BU111 Study
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Steps for breaking down individual/household type problems(ex size of cell phone market in Can)
Population(either individual or household)
Characteristics of the population = % of population x purchase frequency x purchase quantity x unit cost
Ex.
Canadian population = 40mil
Percentage of people using cell phones = 86% = 34.4m people
Purchase frequency(replacment) = 17.2m
Unit cost = 900
People with 2 cell phones(5%) = 0.86m
Total purchasers = 17.2 + 0.86 = 18.06m
Total MV = 18.06 × 900 = 16.25B
Revenue Breakdown
Revenue per day/store/customer → Number of days/stores/customers → multiply to get total revenue
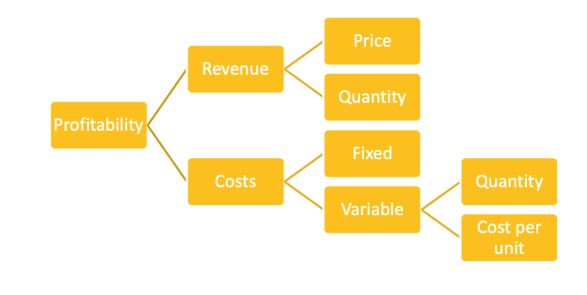
Profitability Framework
Common Knowledge
Canadian Population: 40 Million
Average members per household: 2.5
Average life expectancy: 83 years
Median household income: $61,400
Smartphone penetration: 86%
Online shopping: 28.1 Million people
Cohort distributuion: 15 -(16%), 15-19(6%), 20-25(7%), 25-40(21%), 40-65(33%). 65+(17%)
Opportunities and Threats of Tech
Opportunities: Product innovation, product uniqueness, improved access and sharing
Threats: Imitation(information is costly to develop but cheap to share), disconnection between employees and customers, new tech and entrants in unfamiliar areas
Installed base
number of users
Lock in
The extent in which customers are committed to a product
Switching costs
Expenses that make it difficult for customers to switch from one product/service to another
Complementary goods
2 goods that are used/consumed together and boost each others’ value
Technology standard
enables the compatibility of complementary goods
Network effect
when an increase in user base causes the increase in value of a product/service(ex. social media)
Vicious/Virtuous cycle
Availability of complementary goods → Attractiveness to users → Number of users(installed base) → Attractiveness to producers of complementary goods(Note: like a circle with no beginning)
4 Innovation types and challenges(for large firms) they create
Sustaining: Improves existing products in expected ways and targets mainstream, high margin customers → little no knowledge or structural challenge
Disruptive: targets different performance attributes not valued by mainstream, starts in lower performance segments and improves rapidly then enters mainstream → significant structural and knowledge challenge
Modular: Keeping the same system but changing/improving specific aspects(new camera each year on iphone) → significant knowledge challenge
Architectural: taken existing parts/components and combining them into a new innovative product/service(ex. iphone connecting blackberry’s flip calling with music playback, and internet.) → significant structural challenge
Tactics for small companies to succeed
Target Niche markets(use disruptive innovation, develop, then move up to mainstream to compete with incumbents)\
Once they develop and take over mainstream they are at a high advantage as large firms do not have the structural flexibility to adapt quickly to changing trends in the market
Tech impact on industry profitability using Porter’s 5 forces
Rivalry among existing competitors:
Online price comparison with in person, comparisons with online purchasing(ex. fees, shipping),
Threat of new entrants:
Allows for innovation and differentiation among products/services making it hard for newcomers to replicate
Bargaining power of buyers:
Online price comparisons and reviews make it easier for buyers to compare choices
Bargaining power of suppliers:
Unique chip or IP can allow suppliers to demand more money from large companies who rely on them for their products
Threat of substitues:
Constantly creates new substitutes → streaming vs. cable, taxi vs. uber, newspaper vs. online news
Importance of understanding demographics to business
Powerful predictor of behavior/trends
Predicts supply demand
Cohort work and consumer implications(characterics)
Boomers(1946-1964): prefer in person transactions, long hours in office, 1 career
Gen x(1965-1979): research online → buy in person, brand loyal, flexible work, perfect career
Gen y(1980-1994): digitally savy, quality brand, want authenticity, seek work-life balance, want to have multiple careerss, access>ownership
Gen z: digitally savy, value uniqueness, want to “know” the brand, frugal/avoid debt, work-life balance, several careers
Factors that influence demographic characteristics
Economics, Tech, World events/news, Parenting
Demographic characteristics
values/priorities, lifestyle, habits(digital etc.), mindset
Implications of characteristics
How to attract, retain, motivate/What makes a product appealing/How much they spend and what categories they spend on
Government influence over business
Taxation: income, corporate, sales, property
Laws and regulations: rules around competition, pollution, intellectual property(IP)
Business support: help small businesses through subsidies, funding, trade agreements
Service provider: provides essentially serves(ex. mail/shipping, education, healthcare)
Business influence over government
Lobbying: hired to represent company’s interest, small businesses/individuals join and lobby as an industry lobby group
Advertising: corporations influence voters
Collaboration/input: CRTC consults with industry memebers
Sole proprietorship
Unlimited liability, sole owner, easy and inexpensive to start, all control
Partnership
Unlimited liability, multiple owners, easy and inexpensive to start, less control
General partner: tied liability with the business, decision power
Limited partner: limited liability, no decision power(can only lose what they put into the business)
Joint vs. Several Liabilityy
Joint: shared liability
Several: one person may be liable for all
Social Enterprise
Tradition market: companies only goal is to generate profit for wealth
Social enterprises: Can help with areas that traditional market missed such as education, healthy, and poverty to do something good for society
Globalization(definition, driving forces)
Def: World becoming a single interdependent system(different countries rely on the resources of one another via trading)
Driving forces: Cost and market benefits, tech makes it easier, faster, and cheaper, competitive pressure
Factors to identify where to expand internationaly
larger population → bigger potential market
average income/spending
competition: less is better
customer reachability: is it something that people in that area are interested in
Foreign Entry strategies(How?)
In order from least to most risky: Indirect export, sales agent/distributor, licensing and franchising, joint venture, sales office, foreign subsidiary
Indirect export
Def: sell to third party export merchant in own country
Why: no additional cost, no required market knowledge, export experience, or new infrastructure needed
Sales agent/distributor
Def: hiring an agent/distributor from that area to sell our product using their local network and you manufacture and ship abroad
Why: no resources/knowledge to tap into the foreign market with the agent’s knowledge
Risks: subject to trade barriers(ie. tarrifs), limited marketing control
Licensing and Franchising
giving a local organization the right to use your intellectual property(brand, patent, copyright) in exchange for royalties
Why: faster and larger expansion with fewer financial resources, no need to overcome trade barriers
Risks: damage to intellectual property
Joint Venture
Def: partner with a local firm for mutual benefit; mutual distribution, sharing knowledge, investment
Risks: time, personnel, money, difficult to break up if partnership doesn’t work out
Sales office
Def: establish your own office but ship abroad while manufacturing in your own domestic market
Why: retain market control, insufficient volume to justify facility, don’t want to take any risks(yet)
Risks: trade barriers, no market knowledge
Foreign subsidiary
Def: manufacture and sell in a foreign market
Why: overcome trade barriers, control of intellectual property and marketing, highest risk comes with highest reward
Risks: cost of facility and establishments of operations, sometimes need permission of foreign government
Diamond E
Logic: Internal consistency = good execution/External alignment = right strategy for environment
Management Preferences: vision, mission, preferences and biases
Organization: culture - who are we, capabilities - what are we good at, structure - how do we divide work
Resources: human capital financial(do we have enough money)
Strategy: plan business uses to pursue operatives and avoid threats
Ansoff matrix models(from leas to most risky)
market penetration(same product same market), market development(same product different market), product development(same market different product, diversification(different market and product)
Market Penetration(pros, cons, tactics)
Pros: build on what you have knowledge and resources for(low risk)
Cons: doesn’t leave much room for growth especially for companies already doing well in their current market space
Tactics: cut prices, advertising, increase distribution channels, volume incentives, buying competitors
Market development(description, tactics)
→ Keep what you have and expand to more markets(ie. more geographic locations or age/gender cohorts)
Tactics: spread awareness to new markets, use international expansion knowledge to expand internationally
Product development(description, tactics)
Description: stay in the same market but either change your product our extend your product line
Tactics: extend product line, replace existing products, create bundles of existing products that add value to each other(complementary)
Diversification(description, tactics)
Description: chase new customers with new products, create new businesses
Tactics: acquire other business, use joint ventures, alliances and other forms of collaboration