dental anatomy teeth development part 1
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
___________ is the process of tooth development, developmental disturbances can occur within each stage affecting the physiological processes taking place.
Odontogenesis
___________ of the primary dentition begins between the sixth and seventh week of prenatal development, during the embryonic period.
Odontogenesis
what are the 7 stages of odontogenesis?
initiation, bud stage, cap stage, bell stage, apposition stage, maturation stage, and root development
Most of the ________ dentition is formed during the fetal period.
permanent dentition
__________ is controlled levels of cellular growth present during most of prenatal development.
proliferation
Growth may be by _____________, in which a tissue enlarges its size layer by layer on the outside of a structure.
appositional growth
Growth may be by _____________, which occurs from deep within a TISSUE or organ.
interstitial growth
In the process of ____________, a change occurs in the embryonic cells, which are identical genetically but they become distinct structurally and functionally. (when a cell gets separated into different roles)
differentiation
what are the 3 types of differentiation?
cytodifferntiation, histodifferentiation, and morphodifferentiation
_______________ is the development of different cell types.
Cytodifferentiation
_____________ is the development of different histologic TISSUE types within a structure.
Histodifferentiation
_______________ is the development of the differing ____________, which makes up its structure or shape, for each organ or system.
Morphodifferentiation, morphology
what are the 5 developmental processes in order?
induction, proliferation, differentiation, morphogenesis, and maturation
what is the stomodeum?
the primative mouth
what is the stomodeum lined by?
ectoderm
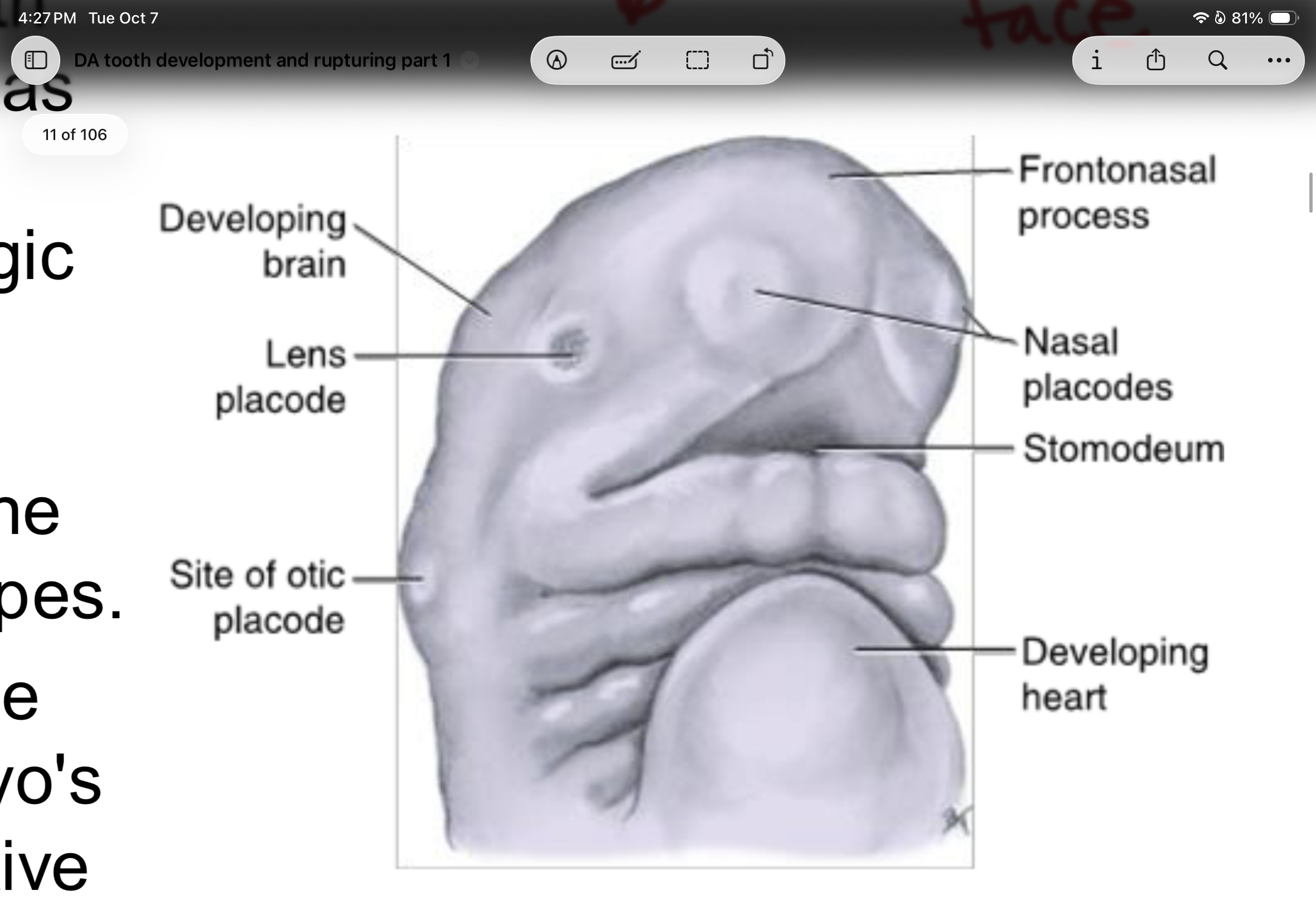
Embryo at the _______ week of prenatal development showing the developing brain, the forming face from the growth of the frontonasal process with its stomodeum and placodes, and the developing heart.
fourth
what does the outer part of the ectoderm give rise to?
oral epithelium
The ______________ consists of two horseshoe-shaped bands of tissue at the surface of the stomodeum, one band for each future dental arch.
oral epithelium
At the same time, deep to the forming oral epithelium there is a type of mesenchyme known as _____________, which is derived from neural crest cells (NCCs) that have migrated to the region. (they form the stuff that is under the enamel)
ectomesenchyme
what separates the oral epithelium and the ectomesenchyme within the stomodeum?
basement membrane
During the later part of the seventh week, the oral epithelium grows deeper into the ectomesenchyme and is induced to produce a layer called the _________.
dental lamina
The _________ begins to form initially in the midline for both arches and progresses posteriorly. The underlying ectomesenchyme also begins to undergo changes.
dental lamina
The second stage of the odontogenesis is considered the ________ and occurs at the beginning of the eighth week of prenatal development for the primary dentition.
bud stage
The bud stage involves _________ of the dental lamina into the surrounding ectomesenchyme in the form of 3-dimensional oval masses tooth buds—together creating the future tooth germs.
extensive proliferation
How many buds will each arch of the primary dentition have?
10
What is the intiation stage known for?
induction, will a tooth form or not?
what is the bud stage known for?
proliferation, will a tooth be too big or too small?
what is the cap stage known for?
proliferation, differentiation, and morphodifferentiation
The third stage of odontogenesis is considered the ________ and occurs for the primary dentition between the ninth and the tenth week of prenatal development, during the _______ period.
cap stage, fetal
At the end of proliferation process of the bud stage, the __________ of the primary dentition of both the future maxillary and mandibular arch and each arch will have 10 buds.
dental lamina
Each of the tooth buds created in the bud stage will eventually turn into a __________.
tooth germ
what stage does the tooth germ form?
cap stage
what does the tooth germ consist of?
enamel organ, dental papilla, dental sac
what is the tooth germ also known as?
the primordium of a primary tooth
what are the 3 processes of differentiation that occur in the cap stage?
cytodifferentiation, histodifferentiation, and morphodifferentiation
There is unequal growth in different parts of the _________ leading to a formation of a 3-dimensional cap shape overlying the ectomesenchyme that is still attached to superiorly to the _________.
tooth bud, dental lamina
During the cap stage a tooth forms and it contains the each of the primordial types of tissue needed for development of the future tooth. Therefore, the predominant physiologic process during the cap stage is one of ______________.
morphogenesis
A depression results in the deepest part of each tooth bud of dental lamina forming the cap shape of the ___________. In the future this physiologic process will form enamel.
enamel organ
Where was the enamel organ derived from and what product does that make it?
the ectoderm, ectoderm product
The innermost margin of the cap-shaped enamel organ is the _________ which will form the shape of the crown and cusps and act as a signaling center for how the tooth should grow.
enamel knot
The dense area of tissue of the ectomesenchyme lying inferior to the cap-shaped enamel organ is considered the _________. In the future this will form dentin and pulp in the tooth.
dental papilla
A basement membrane still exists in the cap stage but now it is between the enamel organ and the dental papilla, being the site of the future _______________.
dentinoenamel junction
The dentin and pulp are derived from what and are what kind of product?
ectomesenchyme, mesenchymal product
The remaining ectomesenchyme surrounding the outside of the cap-shaped enamel organ which is a separate structure from the dental papilla is the _________.
dental sac
In future development, the capsule-like dental sac will produce the periodontium, the within supporting tissues ________, _________, ________.
cementum, periodontal ligament, and alveolar process
At the end of the cap stage these 3 embryonic structures, the enmael organ, dental papilla, and dental sac are now considered together to be called the ________, which is the primordium of the tooth.
tooth germ
Each primordium for the intially formed permanent teeth are appears as an exetension of the dental lamina into the ectomesenchyme on succudaneous teeth, the site of origin is lingual to the developing primary tooth germs and are called, ____________.
successional dental lamina
The fourth stage of odontogenesis is considered the ________, which occurs for the primary dentition between the eleventh and twelfth week of prenatal development.
bell stage
In the _________, differentiation on all levels occurs to its furthest extent, and as a result, four different types of cells are now found within the enamel organ.
bell stage
what are the 4 different cell types found in the enamel organ in the bell stage? (from outer to inner)
outer enamel epithelium, stellate reticulum, stratum intermedium, and inner enamel epitherlium
The outer cuboidal cells of the enamel organ
outer enamel epithelium (OEE)
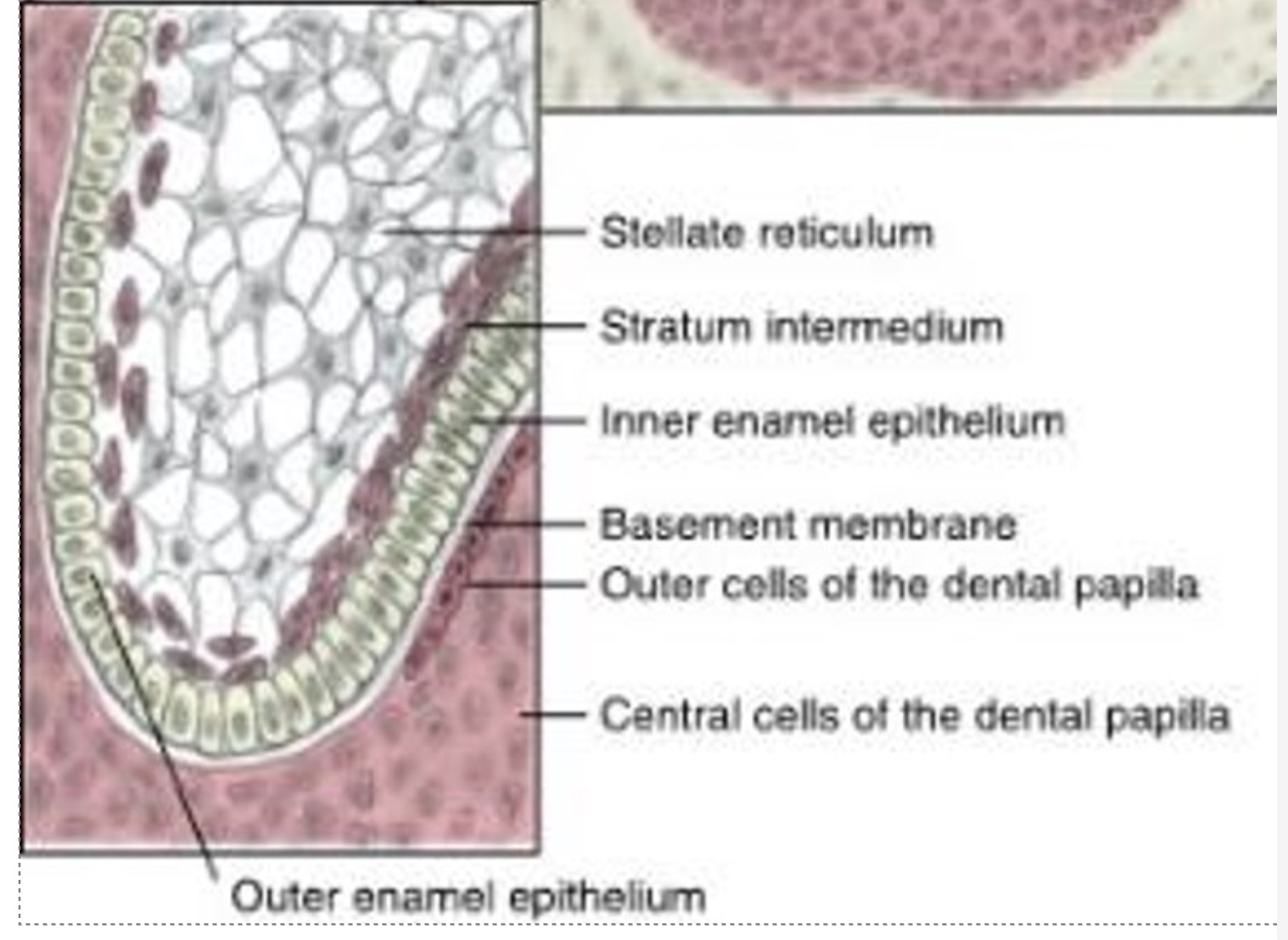
The ____________ serves as a protective barrier for the rest of the enamel organ during enamel production
outer enamel epithelium (OEE)
The innermost tall columnar cells of the enamel organ
inner enamel epithelium (IEE)
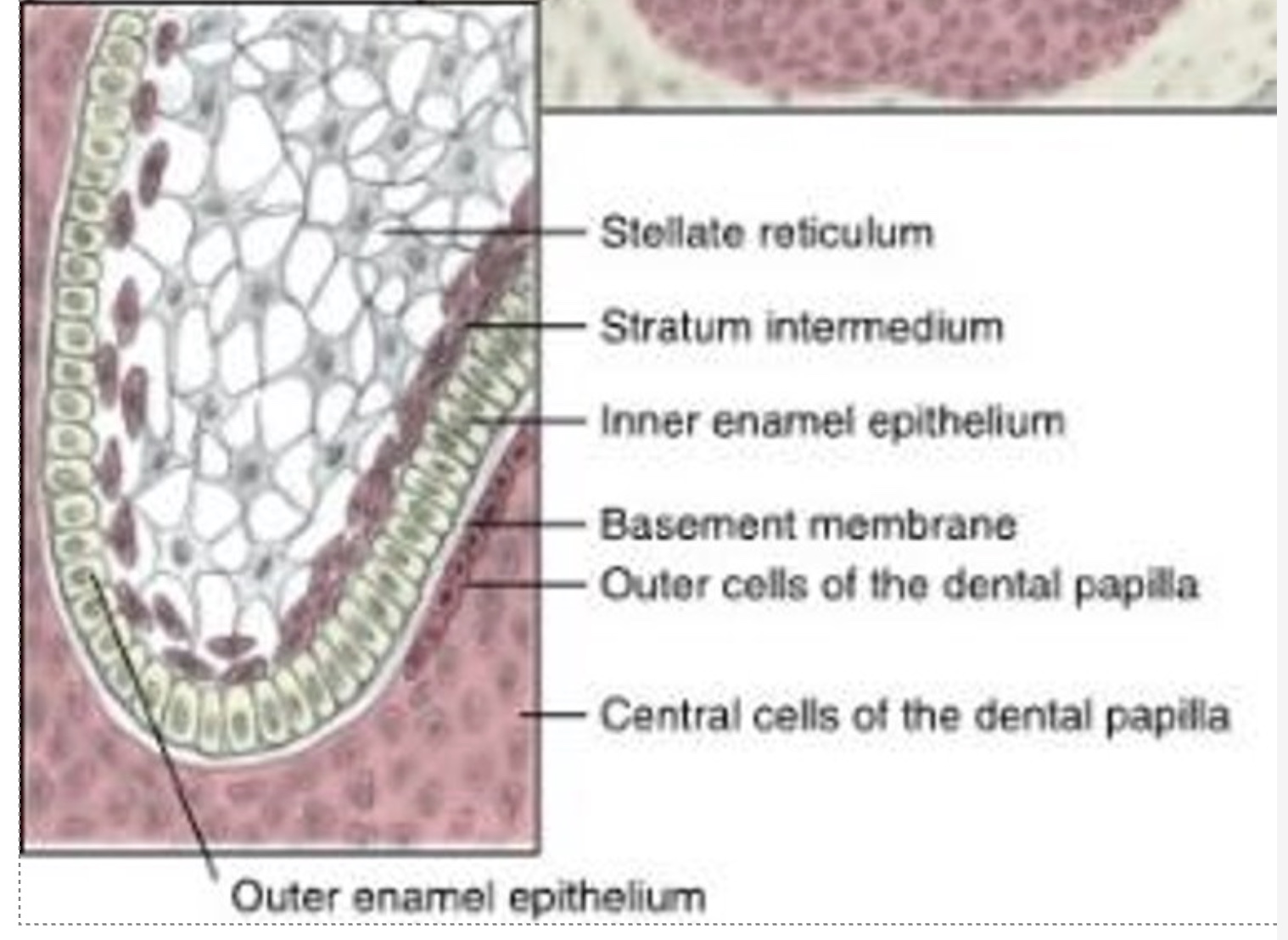
In future development, the ____________ will differentiate by phases into enamel‑secreting cells (ameloblasts).
inner enamel epithlieum
Between the outer and inner enamel epithelium are two layers or dental core: the ________ and the ______________.
stellate reticulum, stratum intermedium
The ________ consists of star‑shaped cells in many layers, forming a network.
stellate reticulum
These cells are star shaped and synthesize ____________. As they are produced, water is drawn in between the cells which stretches them apart to create a spngy and protective layer inside the enamel organ.
glycosaminoglycans
As they are moved farther away from one another with the production of glycosaminoglycans, the stellate reticula maintain contact with one another through cell junctions by way of __________, resulting in their unique star-shaped appearance
desmosomes
The _____________ along with the inner enamel epithelium are responsible for the tooth enamel formation.
stratum intermedium
Eventually differentiation of inner enamel epithelium and papilla cells sweeps down along the cusp slopes and is followed by the deposition of _________ first at the cusp tip.
dentin and enamel
It is also during the bell stage of development that the dental lamina breaks down and the enamel organ loses connection with the _____________. Remnants of the dental lamina may remain in the adult mucosa as clumps of resting cells, the _____________.
oral epithelium, epithelial pearls
__________ are round or whorled clusters of epithelial cells that have undergone abnormal keratinization (hardening) inside tissue.
Epithelial pearls
At the same time as the severing of the dental lamina, the dental papilla within the concavity of the enamel organ also undergoes extensive histodifferentiation so that it now consists of two types of tissue in layers: _________ of the dental papilla and the _________of the dental papilla.
outer cells, central cells
In future development what do the outer cells of the dental papilla become?
odontoblasts (dentin-secreting)
what are odontoblasts?
cells that secrete the dentin matrix that will later harden into dentin
what are ameloblasts?
cells that secrete the enamel matrix that will later harden into enamel
In future development what do the central cells of the dental papilla become?
they become the primordium of the pulp
what does the dental sac do at the bell stage?
increase its amount of collagen fibers
The final stages of odontogenesis include the __________ (or secretory stage), during which the enamel, dentin, and cementum are secreted in successive layers layers upon those already present.
apposition stage
These hard dental tissue types are initially secreted as a _______, which is an extracellular substance or surrounding medium that in this case is partially mineralized.However, it serves as a framework for later full mineralization to the tissue type’s expected level.
matrix
The final stage of odontogenesis, the _____________, is reached when the matrices of the hard dental tissue types subsequently fully mineralize to their correct levels.
maturation stage
list the 3 tissues from hardest to softest
enamel, dentin, cementum
After the formation of the IEE in the bell‑shaped enamel organ, these innermost cells grow even more columnar as they elongate and differentiate into ___________.
preameloblasts
During this differentiation process of preameloblasts, the nucleus in each cell moves away from the center of the cell to the position farthest AWAY from the basement membrane that separates the enamel organ from the dental papilla.This movement of the nuclei in each IEE cell occurs during _____________.
cellular repolarization
In future development, the preameloblasts will induce the OUTER cells of the dental papilla to differentiate into __________________, and then will themselves differentiate into cells that secrete enamel (or ameloblasts).
odontoblasts (dentin-forming cells)
After the differentiation and repolarization, the odontoblasts begin ______________, the appositional growth of dentin matrix, or predentin, laying it down on their side of the now disintegrating basement membrane.
dentinogenesis
Is the enamel matrix or the dentin matrix secreted first?
dentin matrix
when the basement memebrane disintegrates in the appositional stage, what is the name of junction between the enamel and the dentin?
dentinoenamel junction
This disintegration of the basement membrane allows the preameloblasts to contact the newly formed predentin, which induces the preameloblasts to differentiate into __________.
ameloblasts
Ameloblasts begin ____________, the the appositional growth of enamel matrix, laying it down on their side of the now disintegrating basement membrane.
amelogenesis
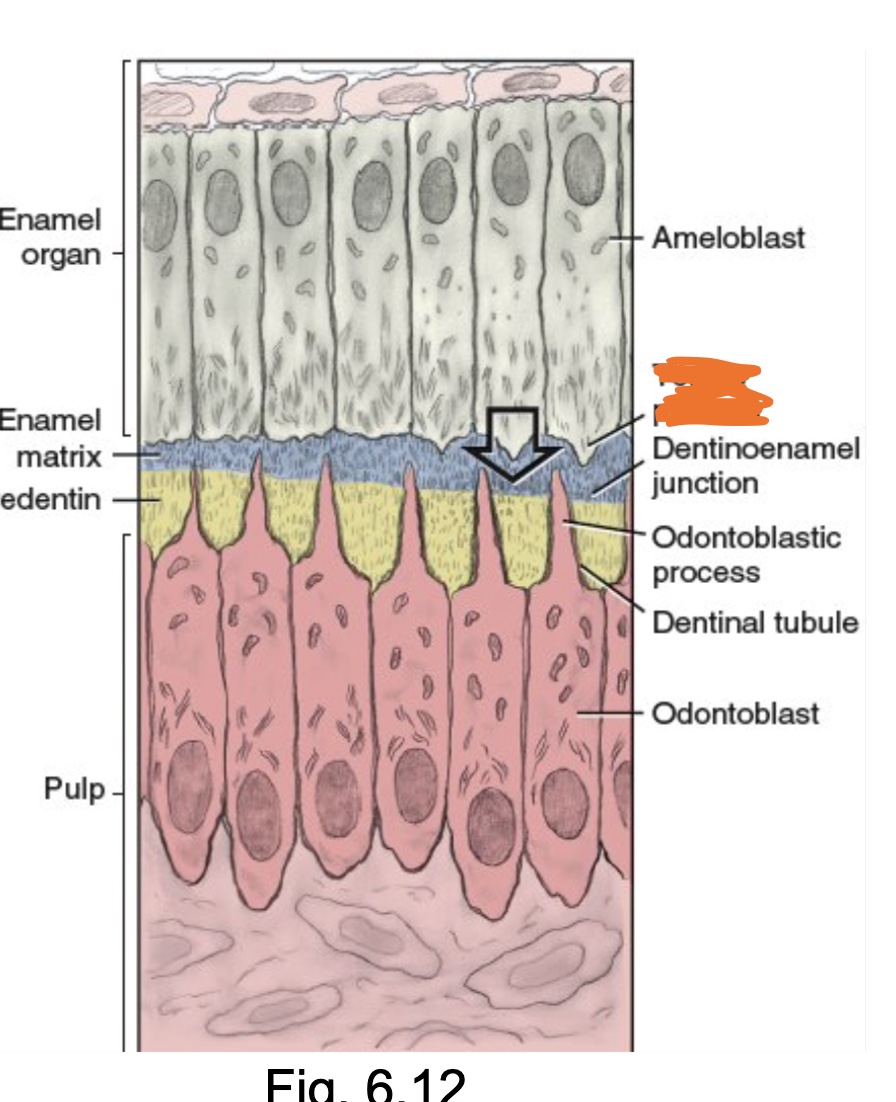
The enamel matrix is directly secreted from __________, an angled distal part of each ameloblast that faces the fully disintegrated basement membrane, as there is group movement of the ameloblasts away from the basement membrane.
tomes process
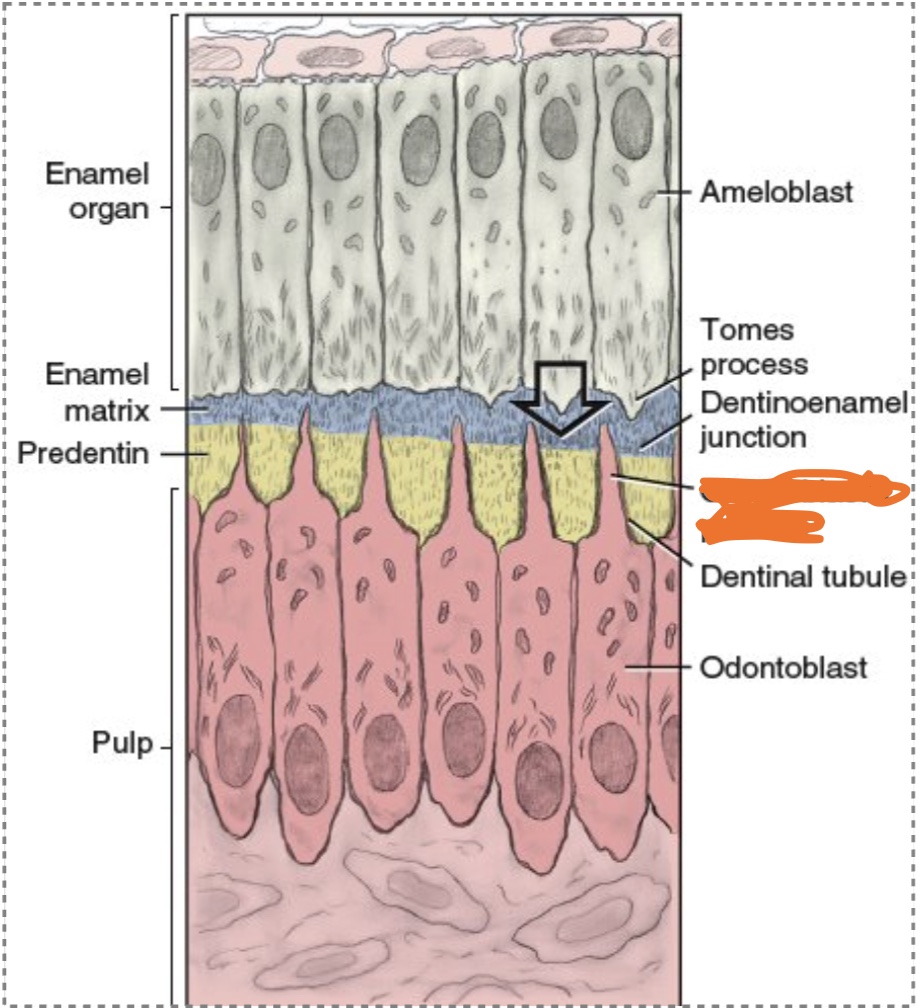
However, the odontoblasts (unlike the ameloblasts) will leave attached cellular extensions in the length of the predentin called the _____________ as they move away from the DEJ.
odontoblastic process
Each odontoblastic process is contained in a mineralized cylinder, the __________.
dentinal tubule
The maturation through mineralization of each type of matrix occurs later and is a different process for both enamel and dentin. However, the cell bodies of odontoblasts will remain within adjoining pulp attached by the ______________.
odontoblastic processes
In contrast, the cell bodies of the __________ (now in the maturation stage) will be involved first in the final phases of the mineralization process and active tooth eruption but will later be lost after tooth eruption. (this is why enamel can not regenerate)
ameloblasts