Lab Midterms Review: Safety, Techniques, and Staining
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
PPE
Personal protective equipment used in the lab.
Sharps waste
Placed into the designated sharp waste container.
Biological waste
Placed into designated biowaste container.
Regular non-hazardous waste
Placed into trash can.
BSL
Biosafety level classifications of microorganisms represent the potential of the organism to cause disease and the conditions under which the organism should be safely handled.
BSL-1
Not likely to pose a disease risk to healthy adults; no special precautions; basic teaching labs.
BSL-2
Poses a moderate risk to healthy adults; unlikely to spread throughout community; effective treatment readily available; need lab coat, gloves, and eye protection.
BSL-3
Can cause disease in healthy adults; may spread to community; effective treatment readily available; biosafety cabinets to prevent airborne transmission.
BSL-4
Can cause disease in healthy adults; poses lethal risk and does not respond to vaccines or antimicrobial therapy; sealed, negative pressure 'Hot zone'-- exhaust air is filtered twice through HEPA filters.
Ubiquity
The presence of microorganisms in various environments.
Bacterial colonies vs. molds
Bacterial colonies tend to be smooth, smaller, and vary in color, while molds tend to be fuzzy, larger, and white/gray/green.
Contamination measurement
The number of colonies indicates how many bacterial cells are present while the size of bacterial colonies shows the rate of growth.
Bacteria on skin
Bacteria on the skin is not a concern, depending on what kind of bacteria; they are a part of normal skin flora.
Microbial control on skin
Wash with body or hand soap.
Microbial control on surfaces
Use disinfectants.
Microbial control in air
Filtration by HEPA filtration system (purifiers).
Bacteria vs. eukaryotic microorganisms size
Bacteria are smaller in size and eukaryotes are larger in size.
Bacteria vs. eukaryotic microorganisms genetic material
Bacteria DNA is located in nucleotide and eukaryotes' DNA is located in nucleus.
Bacteria vs. eukaryotic microorganisms ribosomes
Bacteria have 70 ribosomes in total and eukaryotes have 80 ribosomes in total.
Bacteria vs. eukaryotic microorganisms cell wall
Bacteria cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan.
Bacteria vs. eukaryotic microorganisms respiration and photosynthesis
Bacteria lack membrane bounded organelles and nucleus, but can use organic/inorganic chemicals or photosynthesis for energy.
Bacteria vs. eukaryotic microorganisms motility mechanisms
Bacteria use flagella or pili, while eukaryotes use flagella, cilia, or pseudopods.
Agar plates incubation
Agar plates are incubated 'upside down' / inverted.
Colony
Visible mass of cells usually resulting from the division of a single cell.
Flat (Elevation Type)
Even and level with agar surface.
Raised (Elevation Type)
Slightly elevated but smooth.
Convex (Elevation Type)
Dome-shaped, gently rounded.
Pulvinate (Elevation Type)
Very convex, cushion-like.
Umbonate (Elevation Type)
Raised in the center, like a tiny volcano.
Entire (Margin Type)
Smooth, well-defined edges.
Undulate (Margin Type)
Wavy, gently curving edges.
Lobate (Margin Type)
Deeply indented, almost like flower petals.
Filiform (Margin Type)
Hair-like or thread-like strands.
Curled (Margin Type)
Rings or concentric patterns near the edges.
Circular (Shape Type)
Round and uniform edges.
Irregular (Shape Type)
Uneven, non-symmetrical edges.
Filamentous (Shape Type)
Thread-like extensions—almost feathery.
Rhizoid (Shape Type)
Root-like branches spreading from center.
Swarming (Shape Type)
Spreading motility pattern, often seen in Proteus species.
Ocular lens
The eye piece to look at specimen.
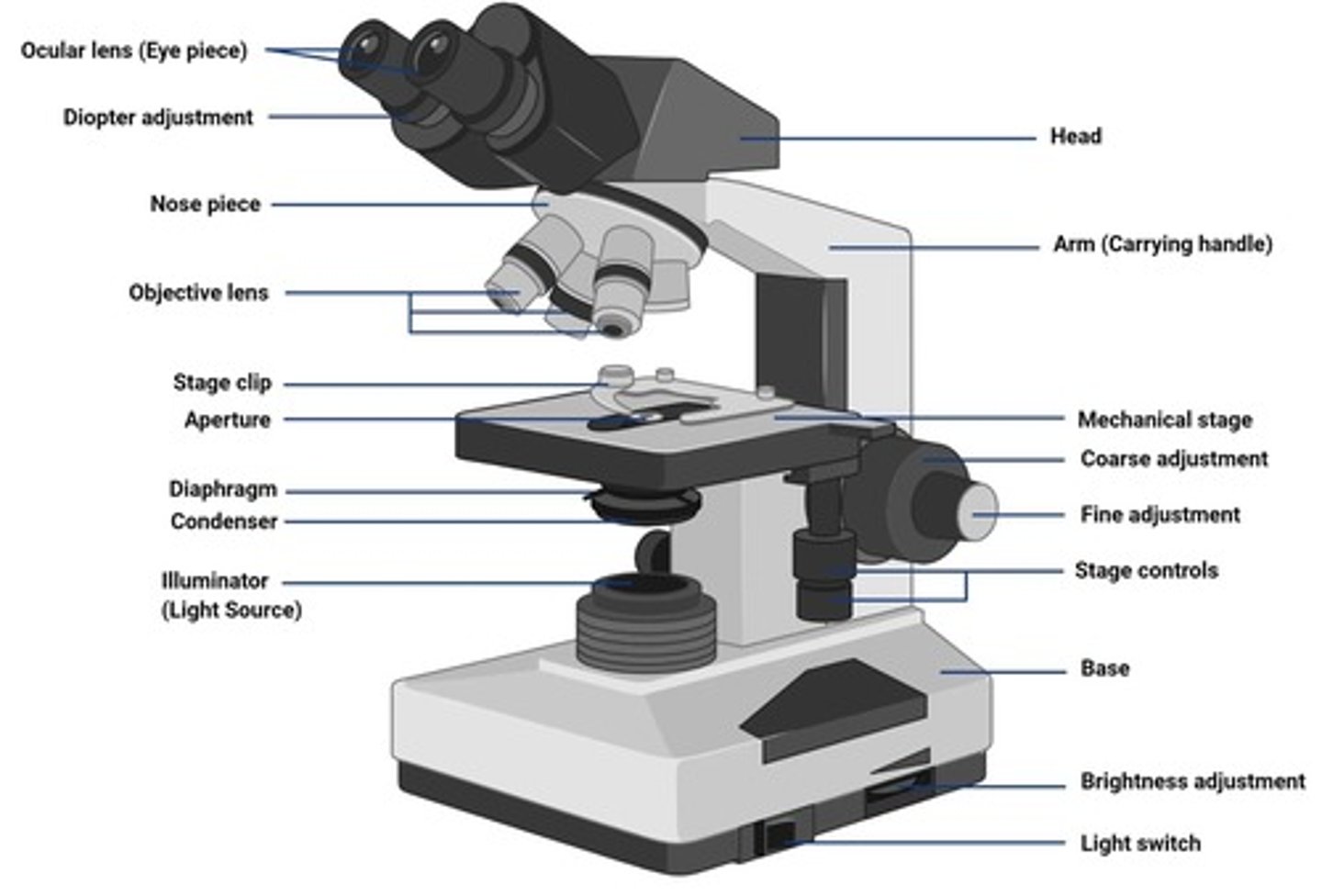
Nosepiece
The rotable piece to move the objective lens in order to switch magnification.
Objective lens
The piece that magnifies the image.
Condenser adjustment knob
Raises or lowers the condenser for optimal lighting.
Condenser
Located beneath the stage; focus light onto the specimen.
Diaphragm
Adjusts the amount of light that reaches the specimen; helps improve contrast.
Fine adjustment knob
Fine-tunes the focus for sharpness (especially with 40x and 100x objectives).
Coarse adjustment knob
Moves the stage up and down rapidly for general focusing (used with 4x and 10x objectives).
Illuminator
Supplies light that passes through the condenser, then the specimen, and finally through the objective and ocular lenses to form an image.
Aperture
Opening in the condenser (beneath the stage) that controls how much light passes through the specimen.
Limit of resolution (light microscope)
0.2 um.
Limit of resolution (unaided eye)
0.2 mm.
Oil immersion lens
This objective lens provides the highest magnification.
High dry lens
This objective lens provides the second-highest magnification.
Low-power lens
This objective lens provides the lowest magnification.
Working distance
The working distance of objective lens decreases as the magnification power increases.
Diopter adjustments
Diopter adjustments can be made to this lens.
Coarse focus knob
The coarse focus knob should be adjusted only when using this objective lens.
Immersion oil
The immersion oil forms a continuous lens system that limits the loss of light due to refraction.
Maximum resolution procedures
Blue filter placed over light source, condenser kept at the highest position, diagram should not be stopped down too much, use immersion oil between the slide and the 100x objective lens.
Starting with low power lens
It is advisable to start with lower power lens because it is easier to focus on the objective due to its big working distance.
Cleaning objective lens
Only lint-free, optically safe tissue should be used to wipe off microscope lenses.
Total magnification capability
The total magnification capability of a light microscope is only limited by the magnifying power of the lens system.
Parfocal microscope
A microscope that maintains focus when the objective magnification is increased.
Total magnification with 100x lens
The total magnification achieved when using a 100x oil immersion lens with 10x binocular eyepieces is 1000x.
Increasing image contrast
The most useful adjustment for increasing image contrast in low-power magnification is closing down the diaphragm.
Resolving power of a microscope
The resolving power of a microscope is a function of the magnifying power of the lenses, the numerical aperture of the lenses, and the wavelength of light.
False statement about acetone
Acetone is not the safest solvent for cleaning an objective lens.
False statement about coarse focus knob
The coarse focus knob can be used to adjust the focus when using any of the objective lenses.
True statement about focus
Once focus is achieved at one magnification, a higher-power objective lens can be rotated into position without fear of striking the slide.
Aseptic techniques
Set of practices used to prevent contamination, protect specimen, and protect you and others by unwanted microorganisms.
Streak plate method
A technique used to isolate individual colonies from a mixed culture.
Significance of a streak plate
Helps obtain pure colonies from a mixed culture, check culture purity, prepare for further testing, and study colony morphology.
Good smear
A thin, evenly spread of bacterial cells.
Chromophore
Color-bearing ionic groups.
Basic dye
Dyes that have positively charged chromophores; they stain negatively charged bacterial cells.
Acidic dye
Dyes that have negatively charged chromophores; they stain the background, leaving cells clear.
Difference between basic and acidic dye
Basic dyes stain negatively charged bacterial cells, while acidic dyes stain the background.
Reason for using basic dye on bacteria
Bacterial cells are negatively charged and basic dyes are positively charged, leading to effective staining.
Simple stain
Uses 1 dye to increase contrast of cells, determining size, shape, and arrangement of cells but cannot differentiate between types of bacteria.
Differential stain
Uses 2 or more dyes to differentiate between organisms or between cell structures.
Steps to improve contrast
Adjust iris diaphragm, lower light intensity, raise/lower condenser, use stains, use phase-contrast/darkfield microscopy.
Steps to improve resolution
Use higher NA objectives, use immersion oil (100x), clean lenses, proper focusing, quality slides/cover slips.
Steps for making a smear from liquid media
Place loopful of culture directly on slide, air dry smear, heat fix.
Steps for making a smear from solid media
Place dot of water on slide, mix dot of water with colony of bacteria, air dry, heat fix.
Purpose of a streak plate
Isolate individual colonies and check culture purity.
Observation of pure colonies
You can tell if a culture contains only one species based on uniform colony appearance.
Uses of pure colonies
Can be used for gram staining, biochemical testing, or DNA analysis.
Characteristics observed in colony morphology
Shape, color, size, and texture of different bacteria.
Gram stain purpose
To differentiate bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative.
Gram negative stain result
Pink.
Gram positive stain result
Purple.
Crystal violet
Primary stain that stains all cells purple (30 secs).
Iodine
Mordant that forms CV-I complex to fix dye in thick walls (1 min).
Alcohol/ethanol
Decolorizer that removes stains from Gram-negative cells (5-15 secs).
Safranin
Counterstain that stains Gram-negative cells pink/red (1 min).
Spore stain purpose
To detect the presence of endospores.
Spore staining results
Spores - Green (retain malachite green) & Vegetative cells- Pink/red (stained with safranin).
Malachite green
Primary stain used in spore stain.
Negative stain purpose
To observe cell shape and size without distortion and to highlight capsules (if present).
Negative stain results
Background: Dark. Cells: Appear clear or light-colored against the dark background. Capsules (if present): Appear as halos around cells.