Horse Management and Nutrition Overview
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the primary use of horses in equine operations?
The primary use of horses is for pleasure, followed by ranch and farm work.
What percentage of equine operations are large enterprises with more than 20 head?
11% of equine operations are large enterprises with more than 20 head.
What are the three main types of equine enterprises?
Pleasure, work, and breeding.
What is the typical body condition scoring scale used for horses?
A 1 to 9 scale.

What is the significance of body condition scoring in horse management?
It helps assess the horse's weight and overall health, indicating if they are underweight or overweight.
What are the dietary needs of young, growing foals?
They need nutrients that meet growth requirements.
What can happen if a mare is fed endophyte-infected fescue during the last three months of gestation?
It can negatively impact abortion rates, rebreeding rates, milk production, and stillbirth.
What are the two main digestive disorders in horses?
Colic and laminitis.
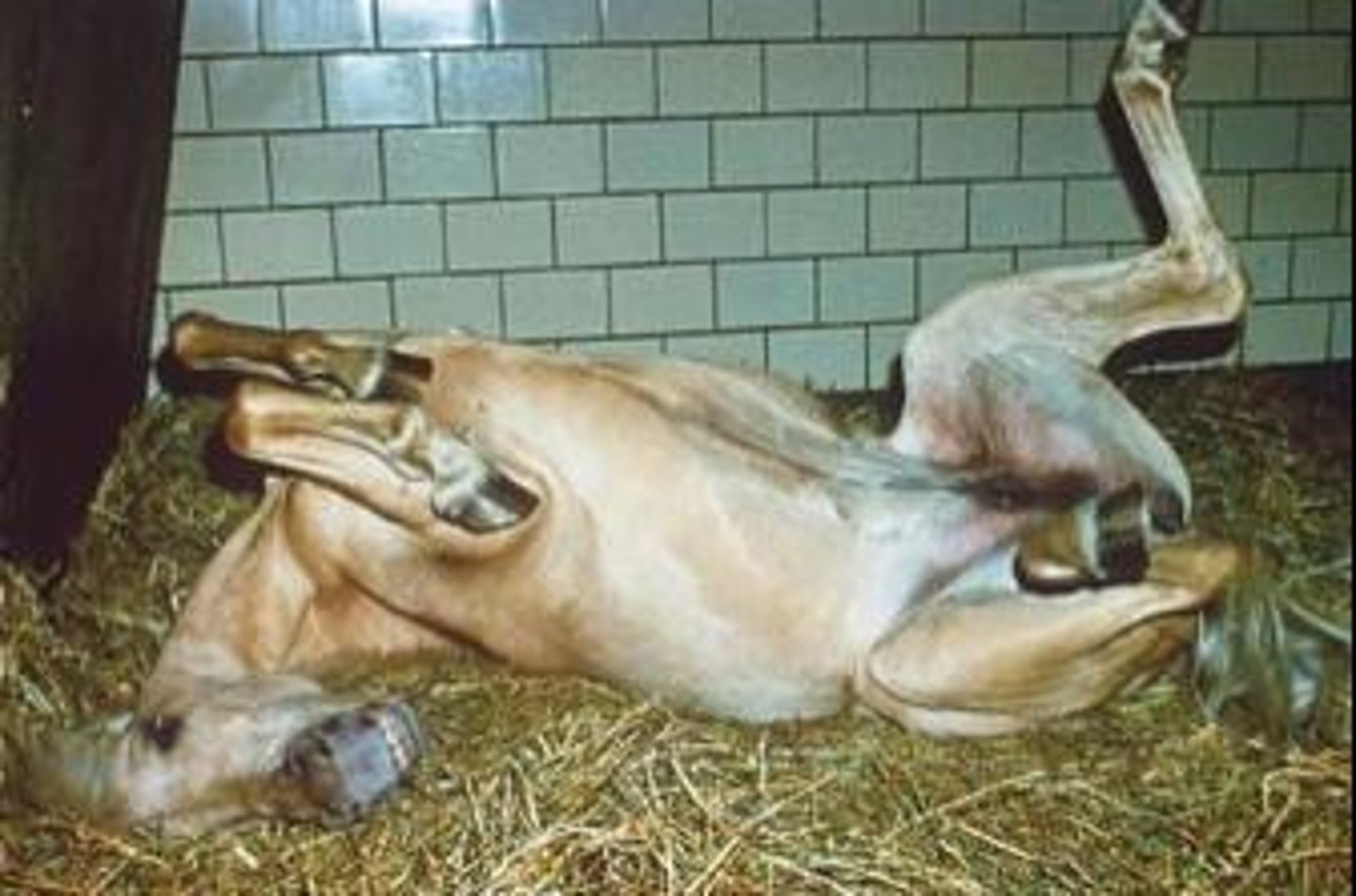
What is colic in horses?
A broad range of abdominal pain that can be caused by various factors such as diet changes or parasitic infestations.
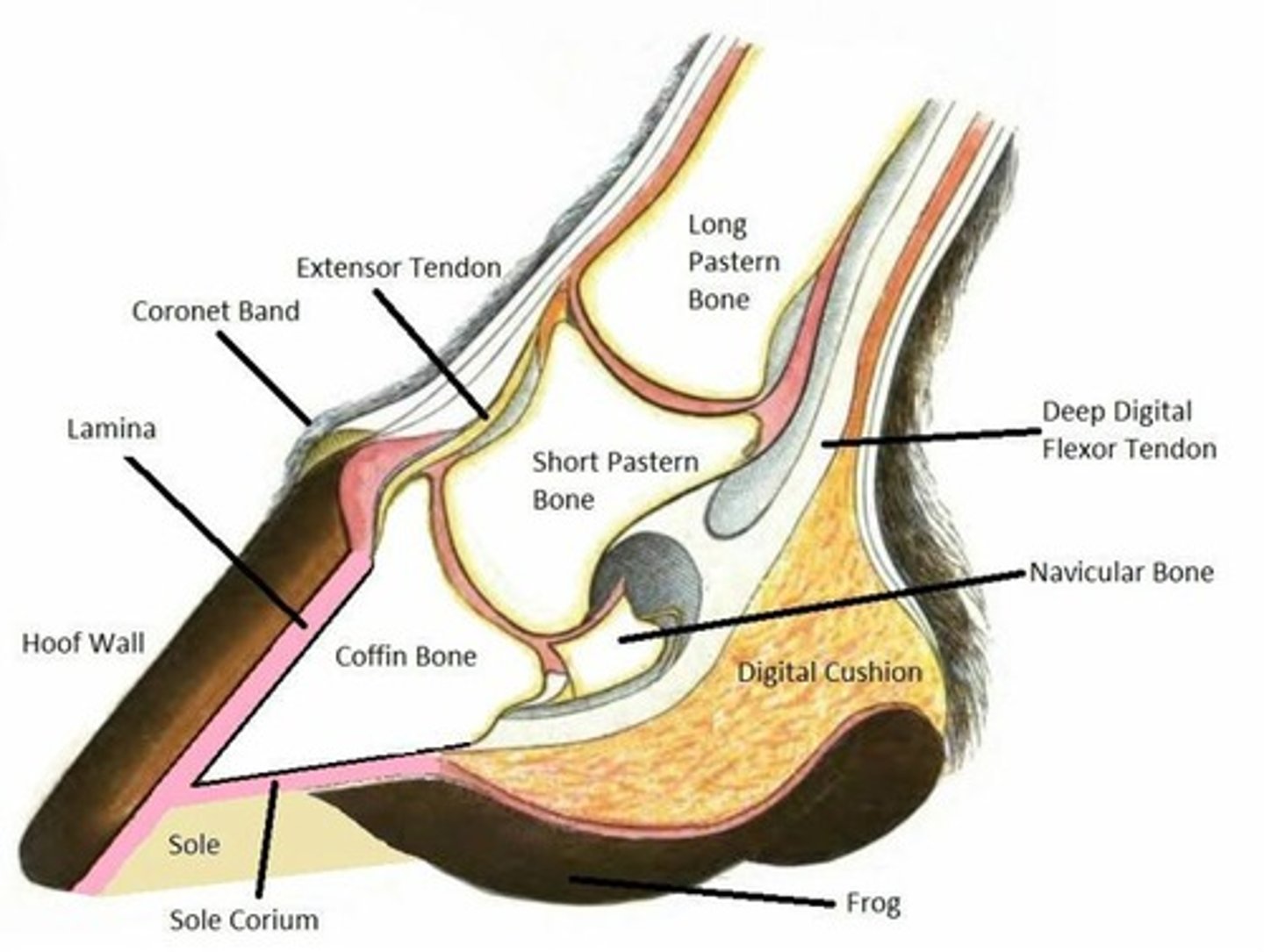
What is laminitis and what are its potential causes?
Inflammation of the laminae of the foot, potentially caused by overeating grain, overwork on hard surfaces, or overconsumption of lush pastures.
At what age do light breeds and draft breeds typically reach puberty?
Light breeds reach puberty at 12-18 months, while draft breeds reach puberty at 18-24 months.
What is the duration of the estrous cycle in horses?
The estrous cycle lasts 22 days.
What is 'foal heat' in mares?
A period 5-12 days following foaling when mares can conceive again if they have recovered.
What is the gestation period for horses?
The gestation period is approximately 340 days.
What is the importance of cleanliness during breeding in horses?
Cleanliness is crucial in both natural and artificial inseminations to prevent infections.
What should be done if a foal is presenting breech during foaling?
Call a veterinarian as early as possible for assistance.
What are the benefits of castrating colts?
Geldings can be handled more safely and are less dangerous.
What percentage of equines have registration papers?
44% of equines have registration papers.
What are some common diseases horses are susceptible to?
Tetanus, strangles, equine encephalitis, and West Nile virus.
How often should horses be dewormed?
Horses should be dewormed at least twice a year, rotating types of dewormer.
What is the typical foaling rate for horses?
The reproduction rate is approximately 90% foaling rate.
What is the average birth weight of a foal?
The average birth weight is between 100 to 120 pounds.
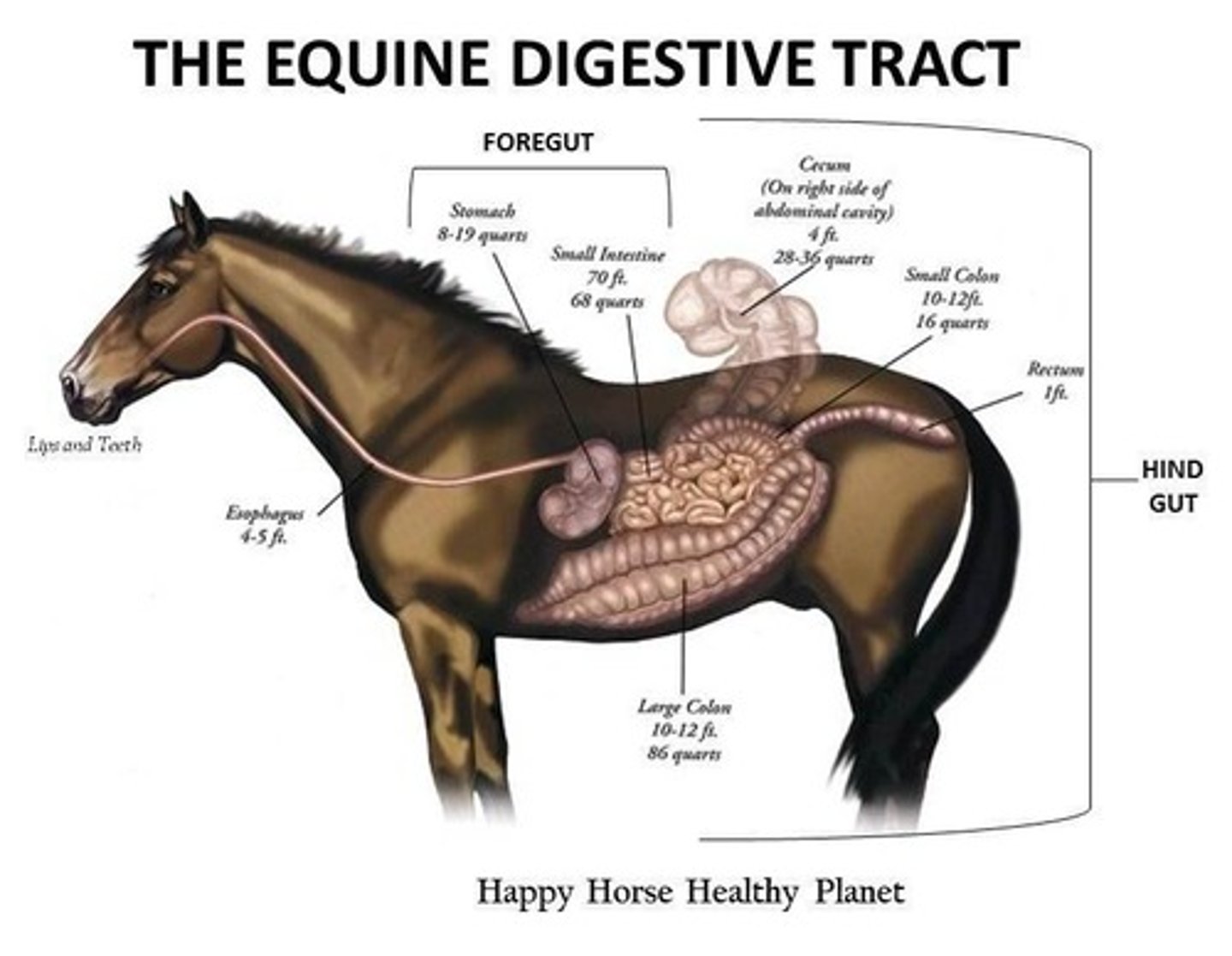
What are the major digestive structures of the equine?
The stomach, small intestine, cecum, and colon.
What factors should determine the nutrient requirements for horses?
Age, work schedule, lactation status, and gestation status.
What is the typical weaning weight for a foal?
The typical weaning weight is between 400 to 600 pounds.
What is the role of exercise on the nutritional requirements of horses?
Exercise increases the nutritional requirements of horses, especially for working and lactating horses.