AQA GCSE Geography - Coastal Landscapes in the UK
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
what do size and energy of waves depend on?
the fetch - how far the wave has travelled
the strength of the wind
how long the wind has been blowing for
what are the two wave types?
constructive and destructive
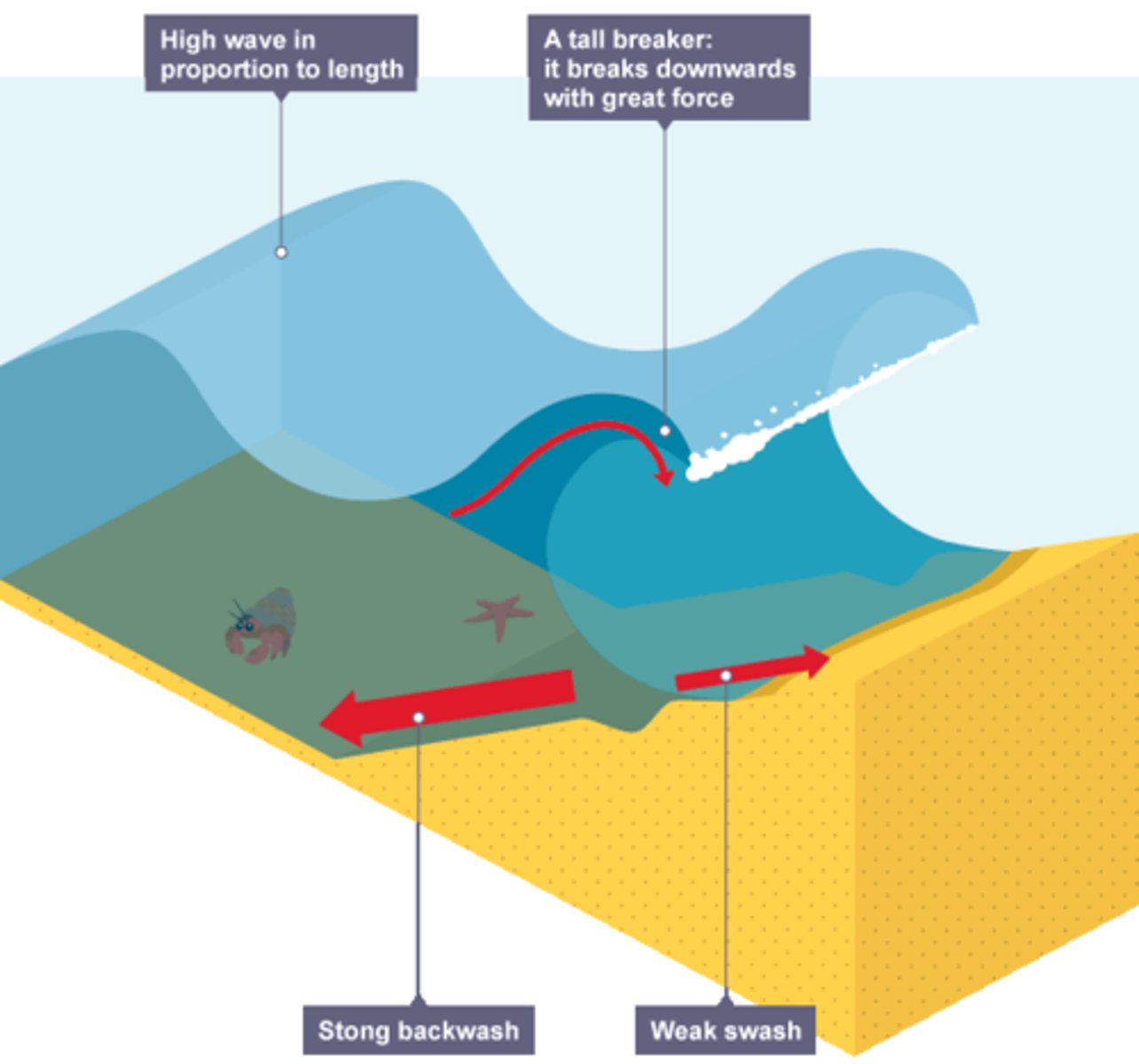
what are the characteristics of a destructive wave?
. weak swash and strong backwash
. removes sediment from the beach
. steep and close together
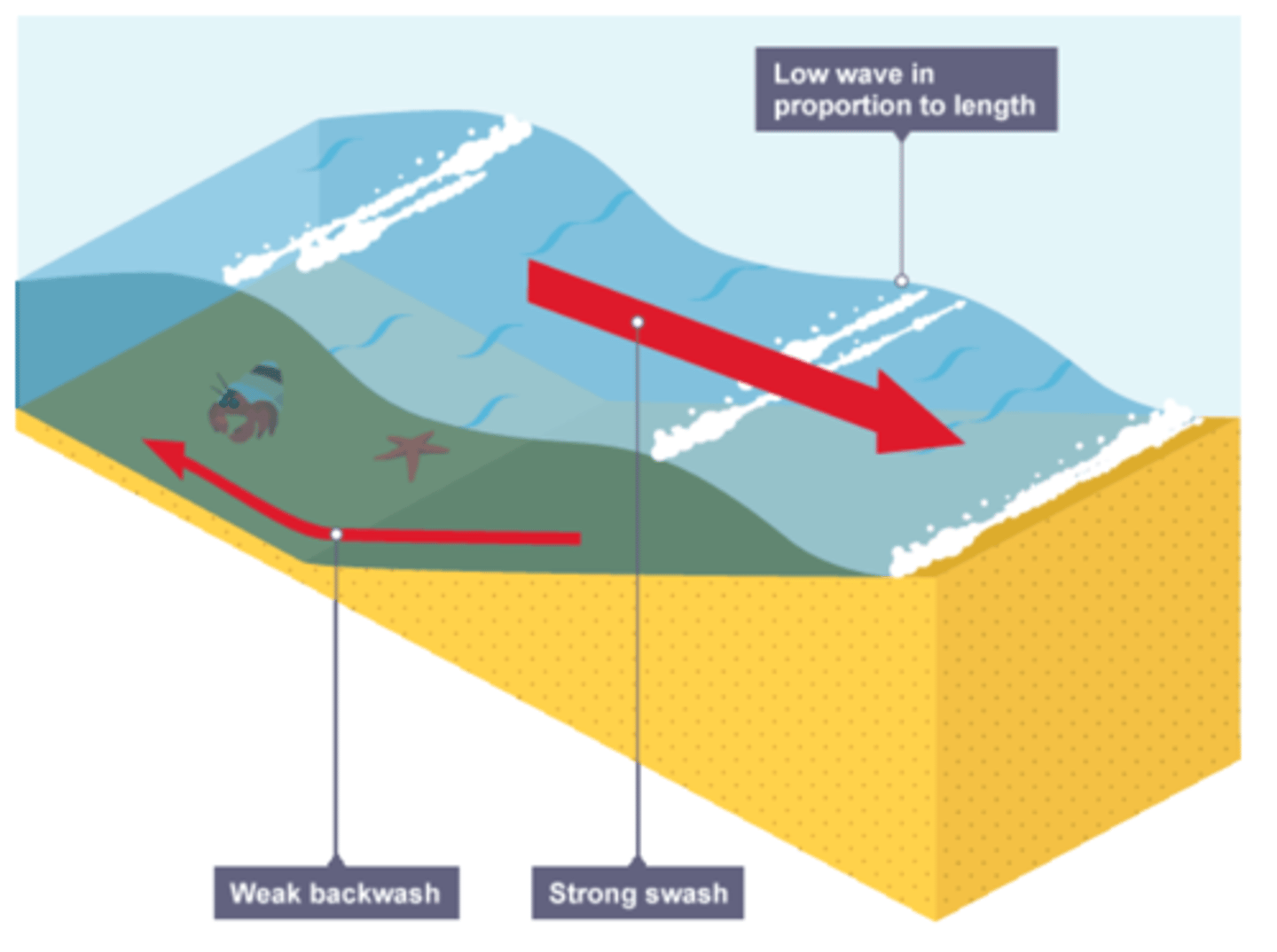
what are the characteristics of a constructive wave?
. strong swash and weak backwash
. brings sediments to build up the beach
. low and further apart
when does freeze thaw weathering occur?
when rocks are porous or permeable
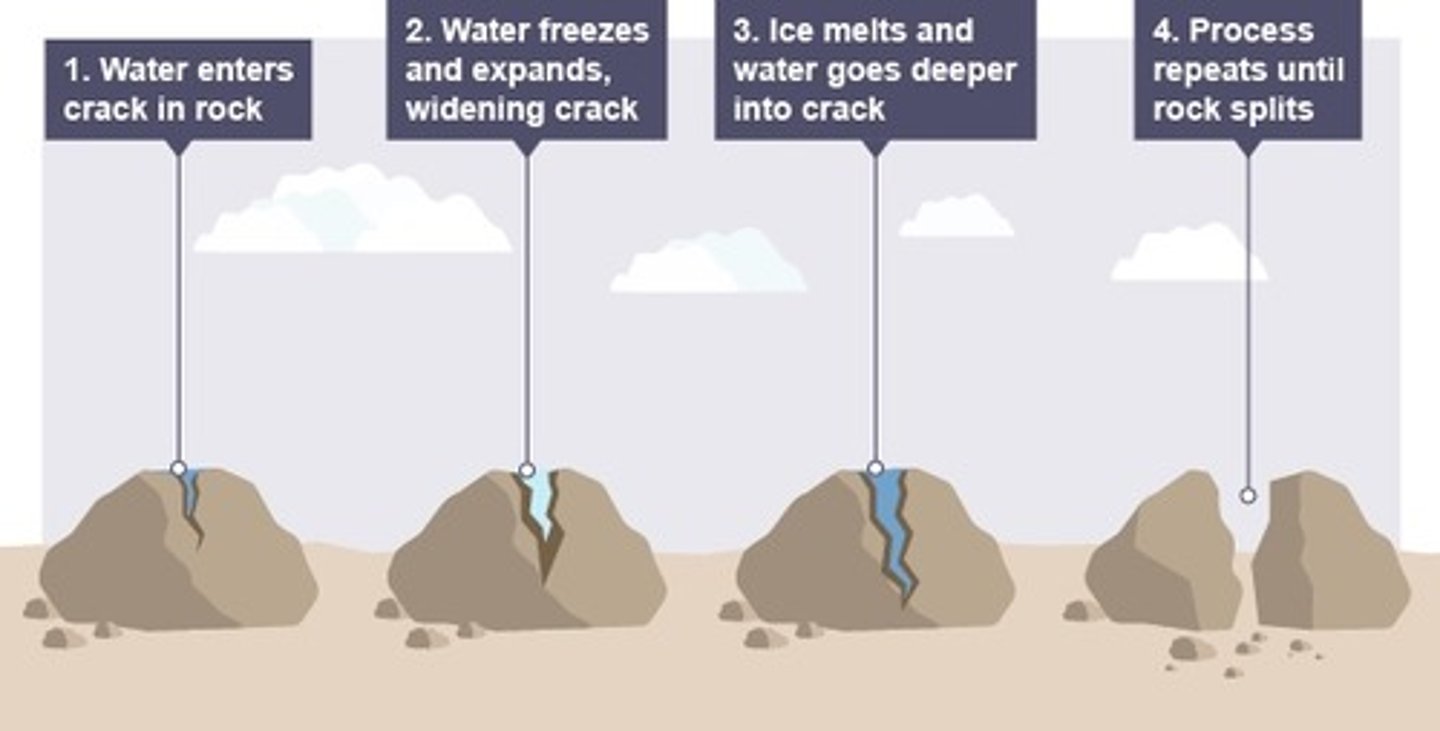
describe freeze thaw weathering
. water enters cracks in the rock
. when temperatures drop, the water freezes and expands causing the crack to widen
. the ice melts and water makes its way deeper into the crack
. the process repeats itself until the rock splits entirely
what is biological weathering caused by?
plants and animals
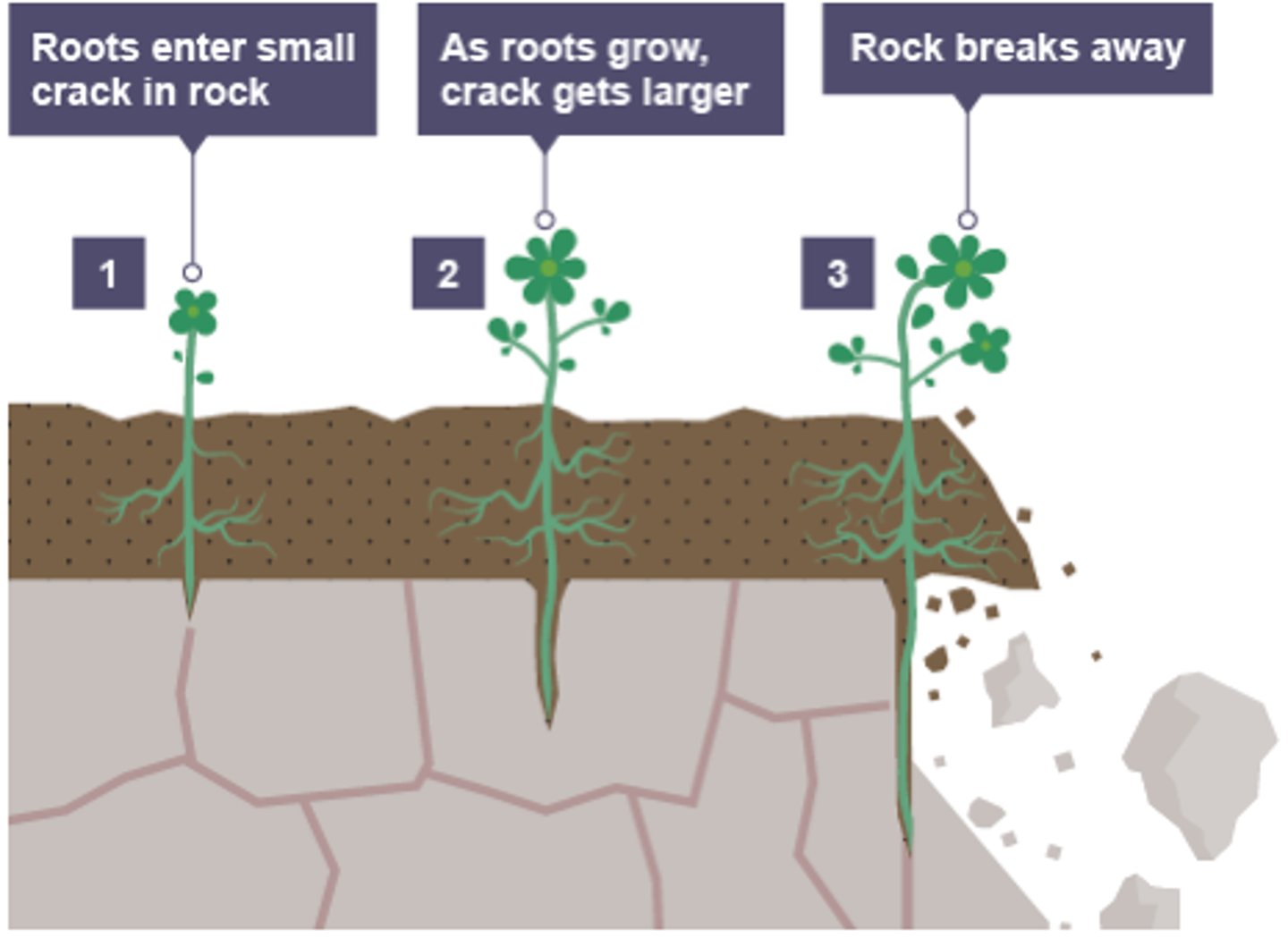
describe biological weathering
. plant roots can get into small cracks in the rock
. as the roots grow, the cracks become larger
. this causes small pieces of rock to break away
what is chemical weathering caused by?
acid in rainwater
how does chemical weathering occur?
. rainwater and seawater can be a weak acid
. a coastline made up of rocks such as limestone or chalk can be dissolved by the acid in the water
what is mass movement?
the downhill movement of weathered material due to the force of gravity
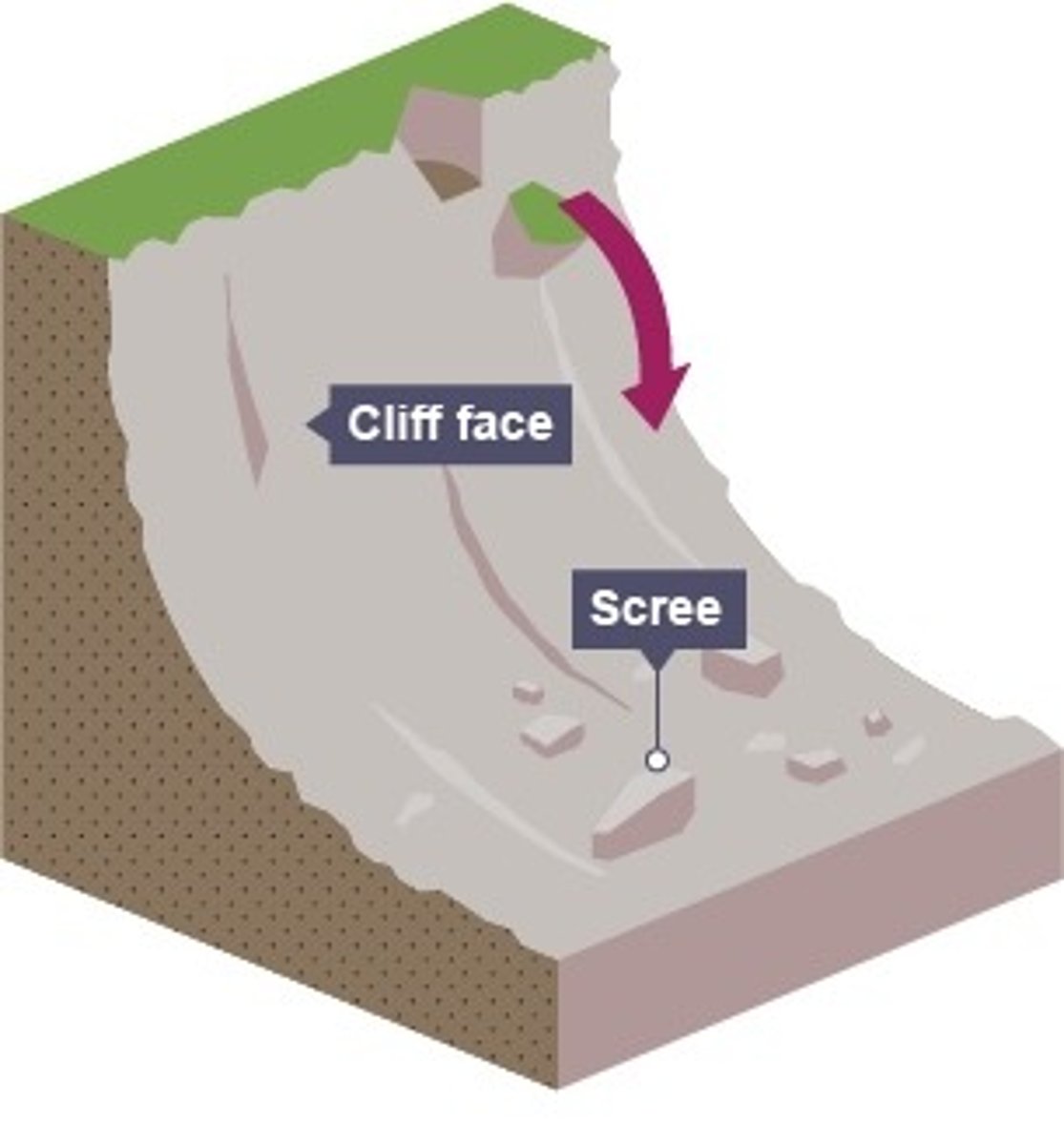
define rockfall
bits of rock fall off the cliff face, usually due to freeze-thaw weathering
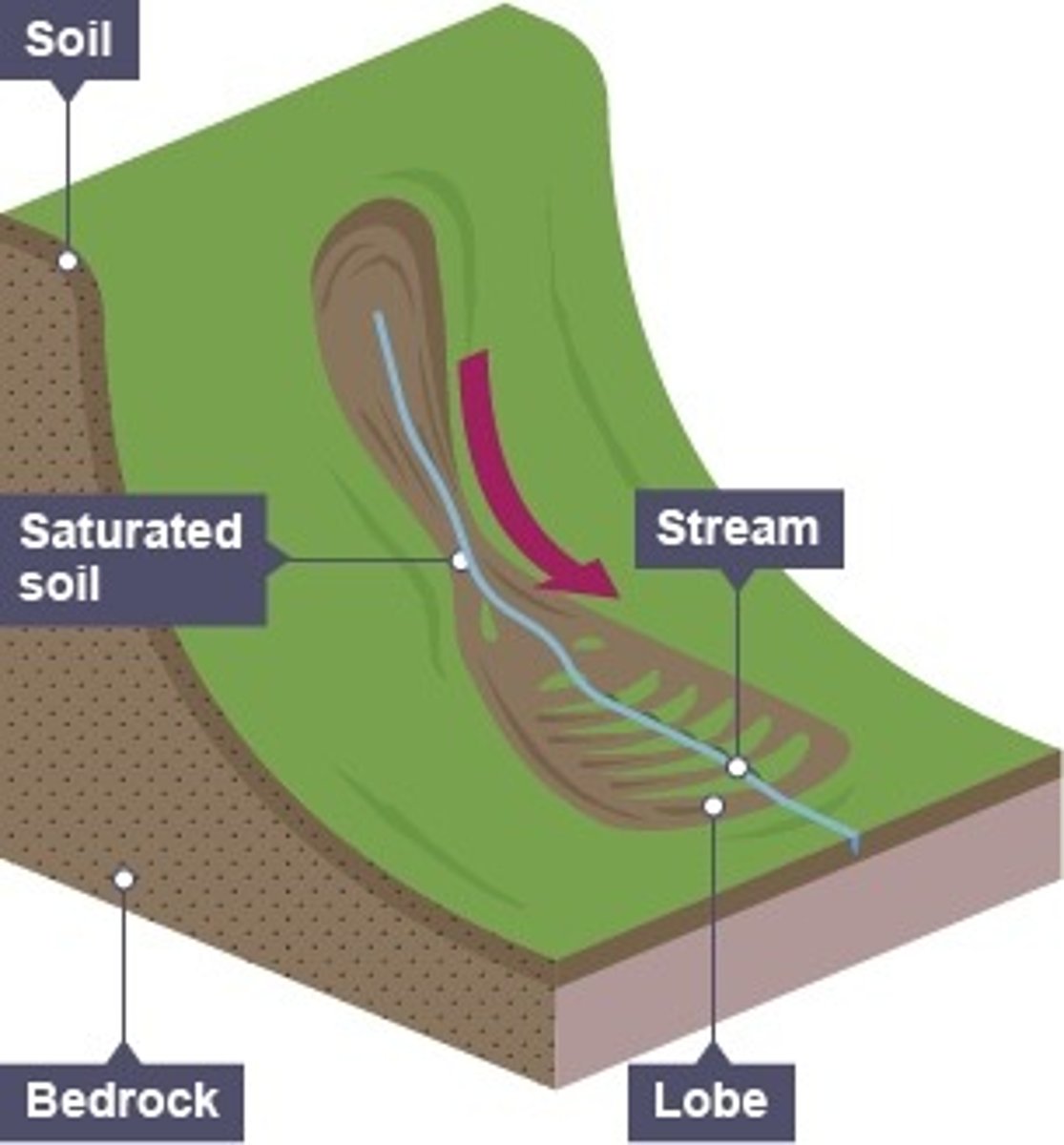
define mudflow
saturated soil flows down a slope
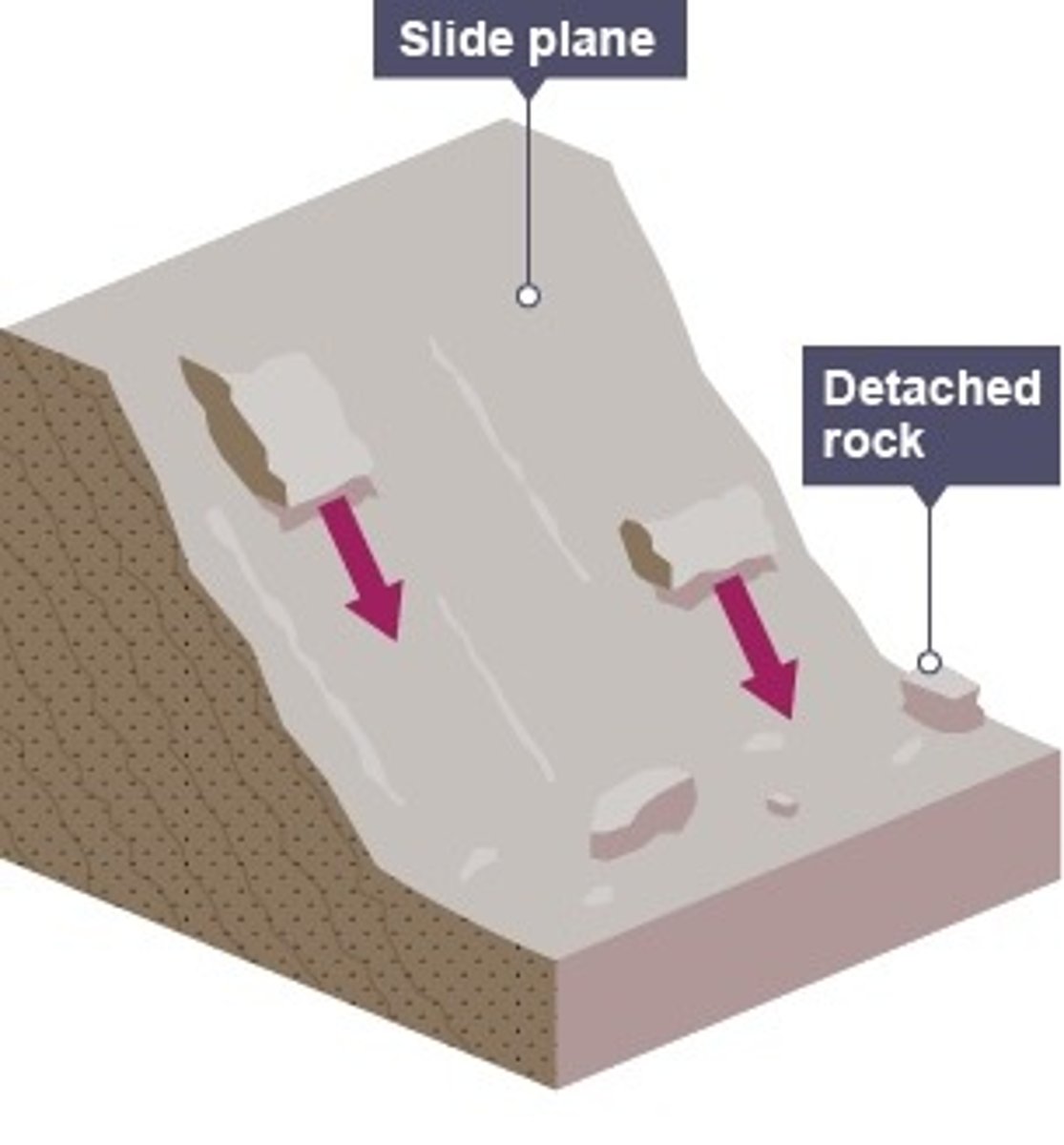
define landslide
large blocks of rock slide downhill
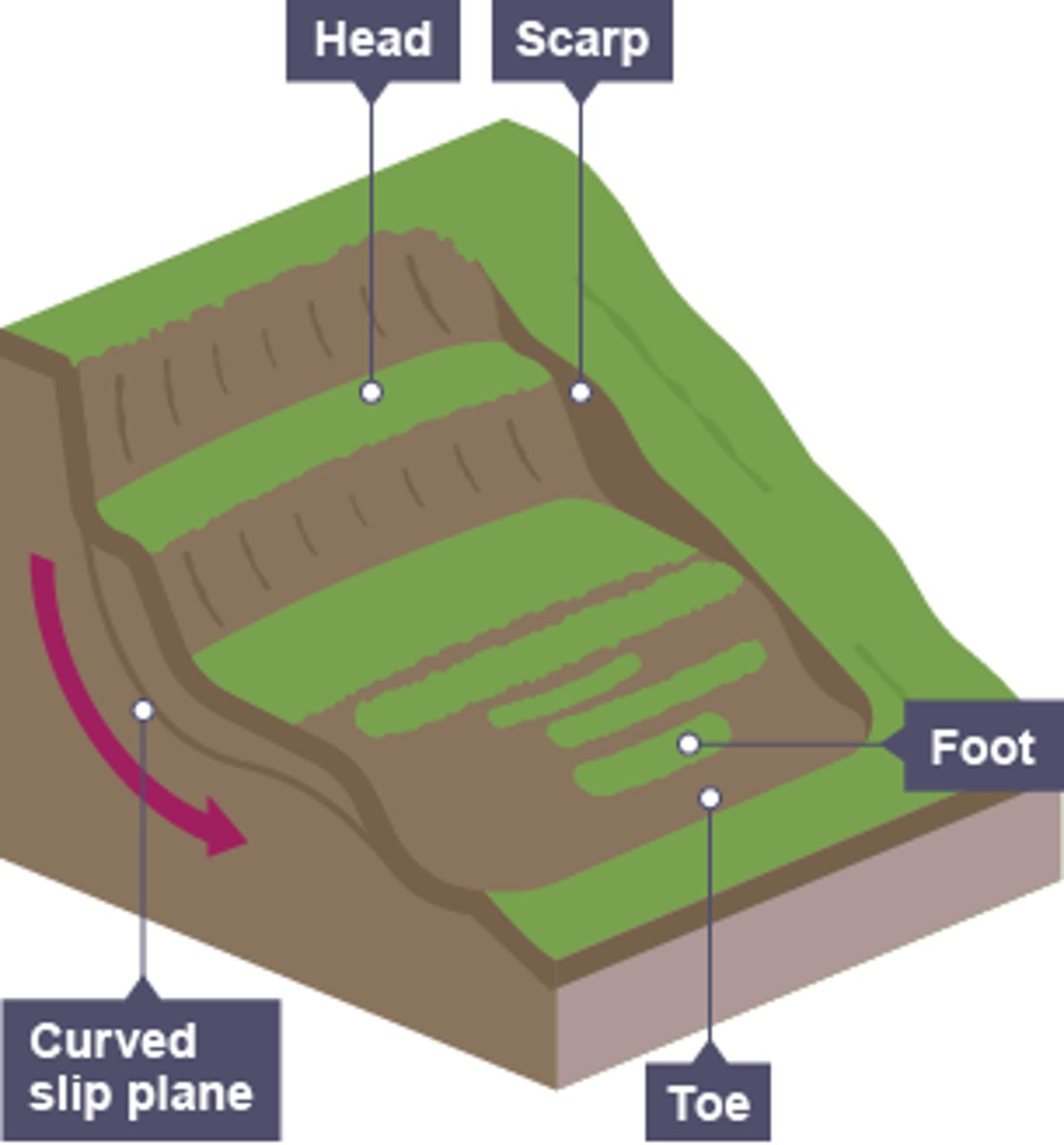
define rotational slump
saturated soil slumps down a curved surface
what is erosion?
the wearing away of rock
what are the four types of coastal erosion?
hydraulic action
abrasion
attrition
solution
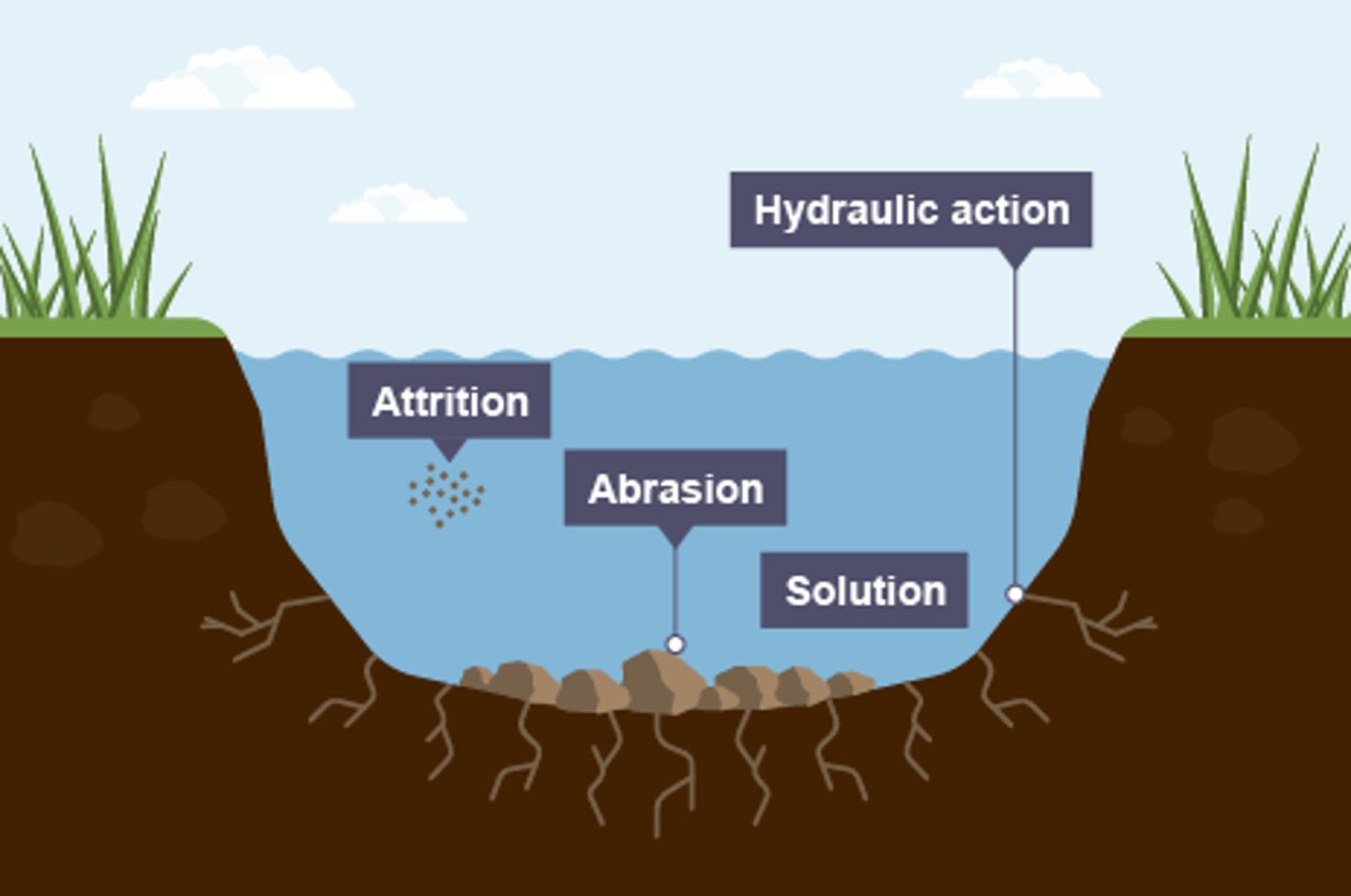
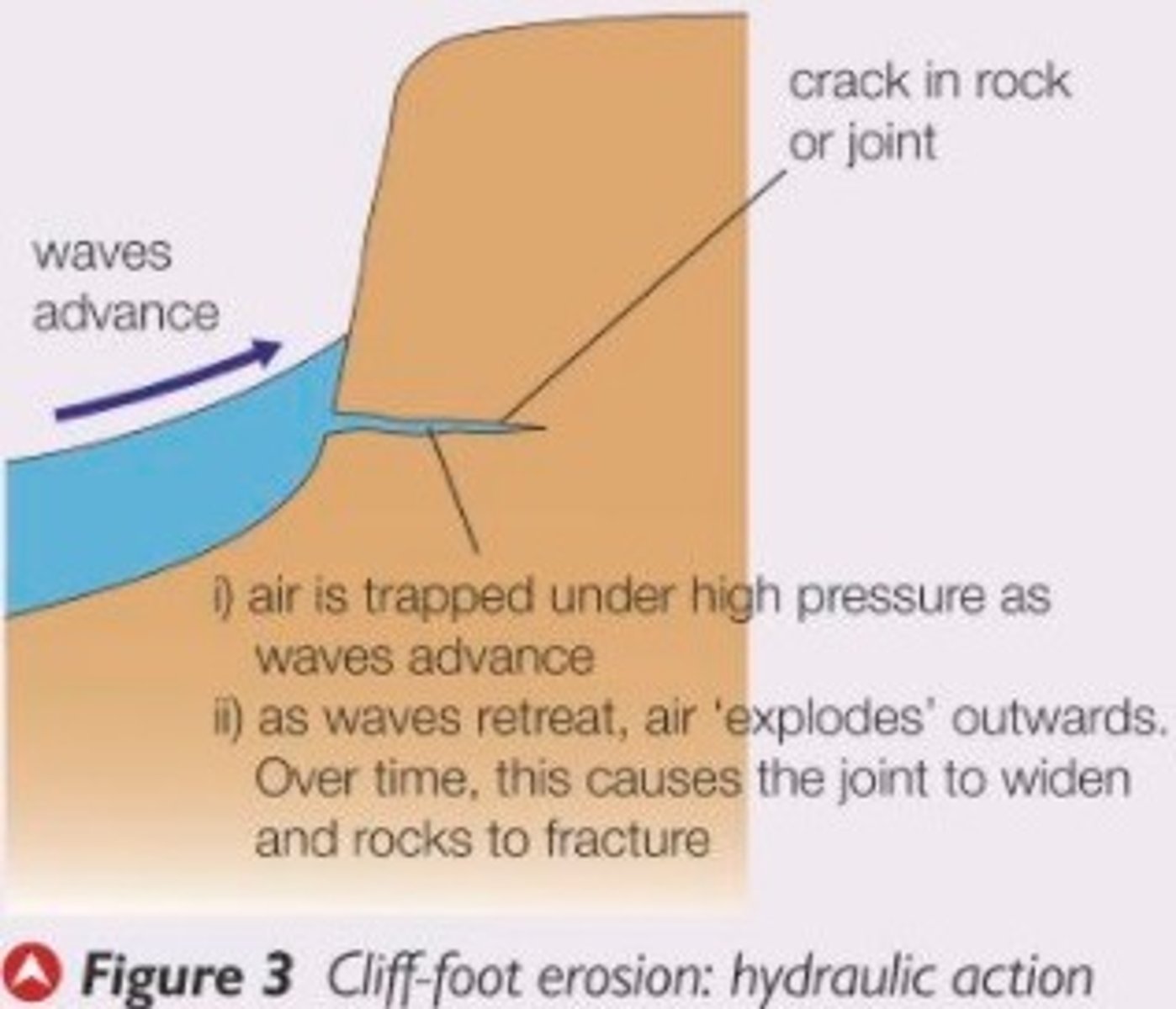
define hydraulic action
the sheer power of the waves as they smash against the cliff
air becomes trapped in the cracks in the rock and causes the rock to break apart
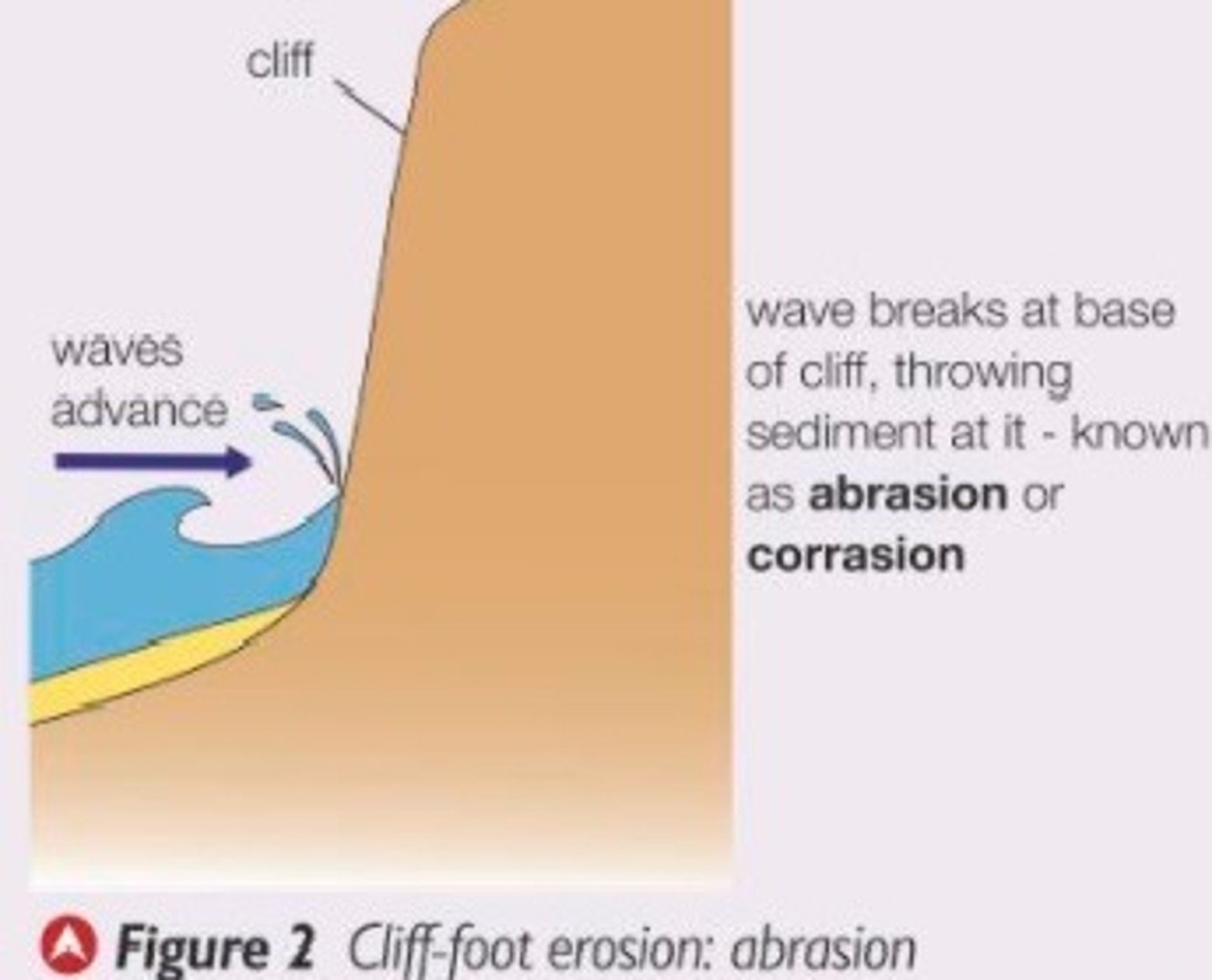
define abrasion
when pebbles grind along a rock platform, like sandpaper
over time the rock becomes smooth
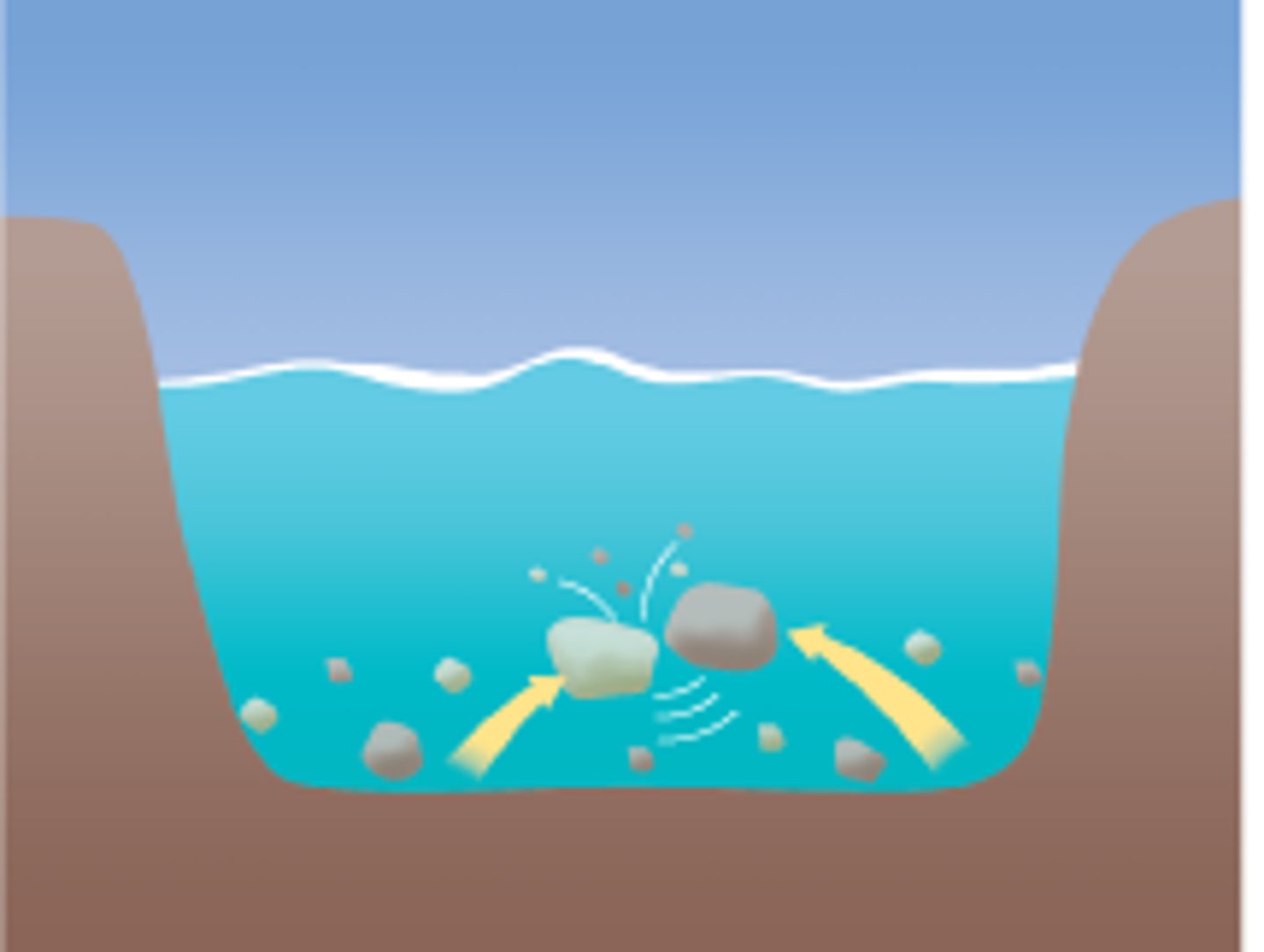
define attrition
when rocks that the sea is carrying knock against each other they break apart to become smaller and more rounded

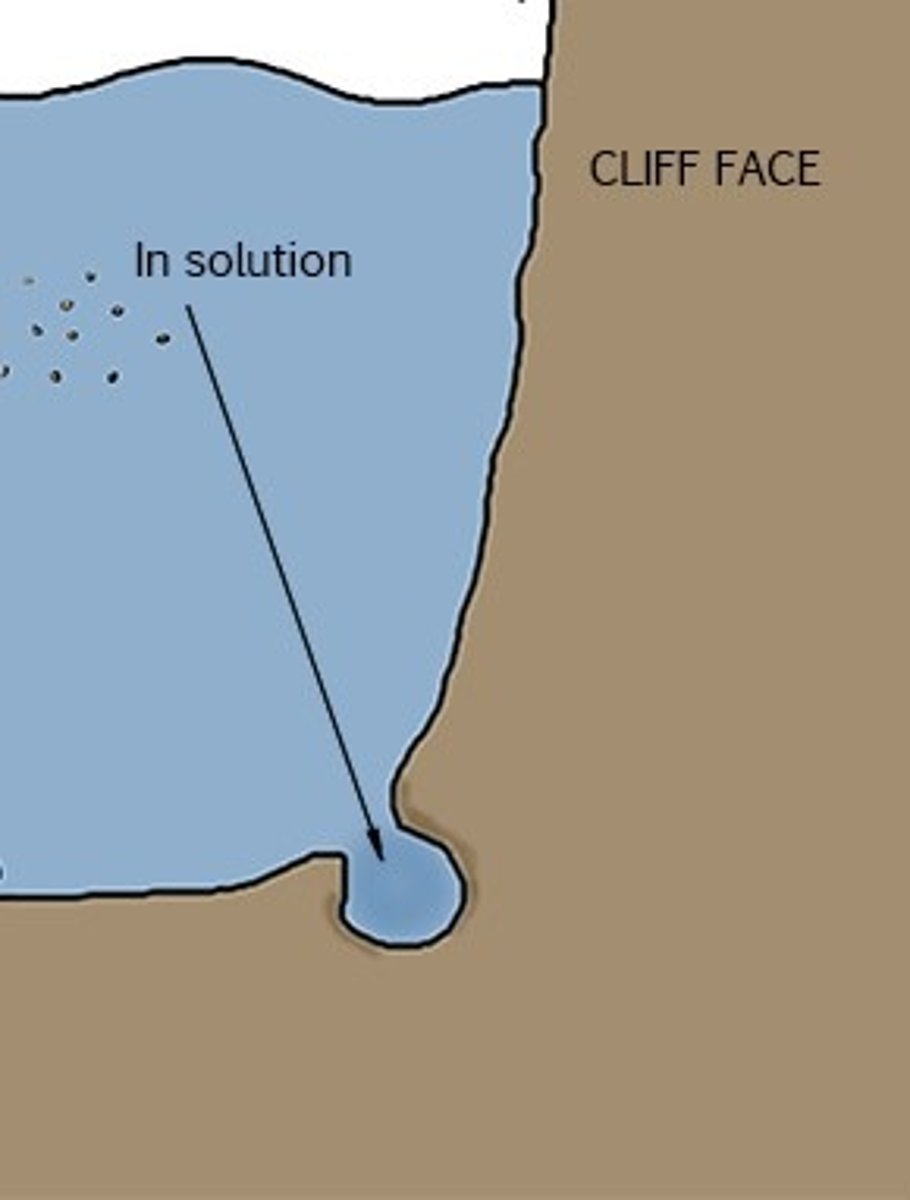
define solution (erosion)
when sea water dissolves certain types of rocks
in the UK, chalk and limestone cliffs are prone to this type of erosion
what are the four types of coastal transportation?
solution
suspension
saltation
traction
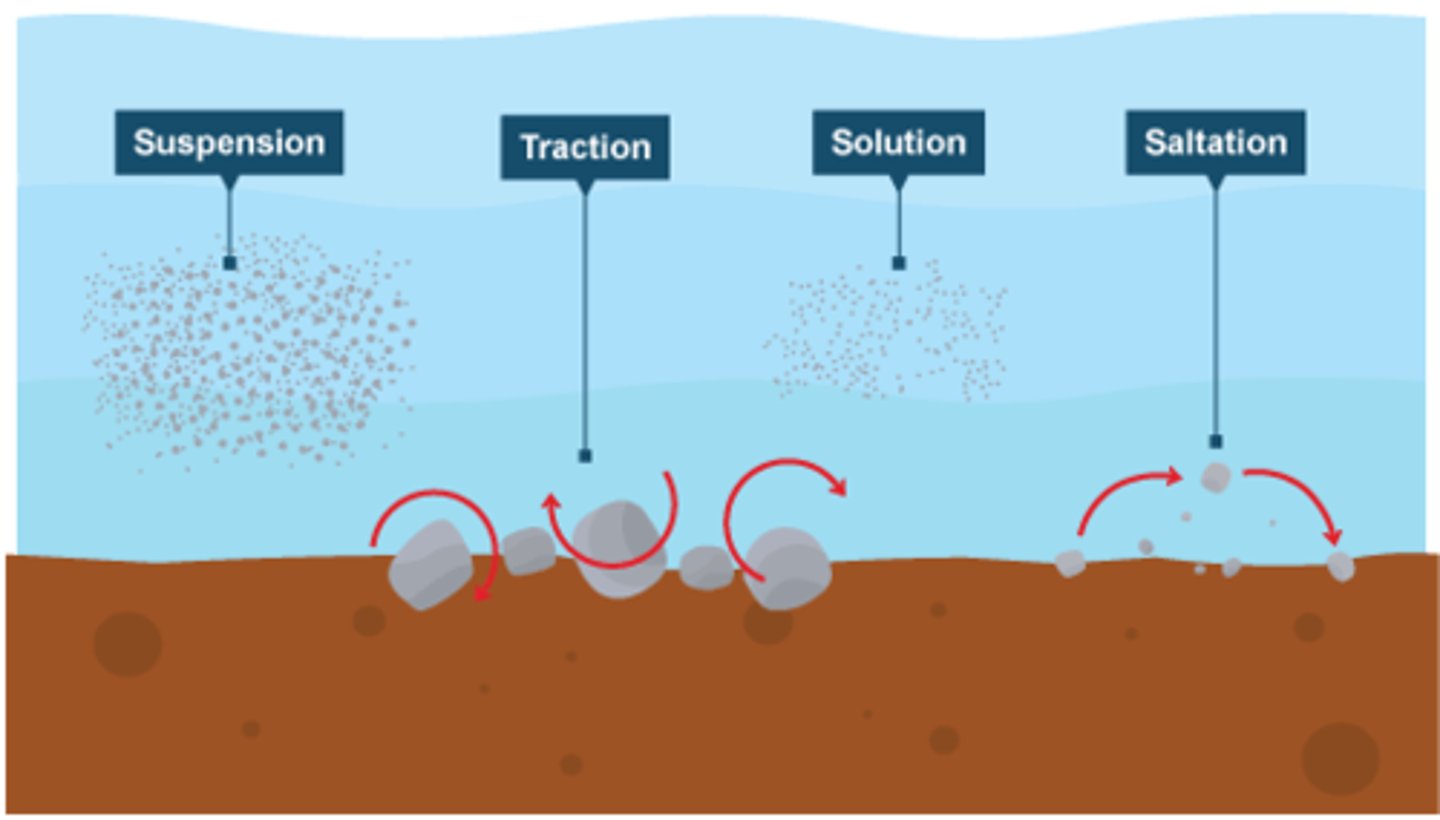
define solution (transportation)
minerals in rocks like chalk and limestone are dissolved in sea water and then carried in solution
define suspension
small particles such as silts and clays are suspended in the flow of the water
define saltation
small pieces of shingle or large sand grains are bounced along the sea bed
define traction
pebbles and larger material are rolled along the sea bed
what is the movement of sediment along the coast known as?
longshore drift
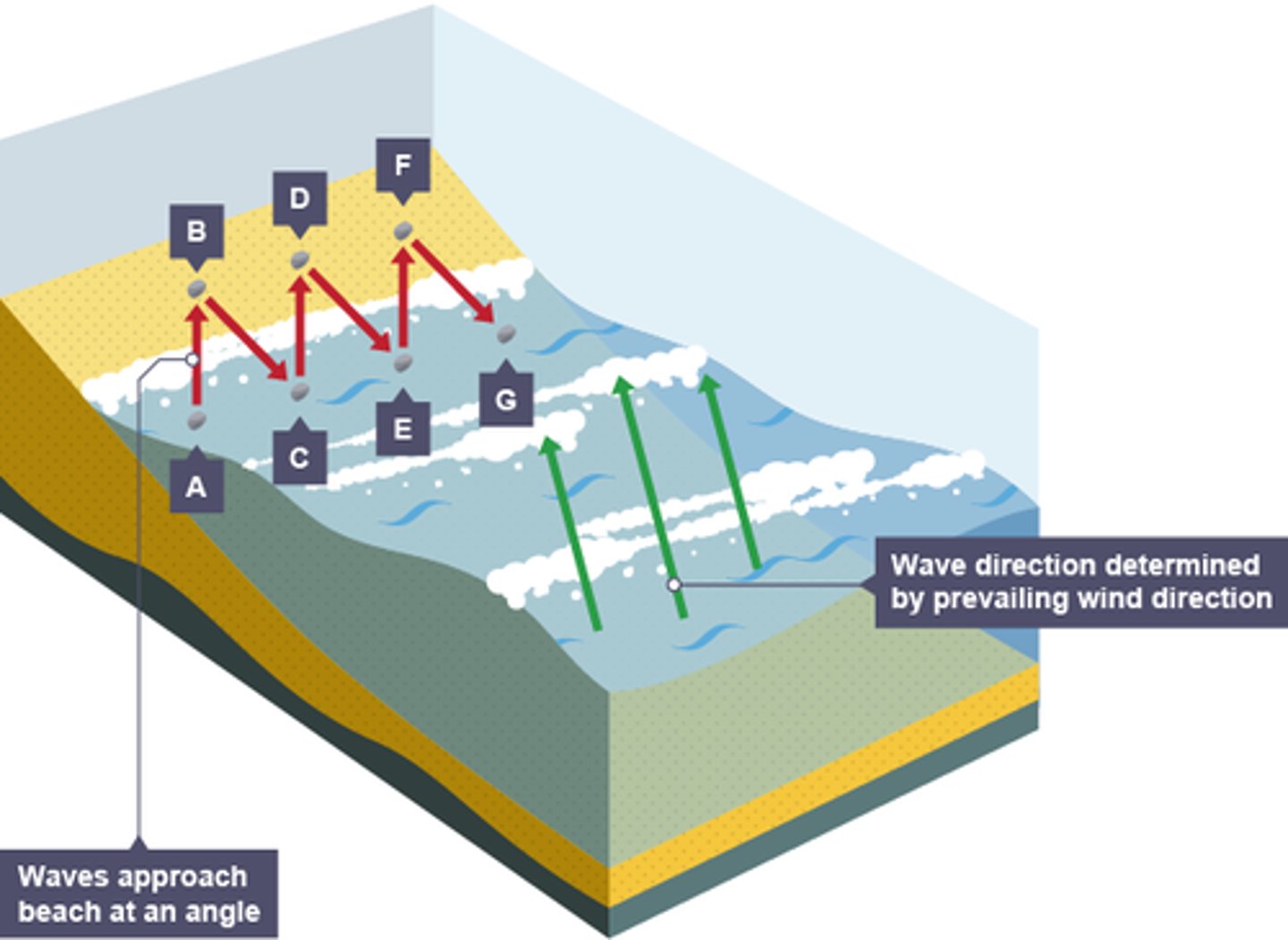
describe the process of longshore drift
. waves approach the coast at an angle because of the direction of prevailing wind
. the swash will carry the material towards the beach at an angle
. the backwash then flows back to the sea, down the slope of the beach
. the process repeats itself along the coast in the zigzag movement
what is the term used to describe the sea dropping material?
deposition
what are four factors leading to deposition?
waves starting to slow down and lose energy
shallow water
sheltered areas, eg bays
little or no wind
what features are found on coastlines with different rock types?
headlands and bays
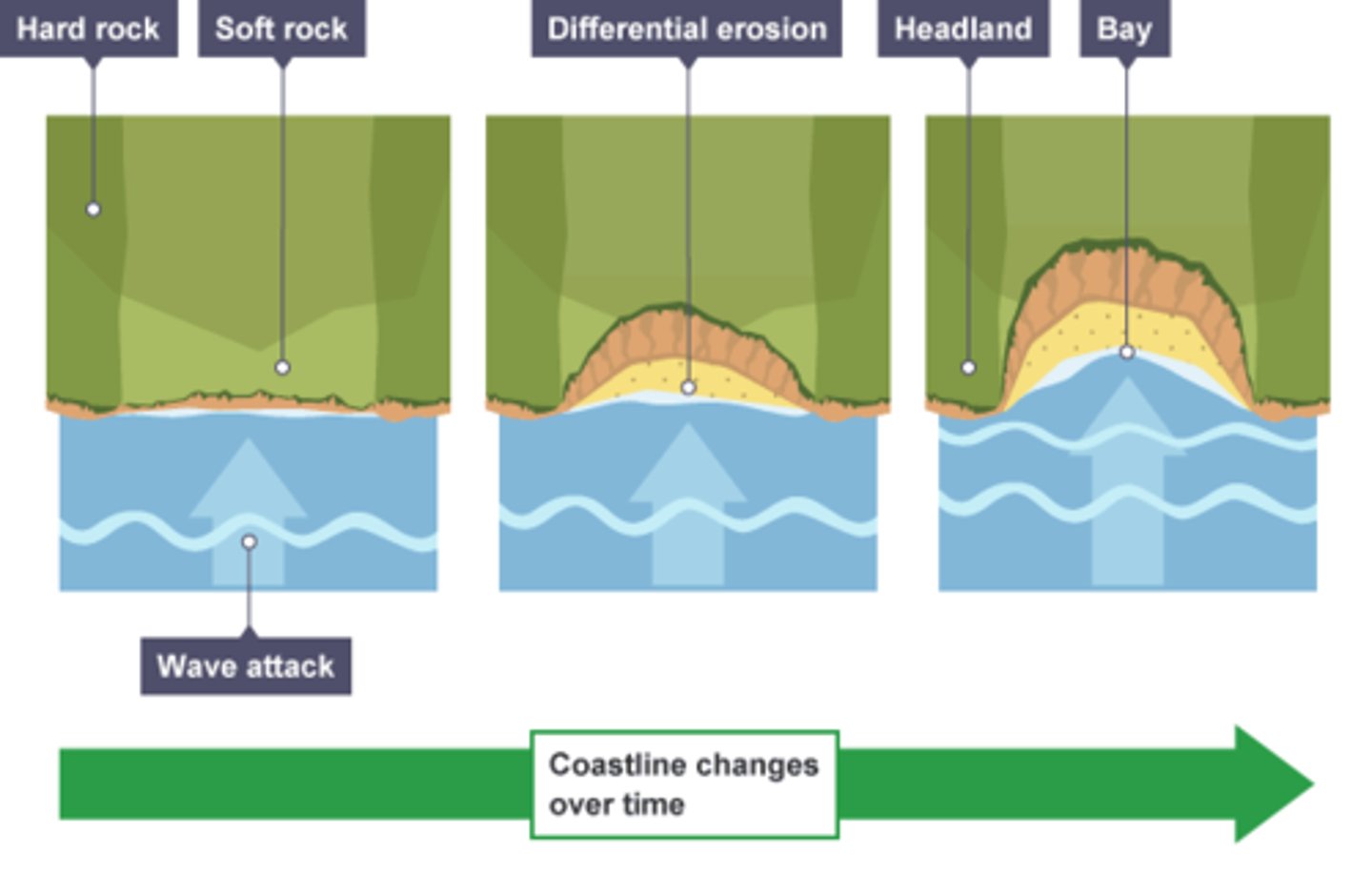
what is a bay?
inlet of the sea where the land curves inwards
how is a bay formed?
bands of soft rock such as clay and sand are weak, therefore they are eroded quickly
what is a headland?
an area of land that sticks out into the sea
how is a headland formed?
hard rock is more resistant to the processes of erosion so when softer rock is eroded inwards, the hard rock sticks out into the sea
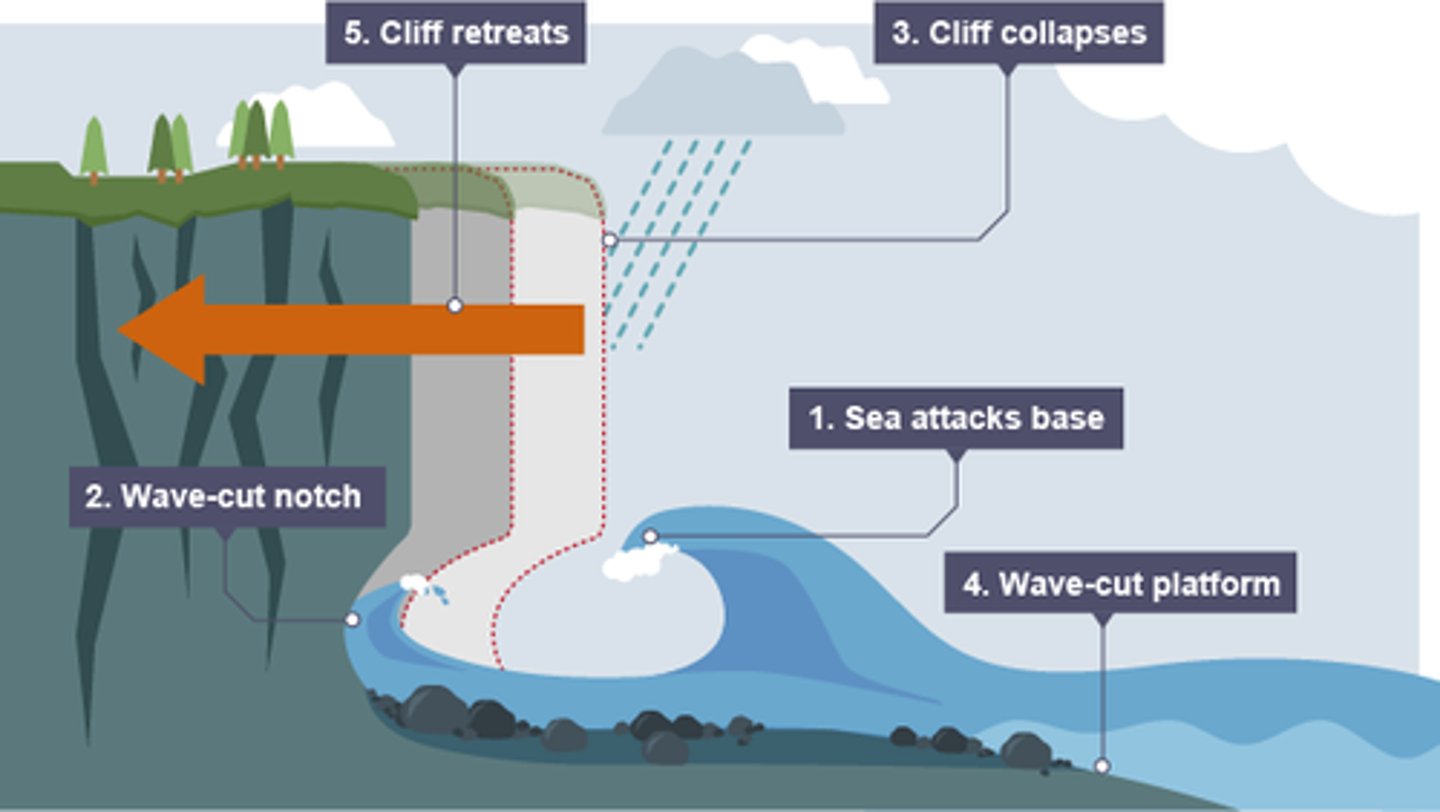
what is a wave cut platform?
wide gently-sloping surface found at the foot of a cliff
how is a wave cut platform formed?
. sea attacks the base of the cliff between the high and low water mark
. wave-cut notch formed by erosional processes such as abrasion and hydraulic action
. notch increases in size, cliff becomes unstable and collapses, leading to the retreat of the cliff face
. eroded material carried away leaving a wave-cut platform
. process repeats, cliff continues to retreat
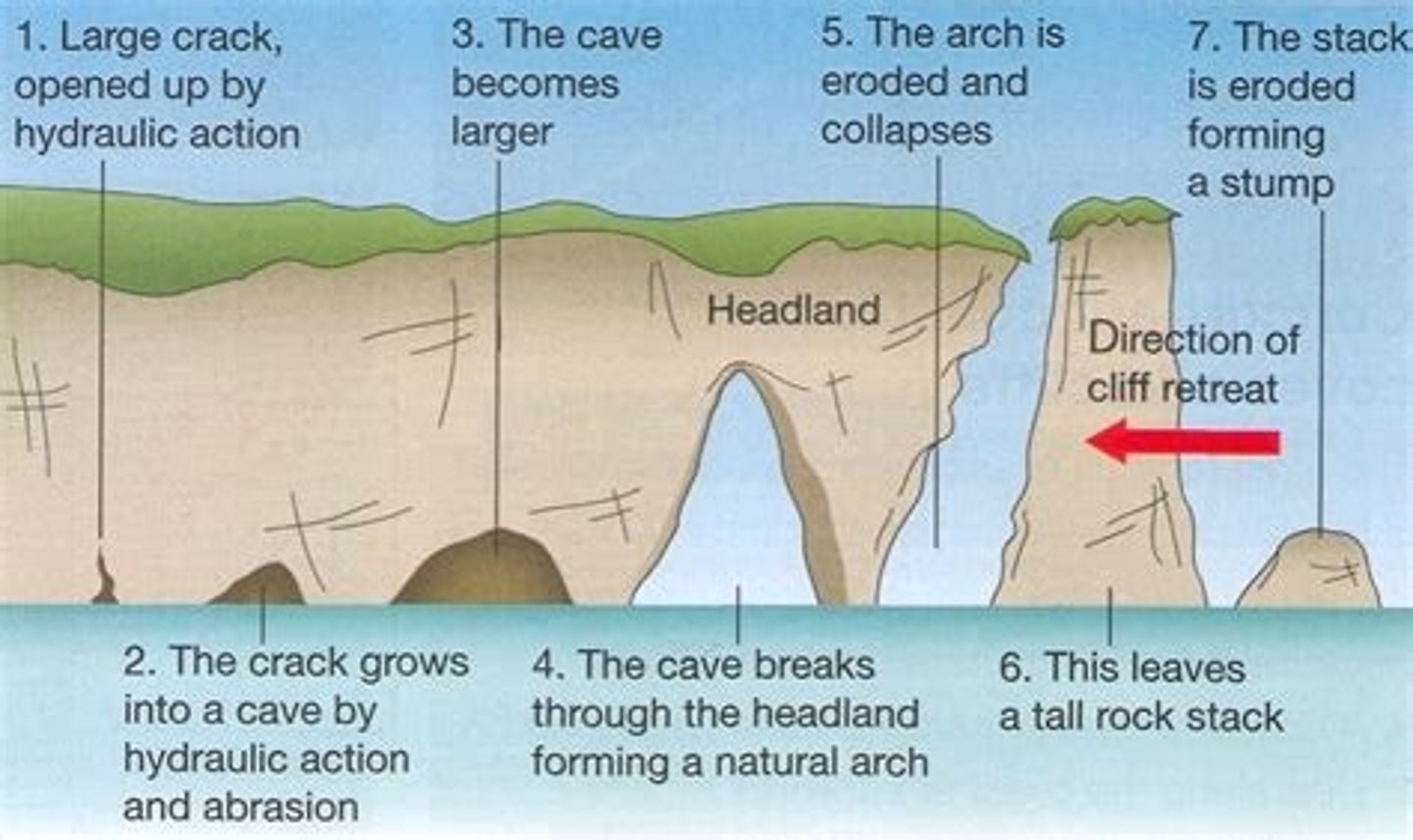
what does CASS stand for?
Cave
Arch
Stack
Stump
explain the process of CASS
. cracks are widened in the headland through the erosional processes of hydraulic action and abrasion
. waves continue to grind at the crack, it opens up to form a cave
. cave becomes larger, eventually breaks through headland to form an arch
. base of the arch becomes wider through erosion until its roof collapses into the sea, leaving a stack
. stack is undercut at the base until it collapses to form a stump
what are 3 depositional landforms?
beaches
spits
bars
how is a beach formed?
waves drop the sediment they carry on the shore
builds up over time to form a beach
how is a spit formed?
. sediment is carried by longshore drift
. when there is a change in the shape of the coastline, deposition occurs forming a thin ridge of sediment
. a hooked end can form if there is a change in wind direction
. waves cannot get past a spit so the water behind is sheltered
what can form behind a spit?
salt marshes or mud flats
how is a bar formed?
. a spit forms across a bay, joining two headlands together
. shallow lakes can be trapped behind the bar, known as lagoons
. lagoons do not last forever and may be filled up with sediment
where is Dorset located?
the south of england on the coast
at what location on the Dorset coast is there a bay and headlands?
swanage bay
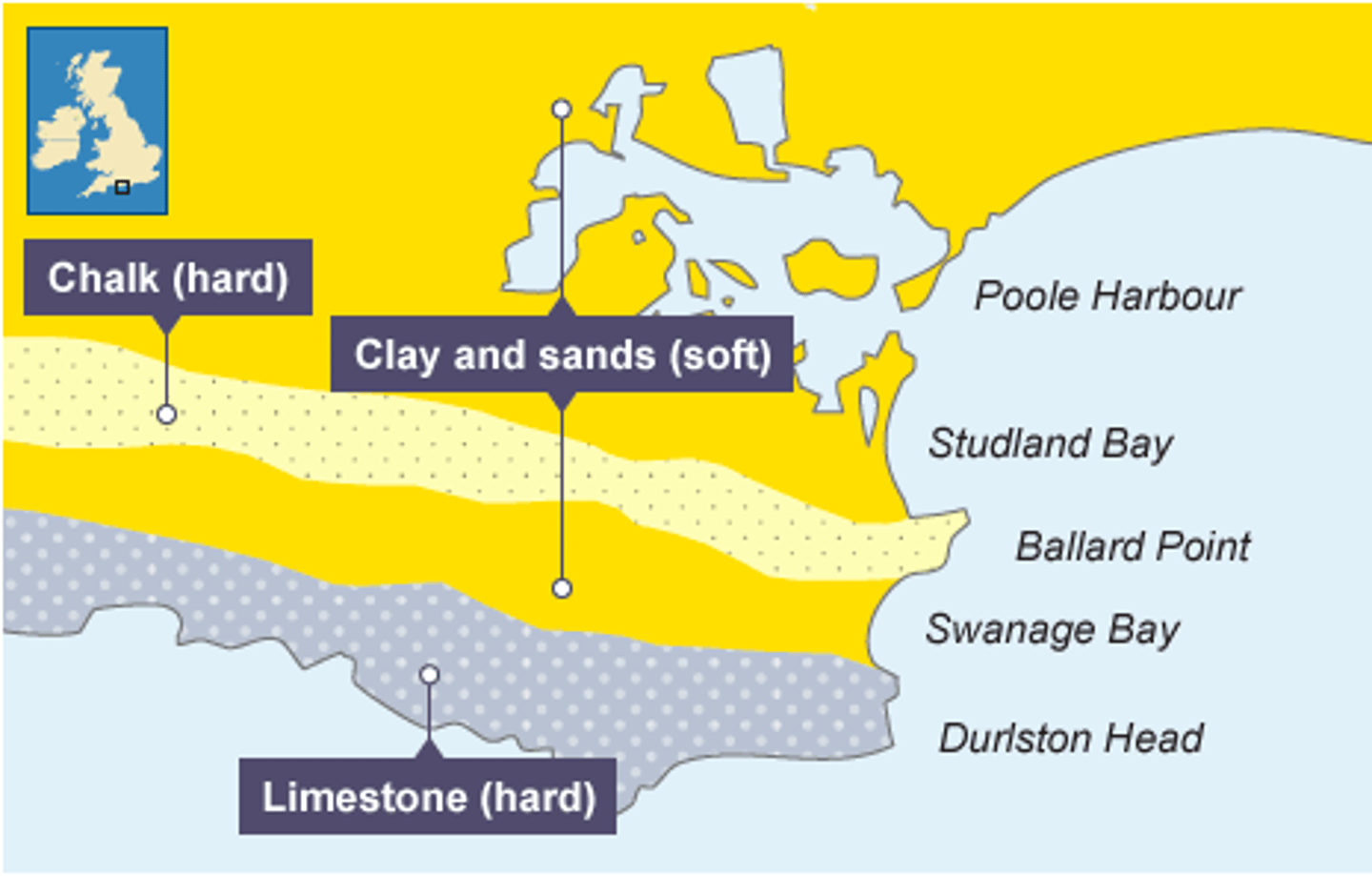
at what location on the Dorset coast is there a stack?
old harry rocks

at what location on the Dorset coast is there a bar?
chesil beach, where the spit has continued to join to the Isle of Portland

what are hard engineering strategies?
hard engineering involves building artificial structures which try to control natural processes
what is a sea wall?
. concrete walls that are placed at the foot of a cliff to prevent erosion
. they are curved to reflect the energy back into the sea
what are some advantages of sea walls?
. effective at protecting the base of the cliff
. usually have promenades so people can walk along them
what are some disadvantages of sea walls?
. waves are still powerful and can erode the sea wall
. expensive - approximately £2,000 per metre
what is rock armour?
. large boulders placed at the foot of a cliff
. they break the waves and absorb their energy
what are some advantages of rock armour?
. cheaper than a sea wall and easy to maintain
. can be used as a fishing spot
what are some disadvantages of rock armour?
. look different to the local geology, as the rock has been imported from other areas
. the rocks are expensive to transport
what are gabions?
. rocks held in mesh cages and placed in areas affected by erosion
what are some advantages of gabions?
. cheap - approximately £100 per metre
. absorbs wave energy
what are some disadvantages of gabions?
. not very strong
. looks unnatural
what are groynes?
. wooden/rock structures built out at right angles into the sea
what are some advantages of groynes?
. builds a beach - which encourages tourism
. trap sediment being carried by longshore drift
what are some disadvantages of groynes?
. by trapping sediment they starve beaches further down the coastline, increasing rates of erosion elsewhere
. they look unattractive
what are soft engineering strategies?
strategies that do not involve building artificial structures, but takes a more sustainable and natural approach to managing the coast
what is beach nourishment?
. sand is pumped onto an existing beach to build it up
what are some advantages of beach nourishment?
. blends in with the existing beach
. larger beaches appeal to tourists
what are some disadvantages of beach nourishment?
. needs to be constantly replaced
. the sand has to be brought in from elsewhere
what is beach reprofiling?
. sediment is redistributed from the lower part of the beach to the upper part of the beach
what are some advantages of beach reprofiling?
. cheap and simple
. reduces the energy of the waves
what are some disadvantages of beach reprofiling?
. only works when wave energy is low
. needs to be repeated continuously
what is dune nourishment?
. marram grass planted on sand dunes stabilises the dunes and helps to trap sand to build them up
what are some advantages of dune nourishment?
. relatively cheap
. maintains a natural-looking coastline
what are some disadvantages of dune nourishment?
. can be damaged by storm waves
. areas have to be zoned off from the public, which is unpopular
what is managed retreat?
. the controlled flooding of low-lying coastal areas
. if an area is at high risk of erosion, managed retreat could be an option
. usually occurs where the land is of low value, for example farm land
what are some advantages of managed retreat?
. a cheap option compared to paying for sea defences
. creates a salt marsh which can provide habitats for wildlife
. natural defence against erosion and flooding
. salt marshes are diverse ecosystems supporting many species
what are some disadvantages of managed retreat?
. land is lost as it is reclaimed by the sea
. landowners need to be compensated - this can cost between £5,000 - £10,000 per hectare
what is the coastal management case study?
the holderness coast - fastest eroding coastline in Europe
why is the holderness coast being managed?
the coastline is eroding at 1.8 metres a year due to:
. rock type
. naturally narrow beaches
. groynes further along coast
. powerful waves
what are the management strategies used on the holderness coast?
. Bridlington is protected by a 4.7 km long sea wall
. Hornsea is protected by a sea wall, groynes and rock armour
. Withersea has tried to make the beach wider by using groynes, also uses a seawall
. Mappleton is protected by rock groynes
. Spurn Head is protected with groynes and rock armour
why is there conflict about coastal management on the holderness coast?
. increase in erosion at Great Cowden because of the groynes used in Mappleton, led to farms being destroyed by erosion and loss of 100 chalets at a holiday park
. some people disagree with where the sea defences are located, especially if it means the land in their community is not protected
. some sea defences negatively impact tourism and reduce the amount of money coming in to the area