SciOly - Anatomy & Physiology (Integumentary, Skeletal, Muscular)
1/1389
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1390 Terms
Anatomy
the scientific study of the body’s structures
Gross anatomy (Macroscopic anatomy)
the study of the larger structures of the body, those visible without the aid of magnification
Microscopic anatomy
the study of structures that can only be observed with the use of a microscope or other magnification devices
Cytology
the study of cells
Histology
the study of tissues
Regional anatomy
the study of the interrelationships of all of the structures in a specific body region, such as the abdomen
Systemic anatomy
the study of the structures that make up a discrete body system
Discrete body system
a group of structures that work together to perform a unique body function
Physiology
the scientific study of the chemistry and physics of the structures of the body and the ways in which they work together to support the functions of life
Homeostasis
the state of steady internal conditions maintained by living things
Fundamental levels of organization
subatomic particles
atoms
molecules
organelles
cells
tissues
organs
organ systems
organisms
biosphere
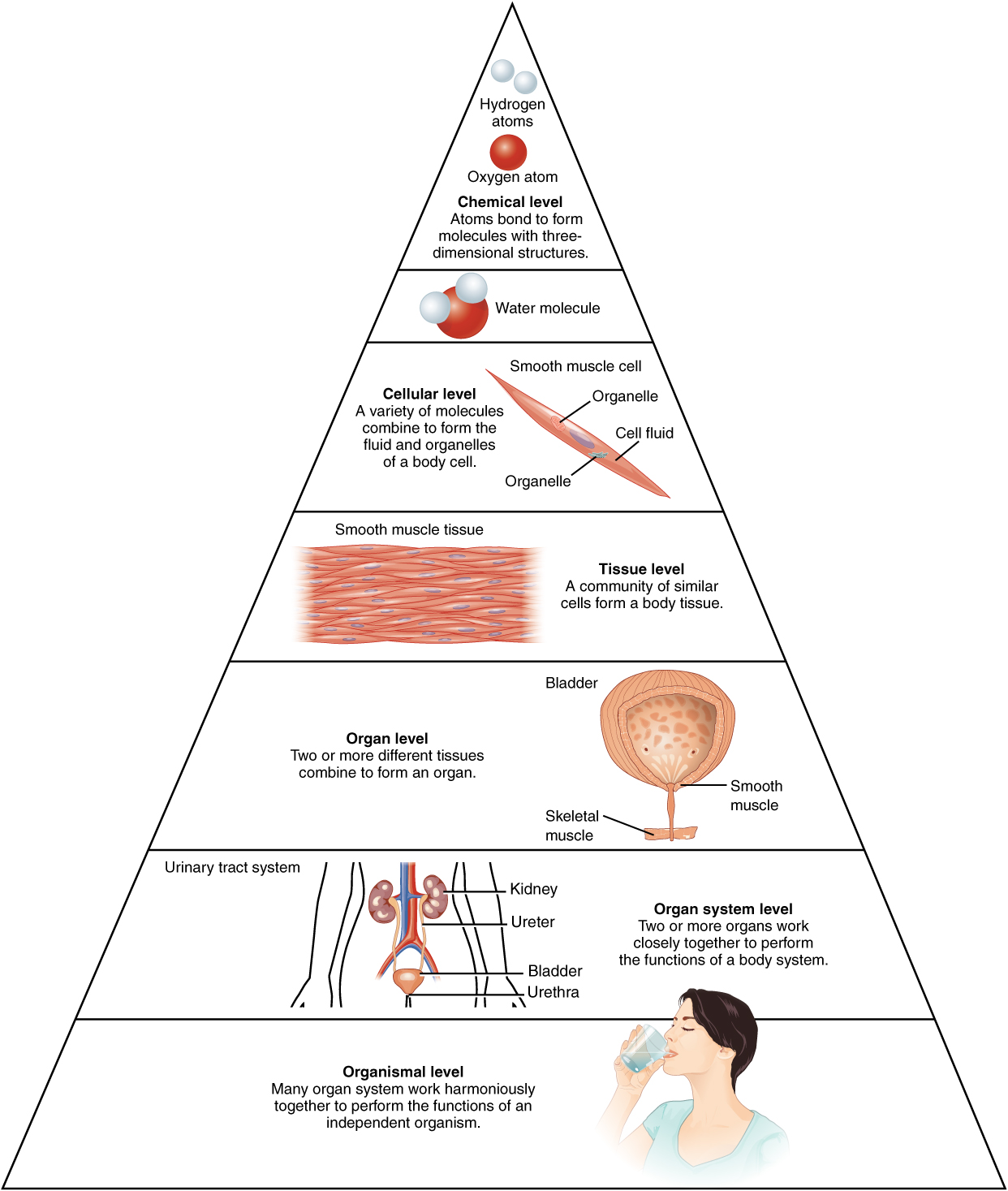
Cell
Smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism, they perform all functions of life
Cytoplasm
a water-based cellular fluid together with a variety of tiny functioning units called organelles
Organelles
a variety of tiny functioning units
Tissue
a group of similar cells (though sometimes composed of a few related types) that work together to perform a specific function
Organ
an anatomically distinct structure of the body composed of two or more tissue types, each performs one or more specific physiological functions
Organ system
a group of organs that work together to perform major functions or meet physiological needs of the body
Integumentary System
Encloses internal body structures
Site of many sensory receptors
The body’s largest organ system
Hair, skin, nails
Skeletal System
Supports the body
Enables movement (with muscular system)
Cartilage, bones, joints
Muscular System
Enables movement (with skeletal system)
Helps maintain body temperature
Skeletal muscles, tendons
Nervous System
Detects and processes sensory information
Activates bodily responses
Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves
Endocrine System
Secretes hormones
Regulates bodily processes
Pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands, testes, ovaries
Cardiovascular System
Delivers oxygen and nutrients to tissues
Equalizes temperature in the body
Heart, blood vessels
Lymphatic System
Returns fluid to bloods
Defends against pathogens
Thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, lymphatic vessels
Respiratory System
Removes carbon dioxide from the body
Delivers oxygen to blood
Nasal passage, trachea, lungs
Digestive System
Processes food for use by the body
Removes wastes from undigested food
Stomach, liver, gall bladder, large intestine, small intestine
Urinary System
Controls water balance in the body
Removes wastes from blood and excretes them
Kidneys, urinary bladder
Male Reproductive System
Produces sex hormones and gametes
Delivers gametes to female
Epididymis, testes
Female Reproductive System
Produces sex hormones and gametes
Supports embryo/fetus until birth
Produces milk for infant
Mammary glands, ovaries, uterus
Organism
a living being that has a cellular structure and that can independently perform all physiologic functions necessary for life
First law of thermodynamics
Holds that energy can neither be created nor destroyed - it can only change form
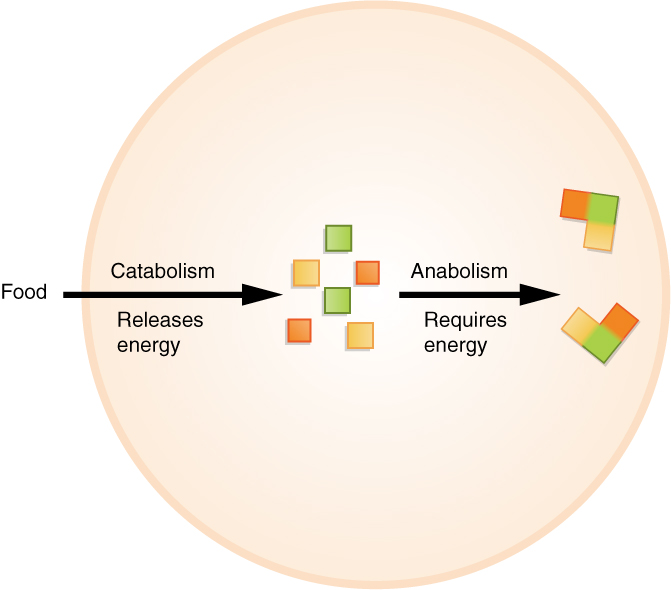
Anabolism
the process whereby smaller, simpler molecules combined into larger more complex substances. Requires energy. Your body can assemble, by utilizing energy, the complex chemicals it needs by combining small molecules derived from the foods you eat.
Catabolism
the process by which larger more complex substances are broken down into smaller simpler molecules. Releases energy. The complex molecules found in foods are broken down so the body can use their parts to assemble the structures and substances needed for life.
Metabolism
the sum of all anabolic and catabolic reactions that take place in the body. Both anabolism and catabolism occur simultaneously and continuously to keep you alive.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
a chemical compound used by every cell in your body to store and release energy
Responsiveness
the ability of an organism to adjust to changes in its internal and external environments
Development
all of the changes the body goes through in life, includes the process of differentiation
Differentiation
unspecialized cells become specialized in structure and function to perform certain tasks in the body
Growth
increase in body size
Reproduction
The formation of a new organism from parent organisms
Oxygen
a key component of the chemical reactions that keep the body alive, including the reactions that produce ATP
Nutrient
a substance in foods and beverages that is essential to human survival
Basic classes of nutrients
Water (Most critical) Macronutrients
Energy-yielding (Carbs and lipids) and body-building (proteins) Macronutrients
Micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) (elements and compounds)
Sweating
response to heat, Removes some thermal energy from the body, cooling it
Shivering
response to cold, random muscle movement that generates heat
Hypothermia
the clinical term for an abnormally low body temperature
Hyperthermia
the clinical term for an abnormally high body temperature
Controlled hypothermia
Used during open-heart surgery because it decreases the metabolic needs of the brain, heart, and other organs, reducing the risk of damage to them. The patient is given medication to prevent shivering
Pressure
a force exerted by a substance that is in contact with another substance
Atmospheric pressure
Exerted by the mixture of gases (primarily nitrogen and oxygen) in the Earth’s atmosphere
Decompression Sickness
a condition in which gases dissolved in the blood or in other body tissues are no longer dissolved following a reduction in pressure on the body. Affects underwater divers who surface from a deep dive too quickly and pilots flying at high altitudes in planes with unpressurized cabins.
Blood Pressure
the pressure exerted by blood as it flows within blood vessels, must be great enough to enable blood to reach all body tissues, and yet low enough to ensure that the delicate blood vessels can withstand the friction and force of the pulsating flow of pressurized blood.
Set Point
the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates
Normal Range
the restricted set of values that is optimally healthful and stable
Negative Feedback
a mechanism that reverses a deviation from the set point, maintains body parameters within their normal range
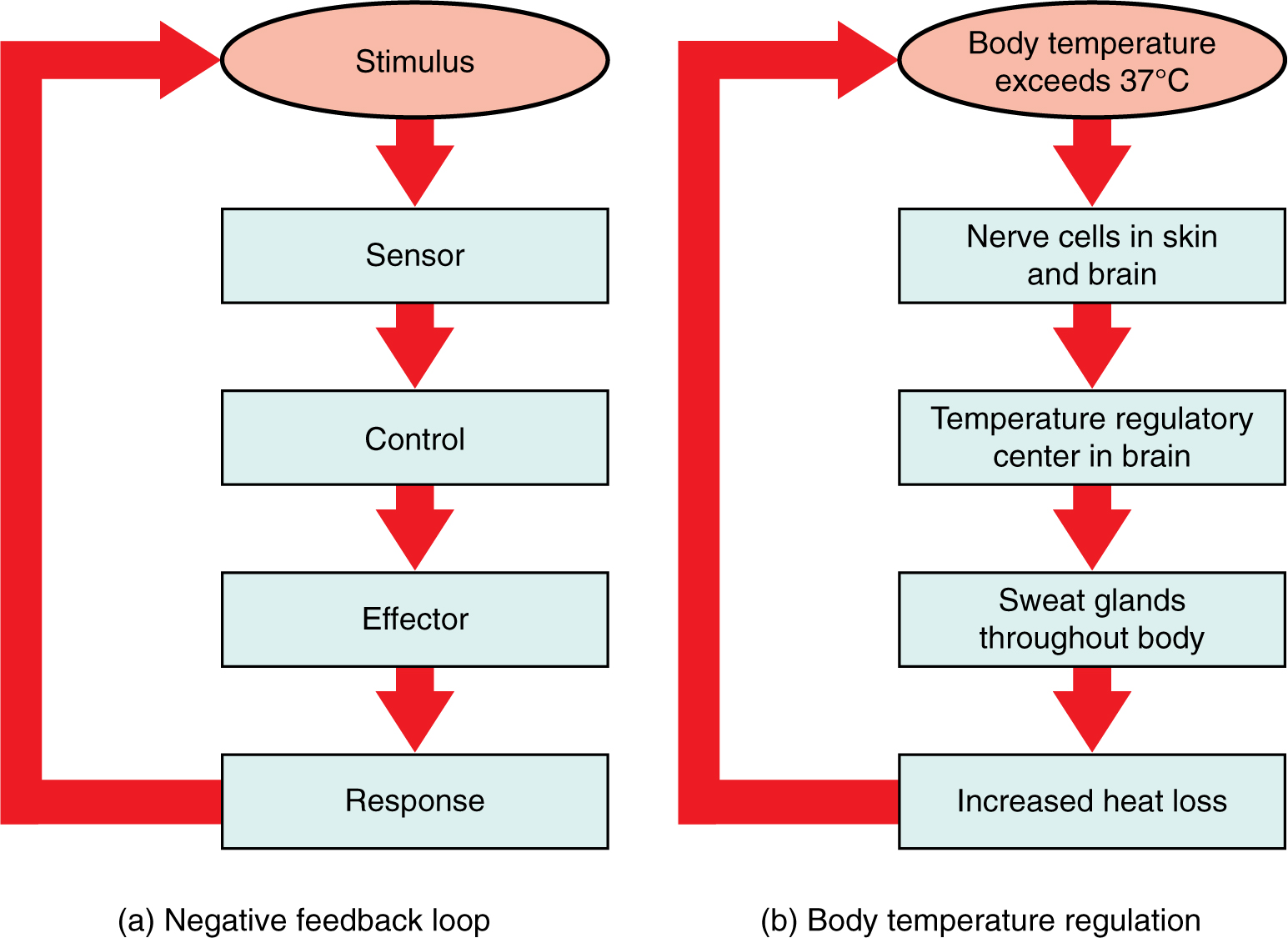
Sensor
A receptor, a component of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value, this value is reported to the control center
Control Center
the component in a feedback system that compares the value to the normal range
Effector
the component in a feedback system that causes a change to reverse the situation and return the value to the normal range
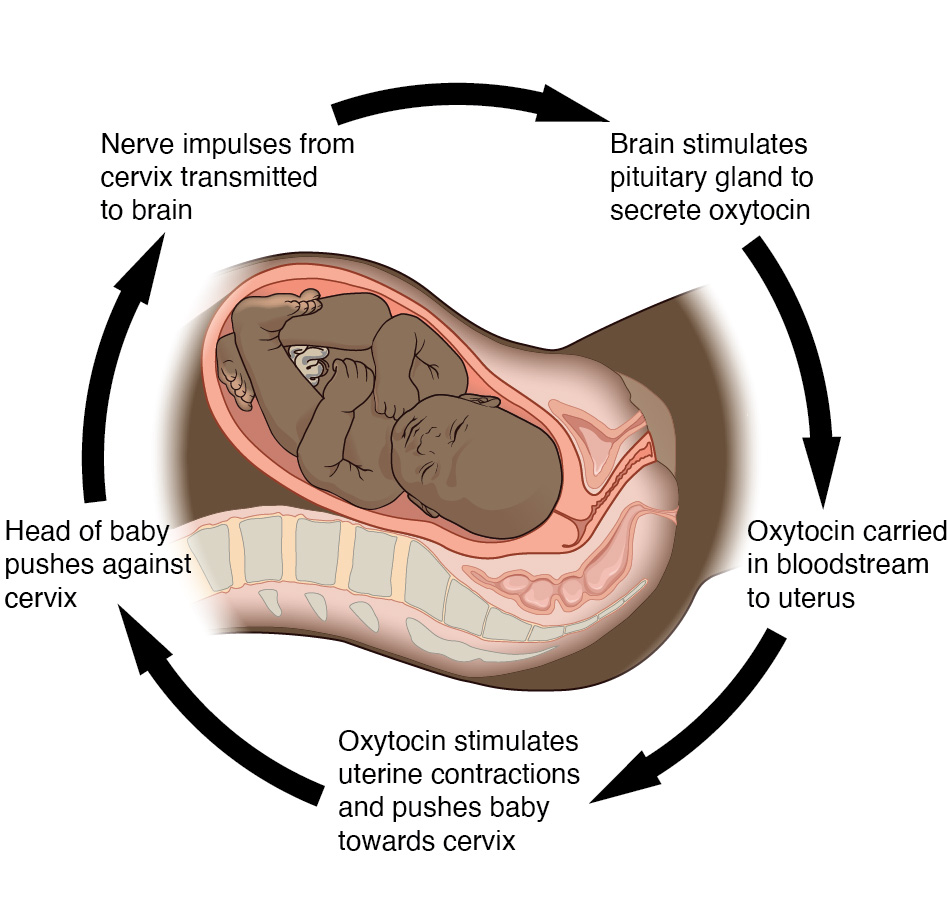
Positive Feedback
intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition rather than reversing it. A deviation from the normal range results in more change, and the system moves farther away from the normal range. Only normal in the body when there is a definite end point. Childbirth or reversing extreme damage to the body are some examples.
Perfusion
penetration of blood
Anatomical position
that of the body standing upright, with the feet at shoulder width and parallel, toes forward. The upper limbs are held out to each side, and the palms of the hands face forward.
Frons
forehead (frontal)
Cranium
skull (cranial)
Facies
face (facial)
Oculus
eye (orbital or ocular)
Bucca
cheek (buccal)
Auris
ear (otic)
Nasus
nose (nasal)
Cervicis
neck (cervical)
Oris
mouth (oral)
Mentis
chin (mental)
Axilla
armpit (axillary)
Brachium
arm (brachial)
Antecubitis
front of elbow (antecubital)
Antebrachium
forearm (antebrachial)
Carpus
wrist (carpal)
Pollex
thumb
Palma
palm (palmar)
Digits (phalanges)
fingers (digital or phalangeal)
Patella
kneecap (patellar)
Crus
leg (crural)
Tarsus
ankle (tarsal)
Digits (phalanges)
toes (digital or phalangeal)
Hallux
great toe
Thorcis or thorax
chest (thoracic)
Mamma
breast (mammary)
Abdomen
abdominal
Umbilicus
navel (umbilical)
Hip
coxal
Pelvis
pelvic
Inguen or groin
inguinal
Pubis
Pubic
Femur
thigh (femoral)
Pes
foot (pedal)
Trunk
Thorcis or thorax, mamma, abdomen, umbilicus, hip
Anterior
front
Cephalon
head (cephalic)
Cervicis
neck (cervical)
Upper limb
Shoulder (acromial) to Manus or hand (manual)
Lower limb
Femur or thigh (femoral) to Planta or sole of foot (plantar)