A&P II: GI Quiz
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Digestive System
Two main components:
gastrointestinal tract (alimentary canal)
tube running from mouth to anus
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus - know the order
Accessory organs
teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas
Process of Digestive System**
Ingestion-process involves taking foods and liquids into the mouth
Digestion- (2 types)
Mechanical-breaking food into smaller pieces (bolus)
Chemical-digestive enzymes to break food into smaller pieces
Mixing and propulsion-contractions and relaxations of the GI tract mix food and propel them onward (motility) - peristalsis
Secretion-release of digestive juices & hormones to regulate digestion or metabolism of nutrients.
Absorption-movement of digested nutrients through the GI mucosa and into internal environment (blood & lymph)
Defecation-wastes, indigestible substances, bacteria, and cells from lining of GI tract leave the body (as feces or stool)
Stages of Digestion
1. Ingestion: the intake of food through the mouth
2. Mechanical digestion: mastication breaks down food into smaller particles
3. Chemical digestion (stomach): food travels of the stomach where gastric juice containing enzymes break particles down further.
4. Chyme formation: partially digested food moves from stomach to small intestine
5. Chemical digestion (small intestines): Enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver break down fats, proteins, carbohydrates into absorbable nutrients
6. Nutrient absorption: Amino acids, fatty acids and sugars are absorbed through the walls of the small intestines into the bloodstream
7. Water and electrolyte absorption: the remaining material moves to the large intestines where water and electrolytes are absorbed
8. Feces formation: the indigestible material forms feces, which is stored in the rectum
9. Elimination: feces are expelled from the body through the anus during the process of defecation
Two Ways to Digest Food**
Mechanical: breaking food down into smaller pieces
mastication - increases surface area of food and allows food to be broken down to smaller pieces to be swallowed safely
deglutition - three phases: oropharyngeal, esophageal, and gastroesophageal (swallowing)
peristalsis - contractions and relaxations of the GI tract to mix food and propel them onward
Chemical: enzymatic breakdown of large molecules into small ones; requires secretion of digestive enzymes & bile into the lumen of GI tract
Order of Digestion
mouth
pharynx
deglutition (swallowing) - oropharyngeal, esophageal, and gastroesophageal
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
anus
defecation
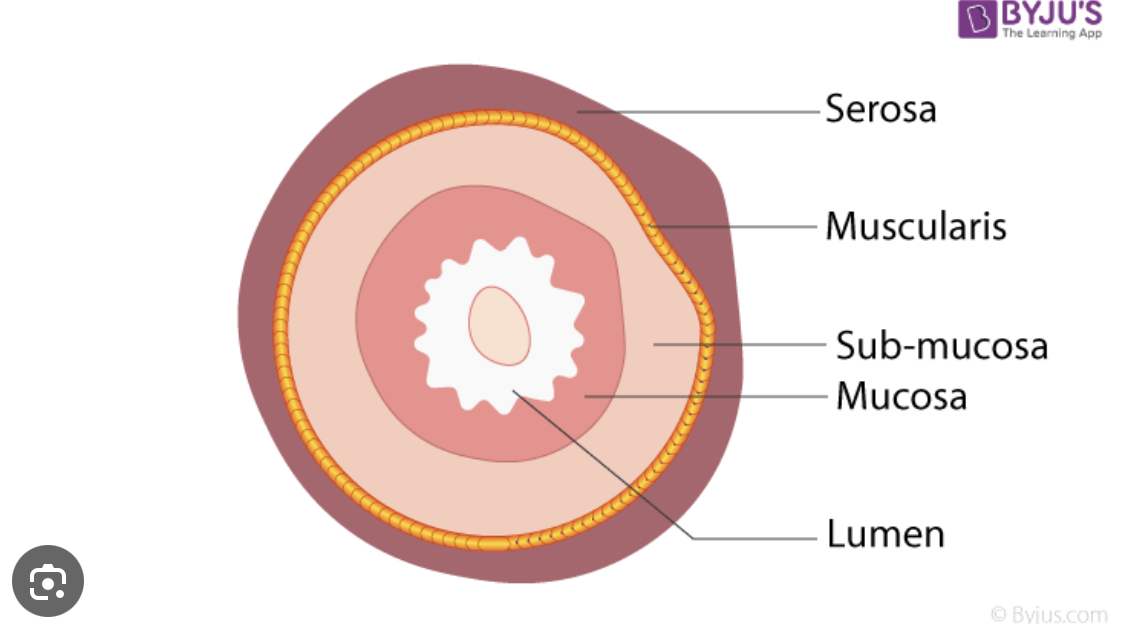
Structural layers of the alimentary tube
Mucosa - inner layer
Submucosa - Meissner’s Plexus is located in the submucosa (nerve network)
Muscularis
Serosa - outer layer
Lumen - inside of the tube
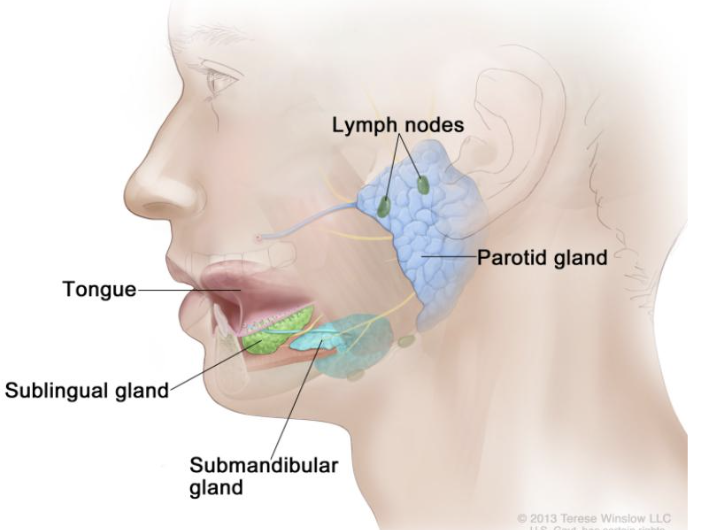
3 Pairs of Salivary Glands
Parotid gland
Submandibular gland
Sublingual gland
Esophagus
posterior to the trachea
Gastric Juices
hydrochloric acid - really strong gastric juice in the stomach
Emulsification
Bile breaks down fat into smaller droplets so that digestive enzymes can work on them; fats - emulsified
What 2 ducts meet in the common bile duct?
hepatic duct
cystic duct
Glycolysis
process of carbohydrate catabolism (break down of carbohydrates
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
pregnancy & lactation can increase BMR
Bile
liver secretes bile
gallbladder stores bile
Pancreas
endocrine & exocrine glands
secretes insulin & pancreatic juices
pancreatic enzymes: amylase, lipase, trypsinogen
Bicarbonates
neutralizes hydrochloric acid
Emulsification
bile salts needed to breakdown fats
Small Intestine
Don’t Judge Ice Cream
Duodenum
jejunum
ileum
What is the process called when contracting and relaxing occurs and propelling food through the system
peristalsis
cardiac sphincter or lower esophageal sphincter (LES)
a muscular ring that controls the flow of food and stomach acid between the esophagus and stomach