aphg unit 1.1-1.7
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
reference maps
maps for general info (two types)
political map
a type of reference map that shows/labels human created boundaries (ex countries)
physical map
a type of reference map that shows/labels natural features (ex rivers)
thematic maps
maps that show spatial aspects of info
choropleth map
type of thematic map that used various colors/patterns to show the location/distribution of spatial data
dot distribution map
type of thematic map used to show the specific location/distribution of something across map
graduated symbol map
type of thematic map that is arranged in a series or according to a scale and uses symbols of diffenrt sizes for diffenrt amounts
isoline map
type of thematic map that uses lines to connect points of equal value to show variations in data across space (lines close together=rapid data and lines far apart=data relatively the same) (ex topographic map)
cartogram
type of thematic map where the sizes of countries are shown according to a specific statistical value
map projection
the process of showing a curved 3d surface on a flat 2d surface (basically the process of showing the earth on a map)
map distortions
globes don’t have perfect squares but maps do which leads to four types of distortions: Shape Area/size Distance and Direction (SADD)
mercator map
commonly used map projection
pros: good for navigation bc shape and direction are accurate
cons: area/size is not accurate
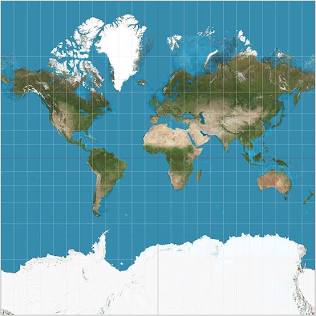
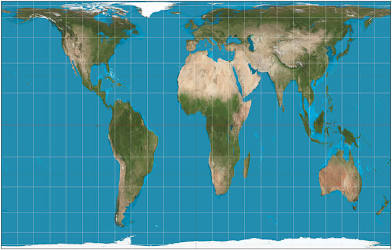
gall-peters map
the stretched out map projection
pros: area/size is accurate
cons: shape is stretched out and inaccurate
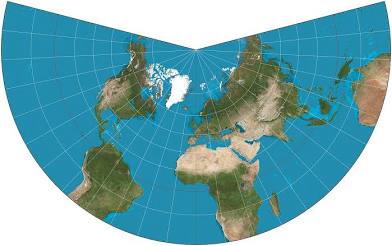
conic map
the map projection that’s shaped like a cone
pros: area/size is accurate and the longitude and latitude is accurate
cons: directions are not accurate
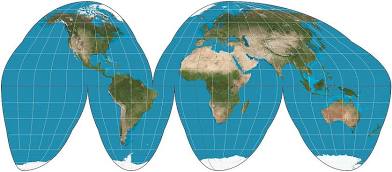
goode-homolosine map
map projection that looks like a lot of wedges
pros: area/size and shape is accurate
cons: oceans are interrupted
winkle tripel map
map projection that is more circular shaped than the robinson projection
pros: area/size and shape is accurate
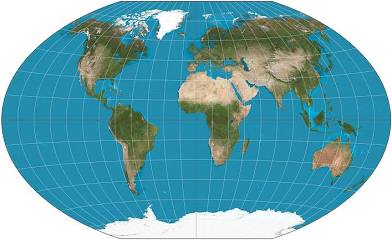
robinson map
this projection is kinda more oval shaped
pros: area/size and oceans are more accurate
cons: antarctica is too big and greenland is too flat so shape is an issue
the five themes of geography
movement, regions, human-environment interaction, location, and place (MR.HELP)
movement
includes the process of migration, trade transportation and communication (the connections between places)
region
areas that are defined by one or more unique characteristics by certain patterns of activities, they can be broken into three categories
formal regions
a geographic region that is traditionally defined by economic political or environmental characteristics (homogeneous culture or set boundaries)
functional regions
geographic area that is centered around a centerpoint/node that is based around specific economys travel or communication
perceptual/vernacular regions
geographic area that has no perfect definition bc it only exists bc of ppls beliefs/attitudes/feelings about a place
human environment interaction
how humans depend adapt and modify the environment (relationship between humans and the environment)
location
the specific position or coordinates of a place, there are two types of it
absolute location
the exact spot of where something is located (gps or lat/long coordinates)
relative location
a description of a location using surrounding geographical features (ex my house is near the store)
place
the unique human/physical characteristics of a location that refers to how people are aware of a space, it’s basically a space with meaning (physical characteristics+human characteristics=place)
site
the physical characteristics of a place (the conditions)
situation
defined by human characteristics, helps us understand the importance of a location PROVIDES A SENSE OF PLACE!!! (the connections)
clustered
type of spatial distribution, the grouping of a phenomenon
dispersed
type of spatial distribution, the scattering of a phenomenon
space
the physical distance between two places on the earths surface (geographic area)
toponym
name given to a place on earth
globalization
the increasing interconnectedness of different parts of the world
flow
part of the five themes of geography, shows movement and is used for functional regions
time space compression
the reduction of time it takes for something to reach another place bc of technology advances in transportation and communication, the spaces are more connected so the time to travel to those spaces have been compressed
distance decay
the effect/outcome from when distance increases and the relationship between two things decreases
friction of distance
the cause/mechanism of when things are farther apart they are less well connected
cartographic scale
the scale on maps
large scale map
shows an enLARGEd area, shows more detail
small scale map
shows larger amount of area but is less detailed
geographic/relative scale
shows the geographic territory on the map (how much land does it show?)
local/city→country→subnational/state/province→national→regional→global
scale of analysis/data
the level at which you analyze or compare the data (a map may be at a subnational scale but you are comparing the data of the counties)
local/city→country→subnational→stateprovince→national→regional→global
regional boundaries
are transitional/relative boundaries that are often contested and overlapping
sustainability
development that serves the needs of the current people without compromising the needs of future generations
natural resources
materials that can be found on earth that can be used for economic gain, there are two types
renewable resources
natural resources that can renew itself (ex solar energy and wind energy)
non renewable resources
natural resources that cannot renew itself (ex fossil fuels)
recreational land use
type of land use (ex parks sport grounds)
transportation land use
type of land use (ex roads railroads subways)
agricultural land use
type of land use (ex farms)
residential land use
type of land use (ex houses apartments)
industrial land use
type of land use (ex manufacturing factories)
commercial land use
type of land use (ex commerce/businesses malls grocery stores movie theaters)
cultural ecology
the study of how humans adapt to the environment, has two main theories
environmental determinism
a theory of cultural ecology that states that the environment determines human development (ex inuit people)
possibilism
a theory of cultural ecology that limits the effects of the environment and focuses on the role of humans in human environment interaction, different cultures react in different ways depending on their beliefs (ex building a bridge to cross a river instead of letting the river determine that you can’t cross it)
GIS (geographic information system)
computer system that layers data on top of eachother
GPS (geographical positioning system)
absolute location to help ppl with directions
remote sensing
process of taking pictures of the earths surface through things like satellites or airplanes
census
official count of a population (in the us it happens every ten years