Human Phys Heart
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
tricuspid valve
prevents backflow of blood; sits between right atrium and ventricle
pulmonary veins
collects blood returning to the heart from the lungs
interventricular septum
wall located between right and let ventricles
pulmonary trunk
pumps blood into the pulmonary artery
aortic semilunar valve
prevents the backflow of blood; sits between the left ventricle and the aorta
inferior vena cava
brings blood back to the heart from the lower parts of the body
right atrium
chamber of the heart that receives deoxygenated blood from the body systems
bicuspid valve
heart valve that prevents the backflow of blood into the left atrium
aorta
the major artery exiting the left ventricle that carries oxygenated blood to the body
pulminary artery
the artery that carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
right ventricle
chamber of the heart that pumps blood to the lungs
pulminary semilunar valve
heart valve that opens to allow blood to flow to the lungs
pulminary veins
veins connected to the heart that return oxygenated blood to the left atrium
apex
point on the inferior surface of the heart
base
area at the superior surface of the heart where all of the large blood vessels are attached
tricuspid valve
heart valve that opens to allow blood to flow into the right ventricle
superior vena cava
vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the heart
chordae tendinae
fibrous cords that help to keep the valves closed during contraction.
left ventricle
the chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium and pumps it into the aorta
left atrium
the chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins and passes it to the left ventricle
AV node
hold signals so it can reach atrium before contraction
purkinje fibers
tells ventricle to contract
SA node
“pacemaker”, starts every beat, sends P wave
AV bundle
gets signal to bottom of heart as fast as possible
bundle branches
splits signal to reach both sides of the ventricles quickly.
why do the purkiinje fibers start at the apex of the heart and then travel up the walls of the ventricles
the heart contracts bottom to top
diastole
relaxed
systole
contracts
stages of heart beat
mid to late diastole
ventricular systole
early diastile
mid-to-late diastole
atria contracts
ventricular systole
ventricles contracting
early diastile
everything is relaxed
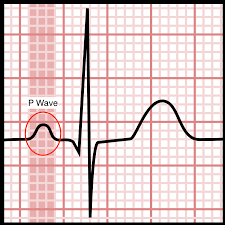
P wave
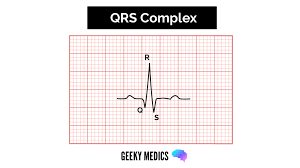
QRS complex
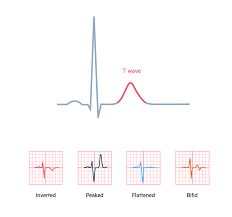
T wave
P wave
atria depolarizes/contracts
QRS complex
venticles depolarize/contract
T wave
ventricles repolarize
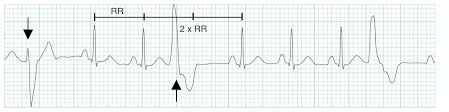
PVC
PVC
premature ventricle contraction
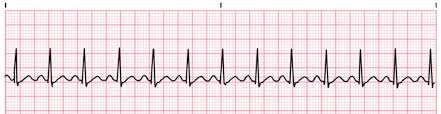
sinus tachycardia
sinus tachycardia
resting heartbeat is too fast
sinus bradycardia
sinus bradycardia
resting heartbeat is too slow
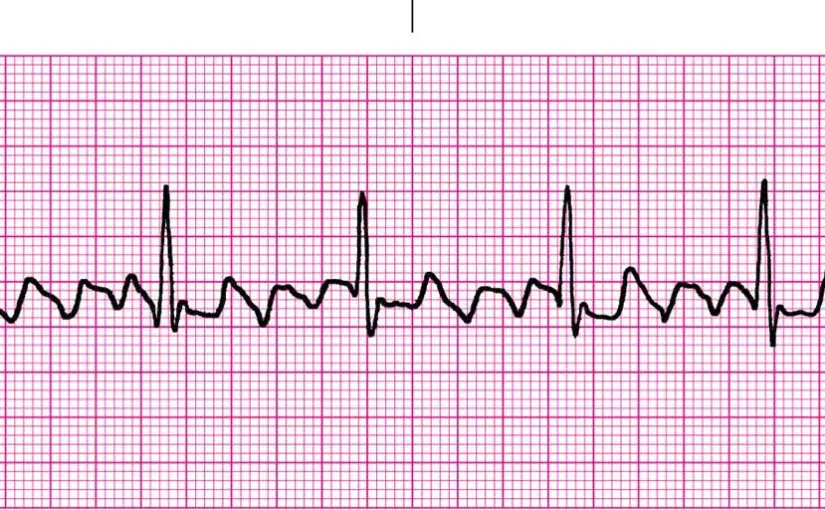
atrial flutter
atrial flutter
atria contracts too often, QRS is normal
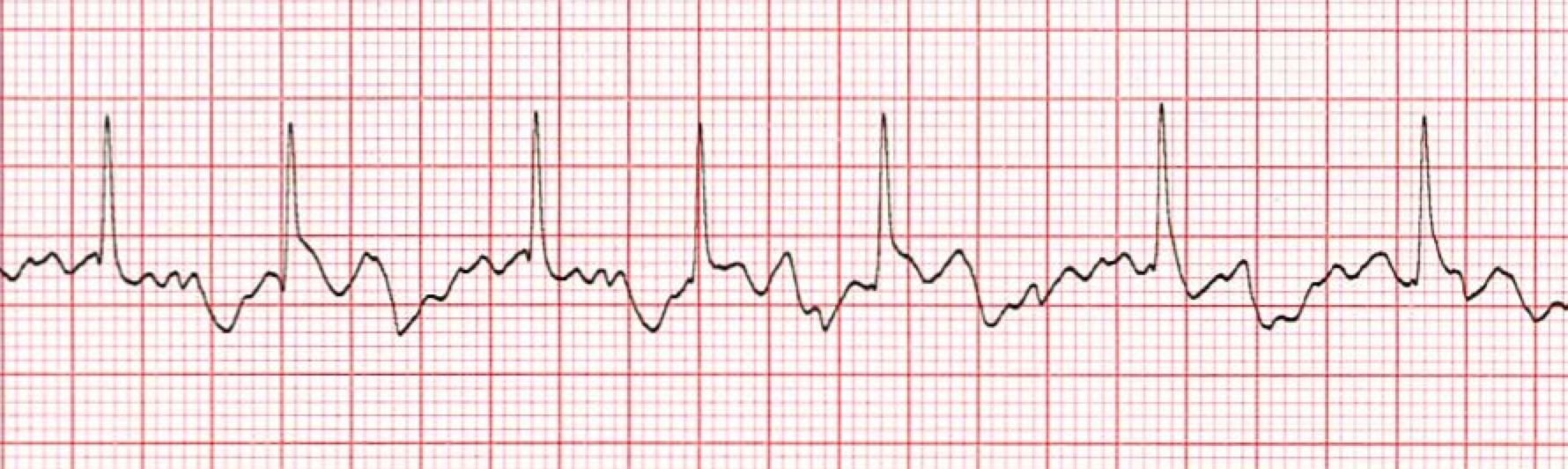
atrial fibrillation
atria fibrillation
atrias contract too often, QRS not spaced evenly
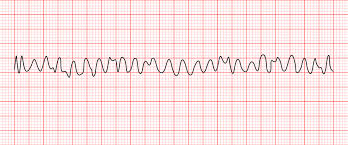
ventricular fibbrillation
ventricular fibrillation
ventricles are not contracting, most dangerous
myocardial infarct
death of heart tissue due to heart attack
full thickness infarct
vessell that’s blocked gives blocks lots of blood
partial thickness infarct
vessell that’s blocked blocks off little blood
15 minutes into heart attack
dizziness
20 minutes into heart attack
500 heart cells die/sec
what pain do you feel when having a heart attack
indegestion, arm pain, jaw pain
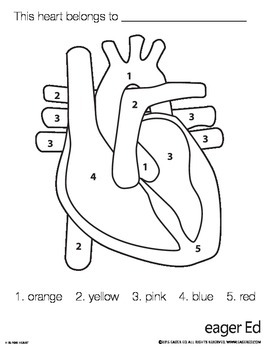
1
aorta
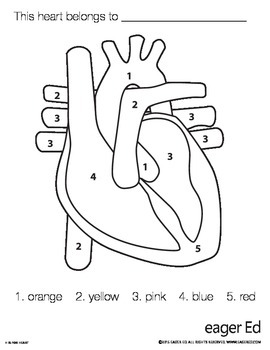
2
pulminary trunk/arteries
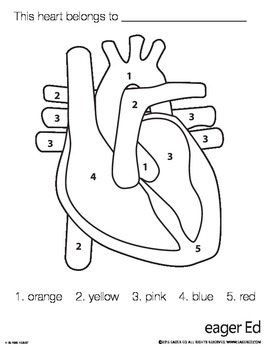
3 (poking out)
pulminary veins
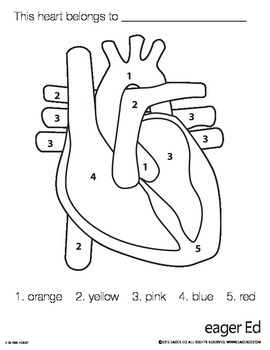
4 (top to bottom)
right atrium, tricuspid valve, chordae tendinae, right ventricle
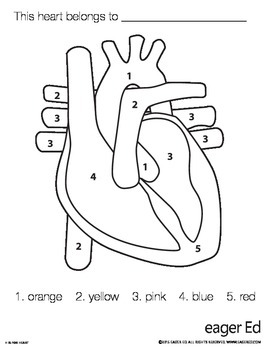
5
apex and interventricular septum
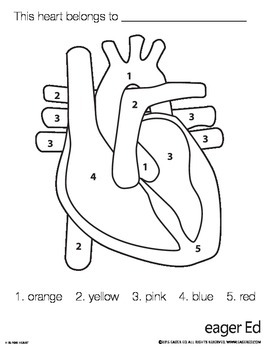
3 (big area) (top to bottom)
left atrium, bicuspid valve, chordae tendinae, left ventricle
path of deoxygenated blood from body
into heart from superior/inferior vena cava, into right atrium, through tricuspid valve, into right ventricle, opens pulmonary semilunar valve, to the lungs through pulmonary arteries, oxygenated, back to heart through pulmonary veins, through bicuspid valve, into left ventricle, opens aortic semilunar valve, through aorta out the heart
chambers of heart
right/left atrium and ventricles
valves of heart
tricuspid and bicuspid valves, aortic semilunar valve, pulmonary semilunar valve
vessels of heart
inferior/superior vena cava, aorta, pulmonary arteries/veins
veins
carry blood to heart
arteries
carry blood away from heart
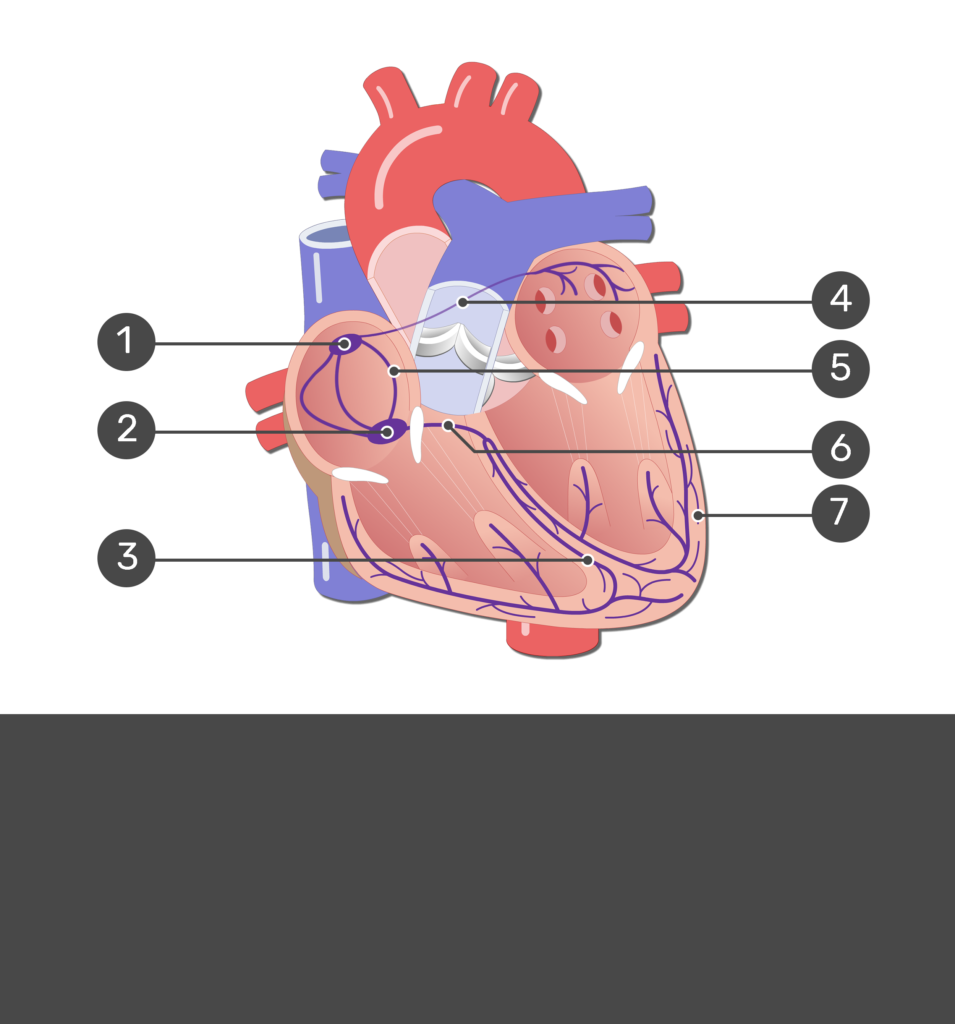
1
SA node
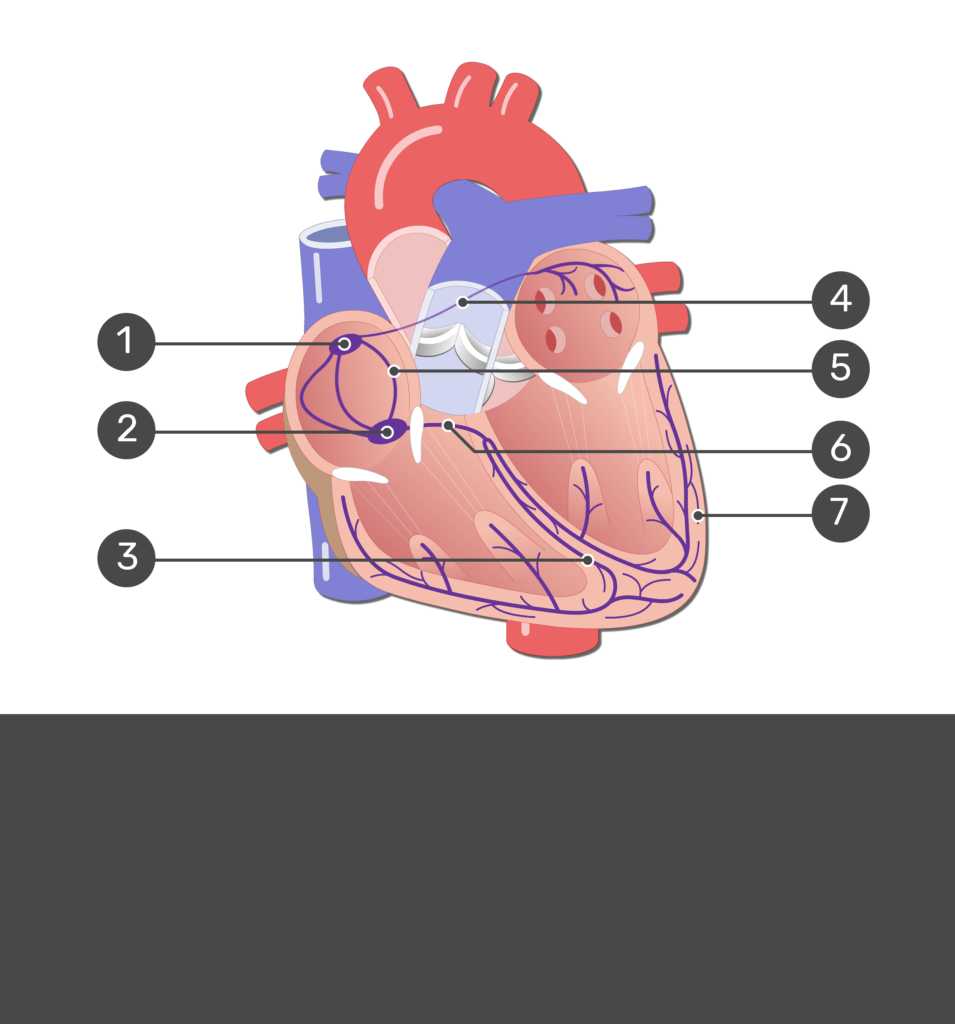
2
Av node
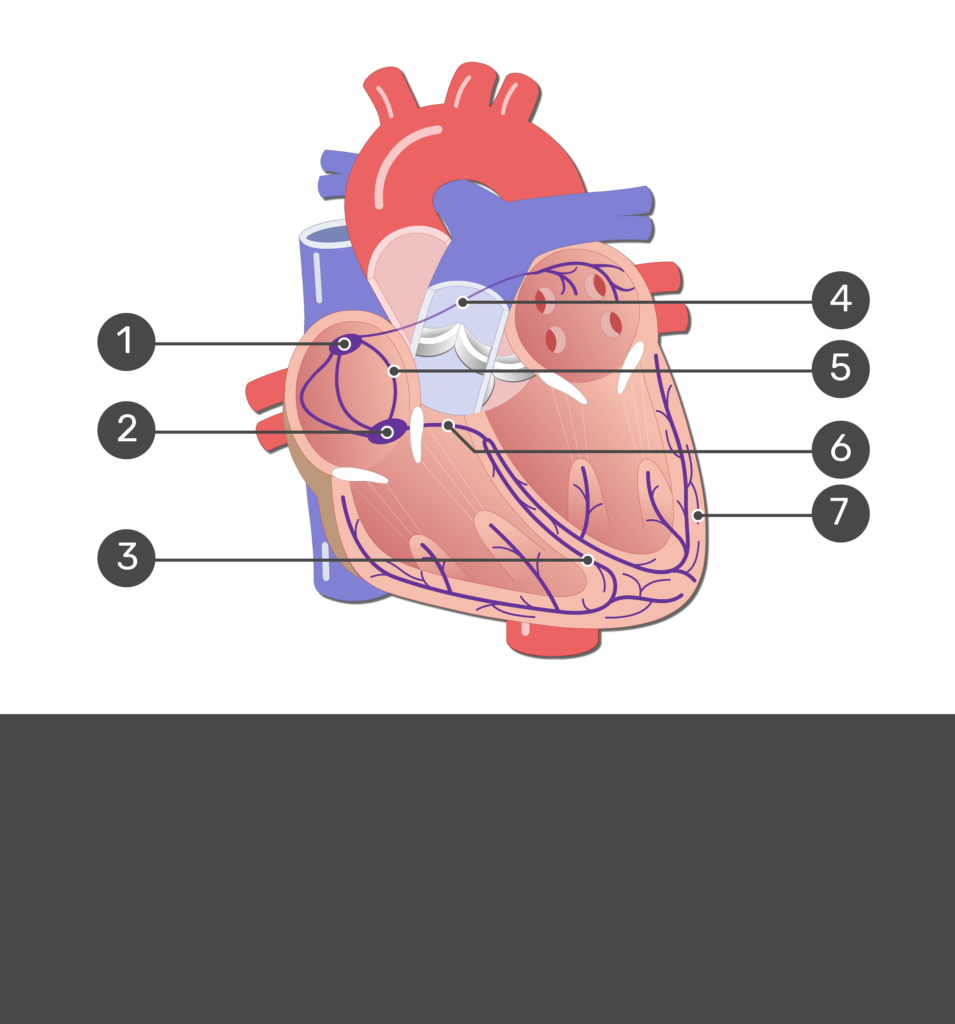
3
bundle branches
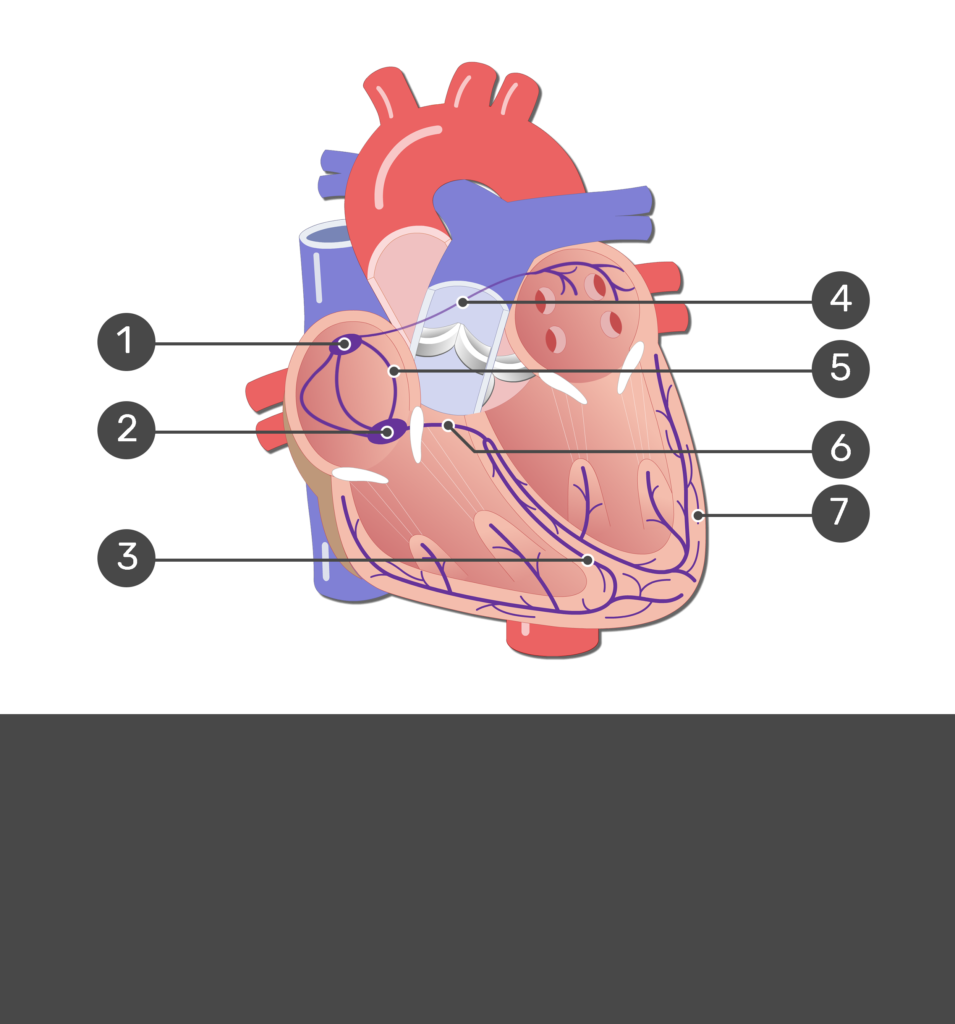
7
purkinje fibers
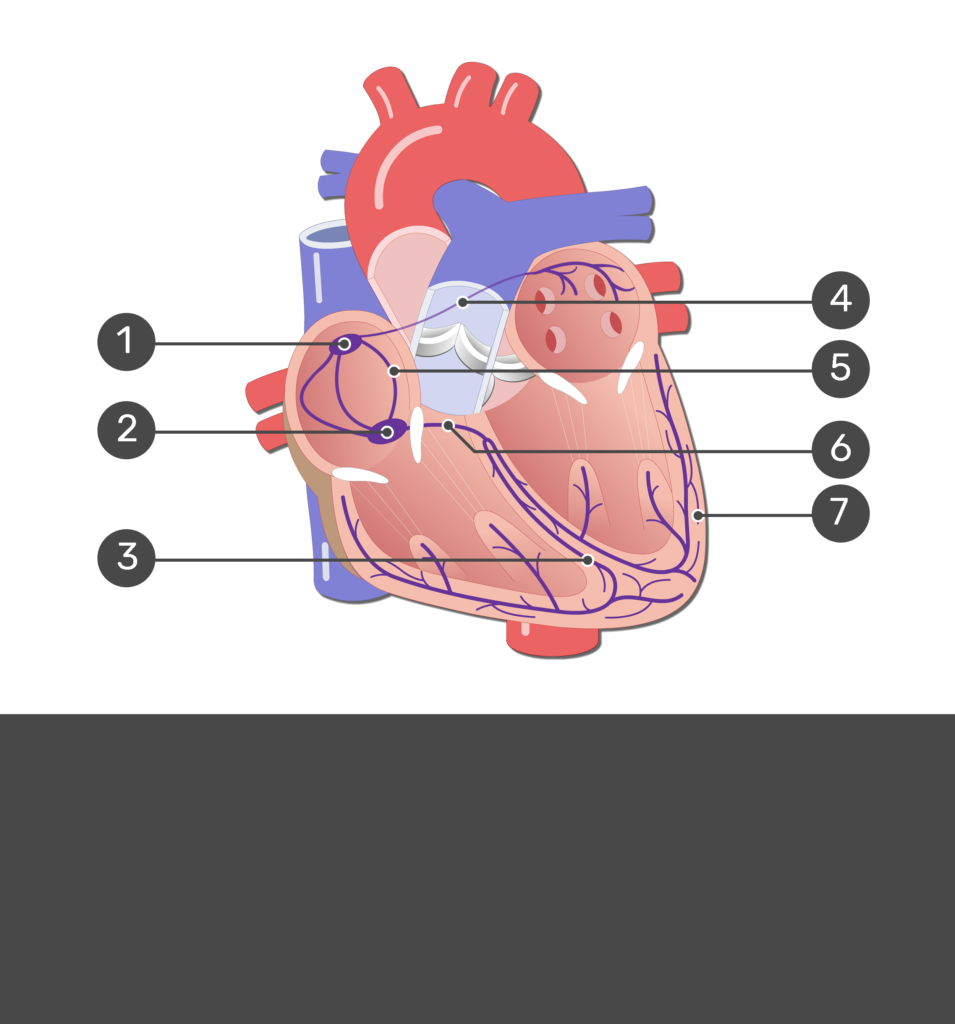
6
AV bundle