Asymmetric Information and Market Regulation
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Asymmetric Information
Knowledge held by one party, not the other.
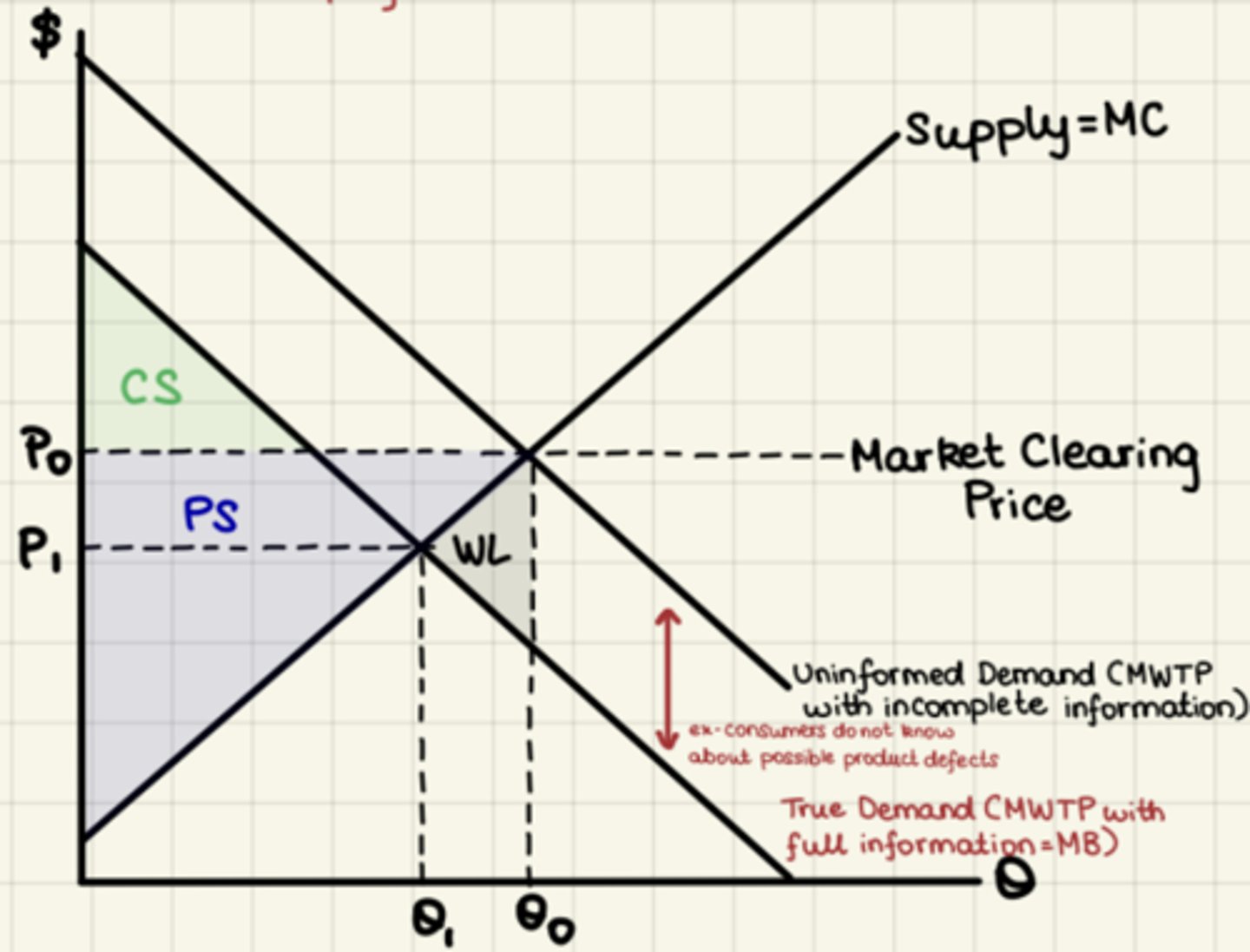
Consumer Overpay
Consumers pay too much due to misinformation.
->
Underinformed consumers = inaccurate WTP =
mispositioned D curve
Consumers pay too much when they do not have full information about product drawbacks
Incomplete information = consumers over-value = ↑ price (P) =Overproduction
WL down
decrease demand
higher (P)/(Q)
- CS shrinks
Regulation
Regulation(gov or private) closes gaps in information =
socially efficient output
Private Regulation
Non-governmental measures to ensure compliance and safety.- efficency generates profit funded by regulatory beneficiaries (firms/people) motivated by demand
NGO Role
Nonprofits that advocate for better regulations.
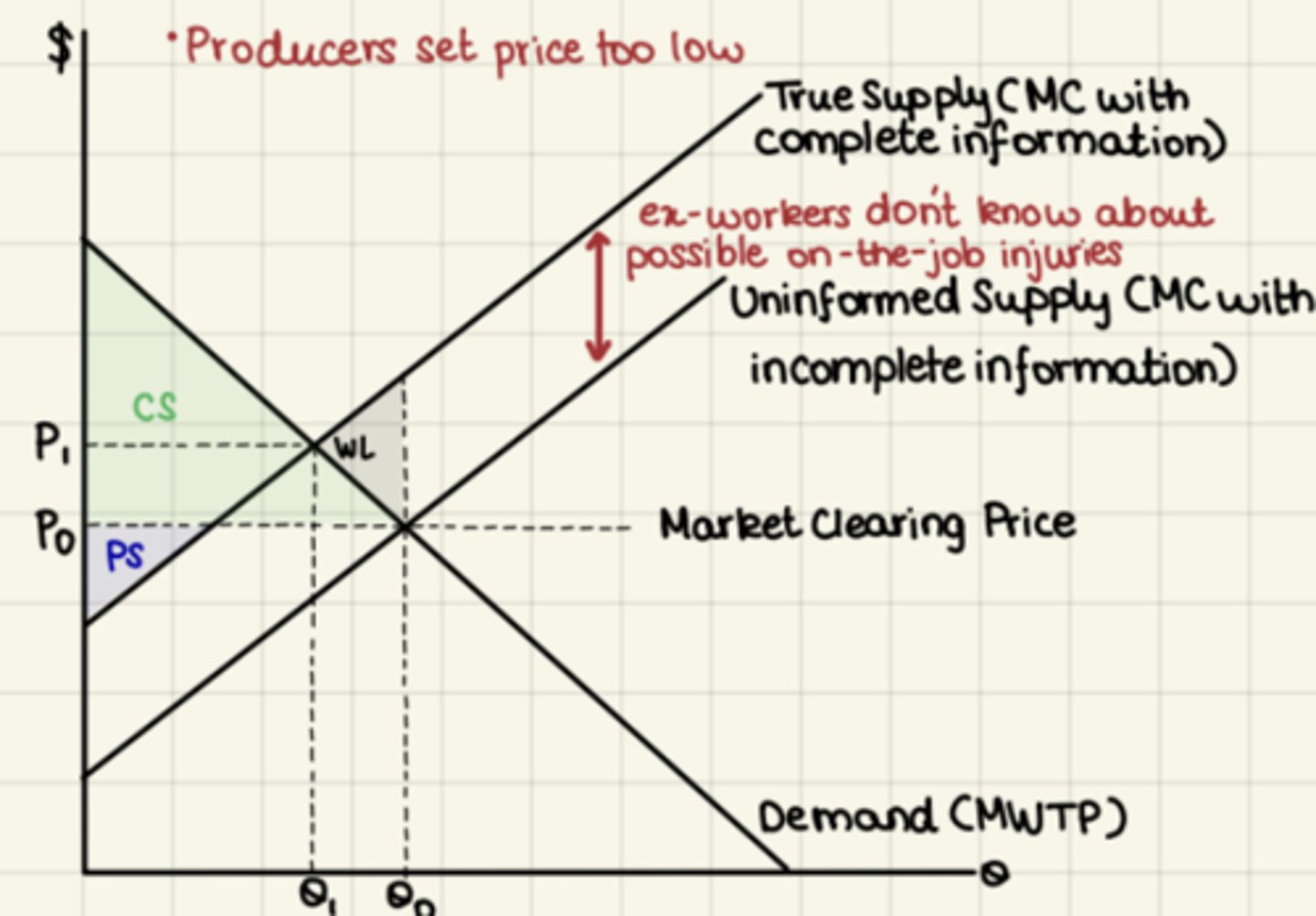
Producers underestimate true cost
Underinformed producers = inaccurate MC =
mispositioned S curve
Original price is lower because producers underestimate true cost -Goods sold too cheaply = overproduction
WL up
supply increases
- Lower (P) & higher (Q) than efficient-
-PS shrinks
Market Failure
Inefficiencies due to information asymmetries.
Government regulation can try to fix it
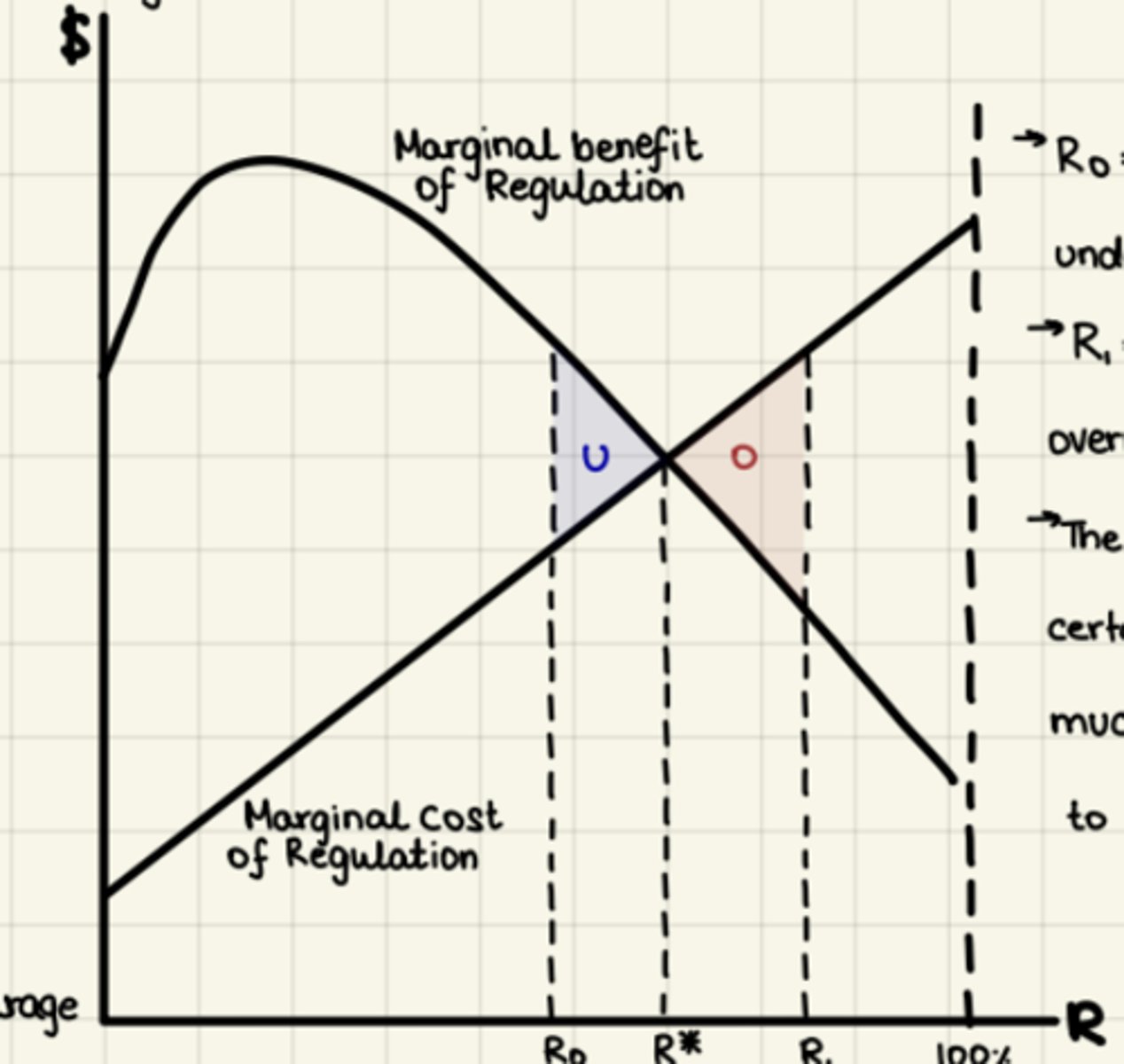
Regulation closes the gap -but 100 % closure is not socially efficient
-Socially efficient regulation R*. MC =MR of regulation
-MB = rises than falls = diminishing Demand (MWTP)
-MC rises more = more resources are required at the margin to achieve incrementally stricter standards
-R1 > R*= overregulation = Wl
-Ro R*= underregulation = Private regulation can profitably close gap + generate economic net = blue triangle
-Ro = too little regulation =underregulation
-R1 too much regulation =overregulation
NGOs take action when
Regulation (gov or priv) is insufficient
- encourage investors, consumers, emp to demand more inv
- is successful when firms fear inaction puts profit at risk
intermediaries make money by
providing info when gov underregulates
Why did Nike face criticism
- didn't pay workers living wage
- employed children long hours
- health and safety violations
- high profits but doesn't reinvest
who is activist that targeted Nike
jeff Ballinger
What did Nike do with the first public criticism
say not mfg company but a marketing brand
response-defensive + deflection of blame
-Invested more in marketing "Business as usual"
who were the first people to attack Nike
students
press target celebrities
protests at store openings
What did the social lobbying do
shift d curve down
- beat Nike's lobbying
- Shifted the demand curve left (lower P & Q)
- shrunk CS
How did private reg restore safety with Nike workers
Shift S curve up
- informed them about unsafe work environment
- This shifted supply curve left (higher P & lower Q)
- Shrunk PS
After losing $400 m what did Nike do
- Hire Dusty Kidd for labor conduct code
- hired Andrew Yang to evaluate new code
- hired EY to audit
- hired Dartmouth to survey workers
Nike knew more than others
(consumers,workers,regulators)
->
True working conditions and wages in outsourced factories
-
overvalued-overproduction of nike products
Information Gap Nike
Workers -
Didn't know their rights how wages compared internationally
Consumers -
Didn't know about child labour, unsafe conditions ; $1-2 day wage
Nike voluntarily
adopted more private regulation than other business
Nike new contractor requirements
- min age 16 apparel & 18 shoes
- comply with US AIR standards
- managers must learn local language
- loans to workers
- Led AIP and FLA
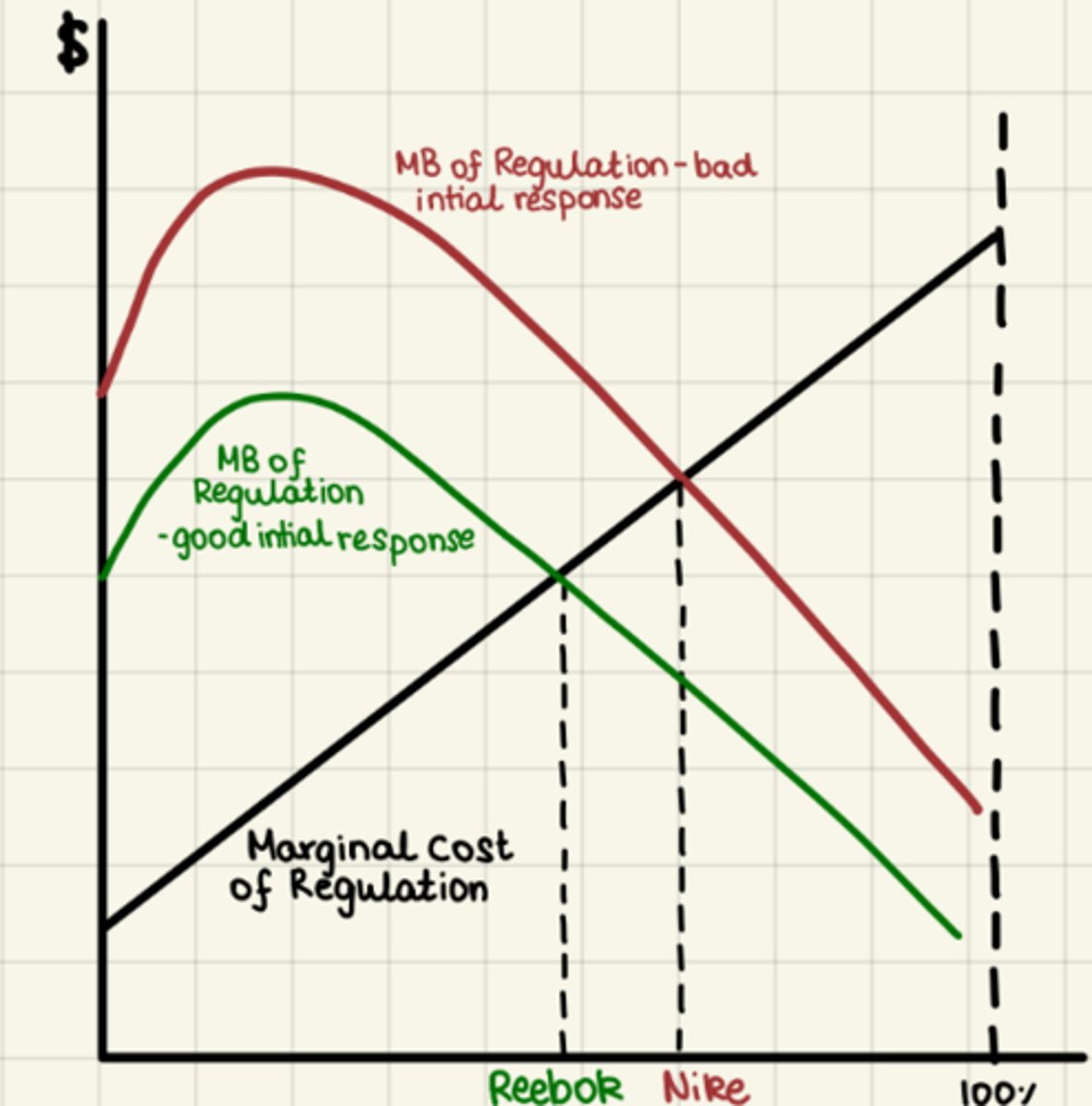
Rebook's better initial response compared to Nike caused
- less investment required compared to Nike- lower Q for MC = MB
Priv regulation did what to Nike in end
kept out of Bangladesh
What happened in Bangladesh
- overcrowded infrastructure killed 1100 workers
- 200 mfgs had to donate 1 billion to upgrade safety
- Nike stayed out and save money
AIP
- Clinton-era coalition of companies
- labor groups, and NGOs formed to create fair labor standards
- establish a code of conduct and monitoring system
FLA
- long-term outcome of the AIP
- independent factory audits and labor standard
- Nike became a founding member
steps did Nike take to address labor criticisms
- Code of Conduct, hired Ernst & Young for internal audits
- Andrew Young to evaluate reforms, and provided training for factory managers,
Why did activists criticize Nike's reliance on internal audits and partnerships like the AIP
- controlled the auditors
- AIP lacked truly independent enforcement.
- Some labor and religious groups left the AIP, believing it was more about PR than meaningful change
why did corporations leave AIP
wouldn't agree to independent monitoring