2.3 Conservation Laws & Particles Interactions
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are 4 fundamental interaction/forces:
________ is the weakest of these forces and the _____ ______ only effects particles with ______, whilst the _____ ______ is the strongest.
Gravity, Electromagnetism, Strong Nuclear (or Strong Interaction), Weak Nuclear
Gravity is the weakest of these forces and the gravitational interaction only effects particles with mass, whilst the strong interaction is the strongest.
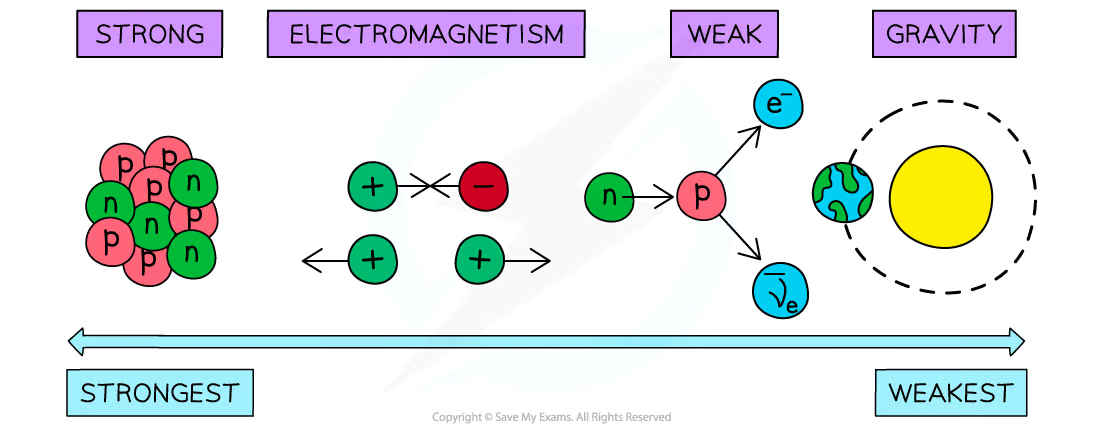
The larger the mass of the gauge boson the …..
The ________ and ________ interactions have an ________ ________ as photons have a ___ _____
Larger the mass of a gauge boson the shorter the range of the force
The electromagnetic and gravitational interactions have an infinite range - photon has 0 mass
What is the strong forces range and the weak forces range?
How does the W boson effect the proton?
Virtual W particle uses so ____ _____ and exists for a ____ ____ _____ and can’t ____ ____
The strong force has a range of 10-15m
The weak force has a range of up to 10 -18m
W boson has a mass of 100x of a proton which gives weak force very short range and
virtual W particle uses so much energy and exists for a very short time and can’t travel far
What is an exchange particle?
Two particles exert a force on each other, a virtual particle is created and only exist for a short amount of time and carry the fundamental force between each particle
What are gauge bosons and example?
Gauge bosons: Each fundamental interaction is transmitted by its own exchange particle
Gravity as a type of interaction:
Gravity is so weak only has noticeable effect on large masses, therefore, gravity does not play a part in particle interactions
Theorised exchange particle for the gravitational force is the graviton, however, has not yet been discovered.
The _____ _______ is only between ______ particles and the _________ particle that carriers this force is ______ _______, _
What are the properties of photons?
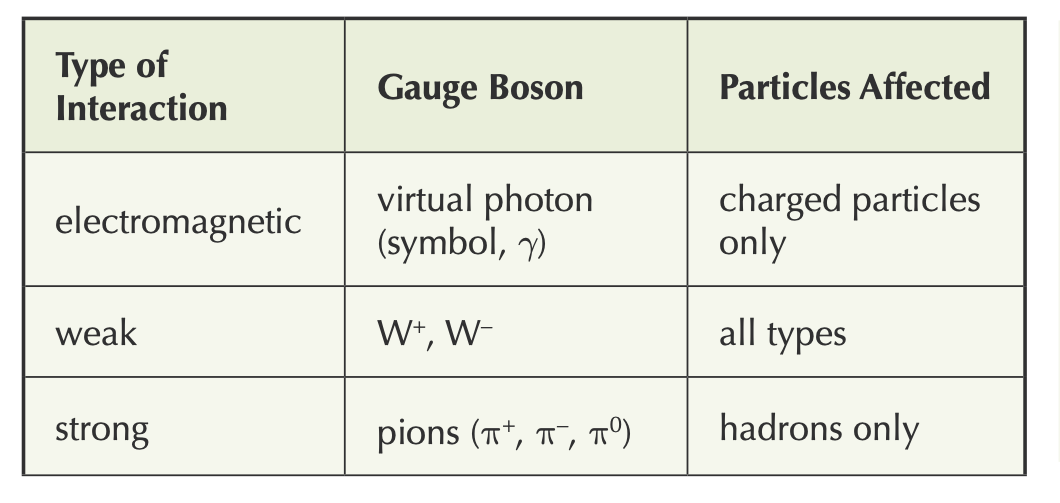
The electromagnetic force is only between charged particles and the exchange particle that carriers this force is virtual photon, γ
Properties of the photon are: no mass, no charge, own antiparticle
When do electromagnetic interactions occur and an example?
Electromagnetic interactions occur whenever two charged particles interact with each other
For example, when two charged particles, such as electrons, are repelled by each other, a virtual photon is exchanged between them to produce this repulsion
What is the electromagnetic force responsible for?
The electromagnetic force is also responsible for binding electrons to atoms due to the attractive force between the negative electrons and positive nucleus

Hadrons are particles that are made up of ____ in the ____ _____
What are the exchange particles of the strong interactions?
Why can’t lepton interact with the strong force?
Hadrons are particles that are made up of quarks in the strong interaction
Exchange particle of the strong interaction: pion (between nucleons), gluon (between quarks)
Leptons cannot interact with the strong force, since they are not made up of quarks

What is the weak interaction responsible for and what is its exchange particle?
Why does beta decay occur?
The weak interaction is responsible for the radioactive decay of atoms
The exchange particle that carries this force is the W–, W+ ,Z0 boson
Type of exchange particle depends on the type of interaction
β decay occurs because of the weak interaction between quarks
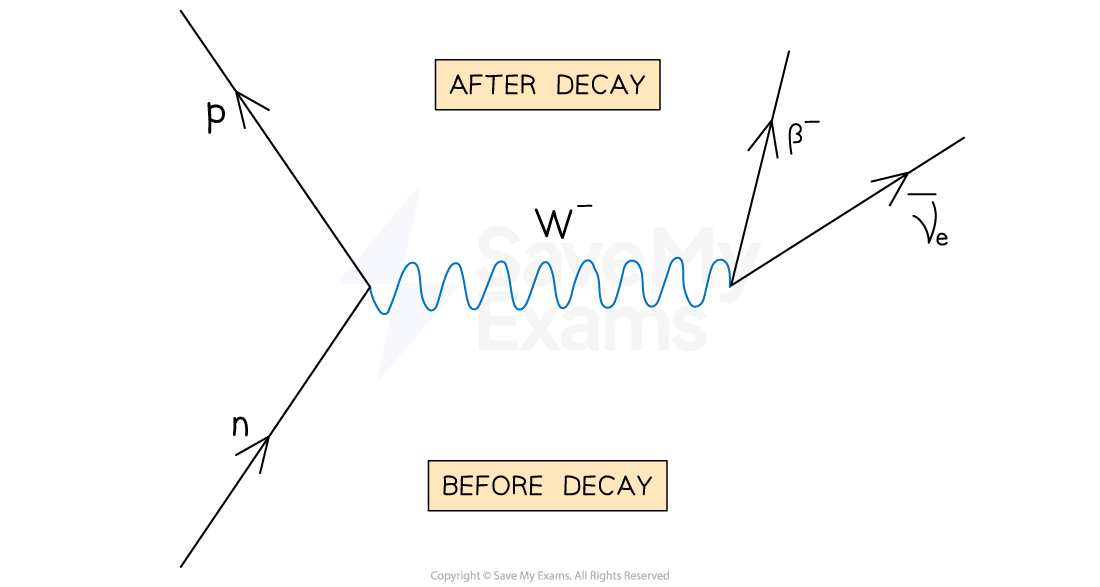
What happens in β- decay, equation ,diagram and exchange particle?
β- decay, a neutron turns into a proton emitting an electron and an anti-electron neutrino (anti-neutrino)
n → p + e- + ̅νe or: n → p + β- + ̅νe
The W- boson is the exchange particle in this interaction

β- decay - ________ interaction - exchange of ___ _______
β- particle (electron) has a…
During beta-minus decay:
Beta-minus decay - Weak interaction - exchange of W- boson
β- particle (electron) has a negative charge
During beta-minus decay:
A neutron decays into a proton and a W- boson
Then, the W- boson decays into an electron and anti-electron neutrino
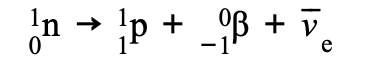
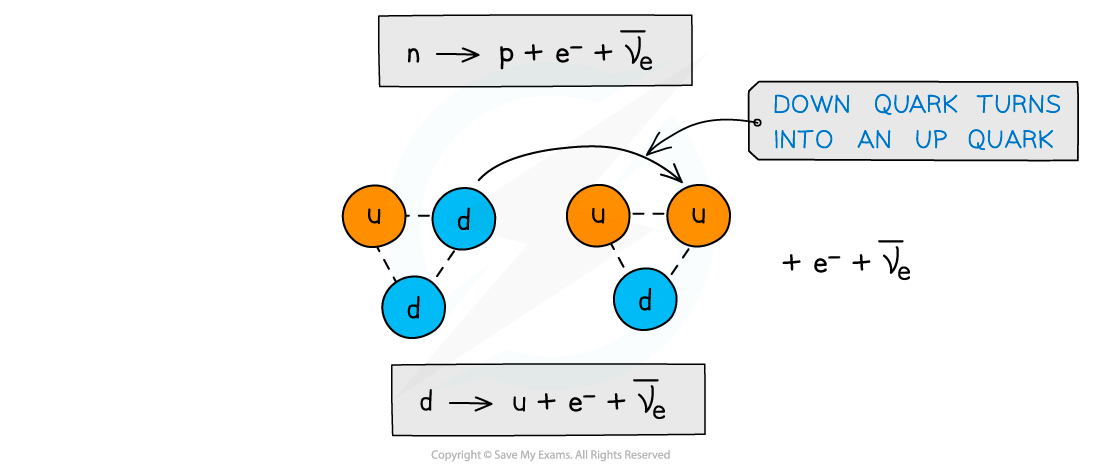
What is the Quark Composition: β– decay?
Neutron turns into a proton so down quark into an up quark emitting electron and anti-electron neutrino
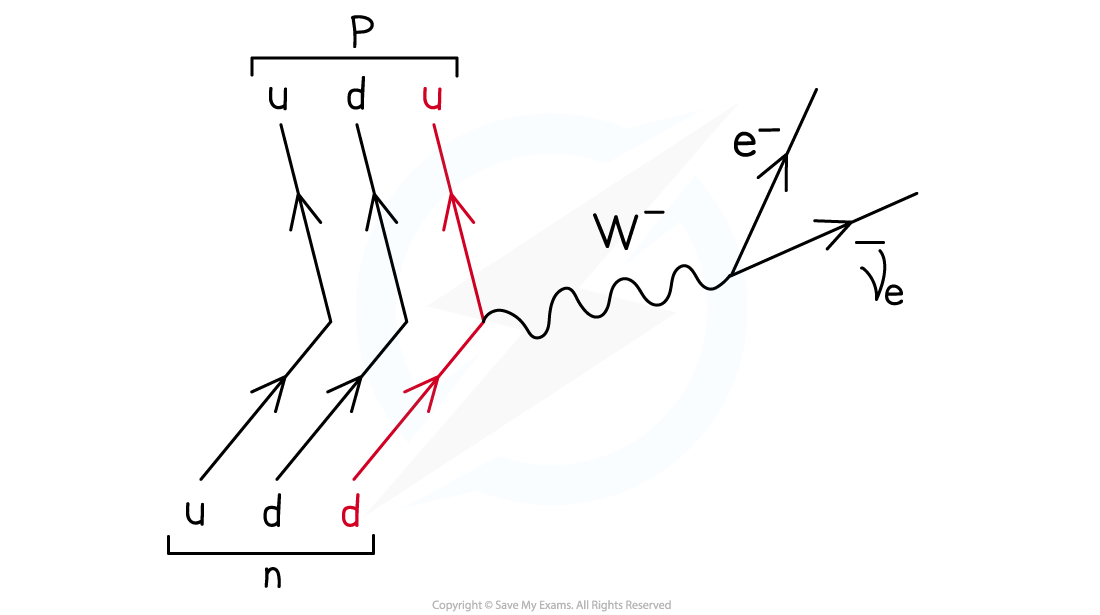
What does W- boson do?
W- boson ‘carries away’ the negative charge of the down quark which provides the negative charge for the electron and anti-neutrino.
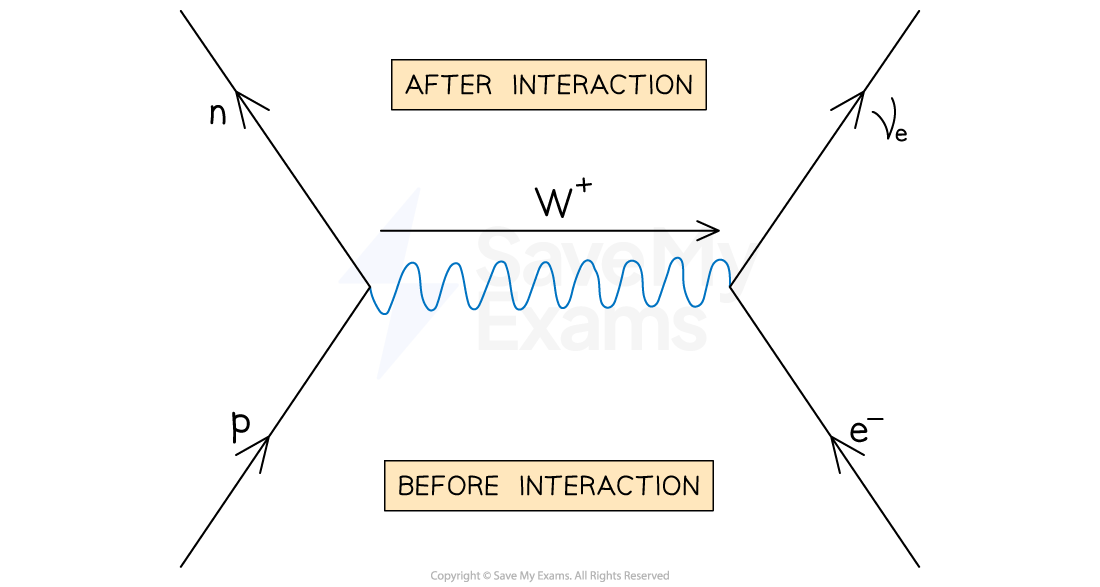
What happens in β+ decay, equation ,diagram and exchange particle?
In β+ decay, a proton turns into a neutron emitting a positron and an electron neutrino (neutrino)
p → n + e+ + νe
The W+ boson is the exchange particle in this interaction

β+ decay - ________ interaction - exchange of ___ _______
β- particle (electron) has a…
During beta-minus decay:
Beta-plus decay - Weak interaction - exchange of W+ boson
β+ particle (positron) has a positive charge
During beta-plus decay:
A proton decays into a neutron and a W+ boson
Then, the W+ boson decays into a positron and electron neutrino
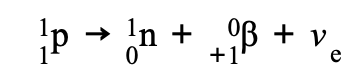
What is the Quark Composition: β+ decay?
Proton Up quark turns into neutron Down quark emitting a positron and electron neutrino
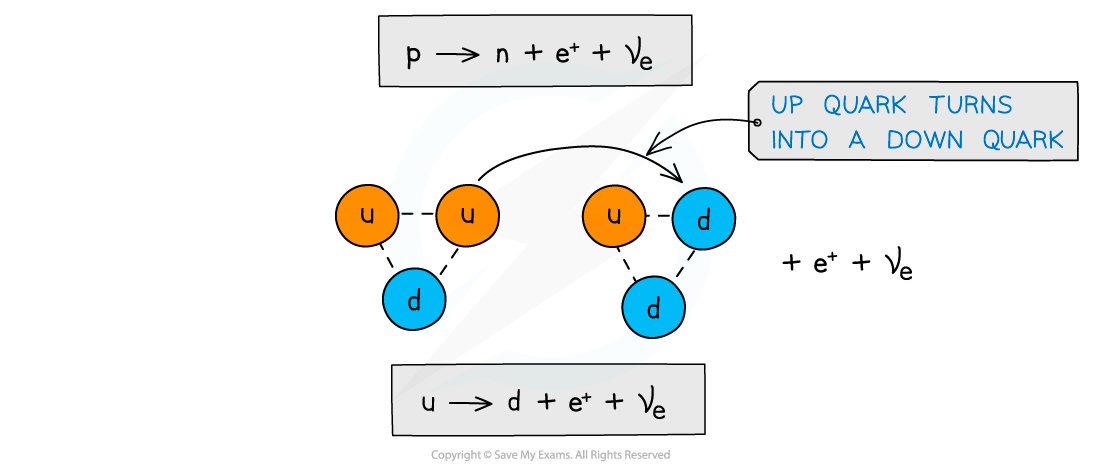
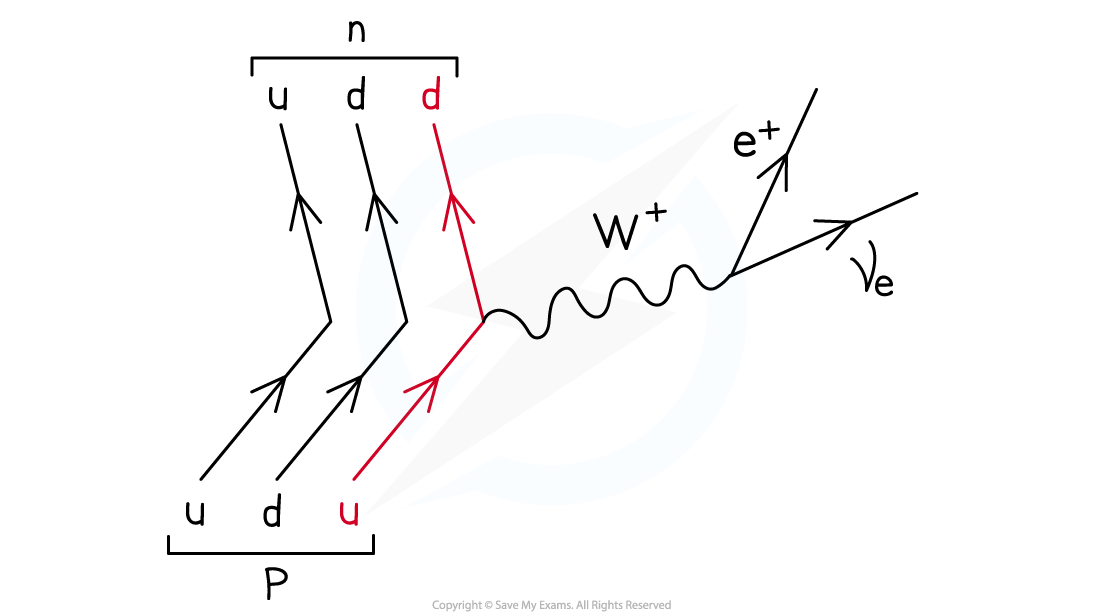
What does W+ boson do?
The W+ boson ‘carries away’ the positive charge of the up quark which provides the positive charge for the positron and neutrino
______ and ______ are attracted by the __________ interaction, when interacting it is the ____ interaction that facilitates the _______
Both _____ _______ and _____-______ _______ have the _____ decay equation:
Draw diagram
Electrons and protons are attracted by the electromagnetic interaction, when interacting it is the weak interaction that facilitates the collision
Both electron capture and electron-proton collisions have the same decay equation:
p + e-→ n + νe

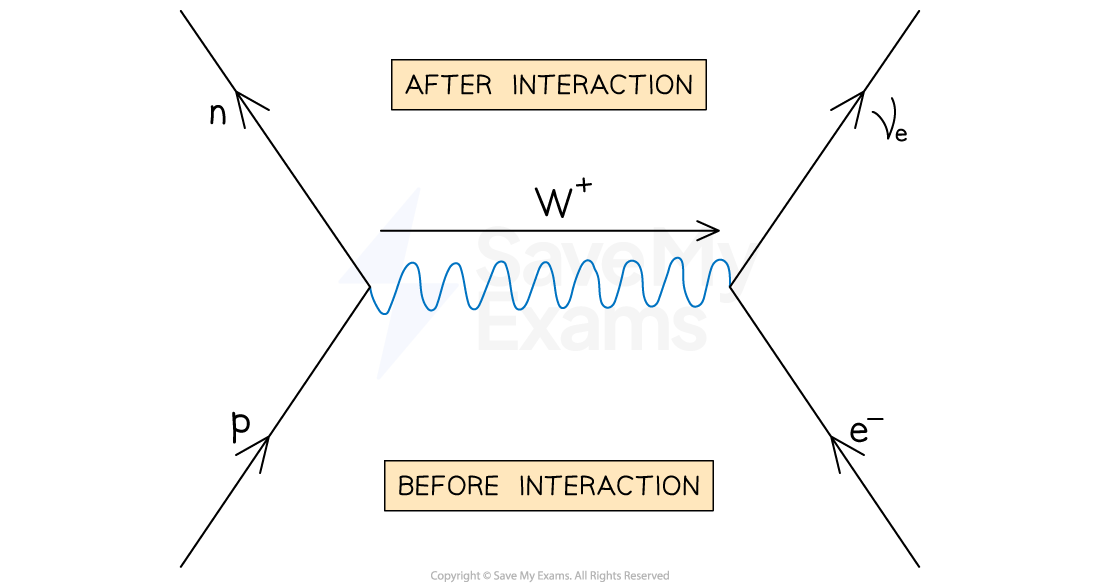
What is electron capture and what particle acts on electron?
an atomic electron is absorbed by a proton in the nucleus so releases of a neutron and an electron neutrino, decay is mediated by the W+ boson
Proton acts on the electron
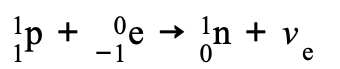
Electron Capture - ________ interaction - exchange of ___ _______
During electron capture:
Electron Capture - Weak interaction - exchange of W+ boson
During electron capture:
A proton absorbs an electron and decays into a neutron and W+ boson
Then, the interaction between the electron and W+boson forms an electron neutrino
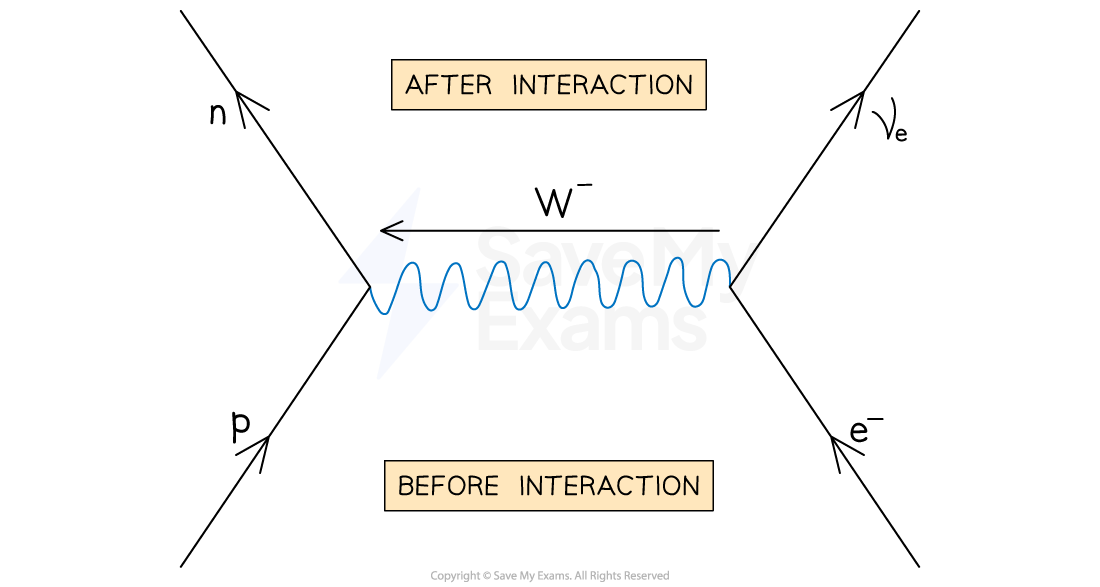
What are Electron- proton collisions and what particle acts on proton?
Electron-proton collisions are similar: an electron collides with a proton, a neutron and an electron neutrino are emitted, decay is mediated by the W^- boson
electron acts on the proton
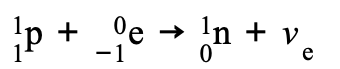
Electron-proton collision -_____ ___ ______
During electron-proton collision:
Electron-proton collision - Transfer W- boson
During electron-proton collision:
An electron collides with a proton and decays into a neutron and W− boson
Then, the interaction between the electron and W− boson forms an electron neutrino
What are feynman diagrams
Particle interactions and decays can be represented using Feynman diagrams
They are a way of visualising particle equations and the exchange particles involved
What are the rules for Feynman diagrams
Hadrons/quarks are present on the left and leptons on the right, they must never meet at a vertex
Charge, baryon number and lepton number must be conserved at each vertex
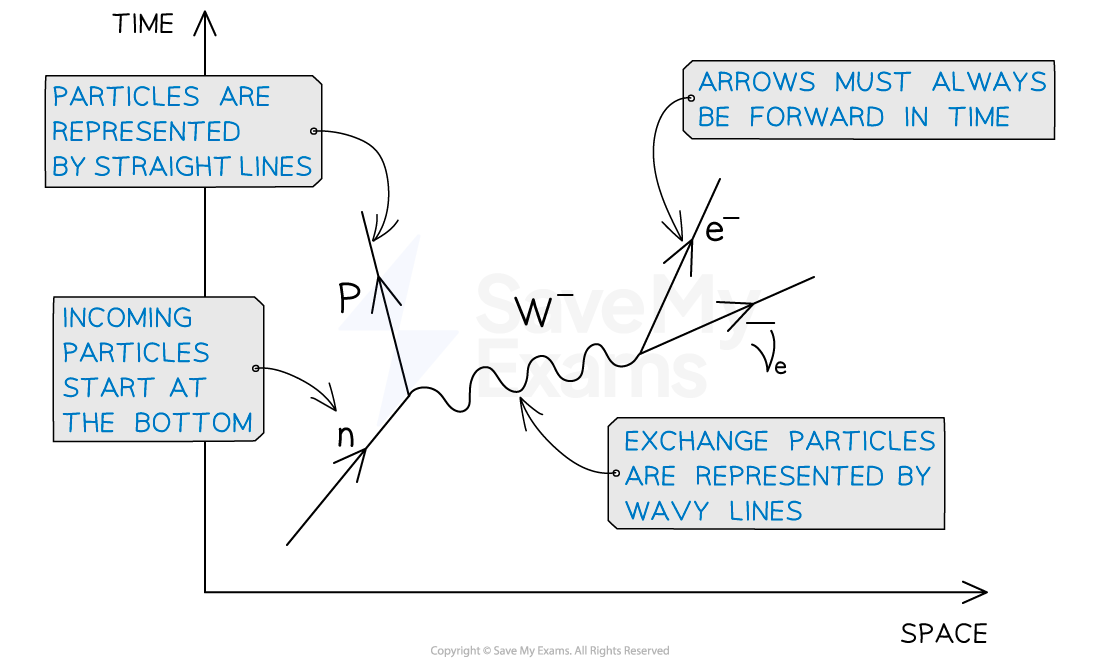
Exchange particles act as a______ _____ between particles in an interaction
W- particle going to the ______ is the same as W+ particle going to the _____
Exchange particles act as a force carrier between particles in an interaction
W- particle going to the left is the same as a W+ particles going to the right

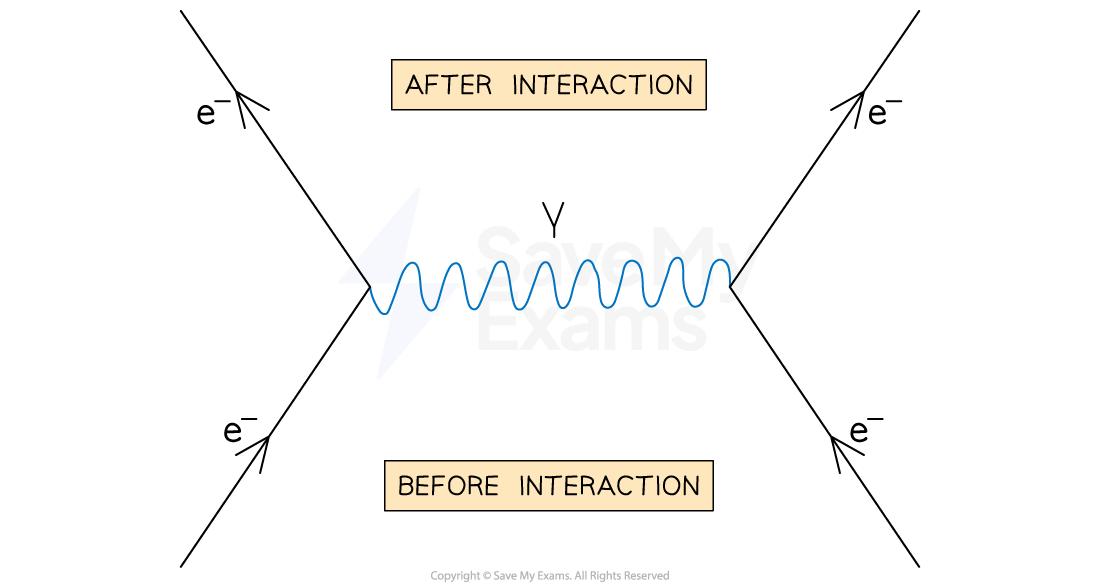
Electromagnetic interactions
Electromagnetic interactions - exchange of virtual photon , 2 electrons approach each other experiences repulsion due to the electromagnetic force.
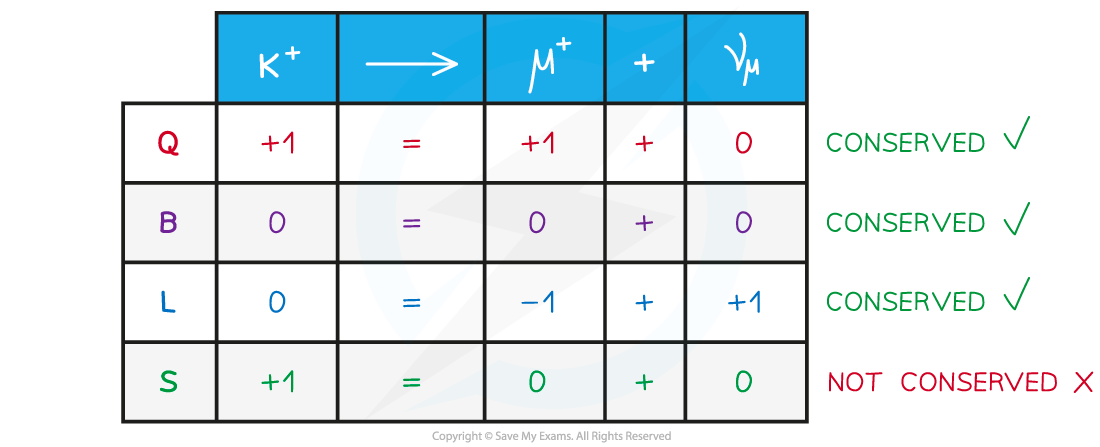
Conservation laws:
Charge, Q (discreet values e.g. 0,+1,-1, 1/2)
Baryon number, B (d)
Lepton Number, L (d)
Strangeness, S (d) : strangeness does not need to be conserved in weak interactions. It can change by either 0, +1 or –1
Energy (or mass-energy)
Momentum
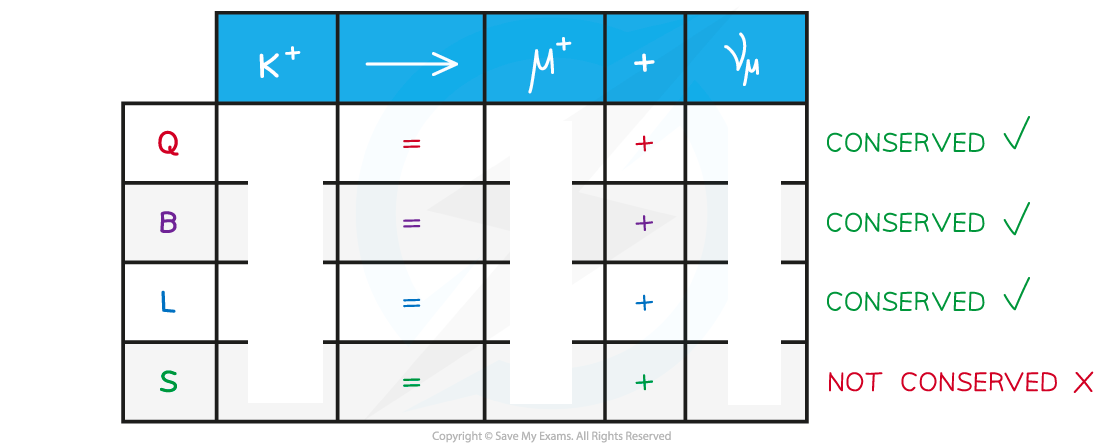
Particle interactions can occur if _______ _________ and ________ _________ is ______ on ______ sides
Particle interactions can occur if quantum number and conservation law is equal on both sides