Algebra Final Review Stack
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
1
New cards
distance
rate x time
2
New cards
infinate solutions
lines are the same
3
New cards
all real numbers
inequality true
4
New cards
no solution
lines are parallel, solutions are not true
5
New cards
intrest
part x rate x time
6
New cards
open circle
less than, greater than, dashed line
7
New cards
closed circle
less than or equal to, greater than or equal to, solid line
8
New cards
and inequalities
both inequalities must be satisfied on number line
9
New cards
or inequalities
only 1 inequality needs to be satisfied
10
New cards
absolute value
The distance of a number from zero on a number line. In an expression, numbers cannot be distributed, and it cannot equal a a negative number before evaluating
11
New cards
slope-intercept form
y = mx + b
12
New cards
horizontal line
0
13
New cards
verticle line
undefined
14
New cards
point-slope form
y - y₁ = m(x - x₁)
15
New cards
standard form
Ax+By=C
16
New cards
parallel lines
Lines that never intercect. They have the same slope, yet different y-intercepts
17
New cards
perpendicular lines
Lines that incerept to form right angles. Their slopes are opposite recipricols, and they have different y-intercepts
18
New cards
relation
a set of ordered pairs
19
New cards
function
each input has exactly one output
20
New cards
x
independant
21
New cards
y
dependant
22
New cards
continuous function
includes all real numbers
23
New cards
discrete function
just the whole numbers of integers
24
New cards
one to one function
every input has exactly one output
25
New cards
parent function
function we start with before transformations, f(x)=x
26
New cards
verticle translation
f(x)=x+k
27
New cards
k>0
verticle shift up
28
New cards
k
verticle shift down
29
New cards
horizontal translation
f(x)=(x-h) , h is not true to its sign
30
New cards
h>0
horizontal shift right
31
New cards
h
horizontal shift left
32
New cards
transformation form
f(x)=(x-h)+k
33
New cards
sequence
an ordered list of numbers that forms a pattern
34
New cards
arethmatic sequence
has a common difference between each term in sequence
35
New cards
recursive formula
a1=___; an = an-1 + d
36
New cards
explicit formula
an = a + (n - 1)d
37
New cards
no association
refers to the absence of a relationship between two variables. If there is no connection between the variables, the value of one variable does not affect the value of the other.
38
New cards
strong correlation
A relationship between two variables where a change in one is consistently associated with a change in the other. This suggests a high level of association and accurate prediction between the two variables.
39
New cards
weak correlations
Weak correlation means little to no relationship between two variables. Changes in one variable do not significantly impact the other variable. Weak correlations are shown by a correlation coefficient close to zero.
40
New cards
line of best fit
trend line that matches the data/points the greatest
41
New cards
correlation coefficent
a statistical measure that quantifies the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables. It ranges from -1 to 1, where -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, 0 indicates no correlation, and 1 indicates a perfect positive correlation.
42
New cards
bivariate data set
data set with 2 variables
43
New cards
residual
difference between the y-value and the corresponding y-value
44
New cards
interpolation
using a model to estimate a value within the range of known values
45
New cards
extrapolation
using a model to make a prediction about a vaule outside of known values
46
New cards
causation
describes a cause and effect relationship
47
New cards
product of powers

48
New cards
quotient of powers
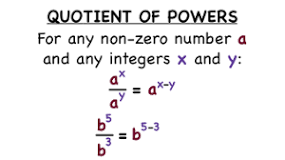
49
New cards
power of product
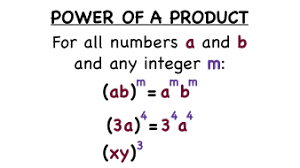
50
New cards
negative exponents
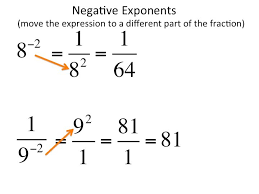
51
New cards
0 exponent
equal to 1
52
New cards
rational exponents
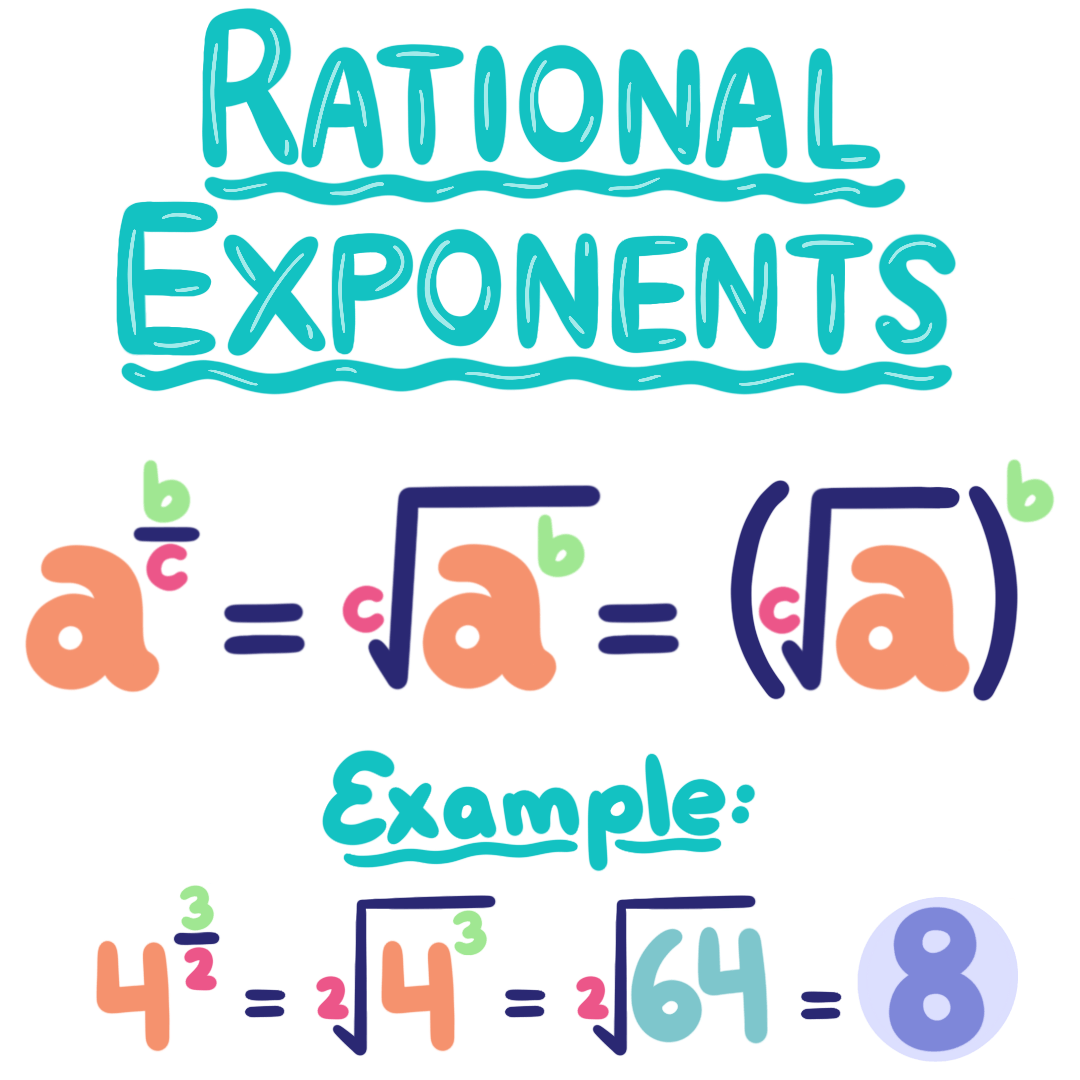
53
New cards
graphing exponential functions
f(x)=ab^x
54
New cards
exponential growth
f(x)= a(1+r)^x
55
New cards
compound interest
a=p(1+r/n)^nt
56
New cards
exponential decay
f(x)=a(1-r)^x
57
New cards
geometric recursive formula
an=(an-1)(r)
58
New cards
geometric explicit formula
an=(a1)(r^n-1)
59
New cards
transformin exponential functions
f(x)=a^(x-h)+k
60
New cards
polynomial
a monomial or the sum or difference of two or more monomials called terms
61
New cards
degree of polynomials
the total of exponents per term
Suppose we have a polynomial with the terms 3x^4 - 2x^2 + 5. The degree of this polynomial is 4, since the highest power of x is 4.
Suppose we have a polynomial with the terms 3x^4 - 2x^2 + 5. The degree of this polynomial is 4, since the highest power of x is 4.
62
New cards
finding vertex
(-b/2a,f(-b/2a))
63
New cards
standard form
f(x)=ax^2+bx+c
64
New cards
multiplying radical expressions
multiply whats in and out of radical expressions
Suppose we want to find the product of √2 and √3. We can simplify this expression by multiplying the numbers inside the radicals: √2 × √3 = √(2×3) = √6. Therefore, the product of √2 and √3 is equal to √6.
Suppose we want to find the product of √2 and √3. We can simplify this expression by multiplying the numbers inside the radicals: √2 × √3 = √(2×3) = √6. Therefore, the product of √2 and √3 is equal to √6.
65
New cards
imaginary numbers
Numbers that cannot be expressed as the product of a real number and the square root of a negative number. Symbolized by "i". Used in complex numbers.
66
New cards
completing a square
(b/2)^2
67
New cards
quadratic formula
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a
68
New cards
vertex form
f(x) = a(x-h)^2 + k
69
New cards
finding x intercepts
make Y 0
EXP: 0=2x^2+6x+5
EXP: 0=2x^2+6x+5
70
New cards
finding y intercept
evauate x for 0
EXP: f(0)=2(0)^2+6(0)+5
f(0)=5
EXP: f(0)=2(0)^2+6(0)+5
f(0)=5