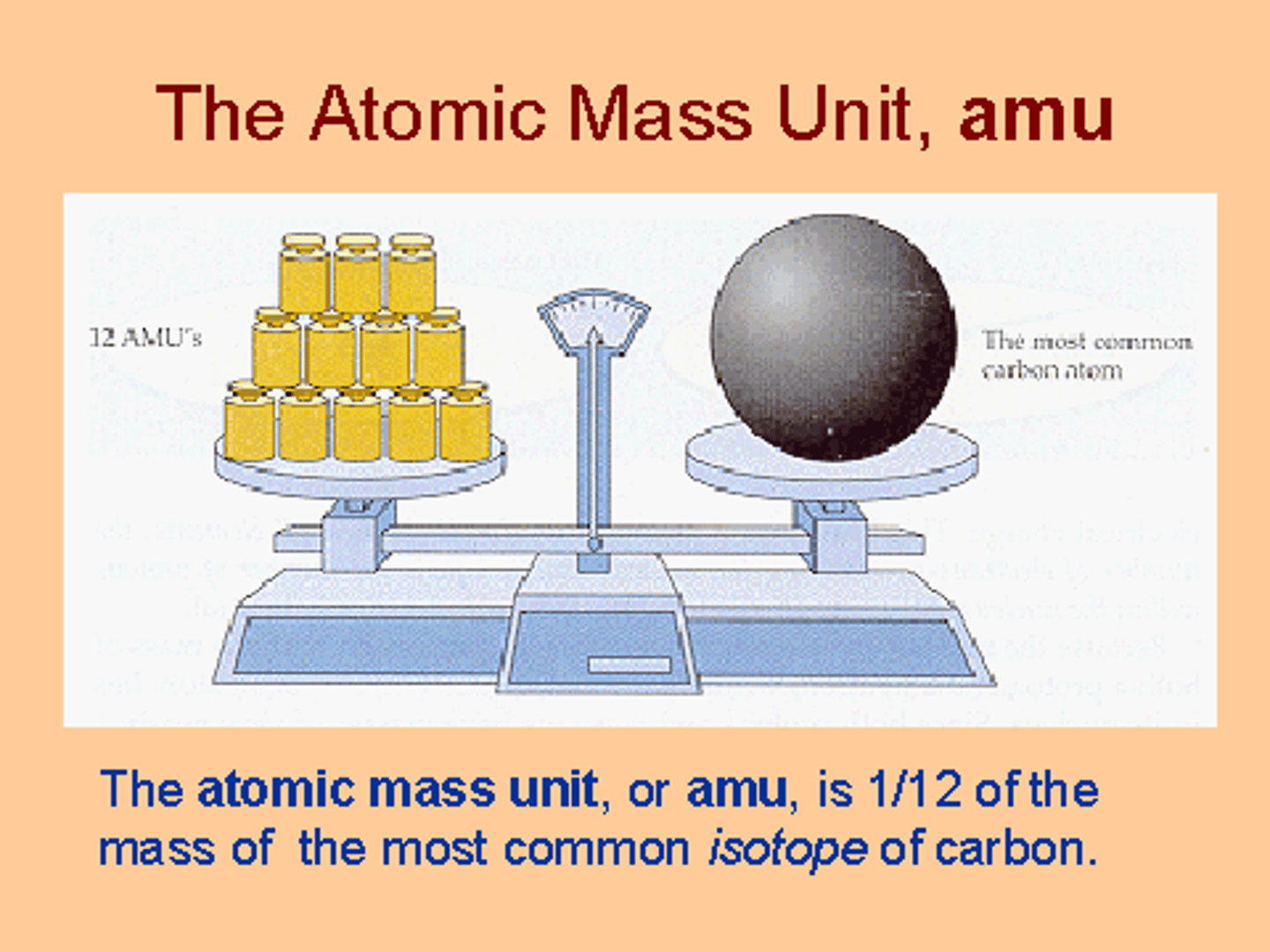
Atomic mass units (amu)
unit used to express the relative masses of atoms and subatomic particles
Mole
the SI base unit used to measure the amount of a substance

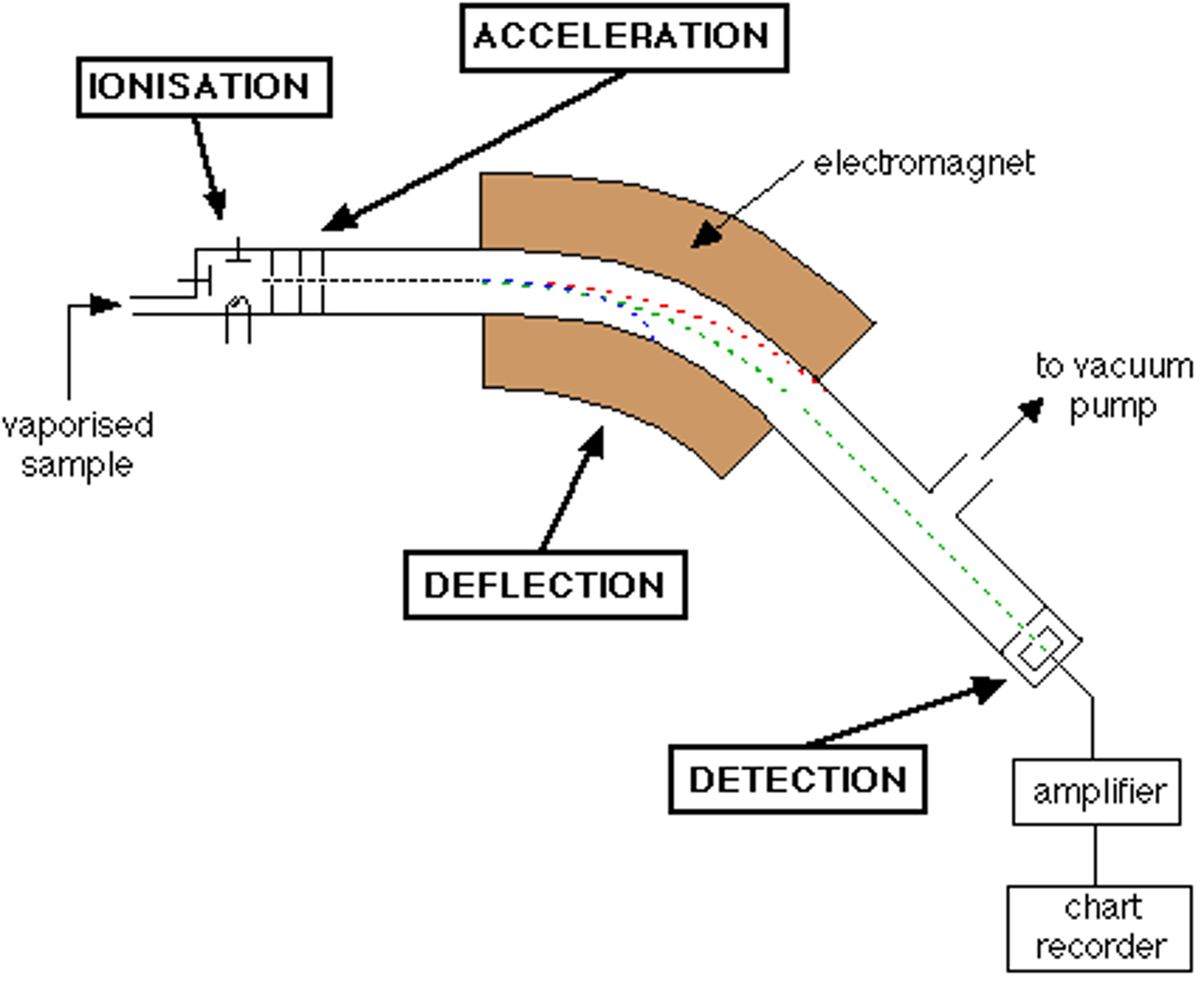
Mass Spectroscopy
Type of spectroscopy used to determine the molecular weight of a compound
Mass spectrum
A graph with % abundance plotted against mass/charge, gained as a result from the mass spectrometer
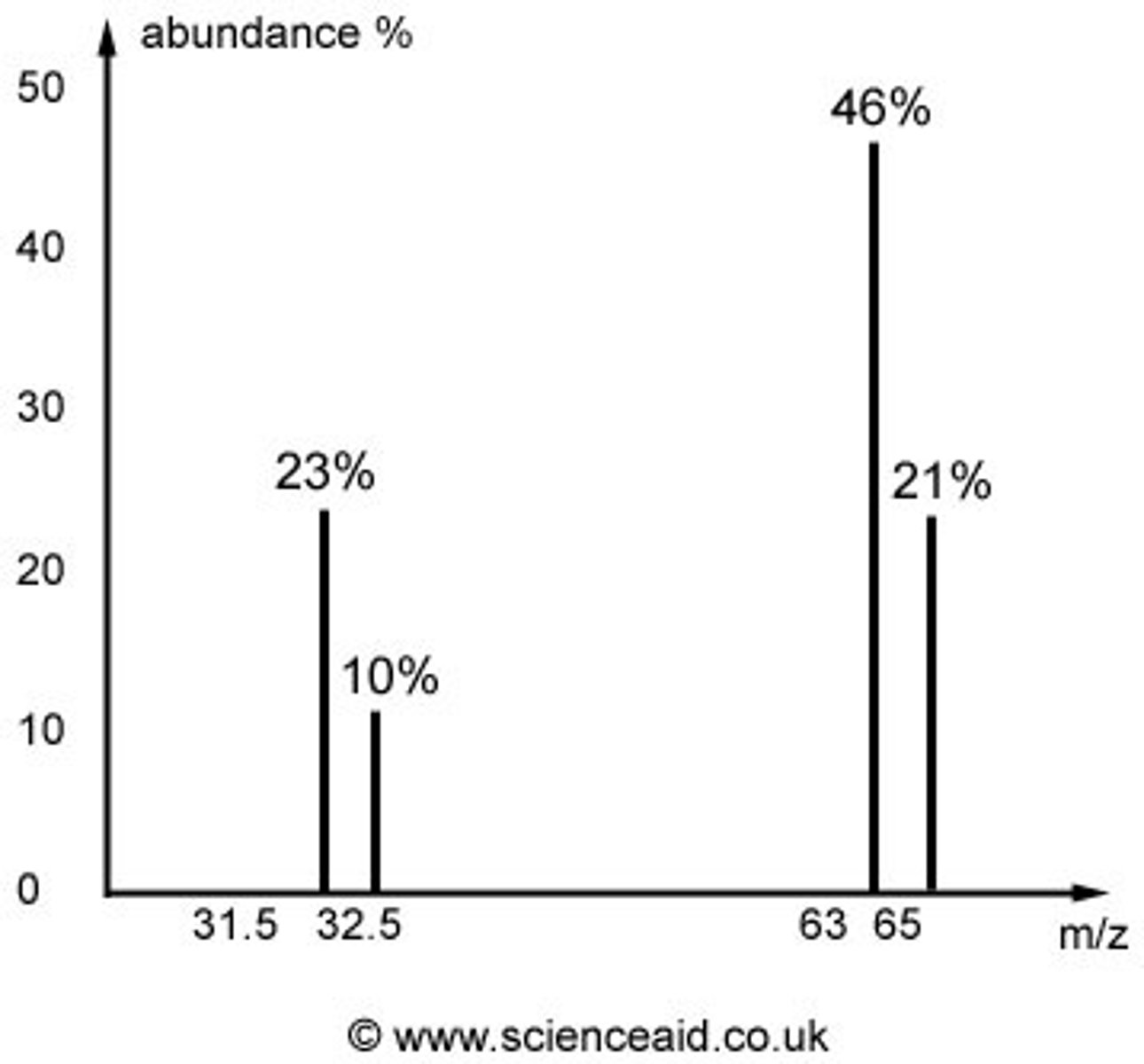
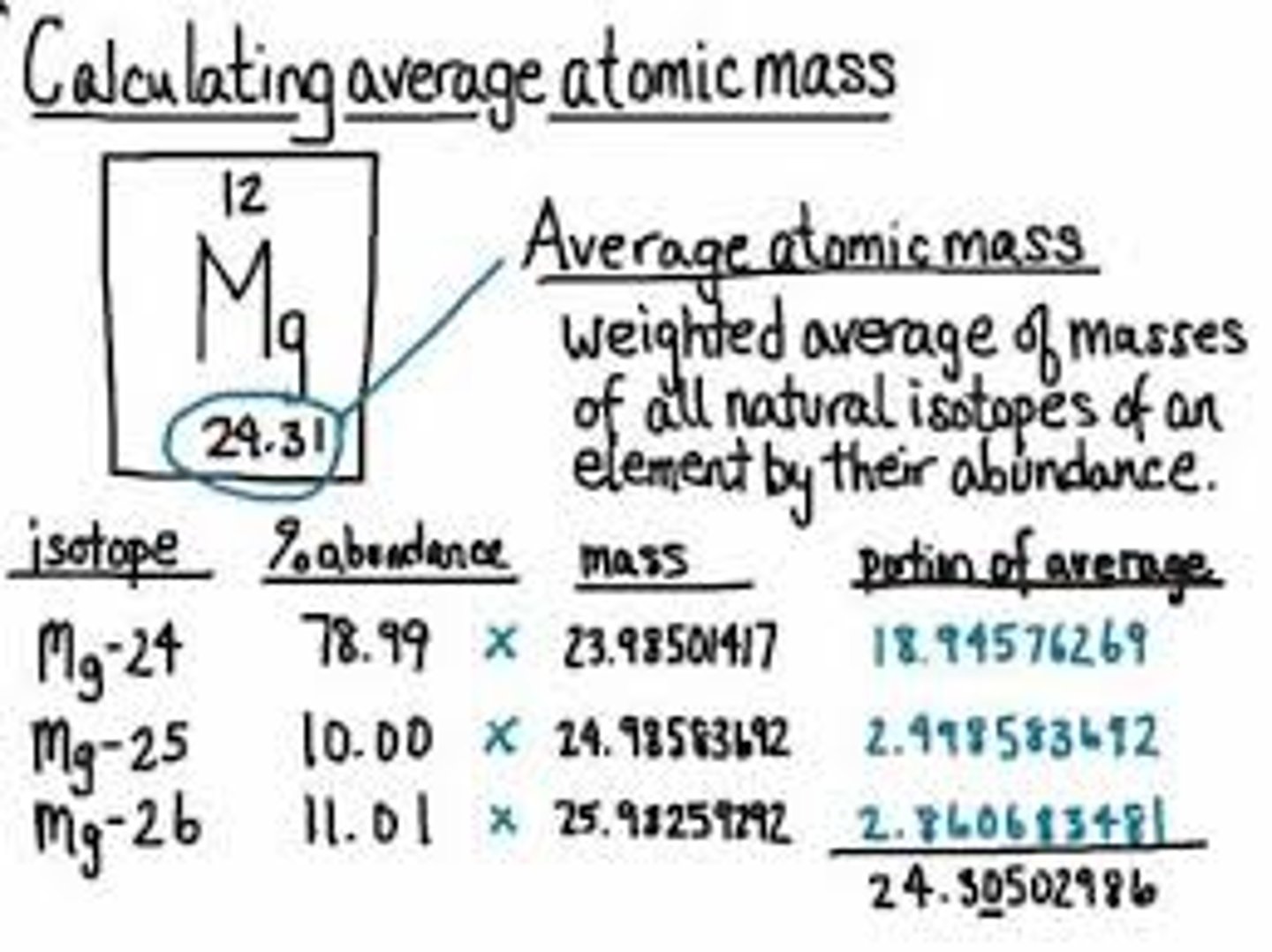
Average atomic mass
the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element

percent abundance
The percentage of atoms of a particular isotope in a natural sample of a pure element
pure substance
A sample of matter, either an element or a compound, that has a uniform composition
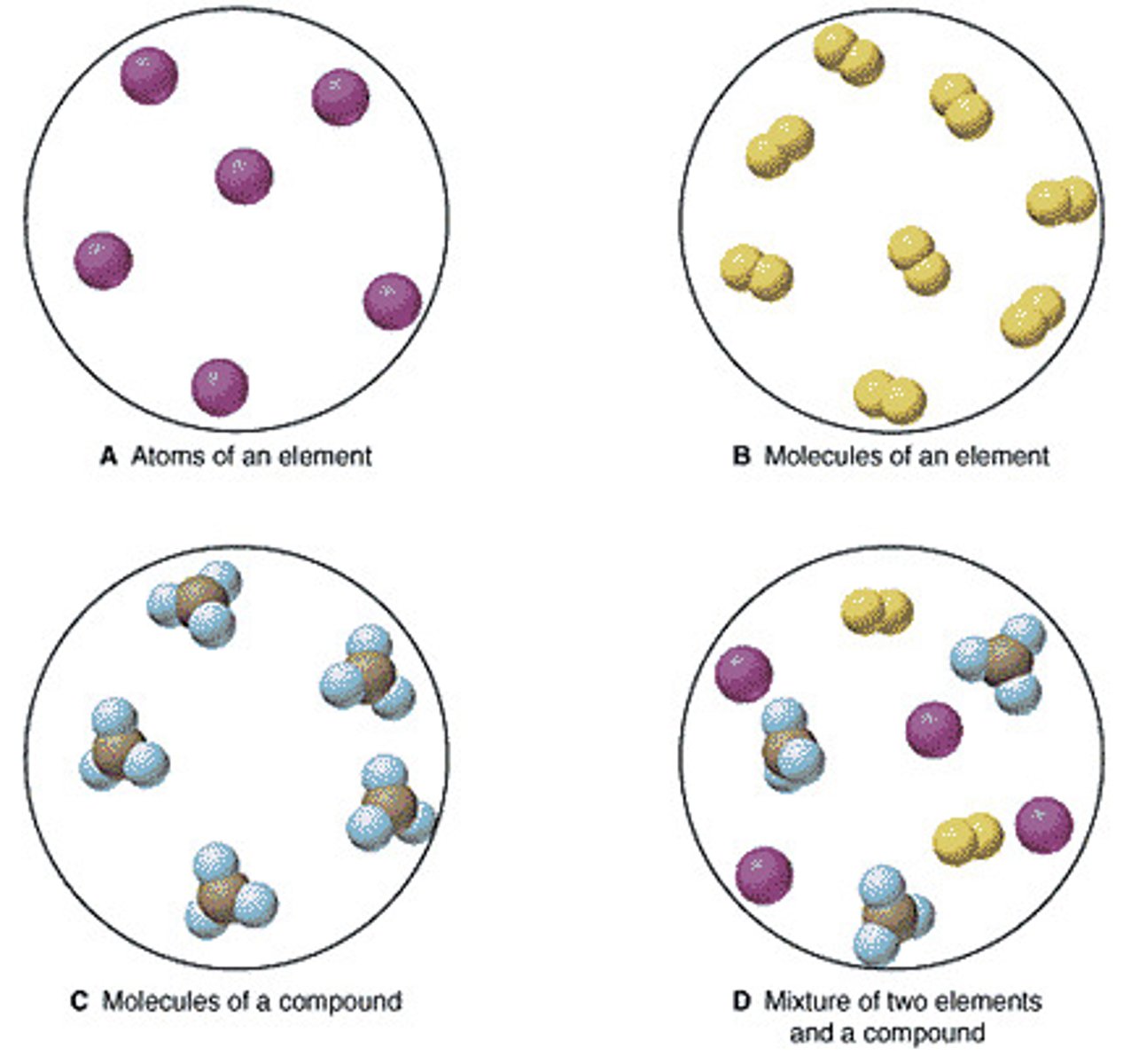
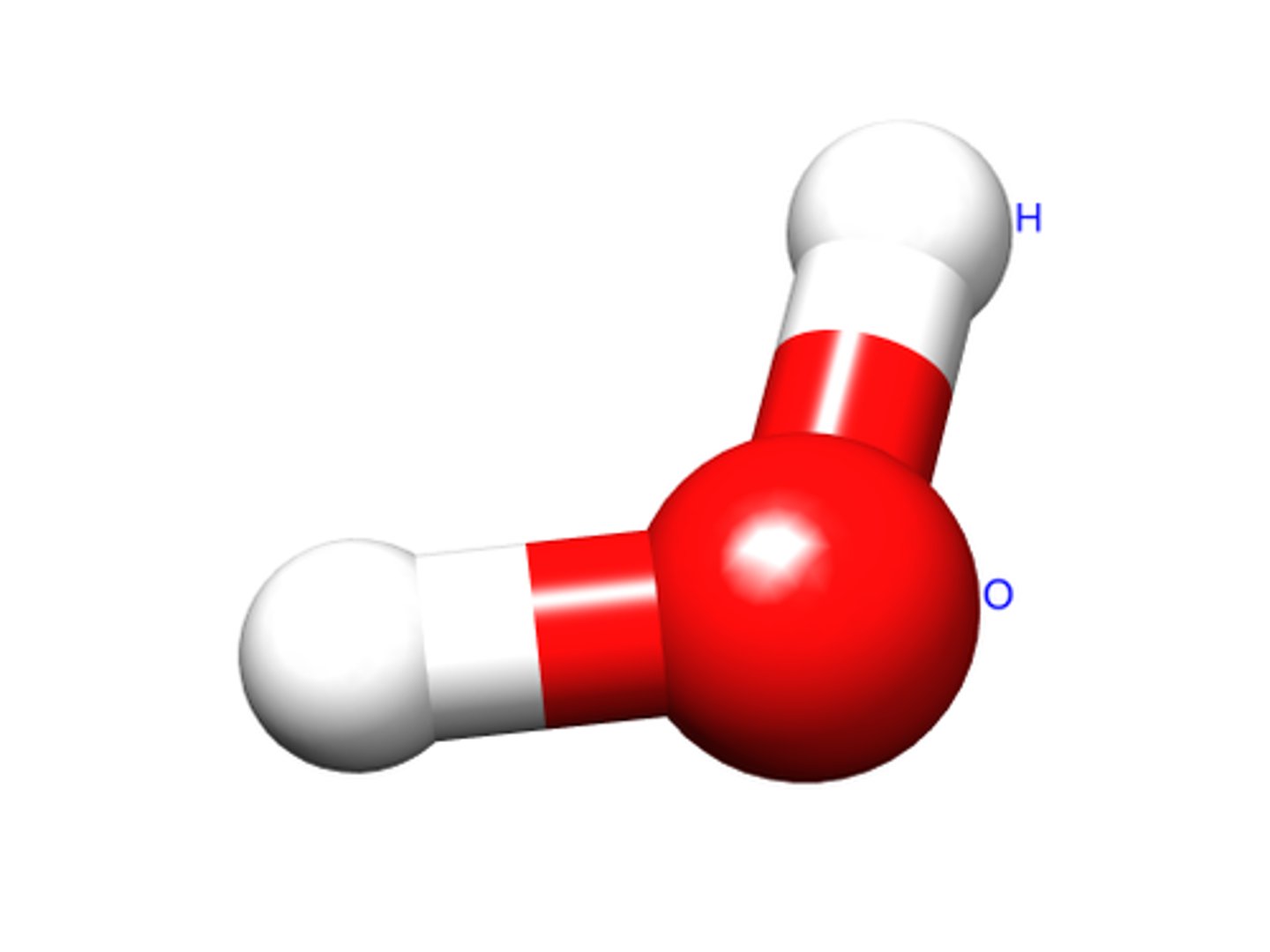
molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
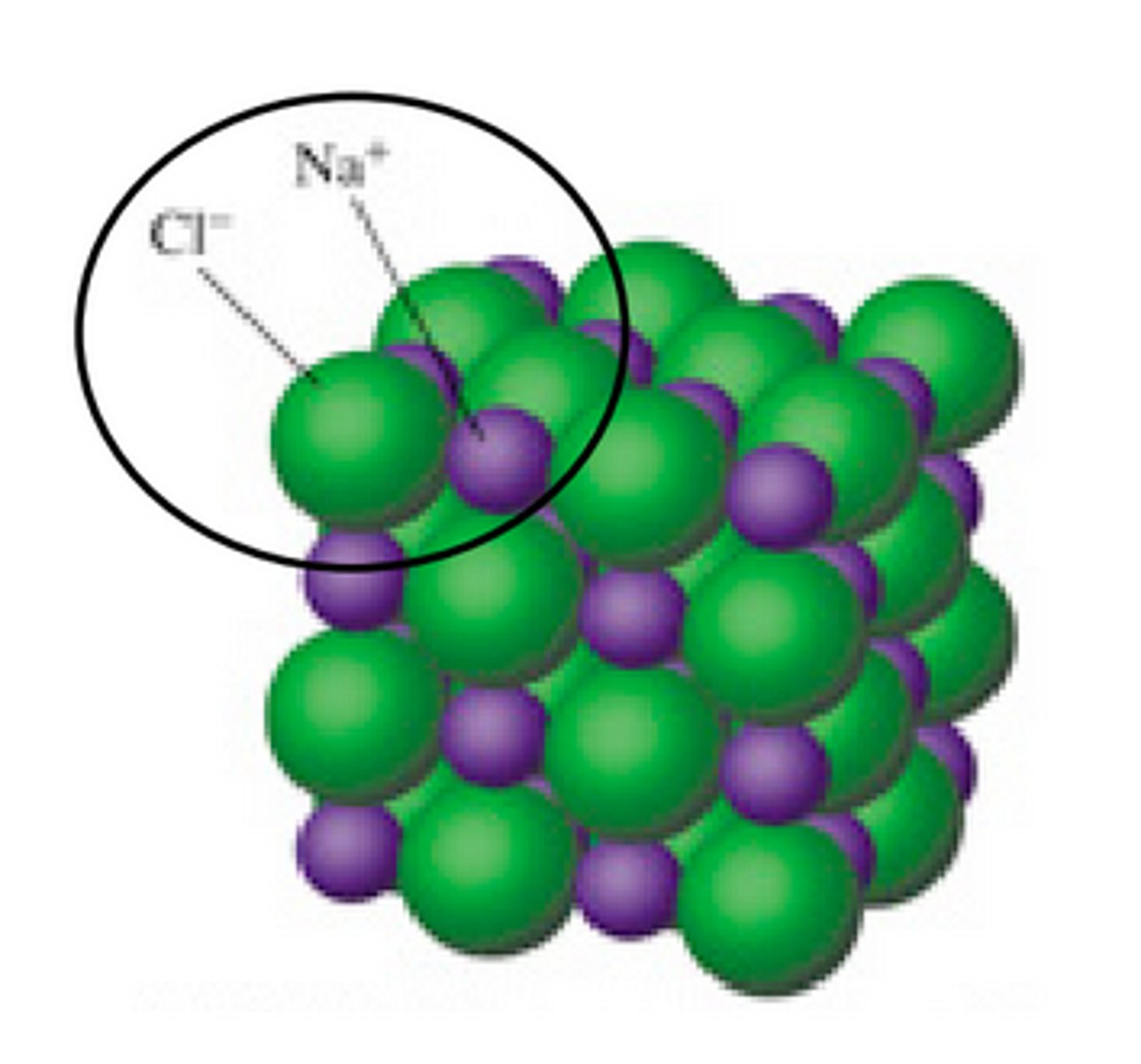
formula unit
The simplest ratio of ions represented in an ionic compound
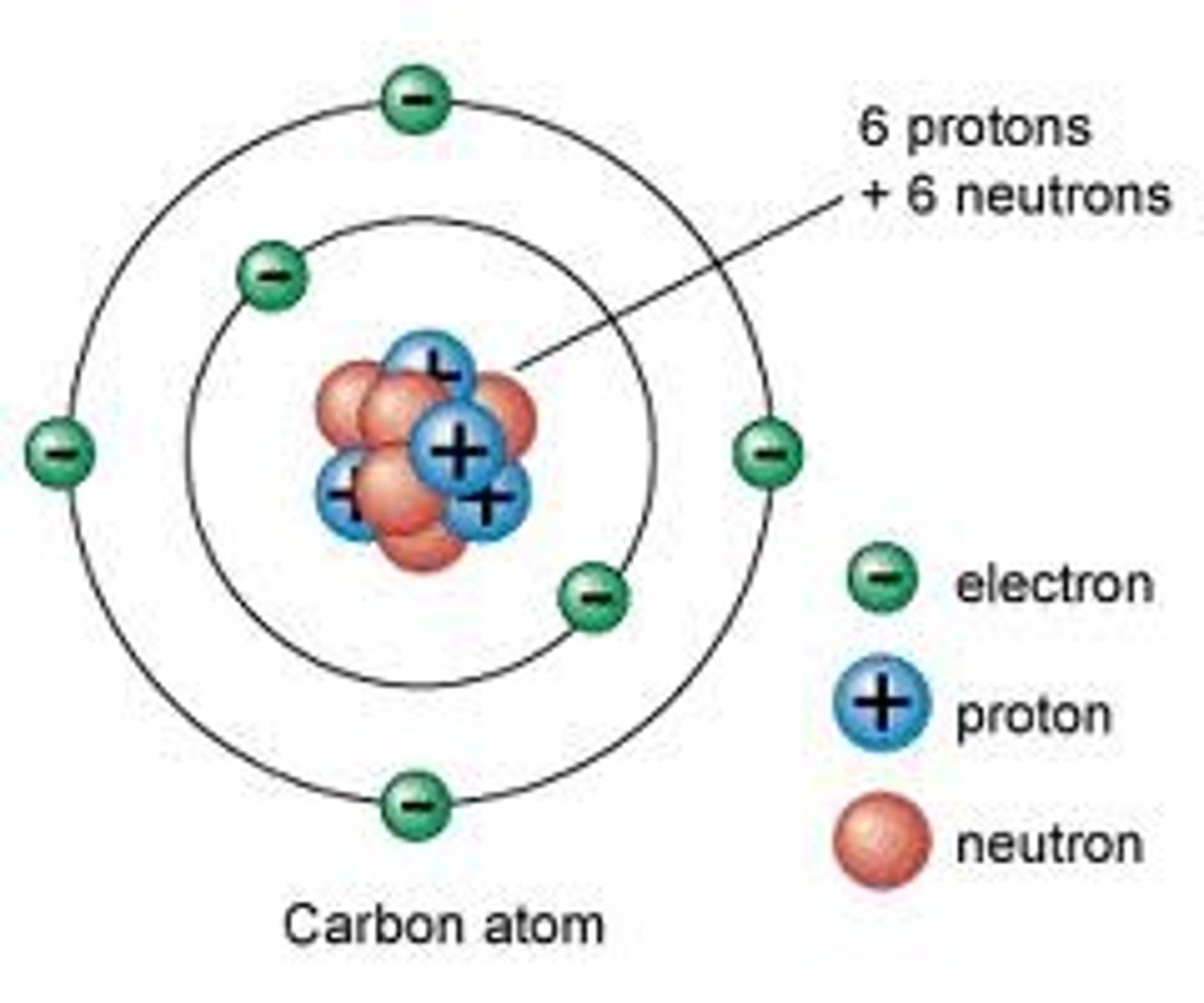
atom
Smallest particle of an element
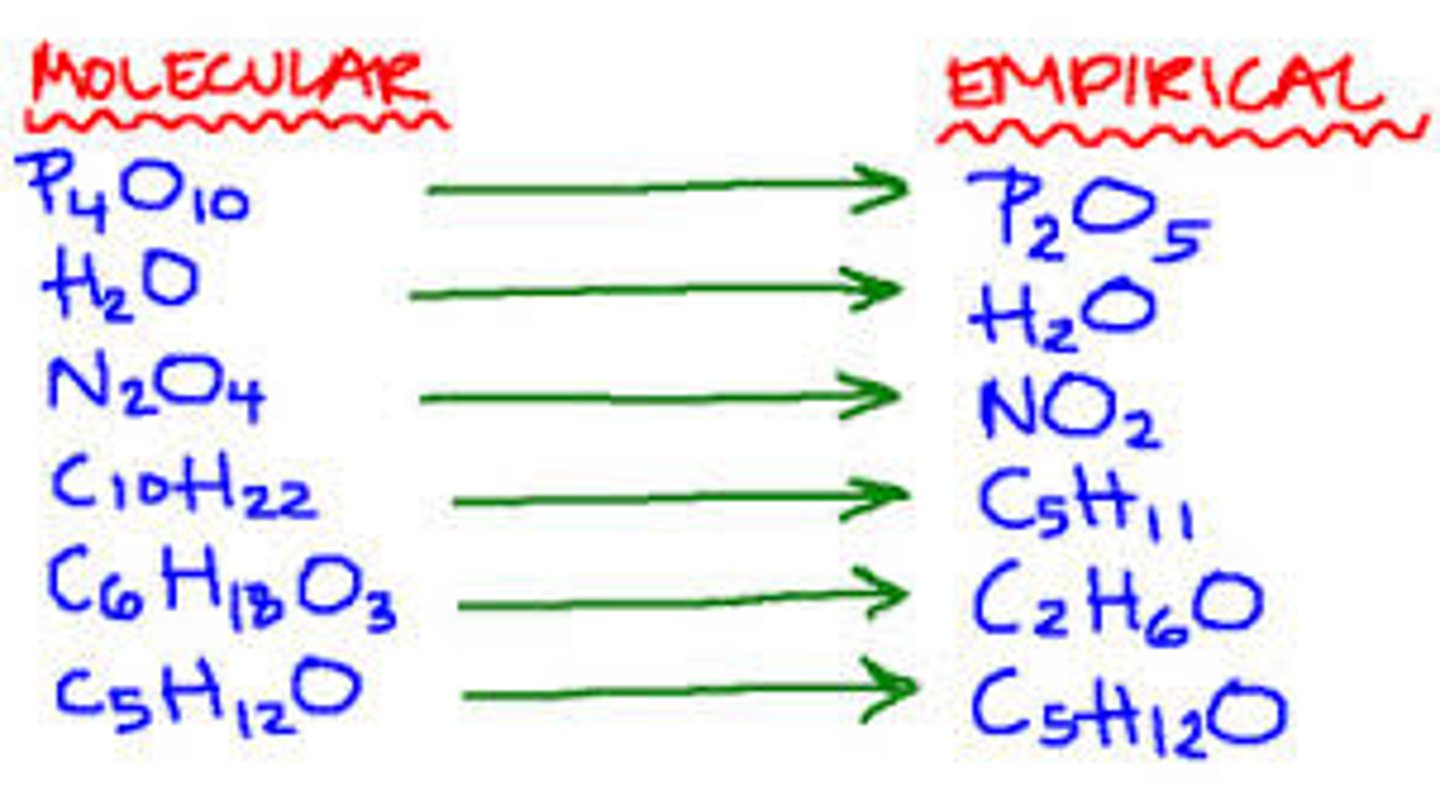
empirical formula
a formula with the lowest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound
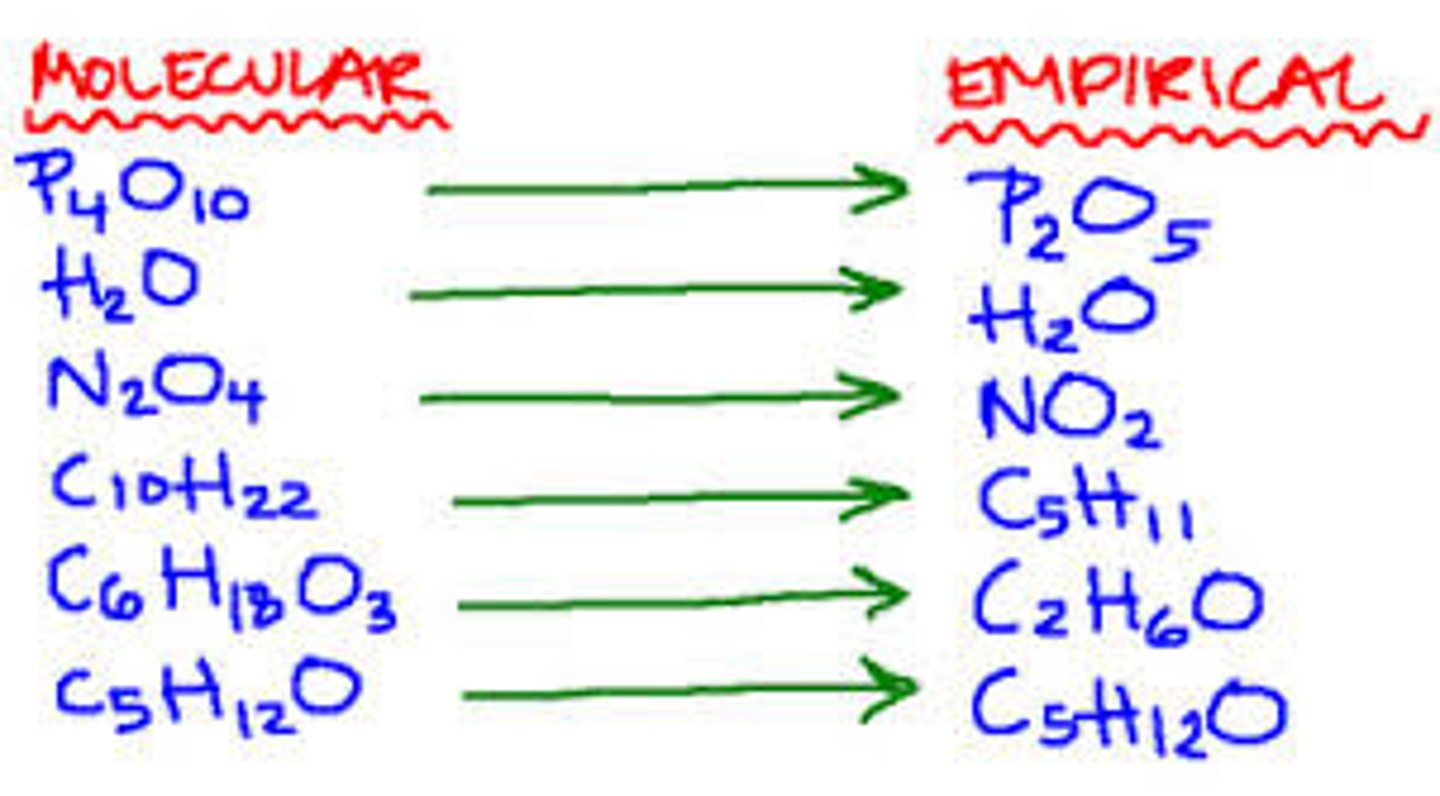
molecular formula
A chemical formula that shows the number and kinds of atoms in a molecule, but not the arrangement of the atoms.
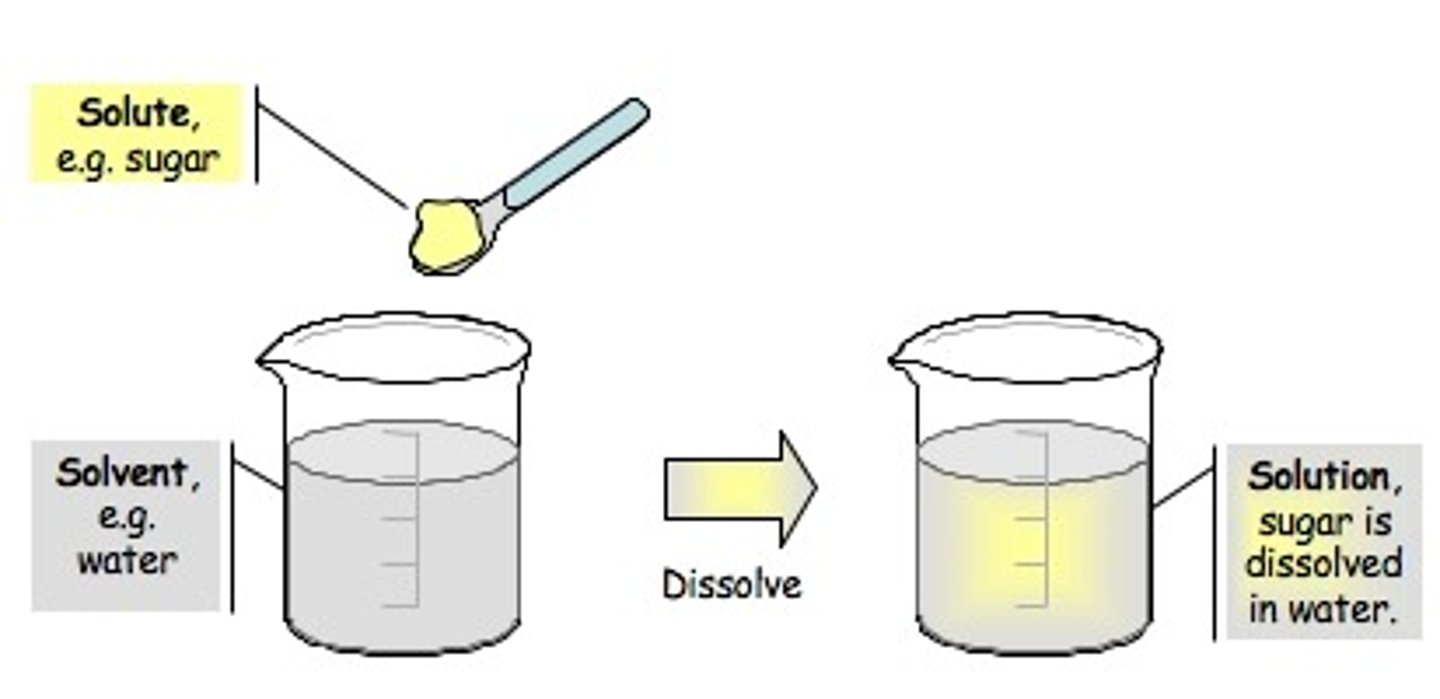
homogeneous mixture (solution)
a mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout
heterogeneous mixture
A mixture that is not uniform in composition; components are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture

electron configuration
the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom
electron orbitals
volumes of space surrounding the atomic nucleus where electrons are likely to be found
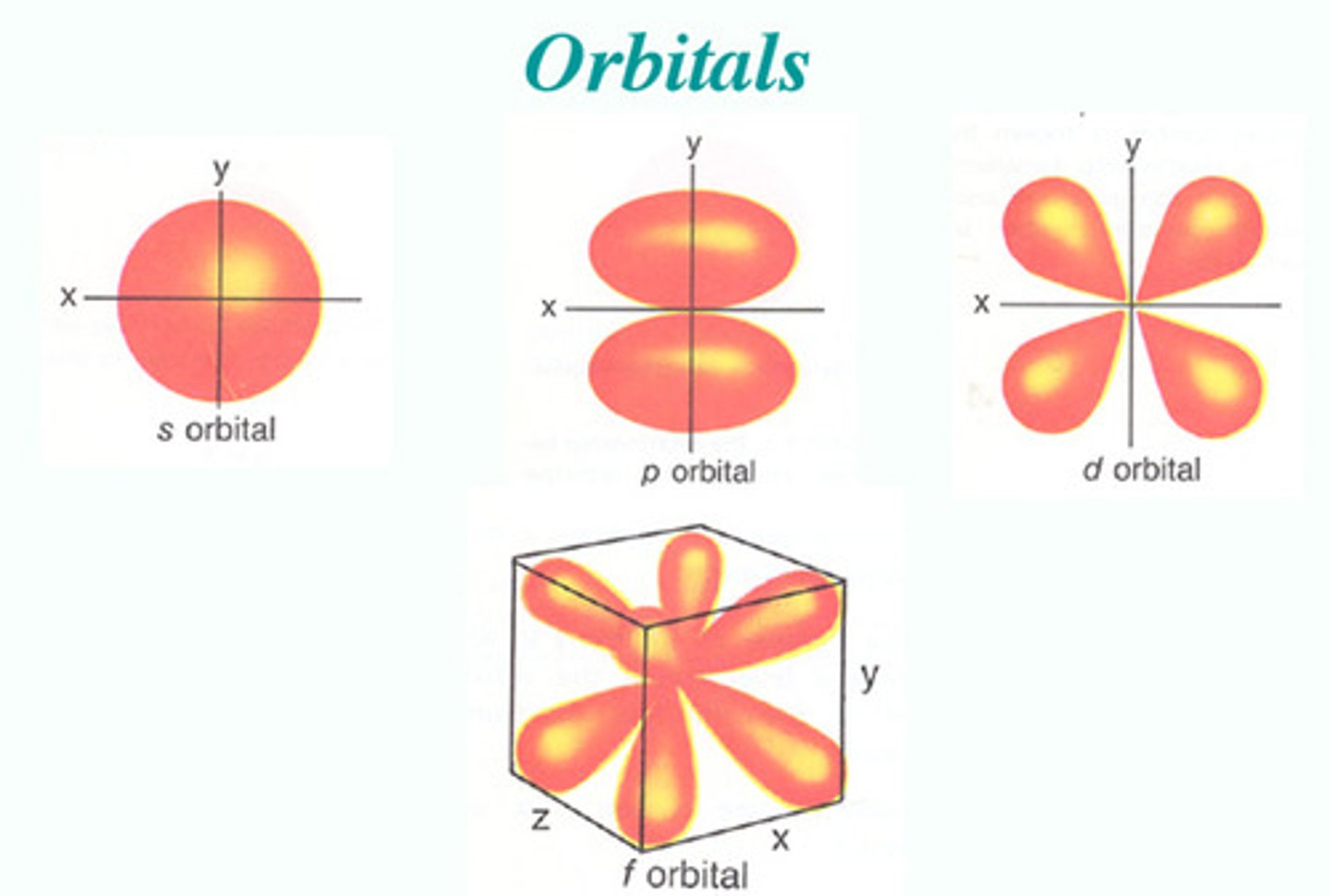
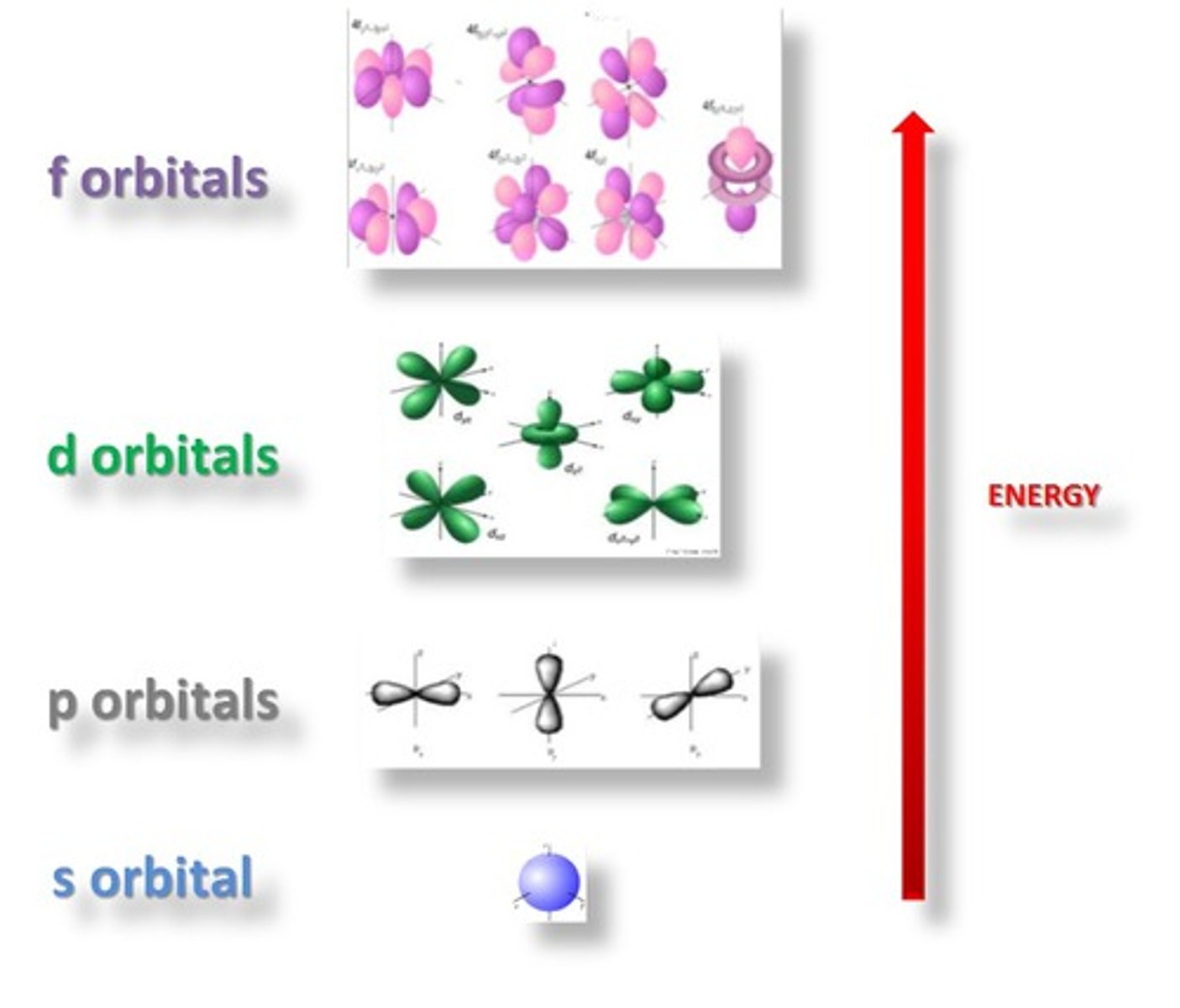
Sublevels (s, p, d, f)
A portion of a principle energy level made up of one or more orbitals
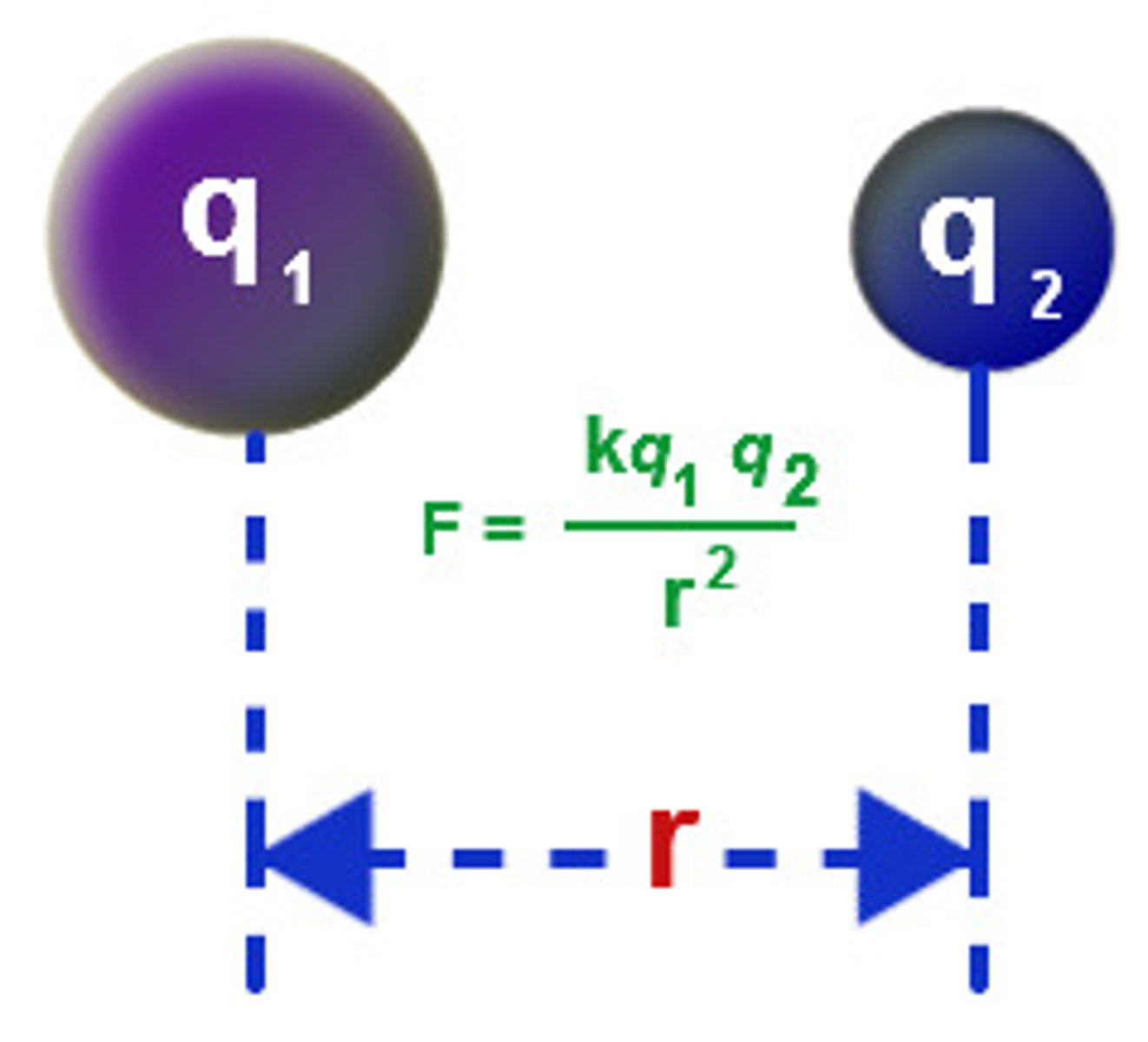
Coulomb's Law
electric force between charged objects depends on the distance between the objects and the magnitude of the charges.
Aufbau Principle
the rule that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first
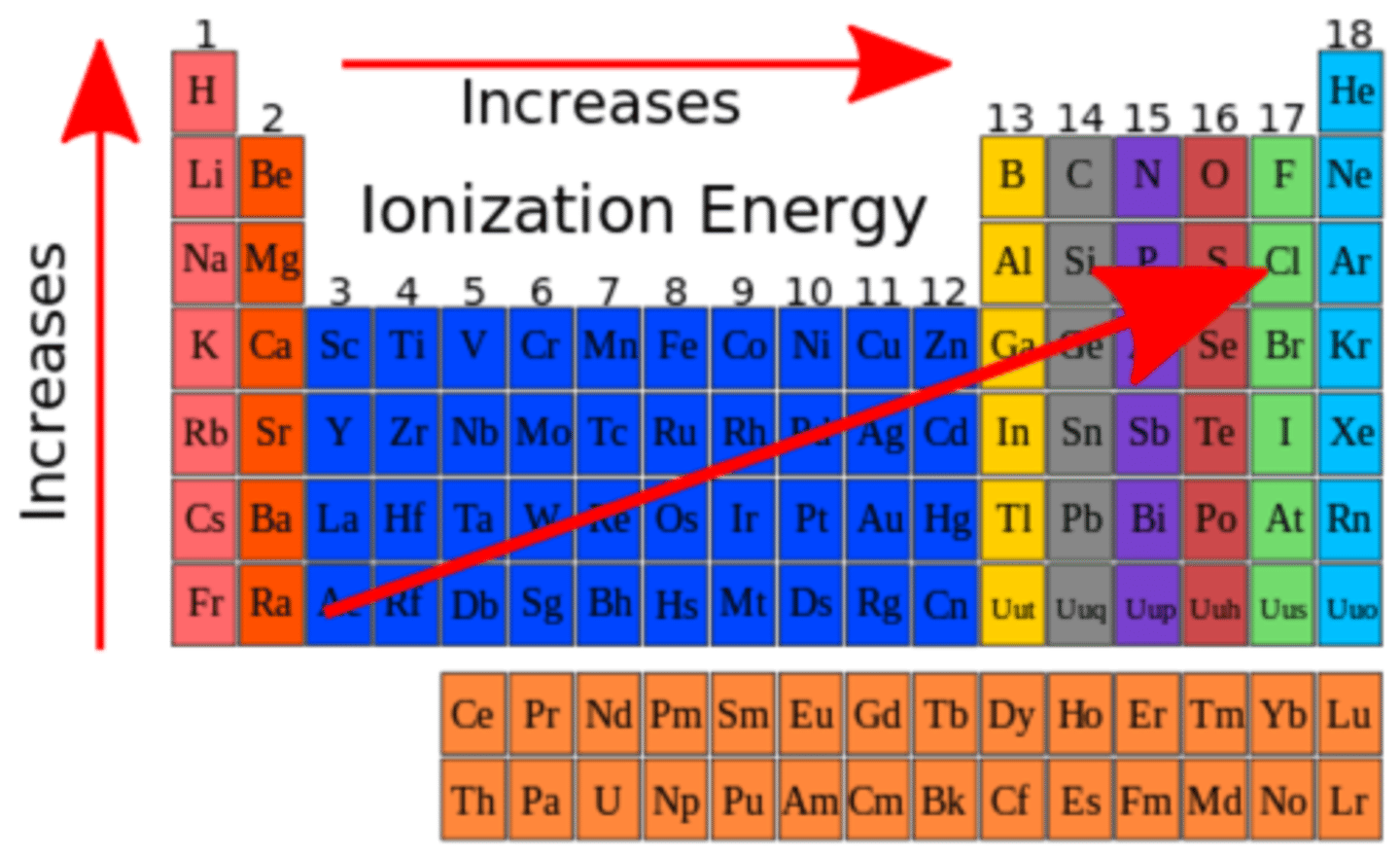
ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
valence electrons
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
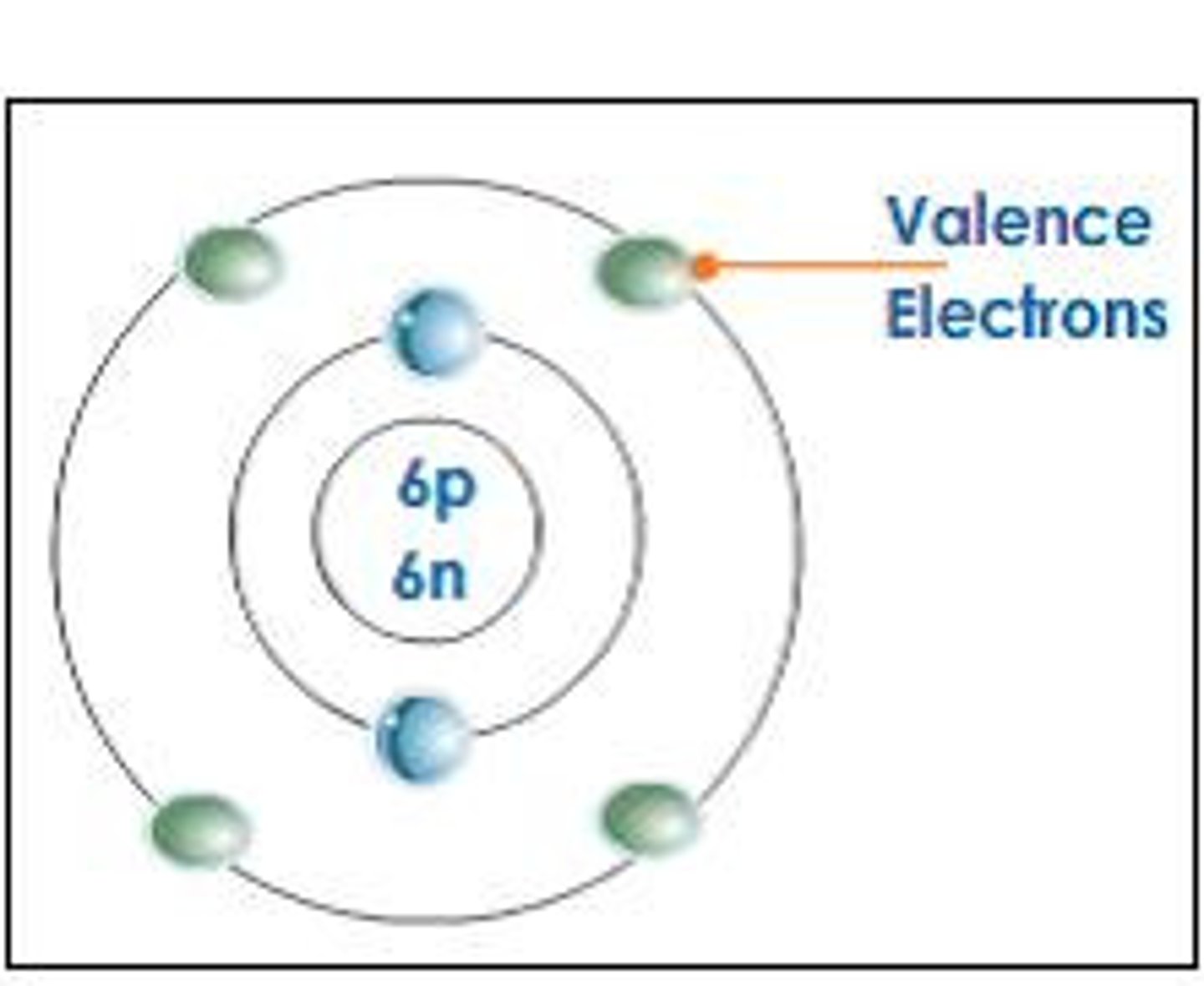
inner shell electrons
electrons not in the highest occupied energy level
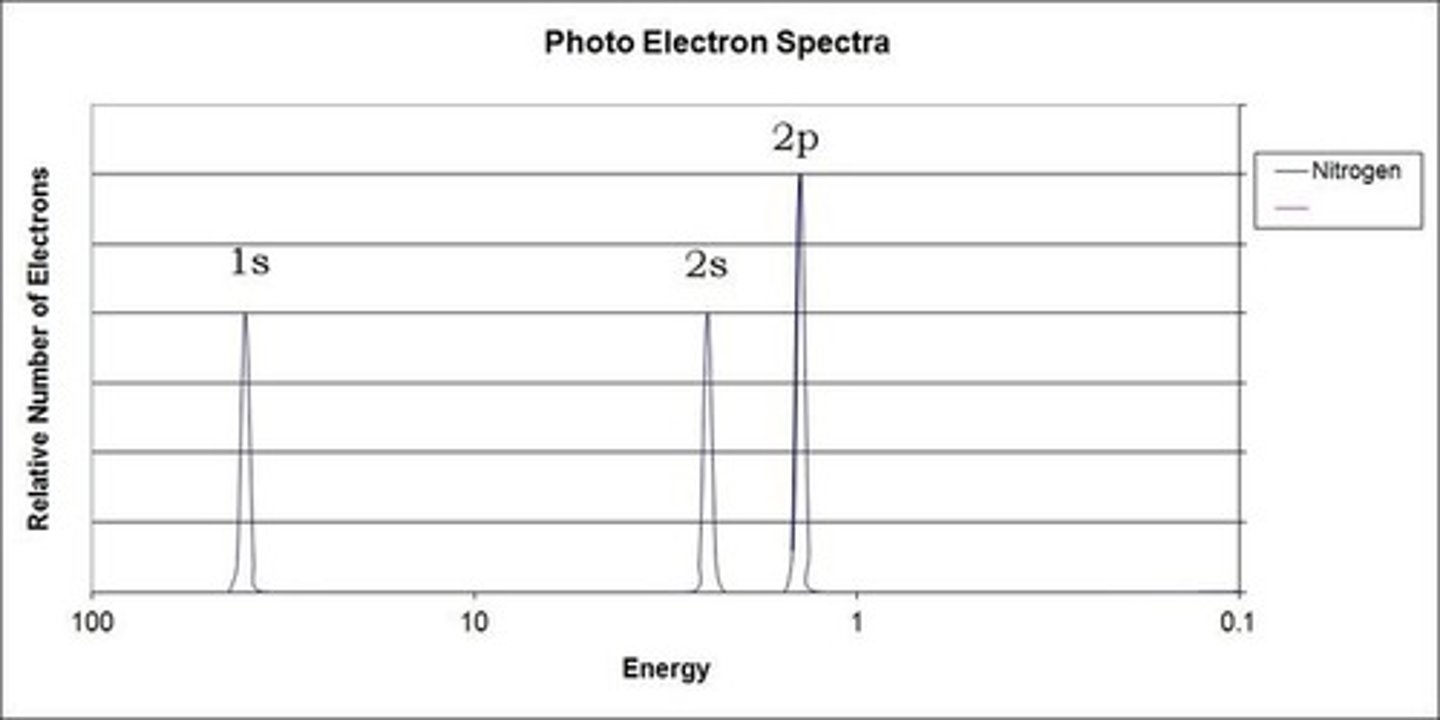
Photoelectron Spectroscopy (PES)
determines the energy needed to eject electrons from the material to determine the shell structure of an atom
atomic radius trend
increases down a group (with addition of orbitals), decreases across a period (due to effective nuclear charge)

Ionic Radius Trend
increases down a group, decreases across a period
Ionic radius
relative size of an ion
atomic radius
relative size of a neutral atom
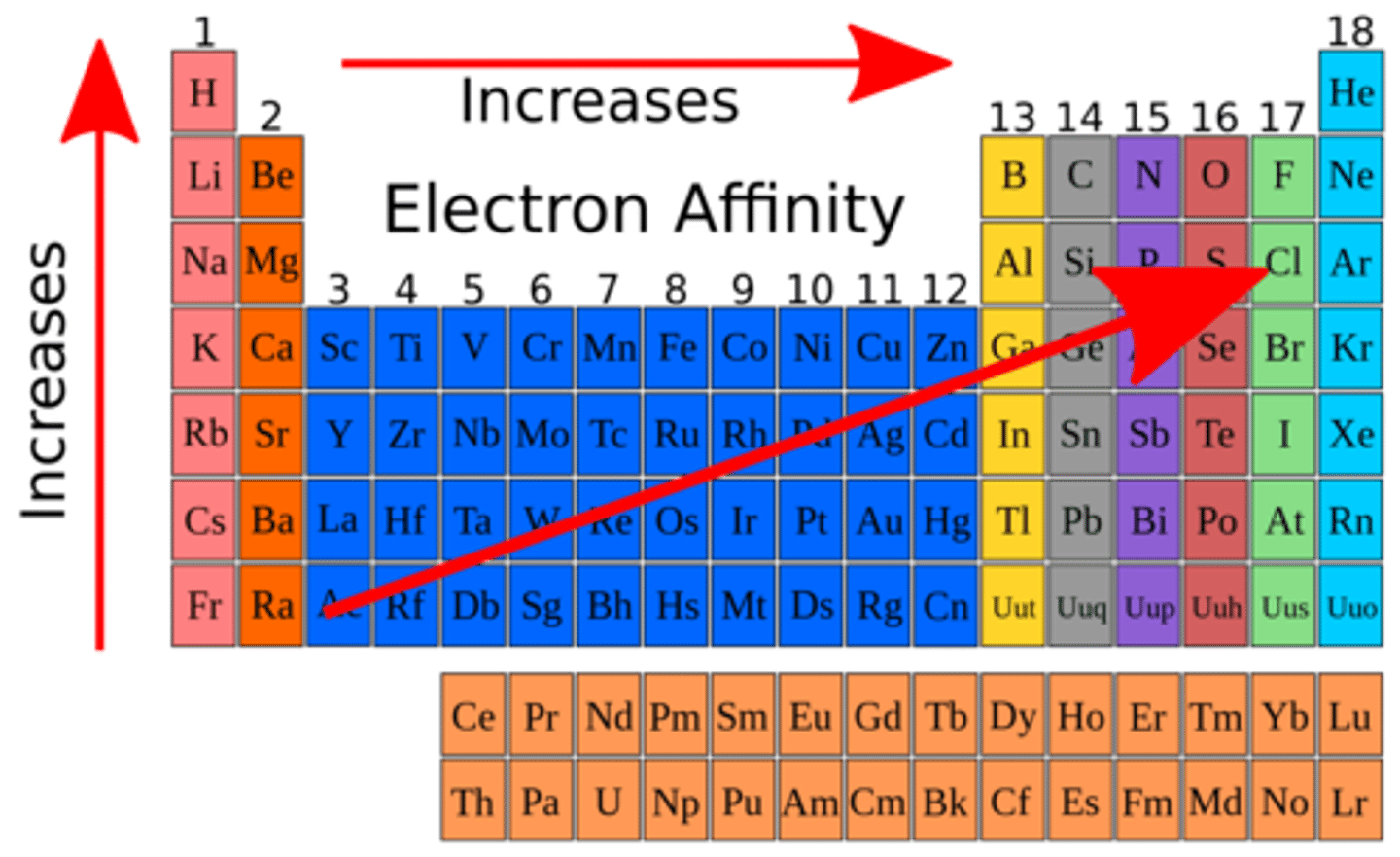
electron affinity
energy change when an atom gains an electron and becomes a negatively charged ion (anion)
electron affinity trend
increases across a period, decreases down a group
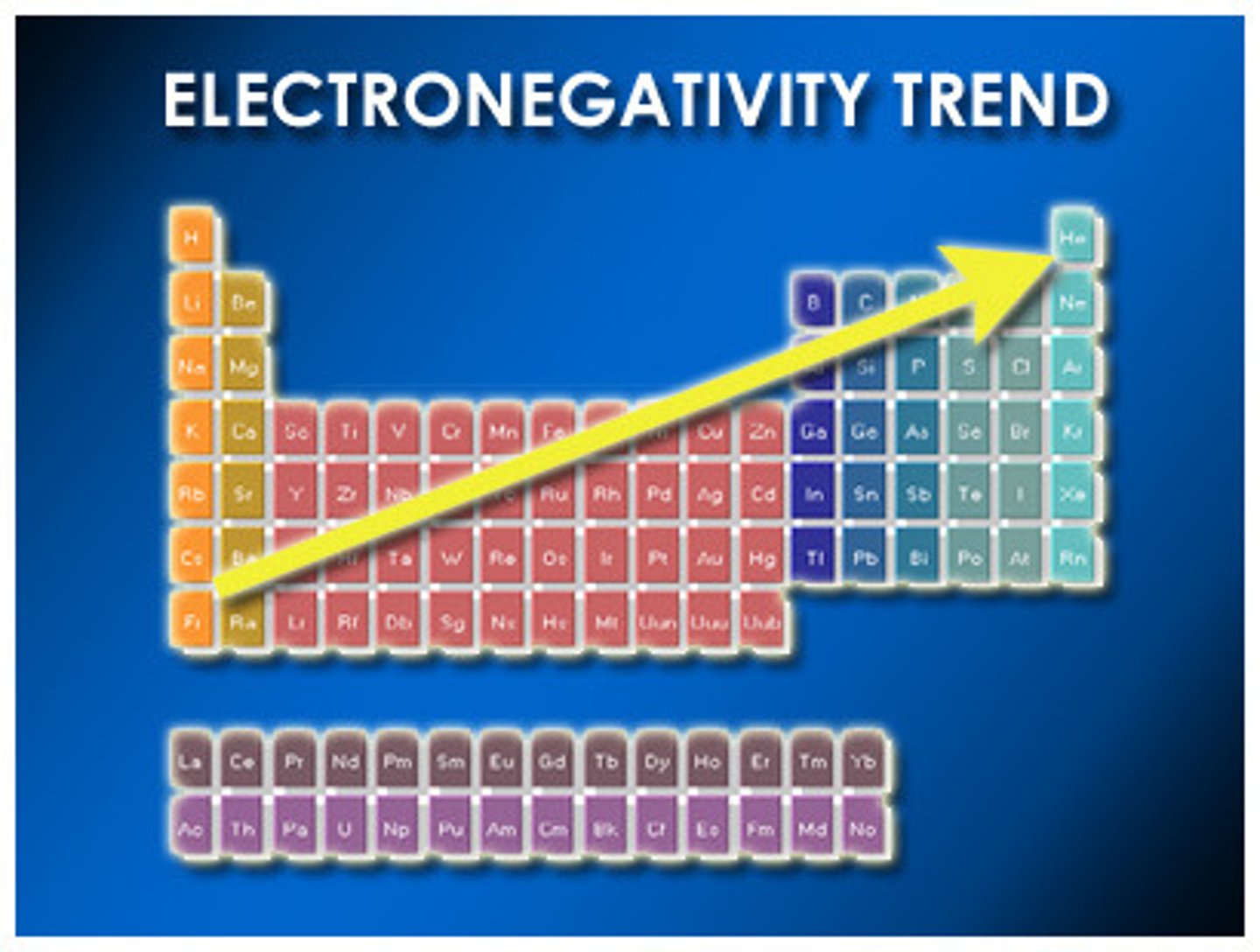
Electronegativity
ability of an atom, when covalently bonded, to attract shared electrons to itself
electronegativity trend
increases across a period, decreases down a group
ionization energy trend
The larger the atomic radius, the further the electrons are from the nucleus/the lower the nuclear effective charge. Therefore, the lower the ionization energy.
The smaller the atomic radius, the closer the electrons are to the nucleus, and the harder they are to remove. Therefore, the higher the ionization energy.