LAST YR 11 EXAM - BIO
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Stages of Mitosis
Prophase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase → (Cytokinesis)
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and become visible.
Nuclear membrane breaks down.
Spindle fibres begin to form.
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up at the equator.
Spindle fibres attach to centromeres.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate.
They are pulled to opposite poles.
Telophase
Chromatids arrive at poles.
Nuclear membranes reform.
Chromosomes decondense.
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm divides.
Two identical daughter cells form.
Genotype
The genetic makeup (e.g., Bb).
Phenotype
The physical trait expressed (e.g., brown eyes).
Homozygous
Two identical alleles (BB or bb).
Heterozygous
Two different alleles (Bb).
Dominant Gene
Expressed when present.
Recessive Gene
Only expressed in homozygous recessive (bb).
Genotype Ratio
2 Bb : 2 bb → 1:1
Phenotype Ration
50% dominant : 50% recessive → 1:1
Pedigree symbols
Circle = Female
Square = Male
Shaded shape = affected
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Every generation.
Affected individuals have at least one affected parent.
Males & females equally affected.
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
Skips generations.
Two unaffected parents can have an affected child.
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance
More males affected.
Affected sons often have carrier mothers.
No father-to-son transmission.
X-Linked Dominant Inheritance
All daughters will possess their father’s genes
No Sons affected bythe father
Approx. Half affected
Y-linked Inheritance
All males, no females
PCR Stage 1
Denaturation, 95°C, Hydrogen bonds are broken, DNA becomes single-stranded
PCR Stage 2
Annealing, 55°C, Primers attach to the single strand of DNA
PCR Stage 3
Extending, 72°C, Primers begin building complementry strands with nucleotides
Purpose of PCR
The purpose of PCR is to amplify (make many copies of) a specific segment of DNA
Restriction Enzymes
Restriction enzymes, or restriction endonucleases, are molecular scissors that cut DNA at specific, short sequences known as restriction sites.
Sticky Ends
Staggered cuts → overhangs (e.g., EcoRI).
Blunt Ends
Straight across cuts (e.g., SmaI).
Role of Gel Electrophroesis
To separate DNA fragments by size.
Gel Electrophroesis Diagram
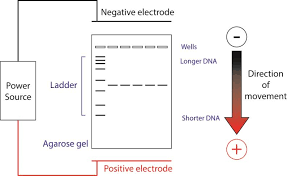
Nuclear Transfer Cloning
Cloning technique, dolly the sheep
SCNT Stages
Remove nucleus from an egg cell (enucleation).
Remove nucleus from somatic cell of organism to be cloned.
Insert somatic nucleus into enucleated egg.
Apply electric shock → stimulates division.
Embryo grows to group of 16 cells, morula
Implant into surrogate.
Surrogate gives birth to clone.
Consequentialism
Right/wrong determined by outcomes.
“Does it maximise good or minimise harm?”
Duty-Based
Right/wrong based on rules, duties, rights.
“Some actions are always wrong regardless of outcome.”
Virtue-Based
Focus on moral character.
“What would a good person do?”
Role of Circulatory System
Transport water, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Carry nutrients and remove wastes
Maintain a constant body temperature
Circulate hormones
Circulatory System Diagram
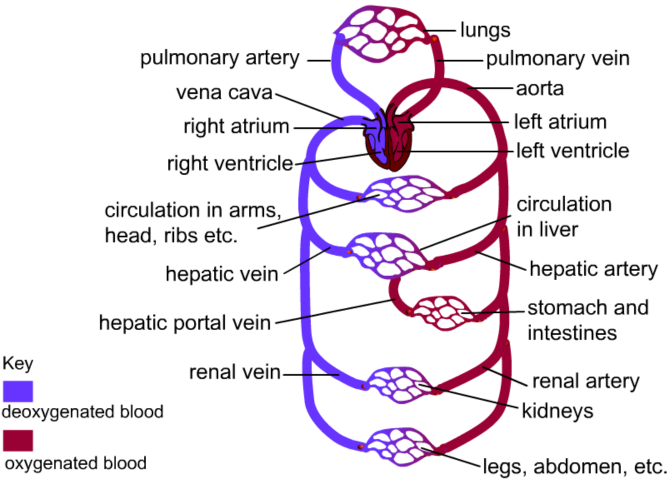
Blood
Made up of Plasma, Erythrocytes, Leukocytes, and Platelets
Erthorocytes
Carries ocygen attached to haemoglobin molecules
No Nucleus
Biconcave shaoe to increase SA
Leukocytes
Defend the body by removing debris and producing antibodies
Platelets
Aids blood clotting
Arteries
Thick elastic walls
high blood pressure as they are close to the heart
Carries blood away from the heart
The main arteries are the Aorta, which sends oxygenated blood to the body and the Pulmonary Artery, which sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs to be oxygenated
Veins
Thinner walls
Valves
Not easily stretched
Carries blood towards the heart
Decreased blood pressure
The main veins are the Vena Cavae, which carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium, and the Pulmonary Vein, which carries oxygenated blod to the left atrium.
Capillaries
Very thin walls
Highly branched and narrow
Link arteries with veins
Essential for the exchange of materials between blodd and other body cells.
Heart
Pump that keeps blood flowing
4 chambered (2 atria, 2 ventricles) and valves to keep blood seperate
Right side pumps deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary
Left side sends blood into the aorta
Valves
Stops backflow of blood
4 valves in heart
2 semilunar valves between ventricles and outgoing arteries
Tricuspid valve between right atrium and ventricle
Bicuspid valve between left atrium and ventricle
Independent Variable
What you change.
Dependant Variable
What you measure.
Controlled Variable
Kept constant.
Precision
How close repeated measurements are to each other.
Accuracy
How close your measurements are to the true value.
Reliability
Consistency of results → repeat trials increase reliability.
Validity
Whether the experiment tests what it is supposed to.
Random Errors
Unpredictable variations (e.g., timing reaction slightly off).
Reduced by repeating trials.
Systematic Errors
Bias that shifts results the same way each time (e.g., faulty scale).
Reduced by calibrating equipment.
Personal Errors
Mistakes, not true scientific errors.
E.g., reading equipment wrong.
Right Atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the vena cava
Left Atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary vein
Right Ventricle
Pumps deoxygnated blood to the lungs, via the pulmonary artery
Left Ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to the body, via the aorta