
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
what is pruritus?
unpleasant sensation that provokes the desire to scratch or itch
what are the main causes of pruritus?
parasitic skin disease
hypersensitivities (allergies)
what parasites can cause pruritus in horses?
lice
mites
ticks
nematodes
What is Werneckiella (previously known as Damalinia equi)?
biting louse in horses
feeds on epidermal debri
mainly on dorsolateral trunk, neck and face
What is Haematopinus asini?
sucking louse in horses
feeds on blood
mainly found on mane and tail, fetlock and pastern
how can lice be transmitted?
directly between horses
indirectly - e.g. sharing rugs
when are lice more common?
more common in winter
more common in young or old animals (immunocompromised or immunonaive)
no breed or sex predilection
how severe are lice infections?
may be asymptomatic in some horses
may cause severe debilitation in others
what is the diagnosis for lice?
coat brush
hair pluck
what are the treatments for lice in horses?
pyrethrins
pyrethroids
permethrin
fipronil
what should we do when treating horses?
clip hair first
product needs to get to the skin
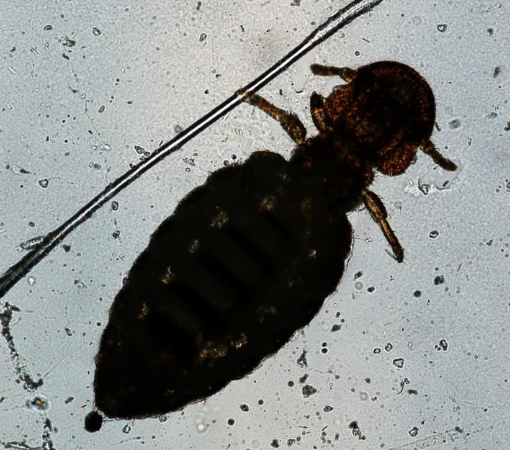

what louse is this?
Werneckiella (biting louse)
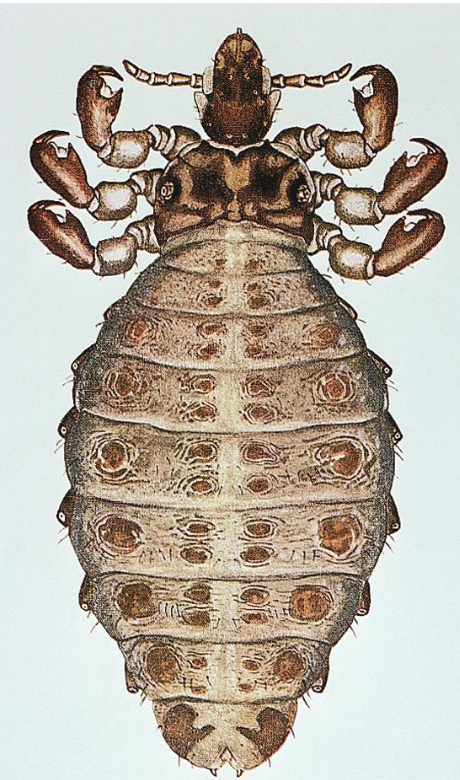

what louse is this?
Haematopinus asini - sucking louse
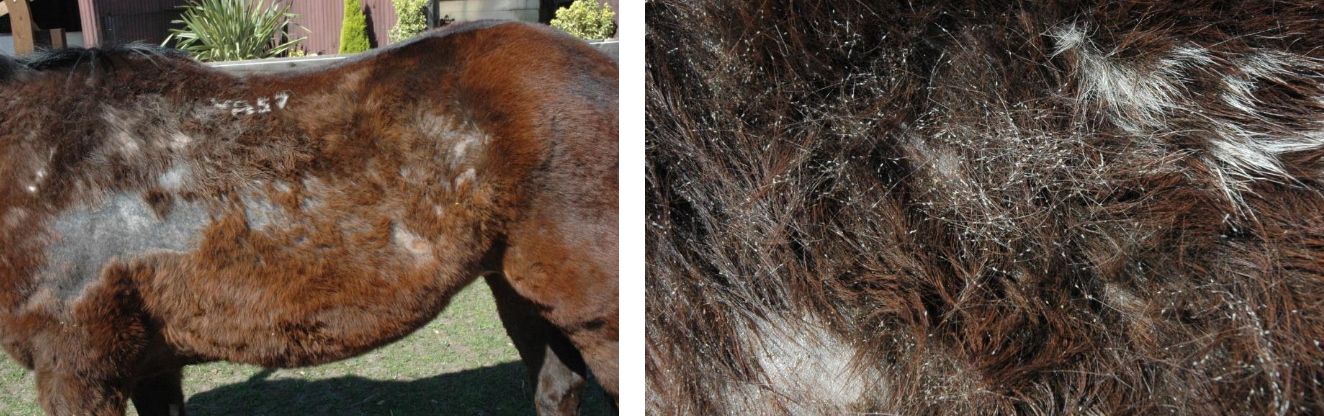
what parasite is likely to be affecting this horse?
lice
What is Chorioptes equi?
mite of horses
mainly on distal limbs
causes intense pruritus with stamping / scratching / chewing of feet
if affected shave feathers when treating
When is Chorioptes equi more common?
in horses with feathers (long hair on bottom on legs) e.g. Cobb, Shire
more common in winter (but happens all year round)
what other condition is common in horses with feathers?
chronic progressive lymphadema (CPL)
What is Sarcoptes scabiei?
mite affecting whole body - entire body will be pruritic
zoonotic
difficult to see on skin scrapings
What is Psoroptes equi?
scab mite
affects forelock, main and tail, trunk
if affecting ears may cause headshaking
What is Trombiculidiasis?
infection with larvae of free living adult Harvest mites
causes papules with small orange or red larvae in centre
affects face, distal limbs, ventral thorax and abdomen
What is Dermanyssus gallinae?
poultry mite
affects head and legs of horses
remove birds if horse is affected
what is the diagnosis of mites?
skin brushings
what is the treatments for mites?
inject macrocylic lactones (cascade)
2 injections 2 weeks apart (subcutaneous)
topical macrocylic lactones (cascade)
once every 4 weeks
topical shampoo - lime sulphur shampoo, selenium sulphate shampoo, topical ivermectin

what mite is this?
Harvest mite - larvae cause trombiculidiasis
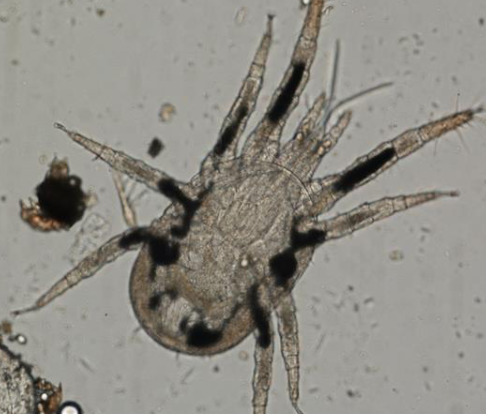

what mite is this?
Dermanyssus gallinae (poultry mite)
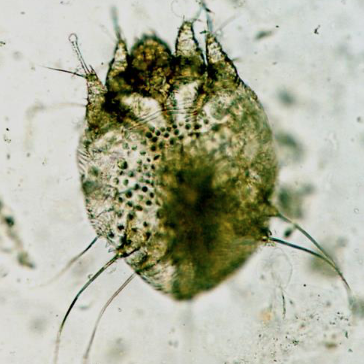
what mite is this?
sarcoptes scabiei
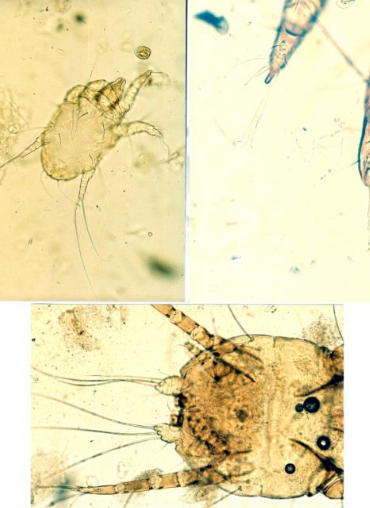
what mite is this?
Psoroptes equi
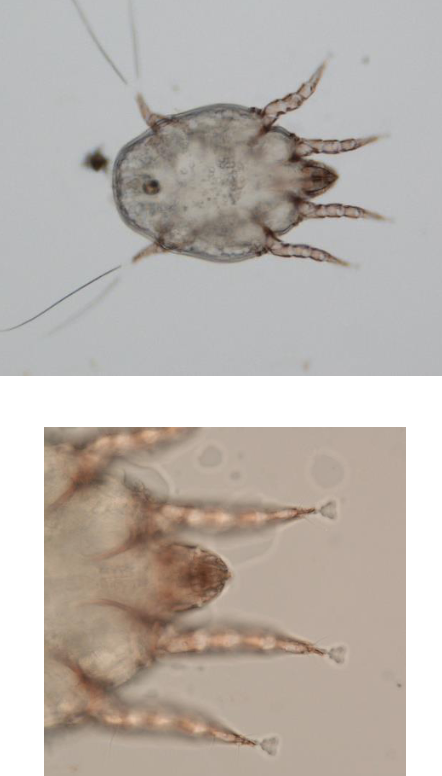

what mite is this?
Chorioptes equi
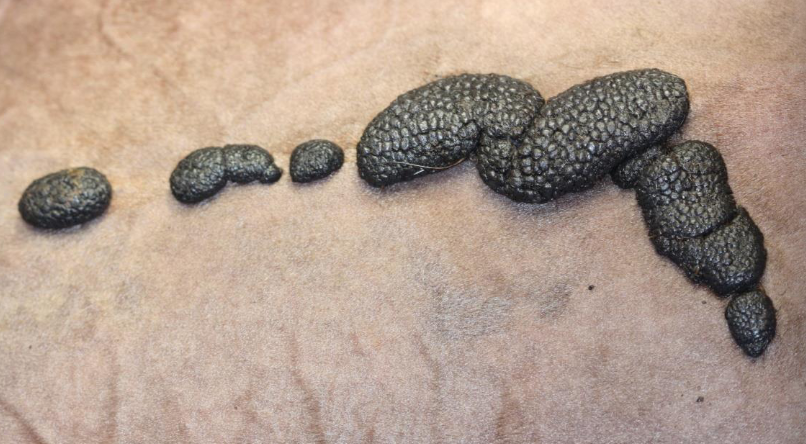
What is Oxyuris equi?
pinworm in horses (nematode)
seen on perianus
causes perianal pruritus
how is Oxyuris equi diagnosed?
clinical signs
cellophane tape
how is Oxyuris equi treated?
anthelmintics
What are the types of hypersensitivities?
insect hypersensitivity
food allergy
contact allergy
atopy
urticaria
what causes insect bite hypersensitivity?
Culicoides spp - sweet itch
affects main, back, tail and ventrum
seasonal
risks - standing water, dawn and dusk
what is treatment for insect bite hypersensitivities?
avoid midge contact
improve skin integrity
what can food allergies cause in horses?
pruritus
diarrhoea
respiratory signs
(food allergies rare in horses)
what is diagnosis for food allergies?
diet elimination
what is atopy?
sensitivity to multiple allergens
what is the diagnosis for atopy?
exclusion
intradermal skin testing can help identify allergens
what is the treatment for atopy?
avoid allergen
immunotherapy
cortiosteroids / antihistamines
improve skin barrier function - using shampoos, conditioners and emolients
what do we see with urticaria / hives?
wheals = raised bumps on skin
oedema
pruritus
what do we need to do when diagnosing urticaria / hives?
easy to recognise, can be itchy
cause is difficult to determine
rule out food and insect / contact allergy
what is the treatment for urticaria / hives?
corticosteroids
antihistamines
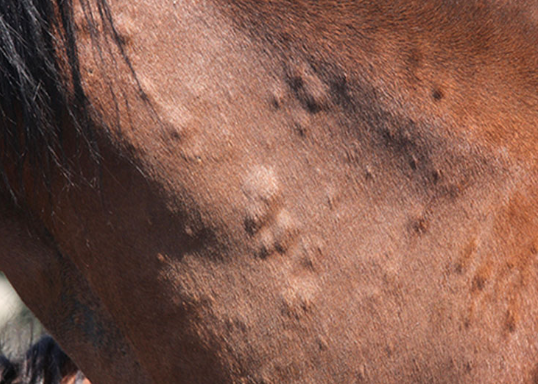
what skin condition is shown here?
urticaria (hives)
what is scaling?
dry flaky dandruff appearance of skin
what is crusting?
yellow, red or brown, wet / damp, oozing on skin, like a scab
what is the difference between erosion and ulceration?
erosion is superficial
ulceration is deeper

what is this?
scaling
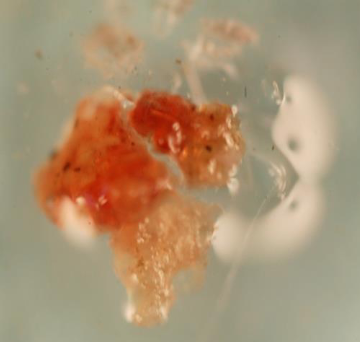
what is this?
crusting
what conditions cause crusting, scaling, erosion or ulceration?
dermatophilosis (rain scald)
bacterial folliculitis
dermatophytosis (ringworm)
photosensitisation
leukocytoclastic vasculitis
pastern dermatitis
pemphigus foliaceous
what is Dermatophilosis (rain scald)?
caused by dermatophilus congolensis (gram positive, facultative anaerobe)
causes chronic moisture and skin damage
see crust and moist mats of hair at the lesion
affects the gluteal area, face, neck and extremities
how is Dermatophilosis diagnosed?
cytology (smear pus onto a slide)
what is the treatment for dermatophilosis?
topical - mild cases
systemic antimicrobials - severe cases
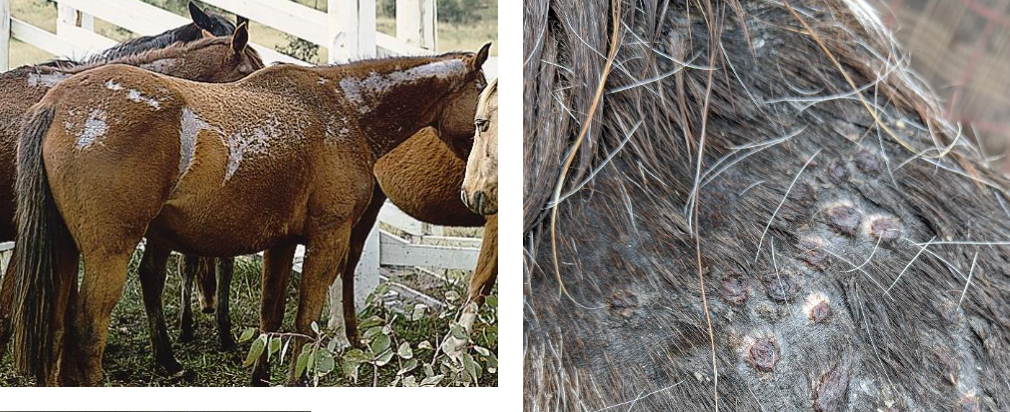

what skin condition is shown here?
dermatophilosis (rain scald)
what is bacterial folliculitis?
caused by staphylococcus and streptococcus
painful lesion
what is the diagnosis of bacterial folliculitis?
cytology, culture
what is the treatment of bacterial folliculitis?
topical - mild cases
system antimicrobial - severe cases
what is dermatophytosis (ringworm)?
highly contagious fungal skin infection
caused by trichophyton and mycrosporum
see circular patches of alopecia
what animals is dermatophytosis (ringworm) common in?
young and immunocompromised animals
what is the diagnosis of dermatophytosis?
fungal culture, PCR, microscopy
what is the treatment of dermatophytosis?
topical antifungals
natamycin
enilconazole
miconazole
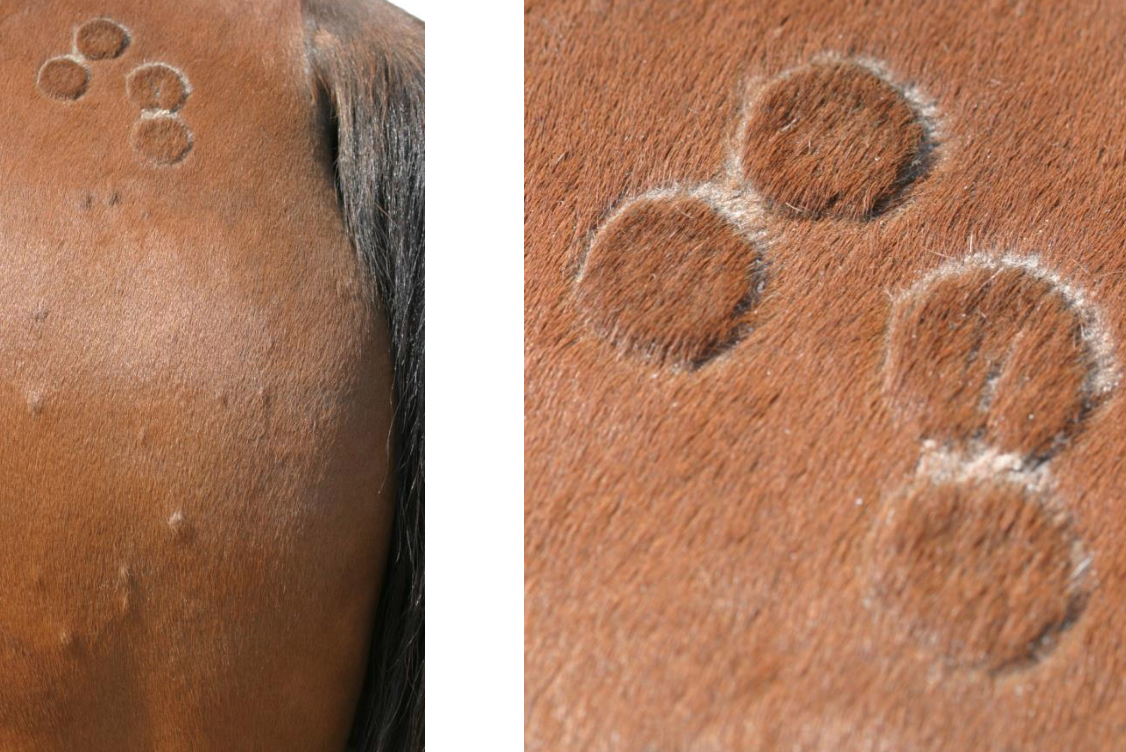
what skin condition is shown here?
dermatophytosis (ringworm)
what are the two causes of photosensitisation?
hepatogenous
ingestion or application of photodynamic agent
where are photosensitisation lesions common?
in white areas
what is the diagnosis of photosensitisation?
clinical signs and blood tests
what is the treatment of photosensitisation?
treat liver disease
removal of agent
what is leukocytoclastic vasculitis?
common disorder that affects non-pigmented areas on distal (or lateral) limb
can be painful
what is the diagnosis of leukocytoclastic vasculitis?
clinical signs
skin biopsy
what is the treatment of leukocytoclastic vasculitis
avoid exposure to light
(corticosteroids - not always affective)
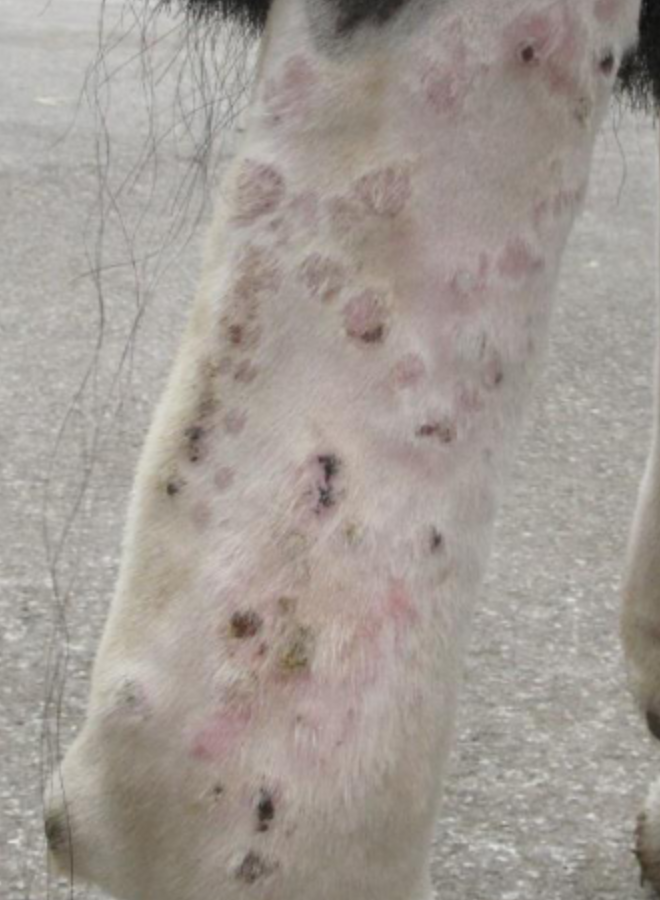
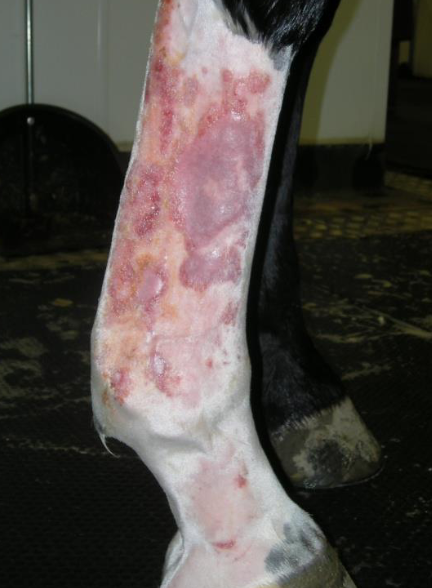
what skin condition is shown here?
leukocytoclastic vasculitis
what is pastern dermatitis?
very common disorder on back of horses distal leg (pastern)
a syndrome rather than a disease
when is pastern dermatitis seen commonly?
in winter (also when more wet) and in white limbs
what can cause pastern dermatitis?
infectious conditions
inflammatory conditions
chronic disease
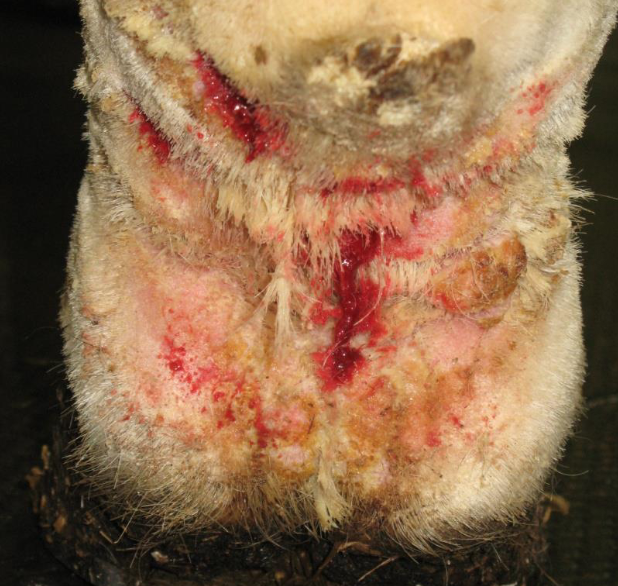

what skin condition is shown here?
pastern dermatitis
what is pemphigus foliaceous?
rare, autoimmune disease
causes severe crusting
no age or sex predilection
what is the diagnosis of pemphigus foliaceous?
skin biopsy
what is the treatment of pemphigus foliaceous?
immunosuppressive drugs
what is the prognosis of pemphigus foliaceous?
guarded - prognosis is better in younger horses, older horses tend to not respond to medication
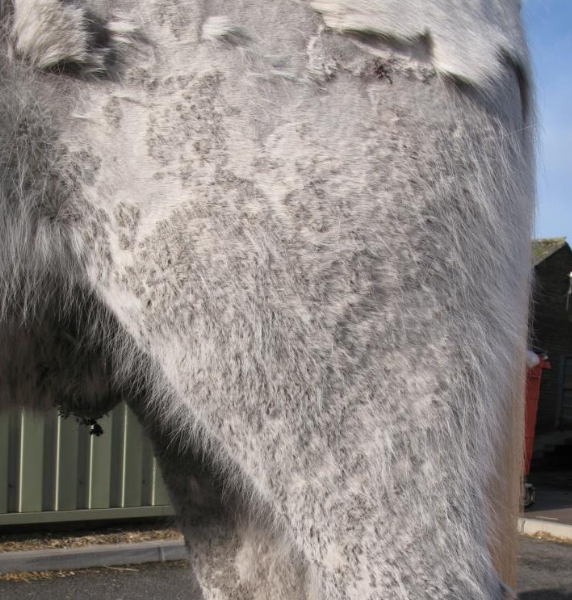
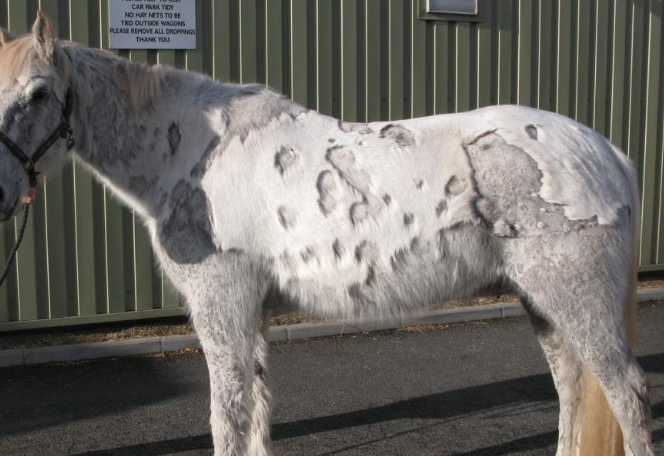

what skin condition is shown here?
pemphigus foliaceous
what cutaneous swellings, nodules and tumours do we see in horses?
viral papillomatosis
warbles
genetic / developmental
eosinophilic granuloma
tumours
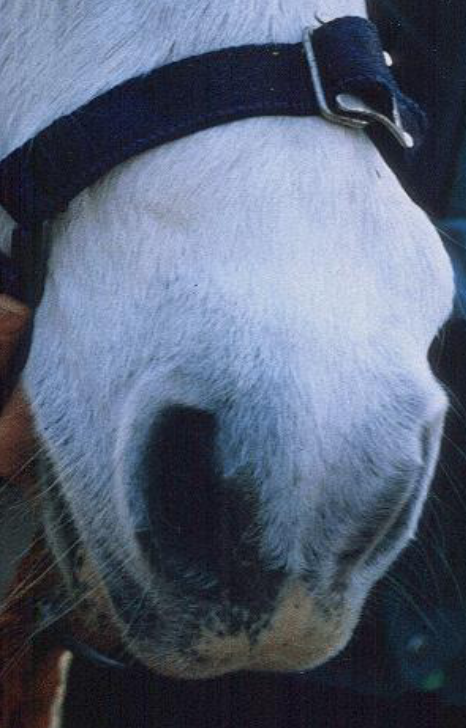
what is viral papillomatosis?
grass warts - seen on muzzle and face of young horses
pinnal acanthosis or aural placks
no need to treat
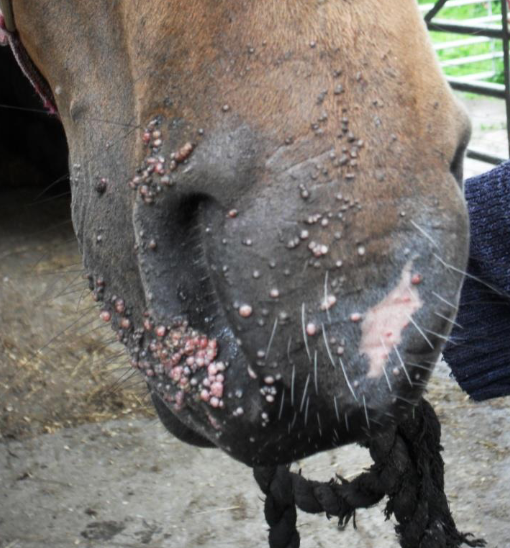
what skin condition is shown here?
viral papillomatosis - grass warts on muzzle
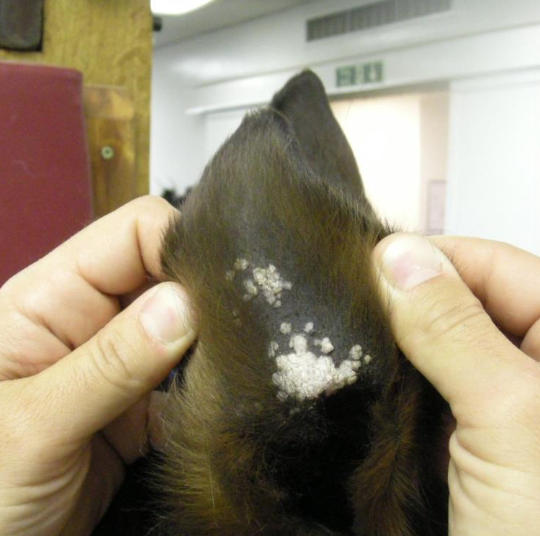
what skin condition is shown here?
viral papillomatosis - pinnal acanthosis / aural placks
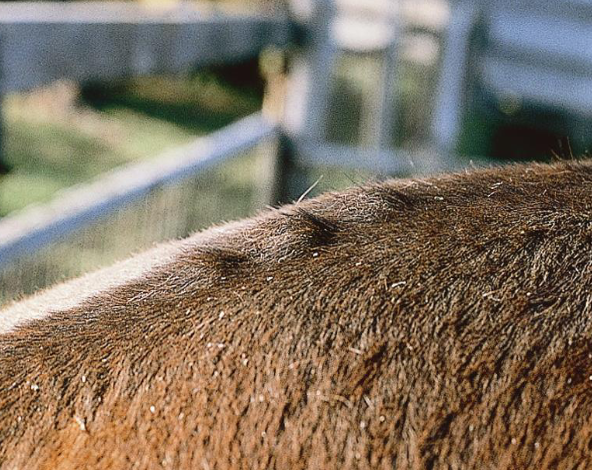
what are warbles?
larval stages of Hypoderma bovis and lineatum
notifiable but very rare due to use of ivermectin
nodules with central pore
painful
what is the treatment of warbles?
enlargement of pore to remove central grub
surgical removal
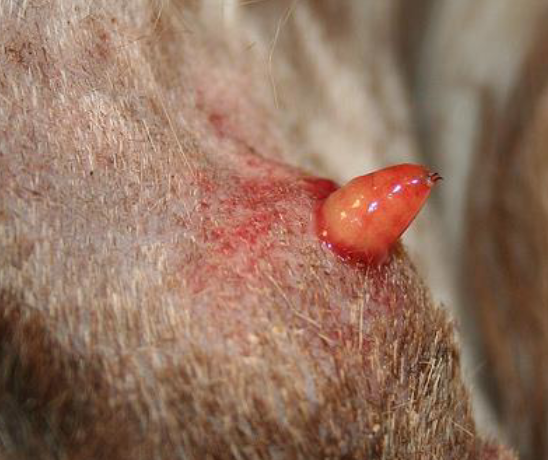
what skin condition is shown here?
warbles
what genetic / developmental cysts / nodules do we see?
dentigerous cyst
atheroma
dermoid cyst
vascular hamartoma
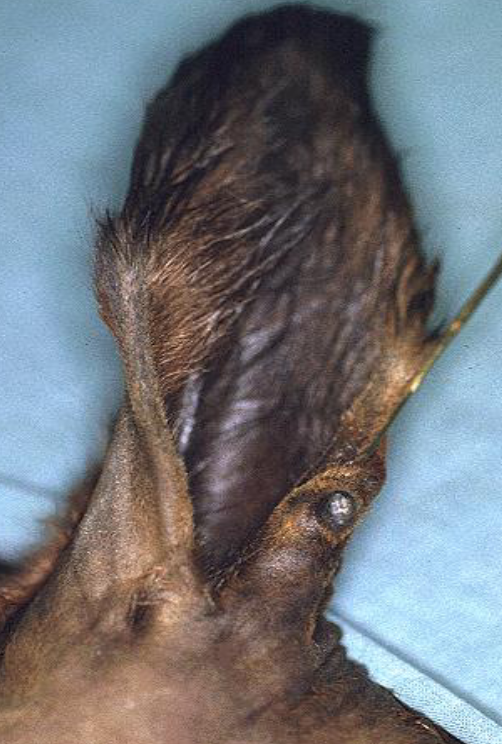
what skin condition is shown here?

what skin condition is shown here?

what skin condition is shown here?

what skin condition is shown here?
what is eosinophilic granuloma?
collagen necrosis
seen very frequently
caused by insect bites or trauma
not painful and not pruritic
what is the appearance of eosinophilic granuloma?
may have single or multiple
0.5 to 10cm

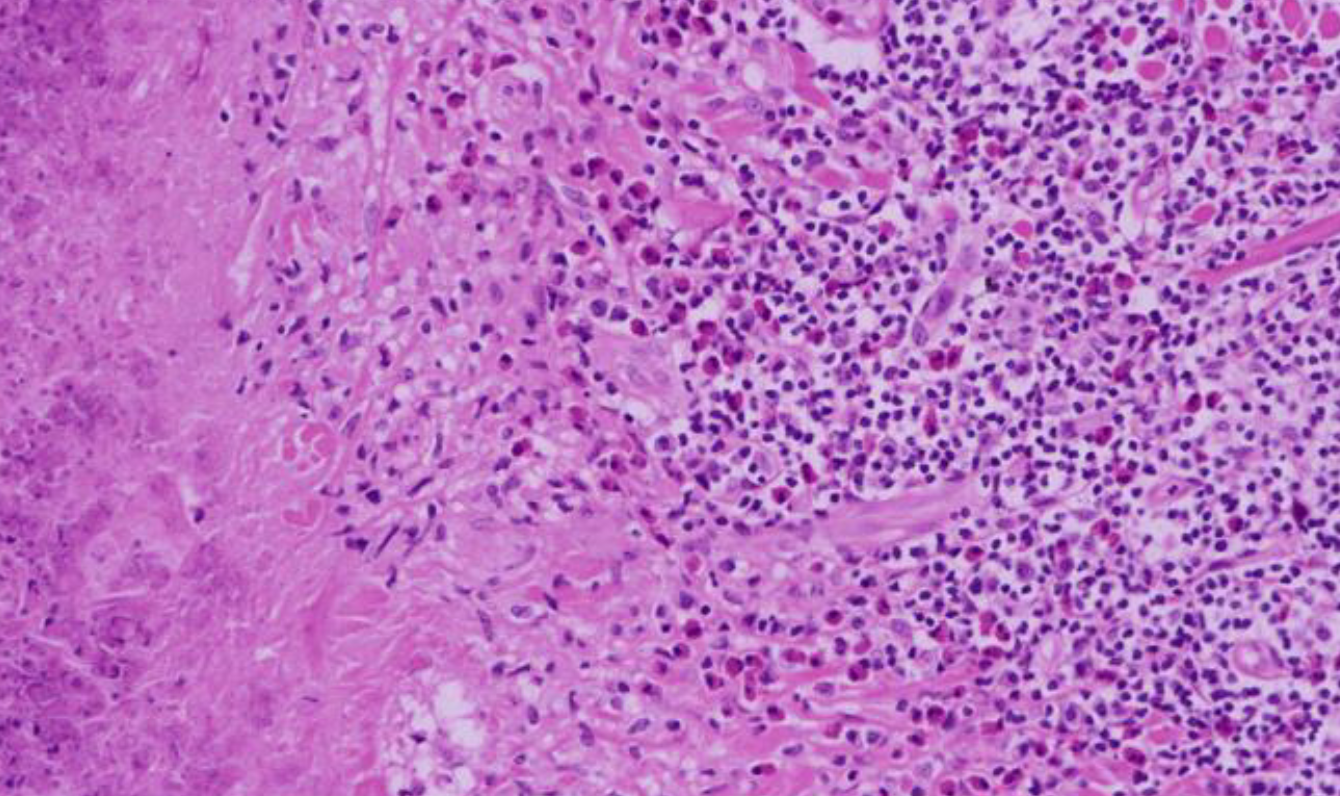
what skin condition is shown here?
eosinophilic granuloma
what are the most common skin tumours that we see in horses?
sarcoids
melanoma
squamous cell carcinoma
mast cell tumour, lymphoma, etc.
what are sarcoids?
most common skin tumour in horses
seen with bovine papillomavirus 1 and 2
genetic predisposition - no sex or breed predisposition
can be seen with flies
what are the 6 clinical presentations of sarcoids?
occult sarcoid
verrucose sarcoid
nodular sarcoid
fibroblastic sarcoid
mixed sarcoid
malignant sarcoid
would we biopsy sarcoids?
not always - as dangers of exacerbation
if we have a positive diagnosis - be ready to treat
what are the treatments of sarcoids?
surgery / laser removal
immune therapy - BCG injections
cytotoxins (topical and injection)
antimitotics (topical)
photodynamic therapy
brachytherapy - most successful but not always available
what is the prognosis of sarcoids?
variable
the more they have the more they will get
they multiply over summer and grow over winter
a single sarcoid implies genetic susceptibility
this remains for life
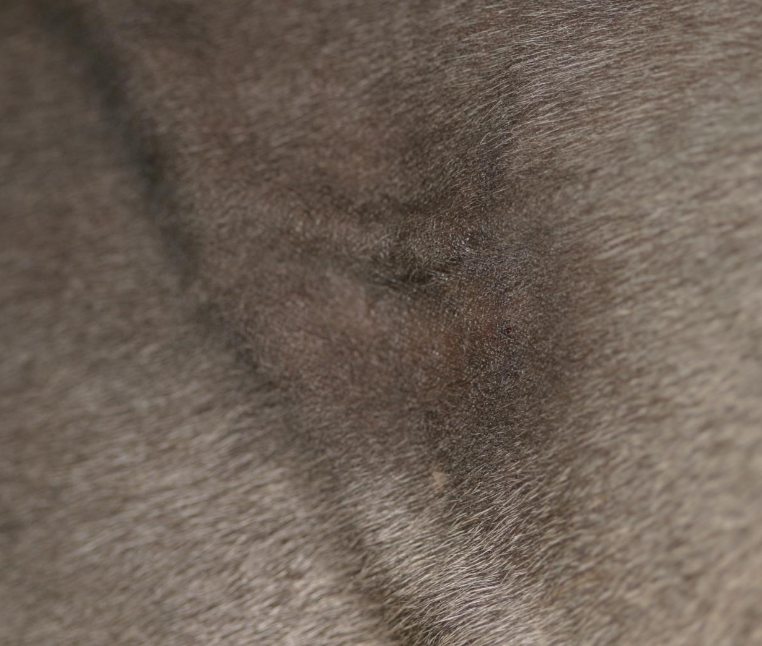
what type of sarcoid is shown here?
occult sarcoid