D103 ECM (ALS 7, Videos 12 and 13)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
function of multi-domain proteins
organize the ECM
binds to multiple other proteins via specialized binding domains
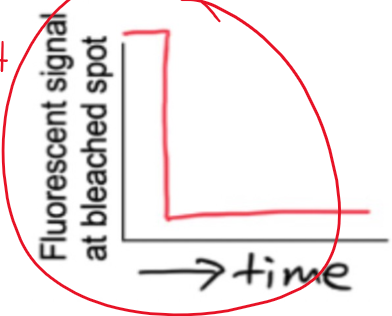
how do you predict a FRAP curve for fibronectin to look
there is a lot of crosslinking, meaning they want to stay together
proteins are not very mobile
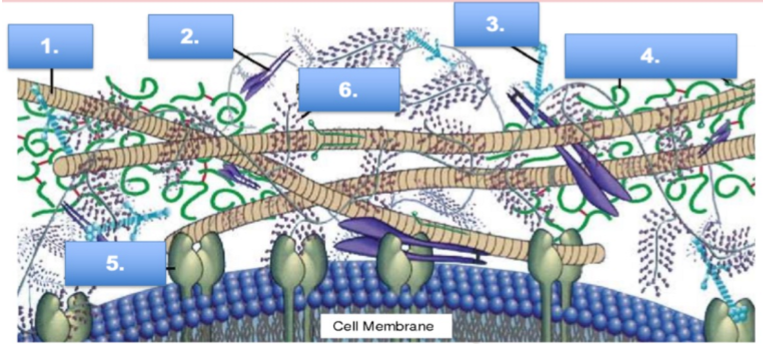
what is #1
collagen
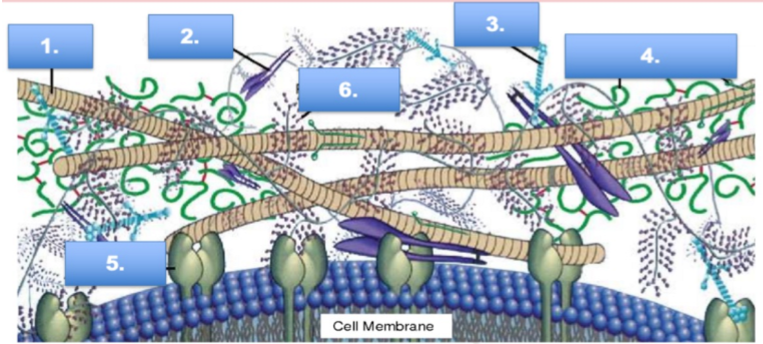
what is #2
fibronectin
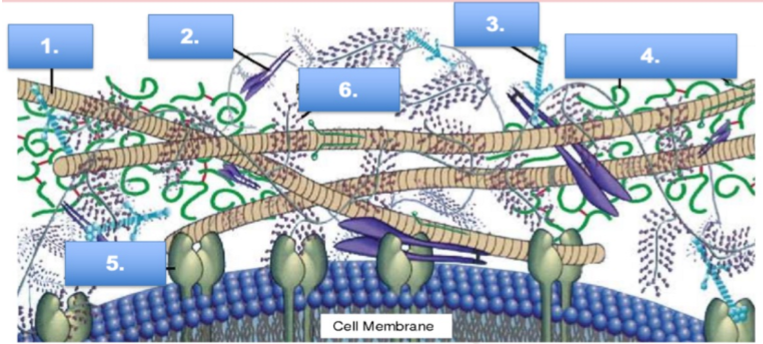
what is #5
integrin
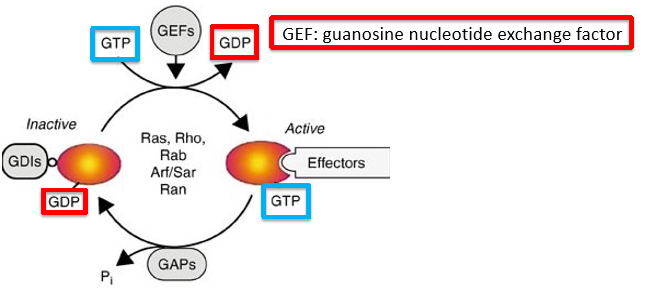
outside-in integrin activation
ecm ligand binding activates integrin and intracellular events
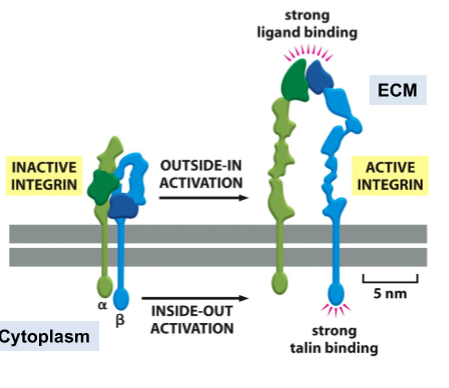
inside-out integrin activation
actin-associated protein binding activates integrin and extracellular events
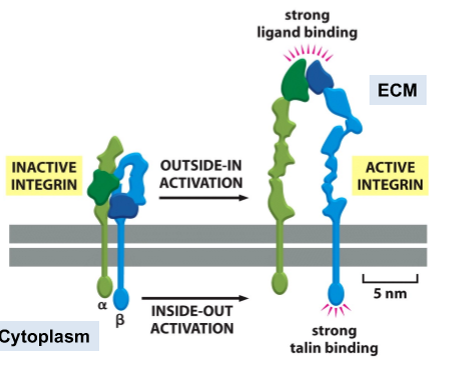
bidirectional regulation
binding of ligand/adaptor on one side of the membrane induces conformational change on the other side
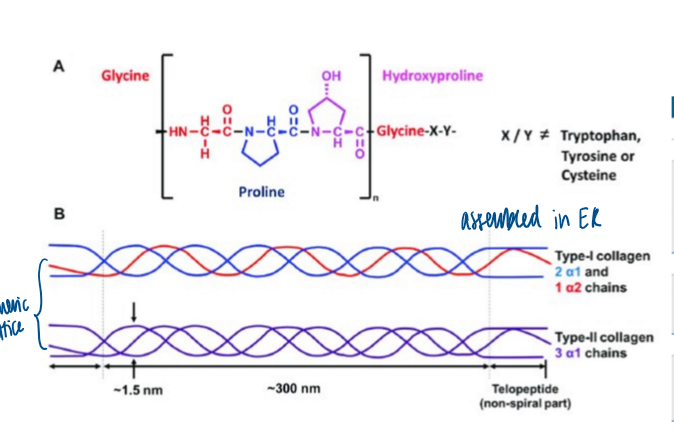
collagen
central component of the ECM
long sturdy, rope structure
many variations of collagen
assembled in ER in a trimeric lattice structure
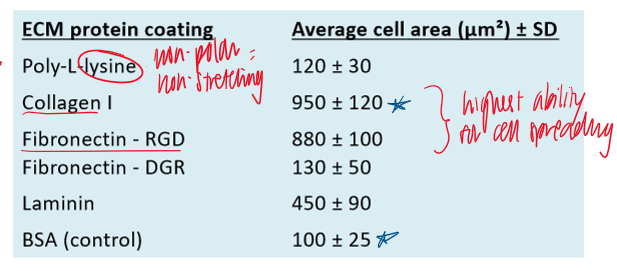
fibroblasts were cultured on dishes coated with different ECM proteins. aftr 2 hours, the average cell spreading area was measured using fluorescence microscopy and image analysis. which of the following conclusions is best supported by these data?
cell spreading is greater on ECM proteins
ECM proteins include collagen, fibronectin, and laminin
epithelial cells
adhere to their neighbors and the basal membrane
tight juntion
seals gap between epithelial cells
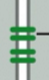
adherens junction
connects actin filament bundle in one cell with that in the next cell
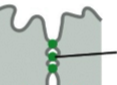
desmosome
connects intermediate filaments in one cell to those in the next cell
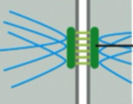
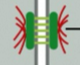
gap junction
allows the passage of small water-soluble molecules from cell to cell
hemidesmosomes
anchor intermediate filaments in a cell to ECM
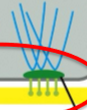
actin-linked cell-matrix adhesion
anchors actin filaments in cell to ECM
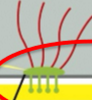
integrins
connect cell to the ECM
ex: actin-linked cell-matrix adhesion; hemidesmosomes
cell-matrix anchoring junctions
cadherins
connect adjacent cells
ex: tight junction, adherens, desmosome, gap junction
ex of occluding junction
tight junction
cell-cell anchoring junctions
adherens and desmosomes
ex of channel-forming junctions
gap junctions
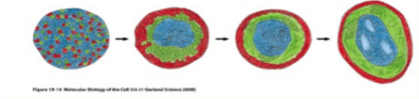
in which buffer would you carry out this cell sorting experiment
CaCl2
Ca2+ binding induces conformational changes
Ca2+ binding proteins: tryponin and calmodulin
e-cadherin and cancer: loss of function mutations of e-cadherin correlate with increased invasiveness and metastasis of tumors. which of the following describes the most direct consequence of this mutation
neighboring cells can no longer adhere to each other
most direct consequence
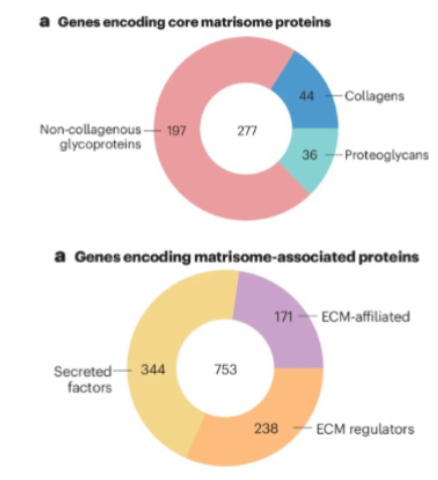
core matrisome
encoded by collagens, proteoglycans, and non-collagenous glycoproteins
genes encoding matrisome associated proteins: ECM-afiliated, ECM regulators, secreted factors
adaptors between actin and ecm
vinculin, talin, kindlin
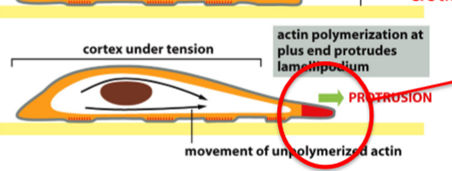
assist in protrusion
cell migration involves the maturation of adhesion sites
how does a cell look in which the GAP of Rho is mutated so that it cannot function
full of stress fibers
which of the following protein-protein interactions are critical for attachment of this migrating cell to the substratum
integrin binding to fibronectin
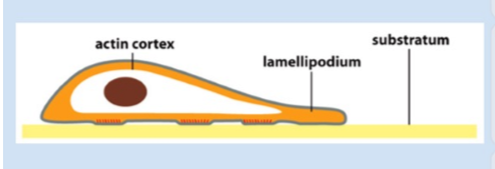
which of the following factors does NOT contribute to cell migration
cadherin
ecm
a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by fibroblasts within ECM including many insoluble fibers
varies between different tissues
provides structural support for the surrounding cells
ecm formation
synthesized and secreted by fibroblasts (within ecm)
remodeled and degraded by proteases in the ecm
reason for specialized properites of the ecm
differential enrichment of ecm components
main components of ecm
collagen (most abundant)
elastin
gags (glycosaminoglycans)
proteoglycans
multi-adhesive proteins (fibronectin, laminin)
osteogenesis imperfecta
brittle bone disease due to a mutation in Gly in COL1A
why is collagen processing necessary
necessary for its assembly and function
intracellular: vitamin C (ascorbic acid) as a cofactor for lysine and proline hydroxylation → scurvy
extracellular: collagent fibril and cross-striations
elastin
essential for tissue elasticity
critical component of tissues that experience mechanical stress (ex: blood vessels, skin, and lungs)
elastin monomer
proline and glycine-rich hydrophobic domain → able to extend and recoil
monomers are crosslinked via Ala and Lys-rich alpha-helical domains
cutis laxa
genetic disorder where there is little skin elasticity bc no elastin
composition of glycosaminogycans (GAGs) and proteoglycans
repeating diassacharides
one sugar: GlcNAc or GalNAc
other sugar: D-glucoronic acid, L-iduronic acid or D-galactose
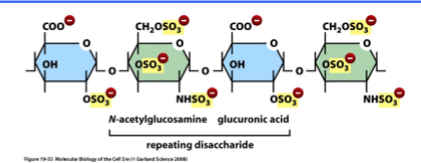
what can GAGs be linked to
proteoglycan as the core protein
unlike glycoproteins, where there is more protein than sugar bound in the complex
purpose of multi-domain proteins
organize the ECM
binds to multiple other proteins via specialized binding domains (ex: RGD)
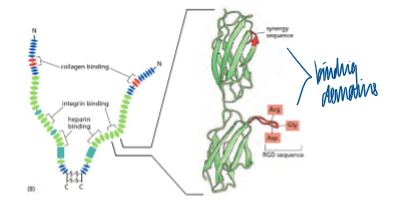
fibronectin and laminin
fibronectin
forms homodimer that is joined by disulfide bonds
used in lab to coat tissue culture dishes
laminin
heterotrimer (has 3 different chains)
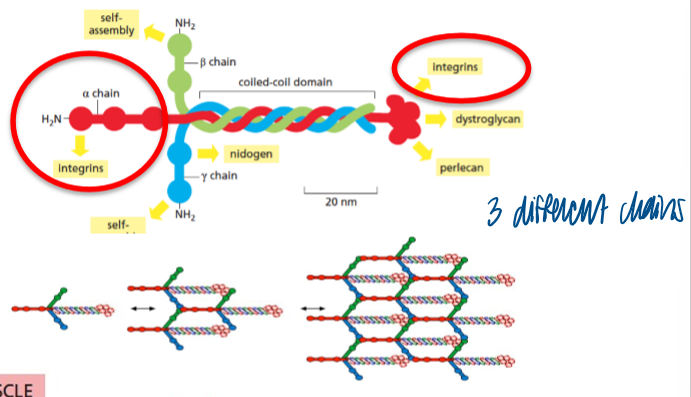
laminin a2 deficiency
congential muscular dystrophy
collagen overview
triple helix made up fo 3 collagen alpha-chains, large protein with complex processing during its secretion
elastin overview
prominent ECM component, makes up elastic fibers that can recoil after a stretch
2 repeating domaints (Ala and Lys rich alpha helices → crosslinking; hydrophobic domains which provide the elastic properties)
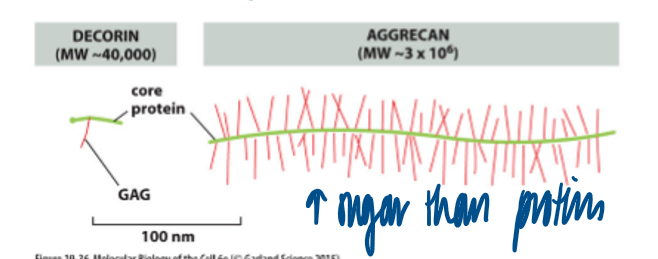
GAGs
large repeated disaccharide chains with highly extended conformation
the presence of charged sugars leads to hydrophilic character
can withstand compressive forces
proteoglycans
95% of weight of those porteins are sugar (GAGs)
several classes that differ in the comp of disaccharide portion (GAGs)
stiff, hydrophilic molecule → attracts water → gel like appearance
multi-domain proteins (fibronectin and laminin)
contain specific bindings sites for multiple other proteins; provides binding sites for cells during migration
all components are secreted by fibroblasts in the ECM
when do cells adhere to each other
during early embryonic development
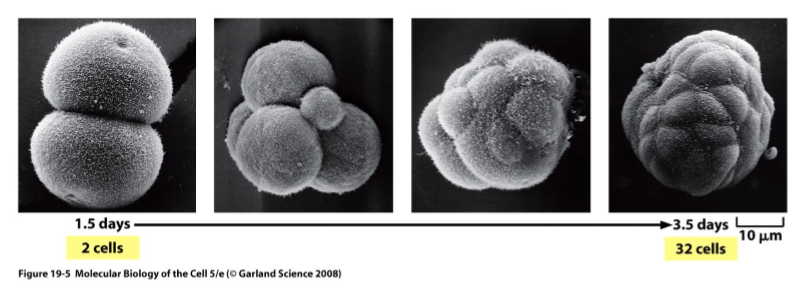
result of loss of e-cadherin function
cells did not adhere and resulted in early embryonic death
suggests a role for e-cadherin in cell adhesion and embryonic development
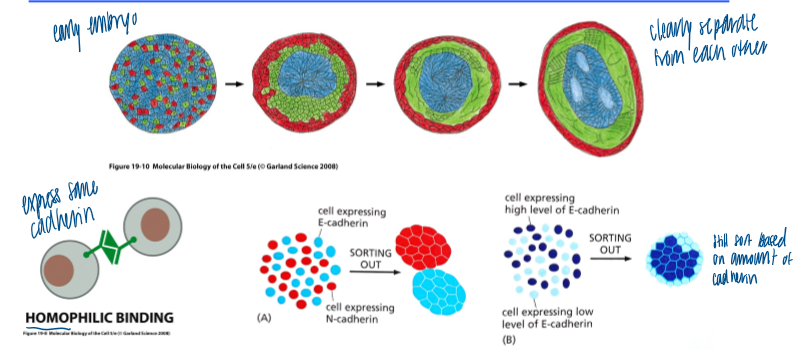
cadherin-mediated sorting out of cells
layers separate as development progresses
cells are segregated from each other because they:
express different cadherins
express different levels of the same cadherin (sort based on the amount of cadherin present)
calcium and cadherin
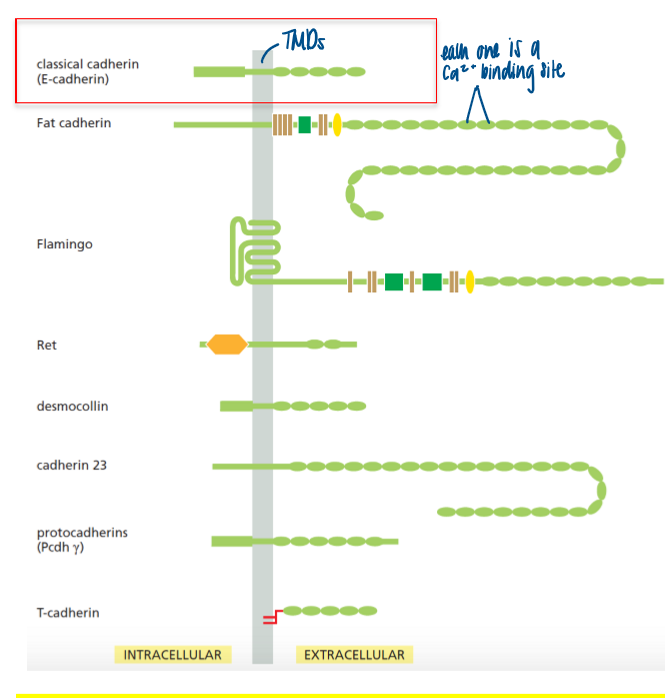
cadherin undergoes a Ca2+ induced conformational change
each cadherin (located extracellularly) has a Ca2+ binding site
desmosomes vs adherens junctions
both are cadherins that link the cytoskeleton of neighboring cells
homotypic binding to cadherins of the neighboring cell
desmosomes: structural support of great tensile strength; link via intermediate filaments
adherens junctions: adhesion/ contractile belt; link via f-actin
pemphigus
autoimmune disease that affects ability to generate antibodies against desmosomal cadherins
causes skin blistering and leakage of body fluids into epithelium
affects cadherin function
purpose of integrins
link the cytoskeleton to the ecm
a family of transmembrane proteins that form heterodimers (a and B subunit)
at least 24 different family members
connect cytoskeletal elements (f-actin/ intermediate fil) to the ECM indirectly via adaptor proteins
individual integrins cluster, which leads to high affinity binding
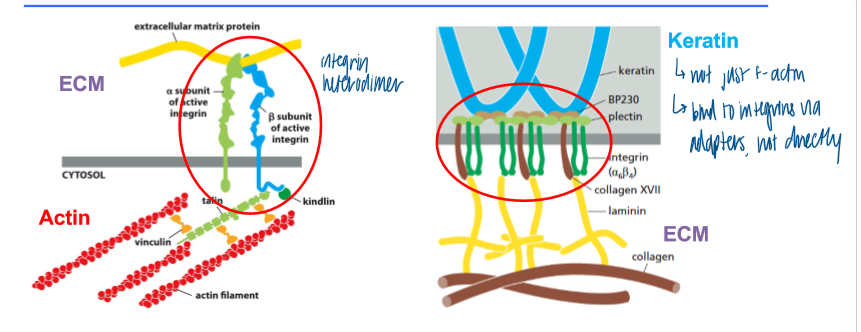
in outside-in signaling, what induces a cell to adhere to the substratum
ecm components (fibronectin) associates with integrin via RGD domain
enhancement of the interaction thru integrin clusterin (leads to high affinity binding)
cells become attached thru association of integrins with f-actin (formation of focal adhesions)
in inside-out signaling, what induces integrin activation and focal adhesion formation
actin polymerization activates integrins via actin-accessory proteins
focal adhesion: protein complex that forms
adhesion proteins overview
TM proteins that participate in adhesion via an extracellular domain and that associate with the cytoskeleton via their intracellular domain
cadherins overview
ca2+-dependnet conformational change, which promotes homotypic/homophilic interactions with neighboring cells
adherens junctions (linkage of actin cytoskeleton → adhesion belt)
desmosomes (linkage of intermediate filament → provides strength to cell layer)
integrins overview
form a heterodimer
help motile cells to adhere to ECM (link between actin cytoskeleton and the ECM)
tightly regulated conformational changes that are induced across the membrane
inside-out and outside-in signaling