Mid-Term Exam Study Guide - Designer Genes
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Genes
Segments of DNA that encode functional products, usually proteins
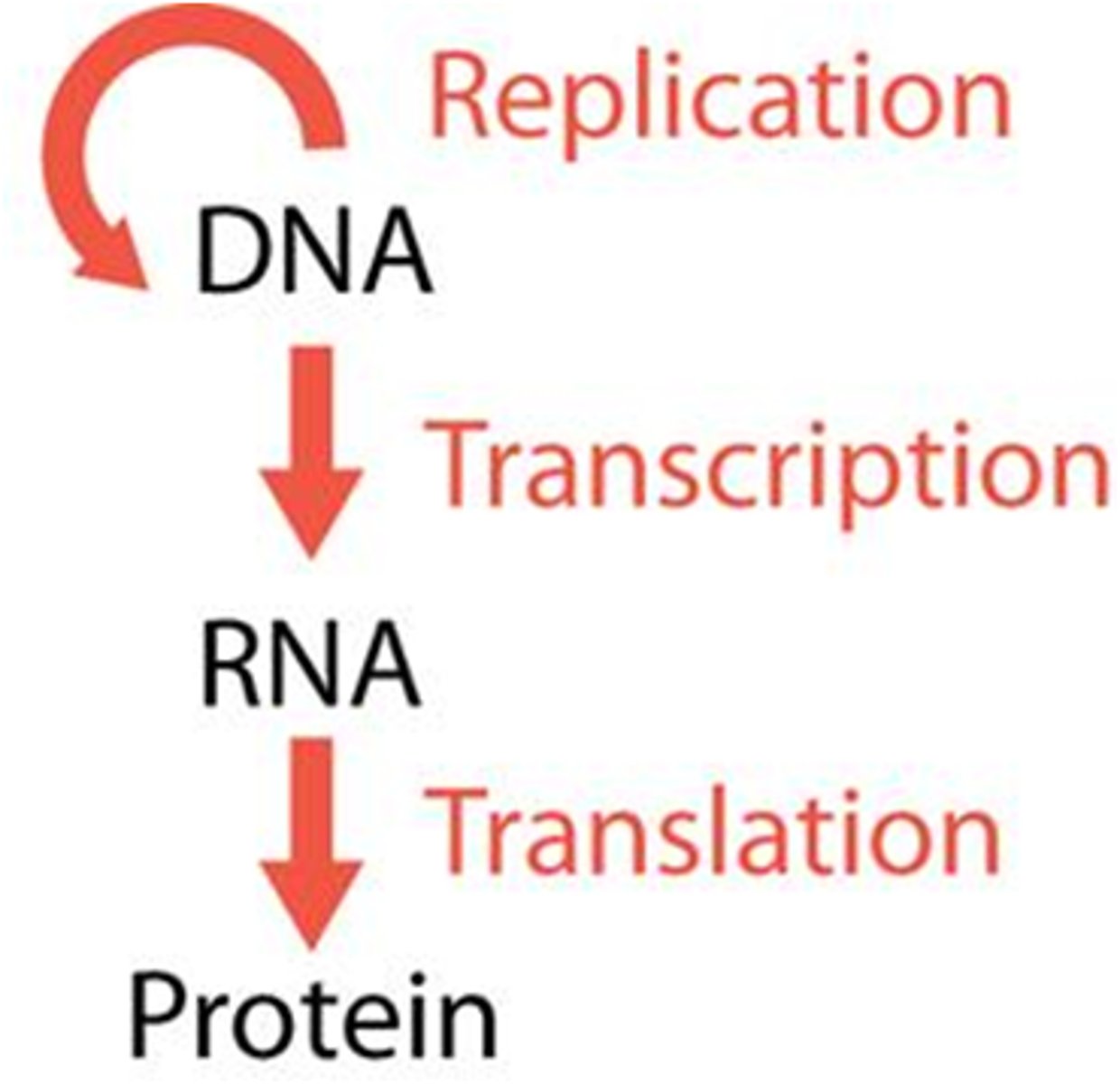
Central Dogma
DNA --transcription--> RNA --translation--> protein
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism
Phenotype
Expression of the genes
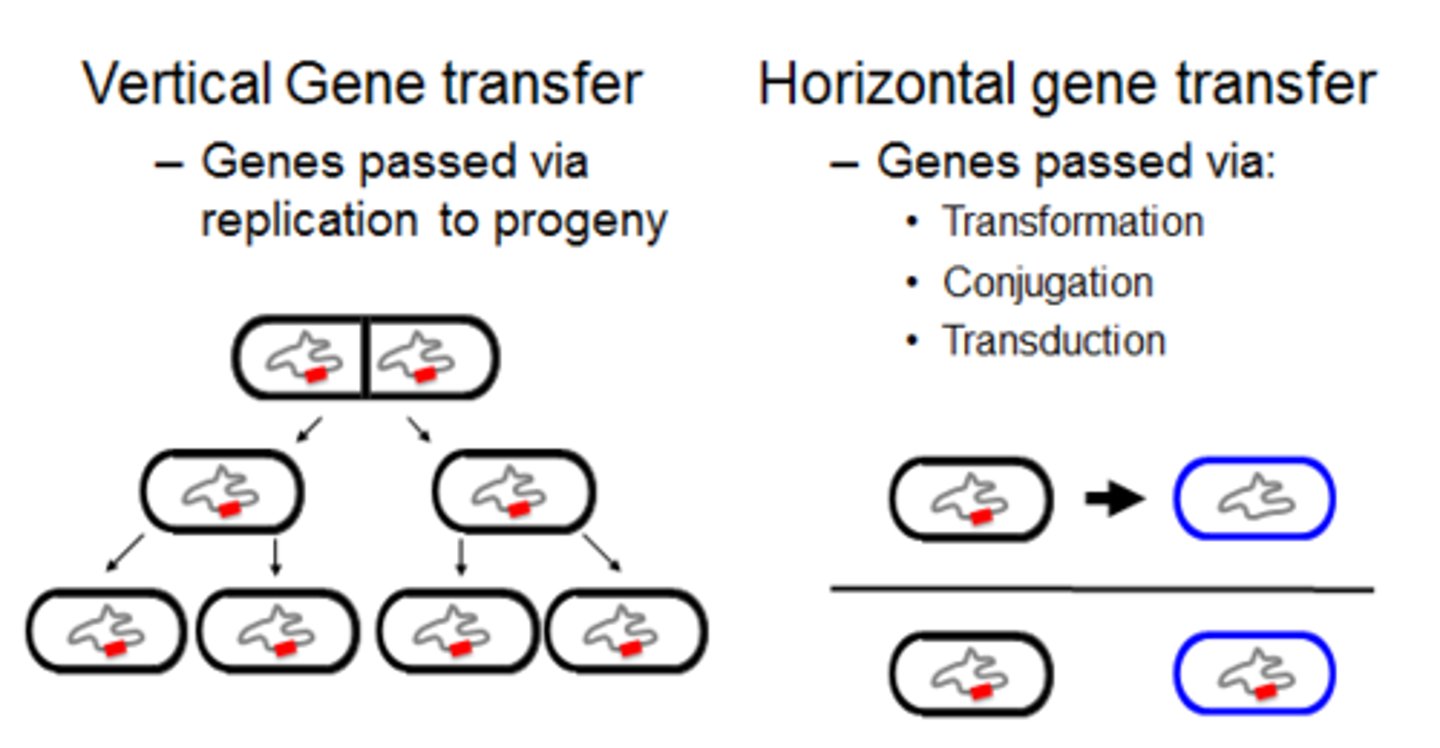
Vertical Gene Transfer
Flow of genetic information from one generation to the next
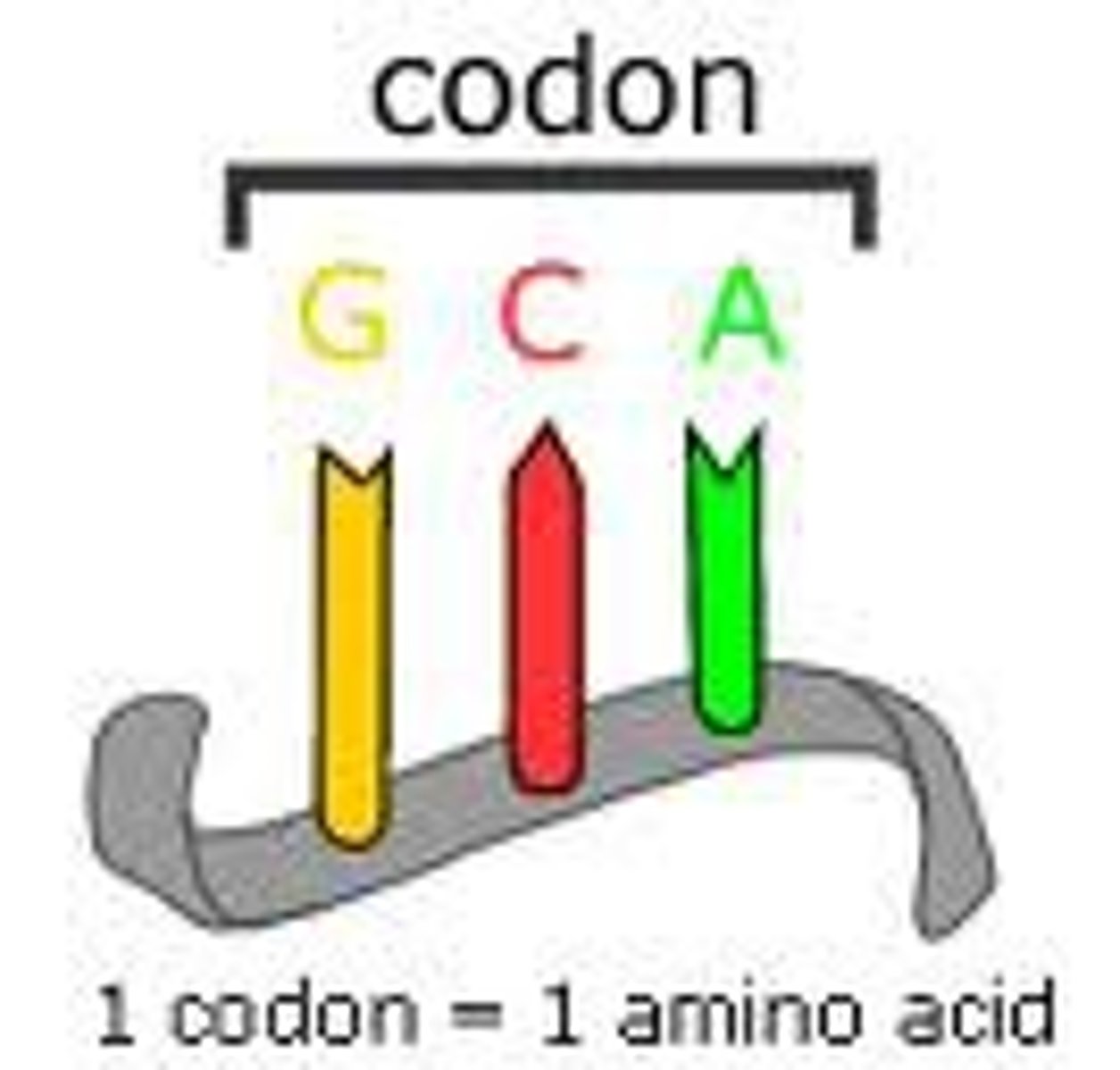
Codons
A three-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code
Mutations
Changes in the sequence of DNA
Homozygous
Two identical alleles for a trait
Dominant or recessive
Heterozygous
Two different alleles for a trait
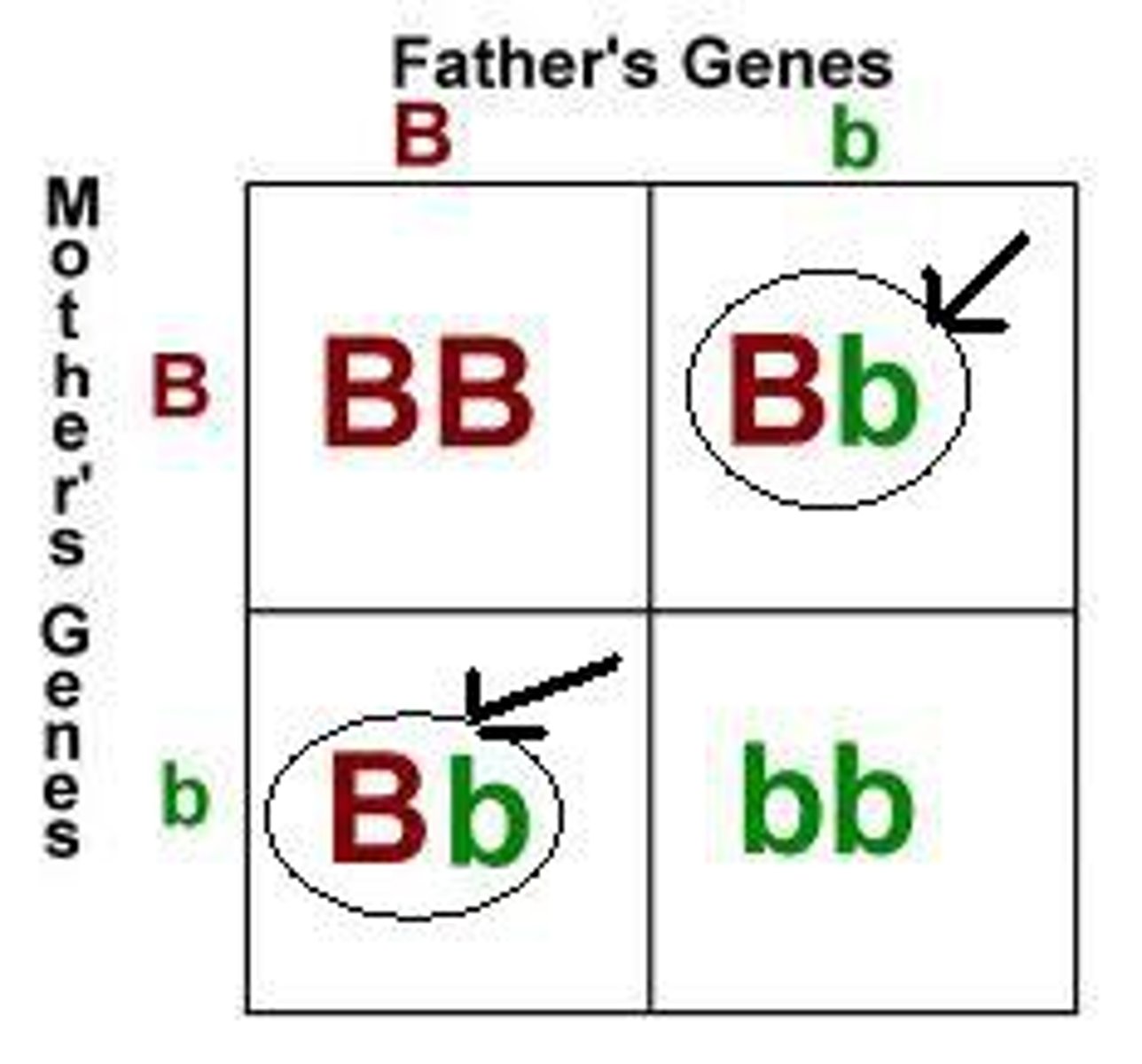
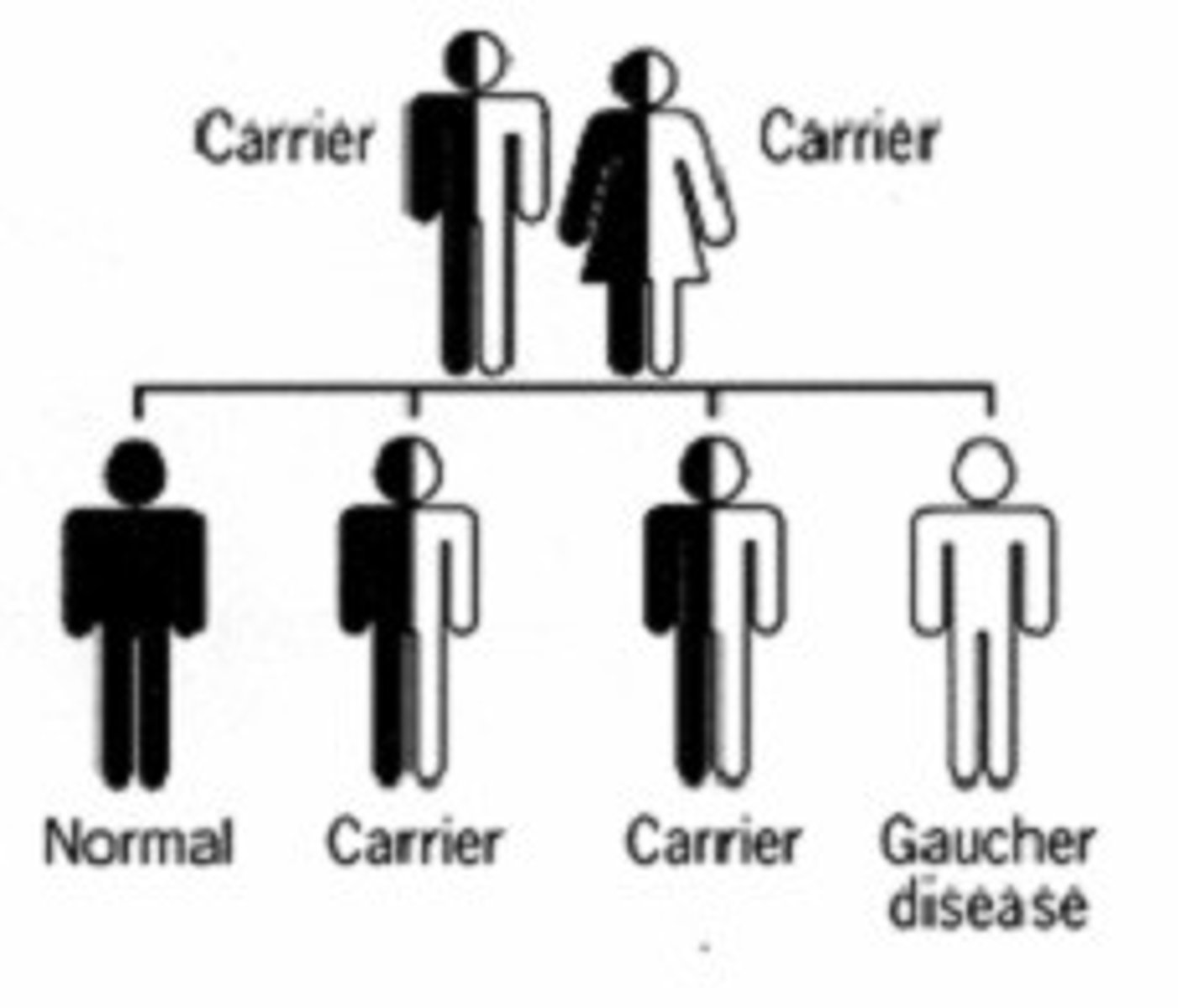
Carriers
Heterozygous individuals who carry the recessive allele but are phenotypically normal
Theory of Consequentialism (Utilitarianism)
-Places greater emphasis on the well-being of the group than that of any individual group member
-Creates the greatest good for the greatest number of people
Theory of Deontology
-The right thing to do is that which fulfills one's moral obligations or duties
-De-emphasis on the impact or consequences of the decision
Theory of Rights
-Identify which specific individuals and social rights are at stake
-Focus on the moral centrality (entitled to have) of the individual in the situation
Theory of Intuitionism
Ethical dilemmas can be resolved by appealing to one's intuition about what's right
Theory of Justice
-Each person should act fairly toward others in order to maintain the bonds of community
-Principles of equality are integral to any normative theory of obligation
Ethical Altruism
Bases its obligations on the good or bad produced for others
Contextual Theories
Importance of contextual factors in determining ethical defensibility
Case-Based Reasoning
A method whereby new problems are solved based on the solutions from similar cases solved in the past
Christian Ethics (Virtue Ethics)
A framework for living a moral life by cultivating virtues such as faith, hope, and love
Salesian Spirituality
-A practical, joy-centered, and accessible approach to holiness named after St. Francis de Sales
-Characterized by the "little virtues"
Autonomy
Acknowledge people's right to make choices for themselves based on their own values and beliefs
Beneficence
Remove harm, promote good
Nonmaleficence
Duty to do no harm
Justice
Treat others equally and fairly
Distributive Justice
The perceived degree to which outcomes and rewards are fairly distributed or allocated
Informed Consent
Adults
An ethical principle that research participants be told enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
Informed Assent
Minors
Participant's agreement to participate in the absence of full understanding
Commonly applies to individuals who have not attained legal majority and/or capacity
Ethical Analysis
-Clarify reasoning
-Identify logical inconsistencies
-Determine strength of argument and its rationale
-The right thing to do is not always fair
Ethical Analysis Example:
Mother steals food from the store to feed her starving children. Should she be punished as severely as someone who loots from a store during violent protests?
Principles of fairness
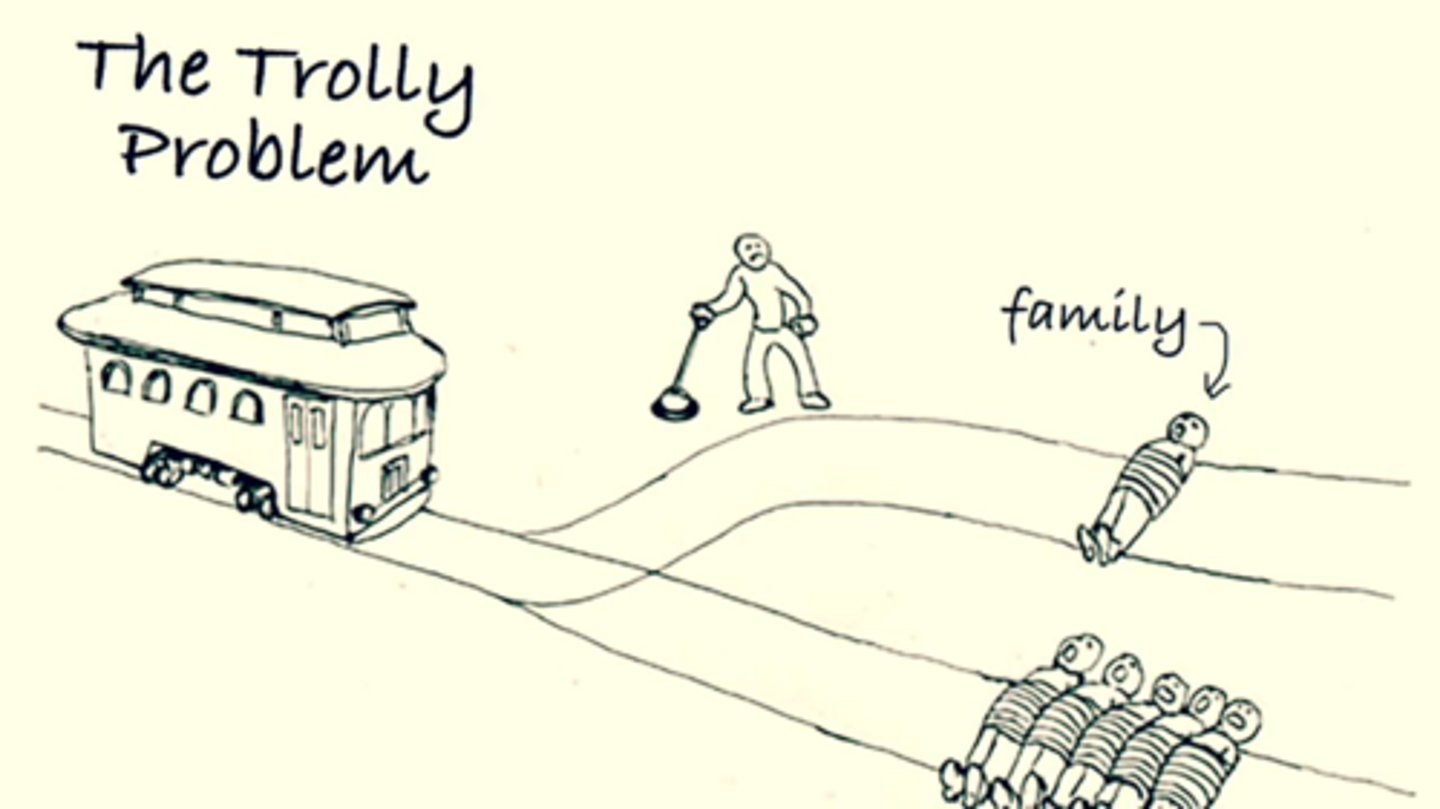
Ethical/Moral Dilemma Example:
A situation in which Agent T believes they morally ought to do action A and B. Agent T can't do both actions A and B, because B is opposed to A is some way or because the situation prevents it.
Trolley problem or murder burger
Scientific Reasoning
Inductive reasoning -> makes generalizations about observations
Immutable, objectively verifiable

Ethical Reasoning
Normative reasoning
"Ought" to do
Eugenics
-The desired improvement of humans' genetic endowment over time (select against undesired traits)
-Improve mankind by applying a knowledge of heredity to social problems

Genetic Screening
Widespread testing of persons having a specific genotype without attention to or knowledge of their family history
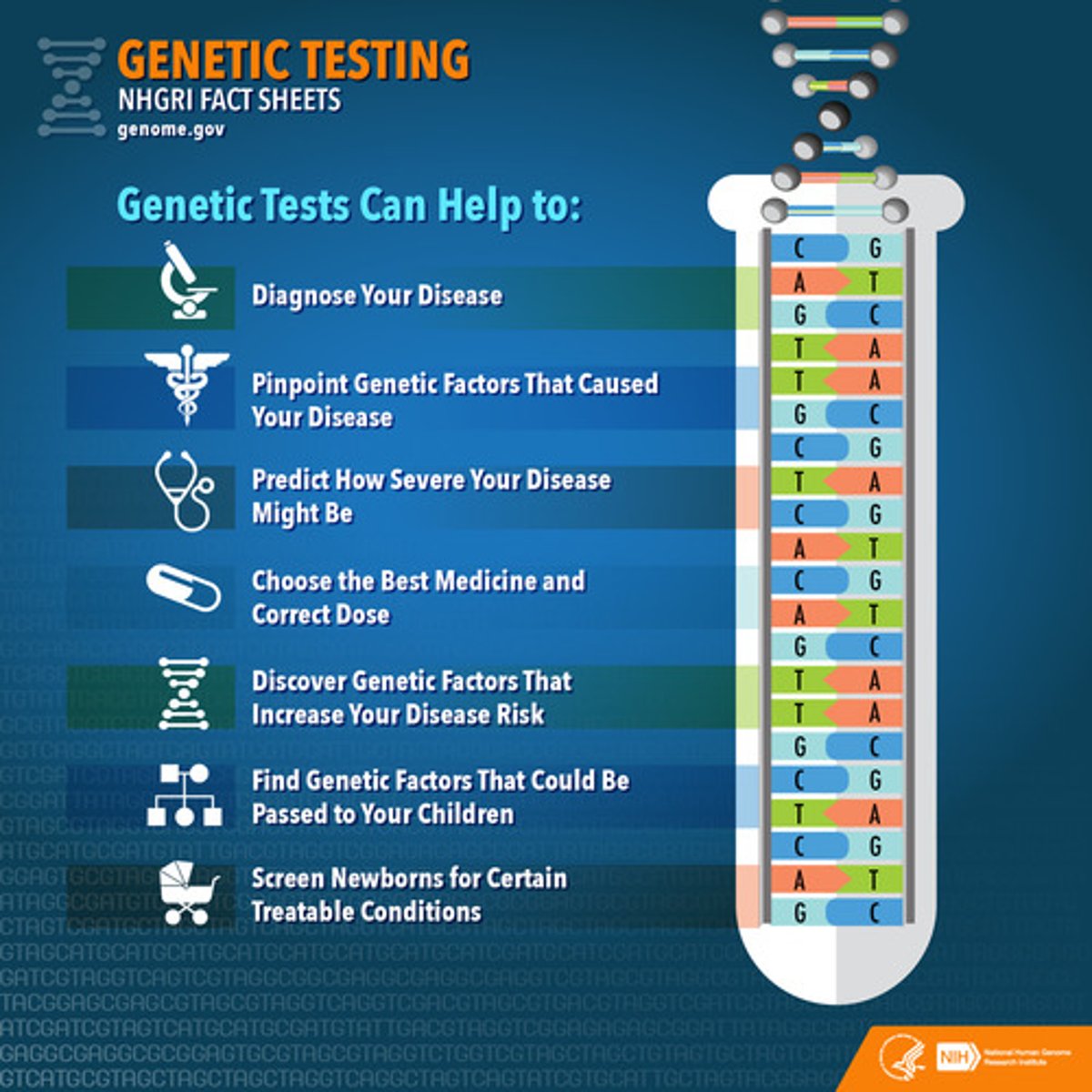
Genetic Testing
-Data about an individual's genetic make-up (DNA!)
-Predictive -> can't tell an individual when they'll develop a disease or how severe it will be
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
The extent of federal protection against genetic discrimination is unclear, and limited at best. The federal courts are divided on the scope of protection of the ADA, particularly for employees who have not yet manifested symptoms of illness. The ADA addresses workplace discrimination, but not privacy. There is no current federal law which prohibits an employer from requesting genetic information or testing employees, and no law protecting the privacy of genetic information
Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA)
-Law prohibits health insurers from denying coverage or raising premiums based on genetic information
-Employers can't use genetic information for hiring, firing, or promotion decisions
-Only apples to individuals on group health insurance plans; persons with an individual health insurance plan, or those employed by a small business of 15 or fewer people, are exempt
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
-Safeguards all patient information -> medical + demographic
-Protects in all forms -> written + electronic
Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
-Protects the privacy of student records
-Must have student consent to release
-Includes date and place of birth, addresses, and emergency contact information -> special education records, medical and health records that the school creates or collects and maintains
Pharmacogenetics
Branch of pharmacology concerned with the effect of genetic factors on reactions to drugs
Nature
The influence of our inherited characteristics on our personality, physical growth, intellectual growth, and social interactions
Nuture
The influence of the environment on personality, physical growth, intellectual growth, and social interactions
Stem Cells
A single cell that can replicate itself or differentiate into many cell types
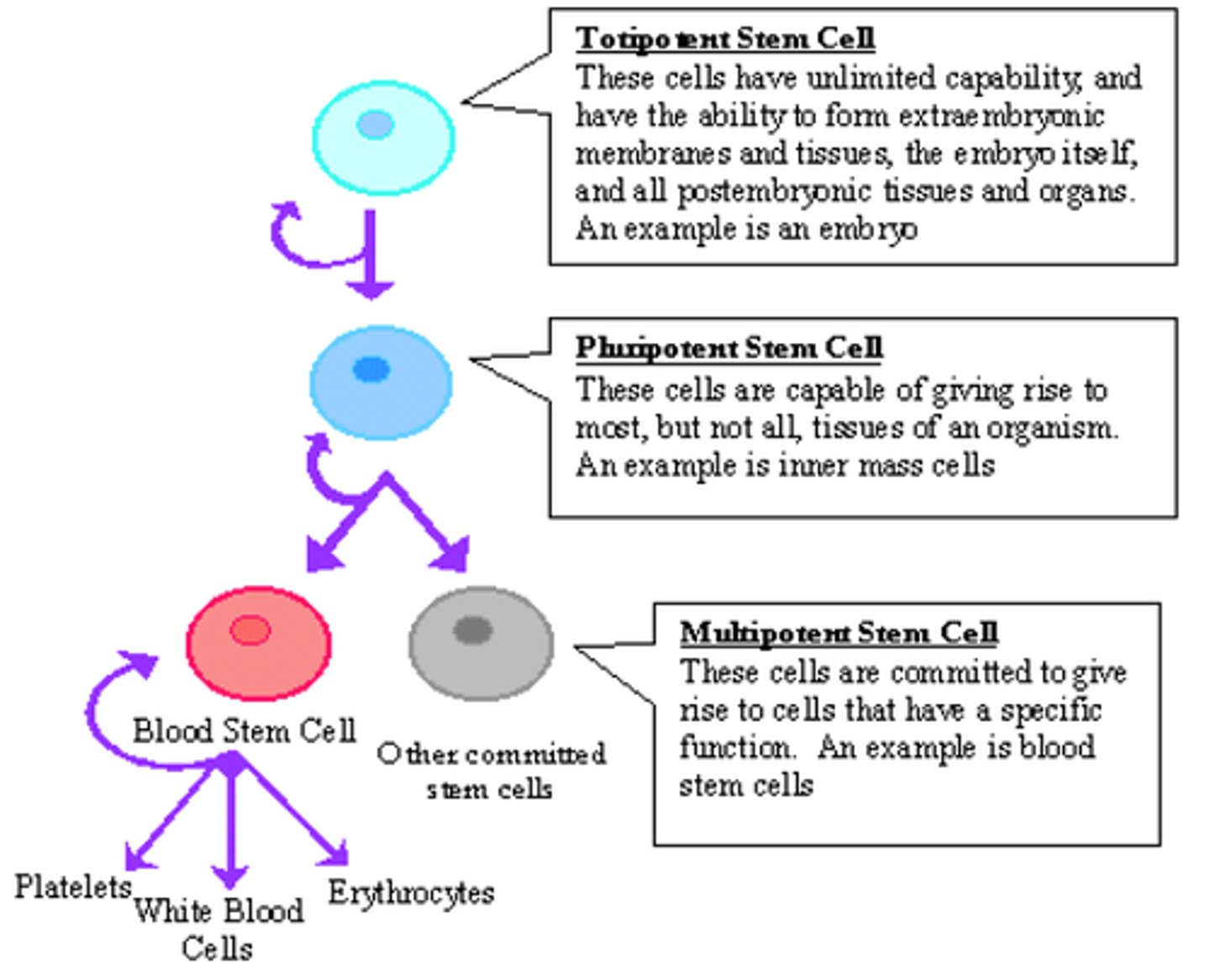
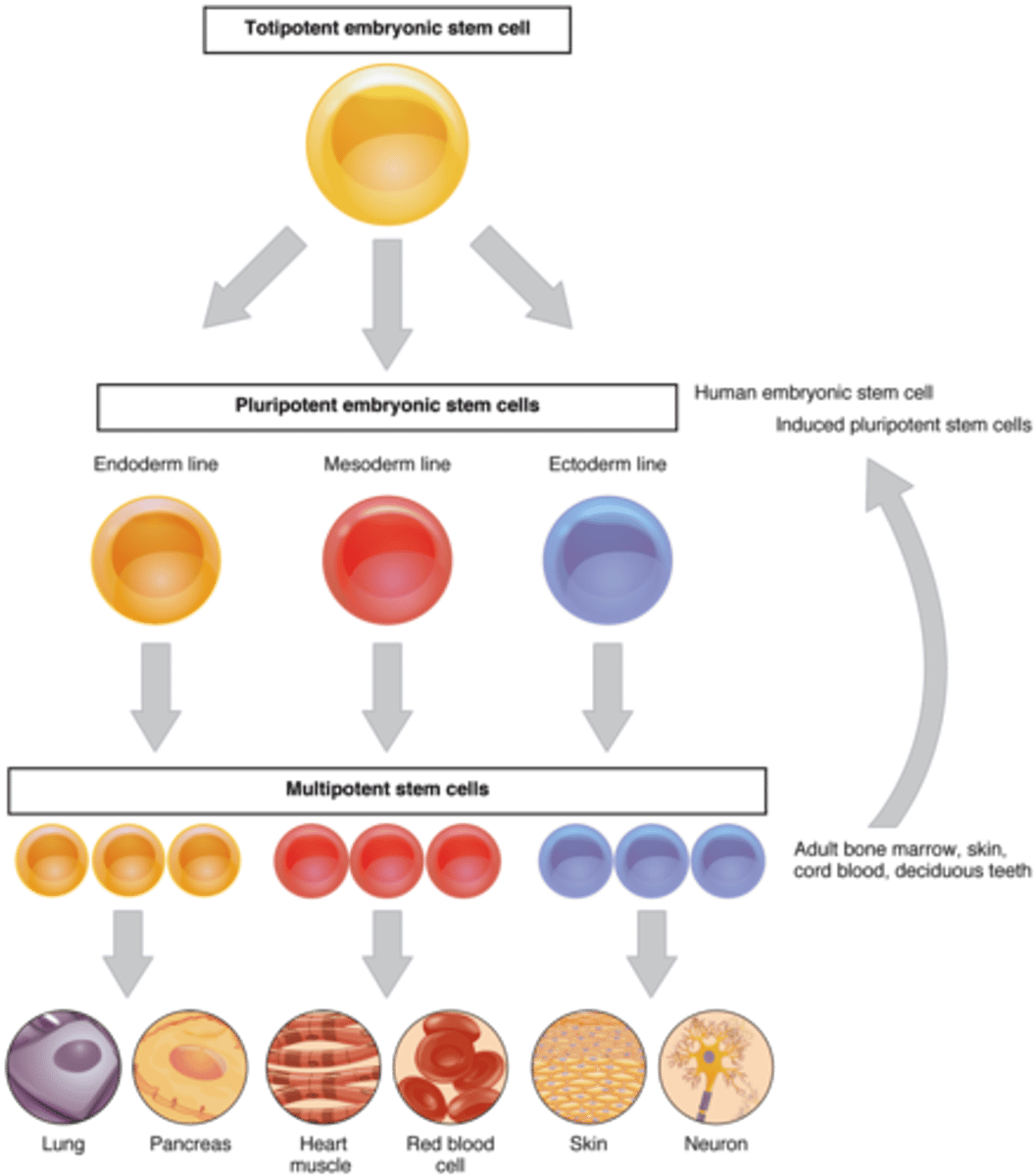
Totipotent Stem Cell
-Capable of "self-renewal"
-Divide and develop into 3 primary germ layers of early-embryo and placenta
-Fertilized egg
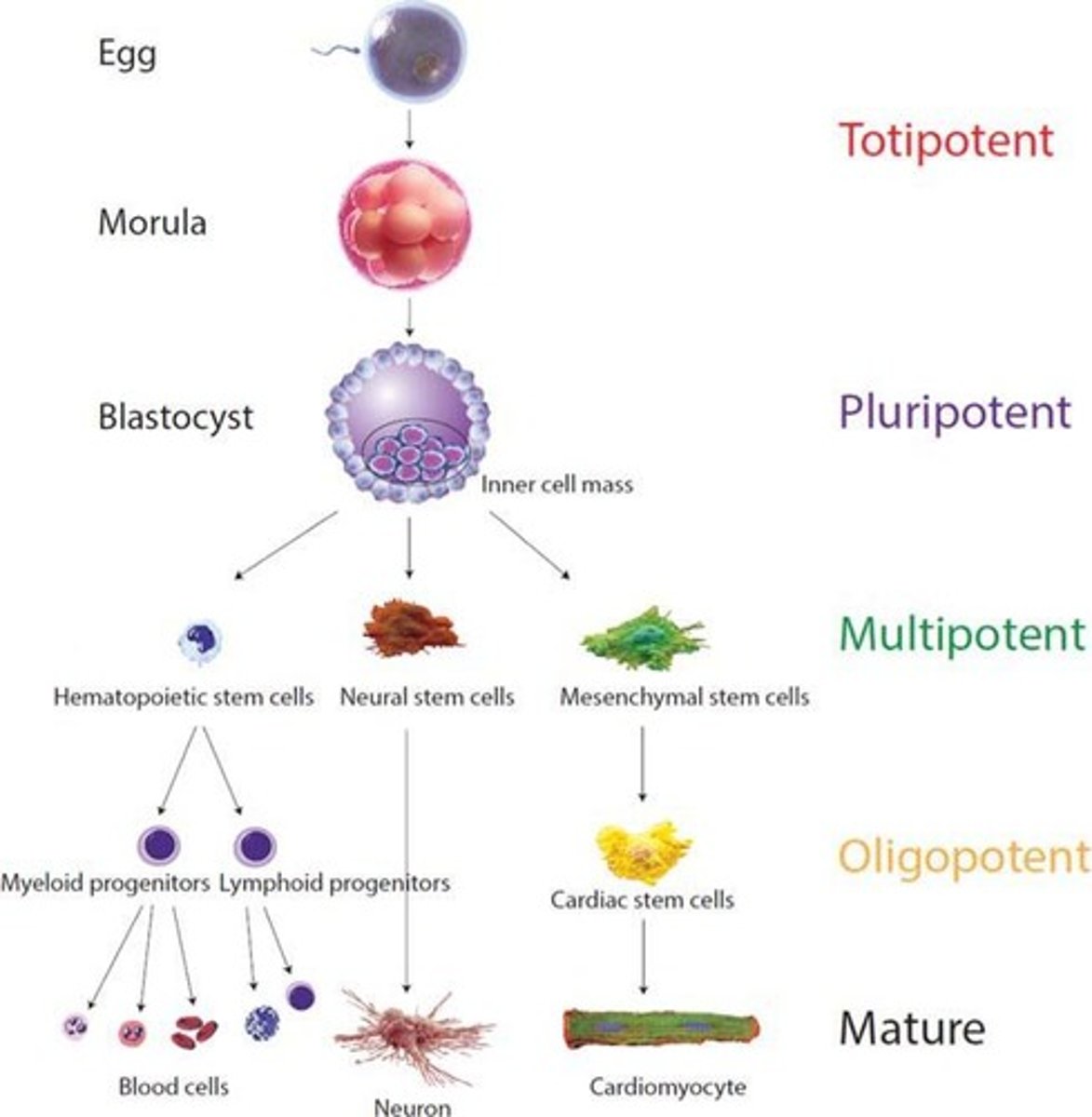
Pluripotent Stem Cell
-Capable of "self-renewal"
-Differentiate into all cells of the body
-Embryonic stem cells
-Considered most powerful for curing disease
Multipotent Stem Cell
-Capable of "self-renewal"
-Differentiate into diverse cell types that specify a particular tissue
-Adult stem cells
-Hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells
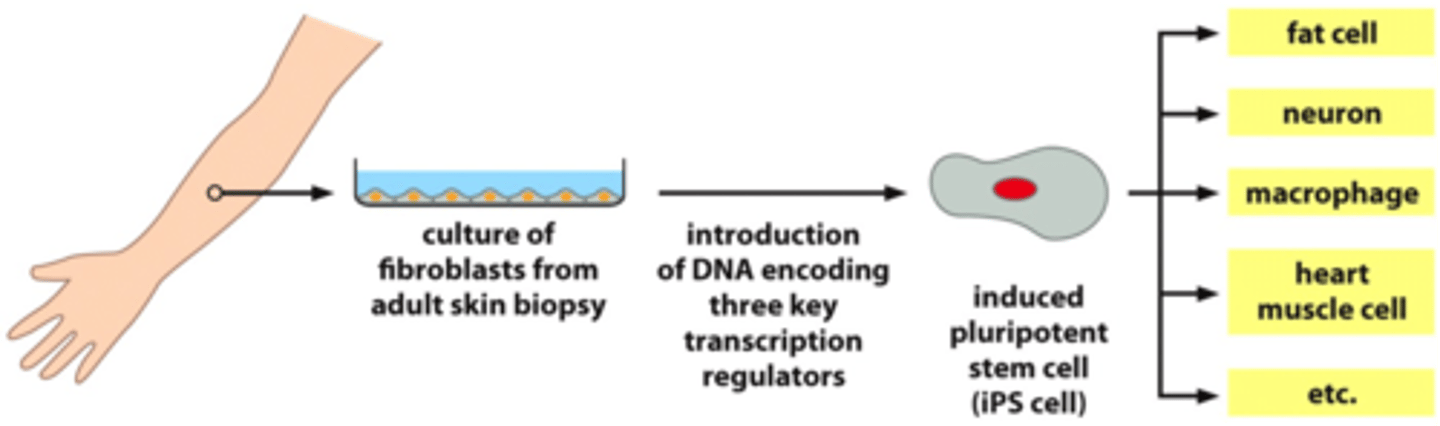
Induced-Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPS Cells)
-Genetic match to patient
-Pluripotent stem cells created by reversing the differentiation of a non-pluripotent cell
-Virtually identical to embryonic stem cells
-Avoid the need to destroy embryos
Jesse Gelsinger Case
-Died in a clinical trial -> first person to die of complications resulting from gene therapy
-Complications related to the adenovirus that was used
-Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (ability to break down dietary amino acids)
-Doctors omitted previous information -> failure to disclose monkeys died with similar therapy and sponsor and investigators
-Jesse's condition was managed well with medications
Abuse of Genetic Information
-Problem of who gets access to this information and why/when
-If genetic tests are available to insurers, will they misuse those tests?
Railroad Company and Carpal Tunnel - Abuse of Genetic Information
Railroad company was looking for genetic markers for carpal tunnel syndrome in its workers who filed for workers' comp after they claimed that their carpal tunnel syndrome came from operating BNSF machinery
Conflict of Interest
A situation in which a person in a position of responsibility or trust has competing professional or personal interests that make it difficult to fulfill his or her duties impartially
Logical Fallacy
An error in reasoning that renders an argument invalid
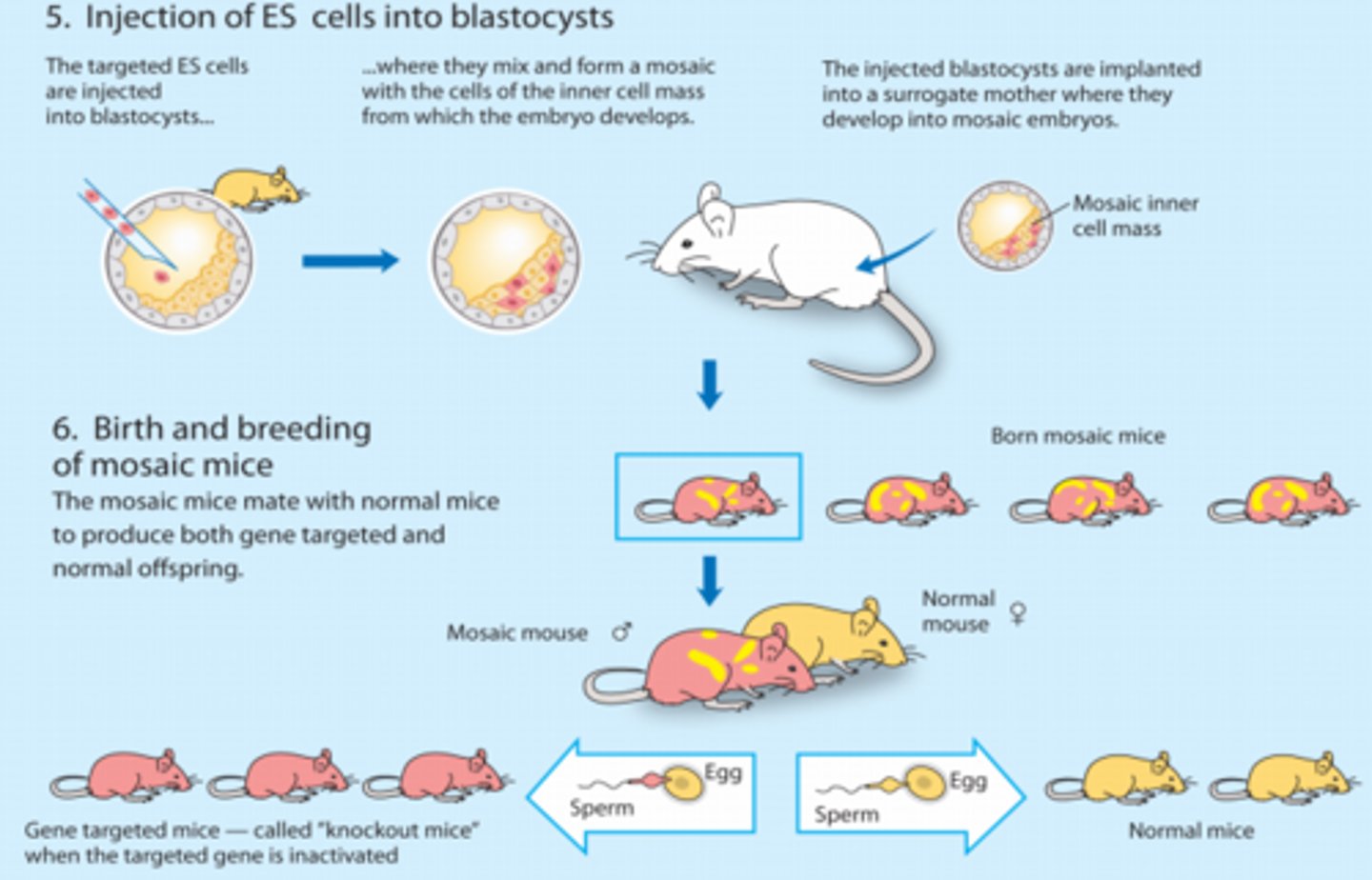
Mosaic/Chimera
An individual composed of two or more genetically different cell types -> some cells are modified, some are not
How is a chimera/hybrid produced?
Created desired version of gene:
-De novo synthesis using DNA-synthesis machine
-Purified copy of gene and make desired changes using recombinant DNA techniques
Introduce gene into stem cells in vitro:
-Electroporation
-Recombination with target gene must occur
-Induce selective markers for screen successful recombination
Turn the stem cells into babies:
-Stem cells injected into blastocysts
-Blastocyst implanted into surrogate mother -> develop into mosaic embryos (chimeras)
-Mosaic (chimera) mice born
-Must mate mosaic mice with normal mice and screen for mice expressing only modified gene
Autism in Iceland
-Iceland is eliminating autism through prenatal testing
-Most embryos that are likely to have autism are aborted
CRISPR - Editing Genes
CRISPR/CAS9 is used by bacteria to fight off phage infections
-Genetic sequence ("guide RNA") matches a piece of DNA they want to modify
-Sequence added to a cell along with a protein called Cas9 (acts like a pair of scissors that cut DNA)
-GUide RNA homes in on target DNA sequence and Cas9 cuts it out
-Another piece of DNA is swapped into the place of the old DNA and enzymes repair the cuts (edited DNA!)
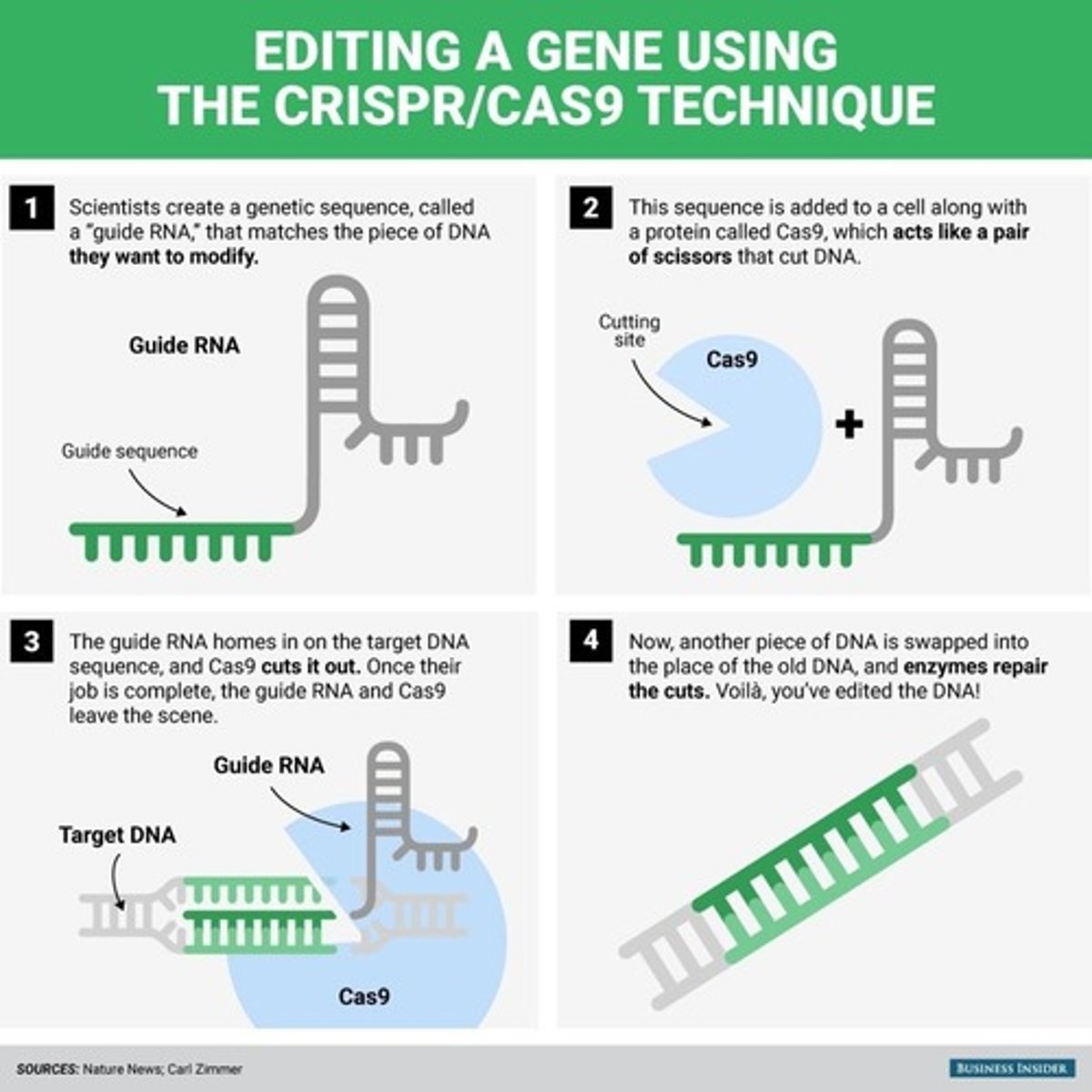
CRISPR Applications
Fuel, food, materials, rapid genetic studies, gene regulation, drug development, gene therapy, designer babies
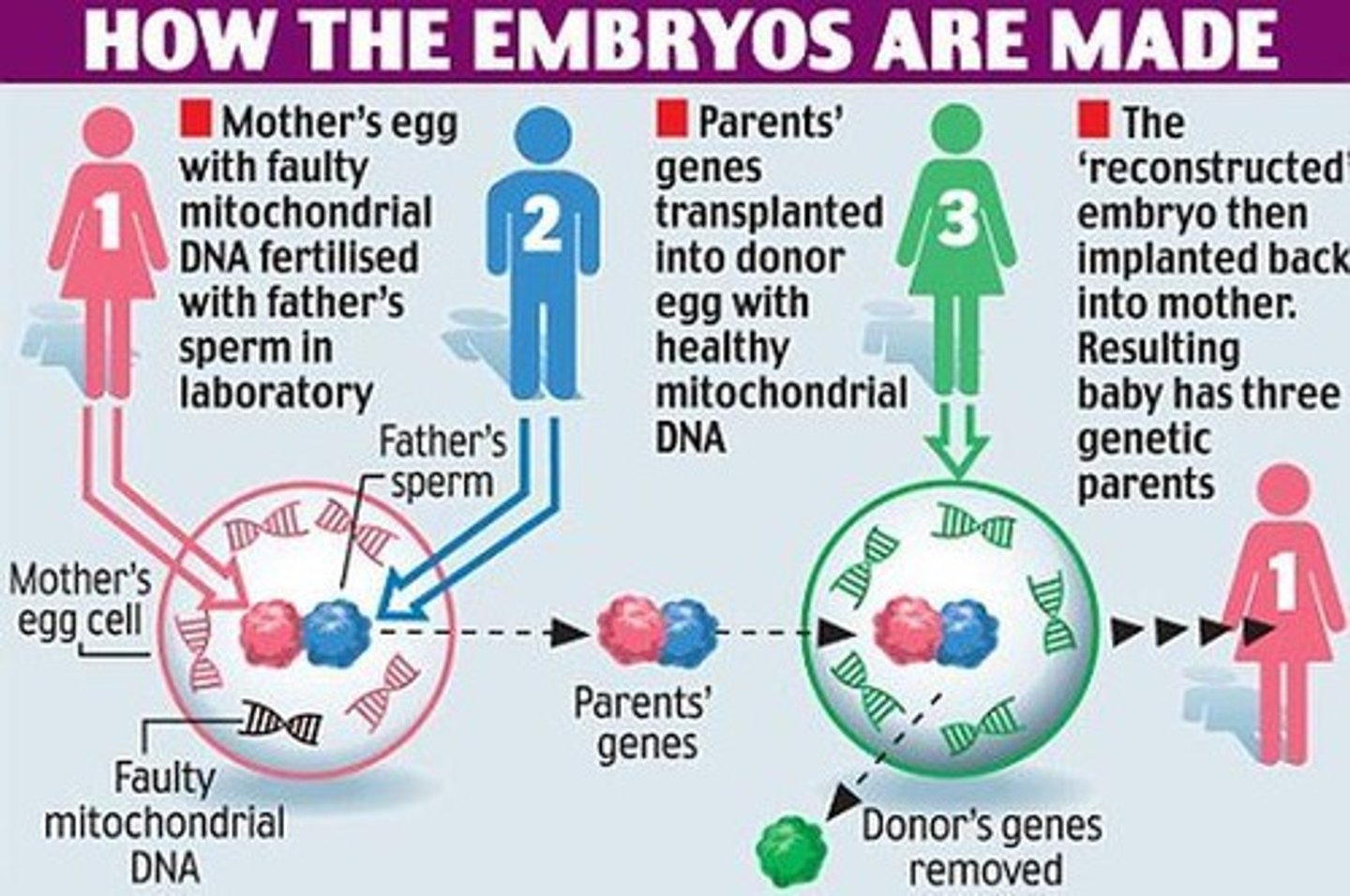
Designer Babies
Original designer baby -> throuple, making a three-parent embryo -> nuclear DNA from patient's egg (1) transplanted into donor egg with healthy mitochondrial DNA (2), reconstructed egg cell fertilized with sperm and implanted into patient (3)
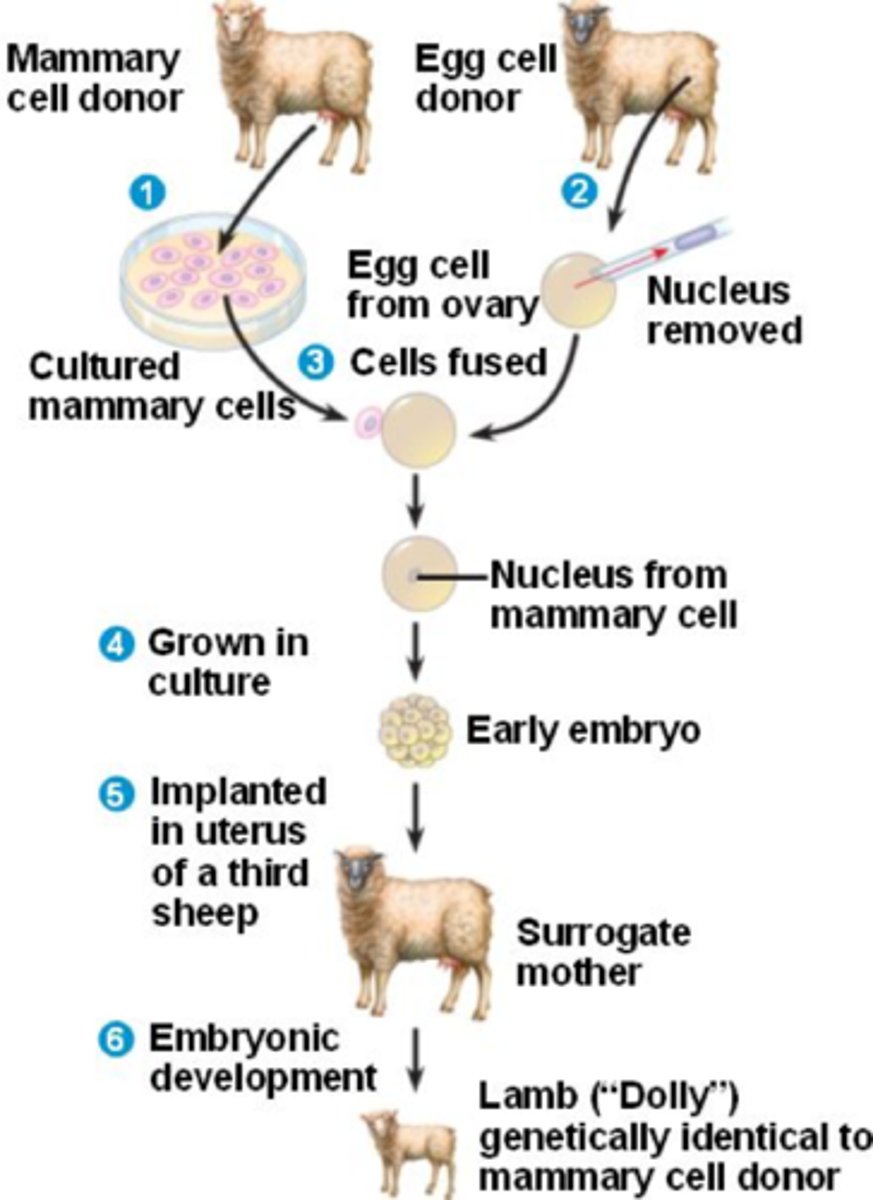
Cloning/Editing Animals/Humans
-CRISPR is used to edit genes
-Molecular cloning is not the same as animal cloning
-Dolly the sheep -> egg cell removed from a donor and combined with a mammary cell from a different donor through an electric shock -> becomes a blastocyst and is implanted into the uterus of a surrogate
Can ethical theories justify designer babies?
Know how to explain this, will be a question!!!
Ethical Issues with Cloning
-Aborting embryos is likely to be widespread
-Eugenics
-Will clones have a soul?
-Have we become our own creators?
-Will men still be required?
-"Artificial identical twin"
-Nature vs nurture
-Identity crisis being genetically similar to someone else
Therapeutic Cloning Without Embryos
iPS cells -> cells taken from a patient that are reprogrammed so that they can undergo differentiation
Public Opinion of Gene Editing - Knowledge Level
-Those with high scientific knowledge are more inclined to see gene editing techniques as appropriate
-Those familiar with gene editing are more inclined to see different uses as appropriate
Public Opinion of CRISPR
CRISPR is a "hot" topic -> publications pertaining to CRISPR have risen dramatically
Public Opinion of Changing a Baby's Genes
-People agree it is okay to let a parent choose a child's traits to prevent a health condition (32%), but some believe it's immoral (30%)
-Majority say changing a baby's genes to treat a serious congenital disease is appropriate (72%), but it lowers when it just reduces the risk of a serious disease that could occur over their lifetime
Public Opinion of Embryonic Testing + Gene Editing
65% of Americans say if gene editing relies on embryonic testing, it would take technology too far
Public Opinion of Gene Editing - Religion
Highly religious Americans are more likely to see gene editing for babies as taking medical technology too far, with white evangelicals being the most prominent
Public Opinion of Gene Editing - Men vs Women
-Men are more likely than women to view gene editing for babies as appropriate
-More women than men anticipate negative effects of gene editing
Public Opinion of Gene Editing - Effects
-Larger shares of Americans believe negative effects of widespread use of gene editing are very likely
-Public expresses more worry than enthusiasm about each of these potential human enhancements
Public Opinion of Cloning
Most Americans oppose cloning, especially of human beings