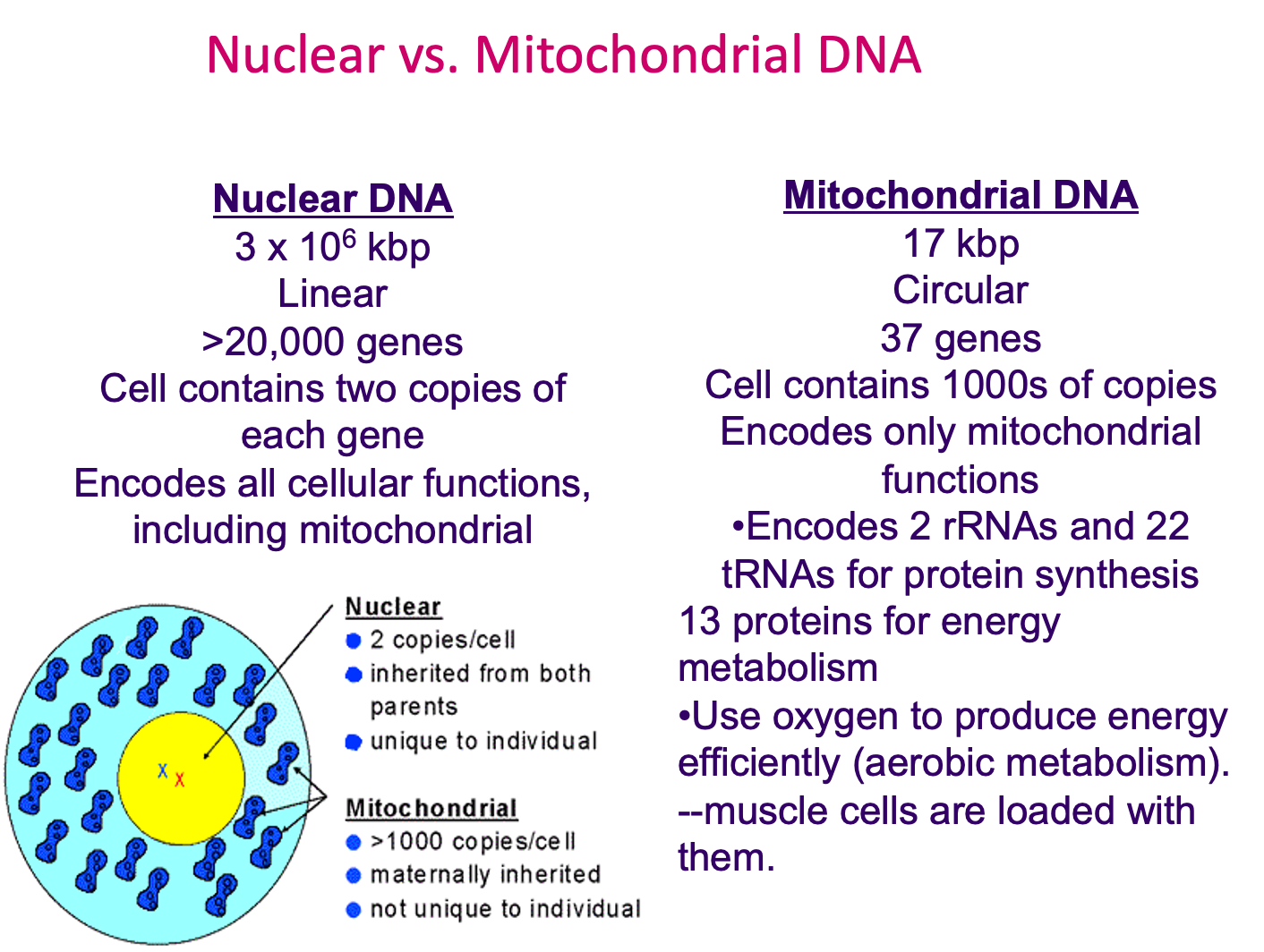
Mitochondrial DNA
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are mitochondria?
Organelles that produce energy
Who is mitochondria inherited from?
Only the mother
Does mitochondrial DNA mutate faster than nuclear DNA?
Yes as it lacks repair enzymes
What happens to mitochondrial DNA after death?
DNA slowly degrades
Can you amplify mtDNA form preserved tissues and skeletons?
Yes, you can often amplify mtDNA but nuclear DNA from preserved tissues and skeletons
What type of genome does mitochondrial DNA have?
Circular genome, with no non-coding DNA
Can mitochondrial DNA survive in fossils?
Yes
What are the differences between nuclear and mitochondrial DNA?
What does mtDNA analysis involve?
Hypervariable segment (D-loop)
Restriction digestion → DNA cut → RFLPs → Haplogroups (shared with specific ethnicities)
Sequencing of control region (HVR1 & HVR2) → Haplotype (individual family type)
Sequence DNA → pair-wise comparisons
When was the use of mtDNA pioneered?
In the 1980s, Allan Wilson pioneered the use of mtDNA to study human evolution. mtDNA sequences of indigenous people worldwide were compared to determine the common ancestral mtDNA sequence
What was found regarding mtDNA and human evolution in the 1980s?
The root of the tree is in Africa and is 200,000 years old
Calibration of the molecular clock with chimp out-groups indicate the common ancestral sequence existed 100,000 to 300,000 years ago
African populations are more diverse than non-African
Non-African mtDNAs are closely related
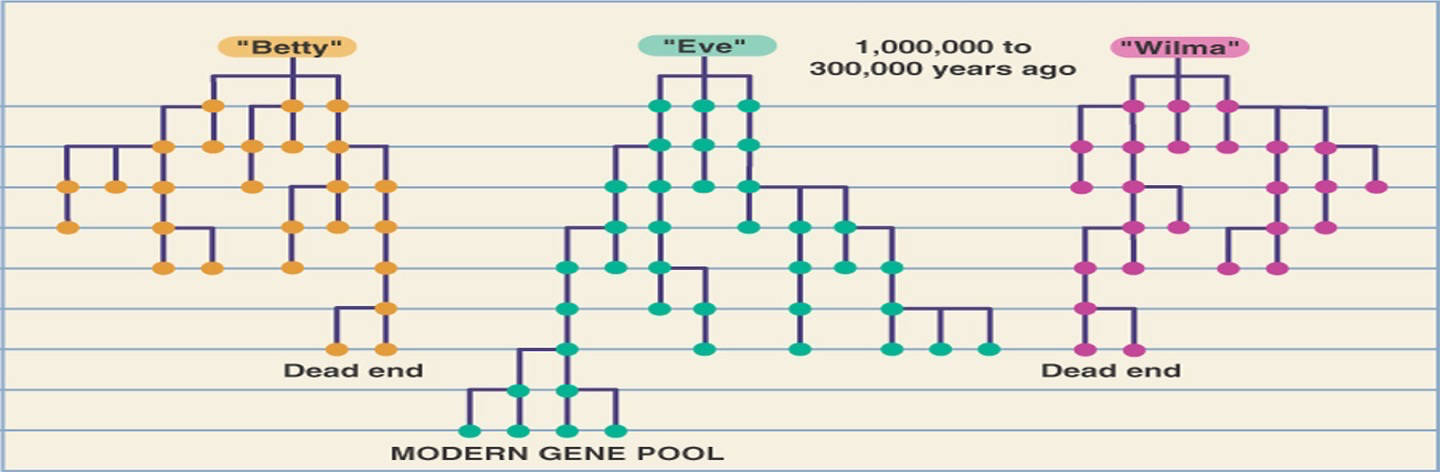
What is coalescent theory?
A method to trace genetic lineages backward in time to their common ancestor
Who is Mitochondrial Eve?
The most recent common ancestor of all humans through the maternal line, identified using mtDNA and coalescent theory