Anatomy Lecture Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
1
New cards
Concentration Gradient
Difference in electrical charges across a membrane
2
New cards
Neurons
Most common cells in nervous system, respond to stimuli by propagating action potential along a membrane, non-mitotic
3
New cards
Recepters
Sensory neurons, afferent
4
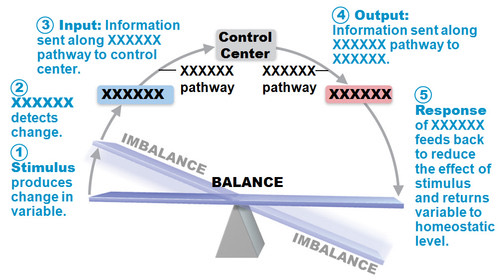
New cards
Association control center
Central nervous system: Brain and spinal cord
5
New cards
Interneurons
Integrate sensory information (input) into motor response, found in CNS, most prevalent type of neuron in the body
6
New cards
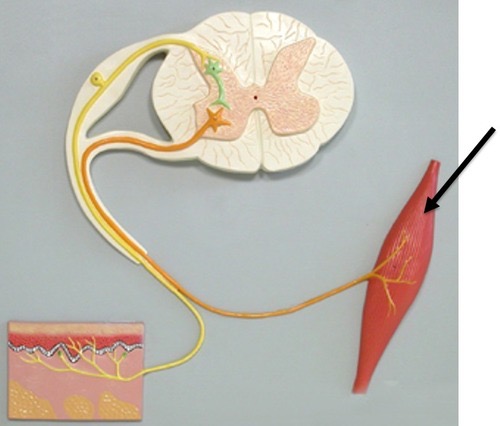
Effectors
Motor neurons - bring about the change, either skeletal, smooth, or cardiac muscle or glands
7
New cards
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord - deliver information to PNS
8
New cards
Peripheral Nervous system
Cranial and spinal nerves that spread throughout the body
9
New cards
Sensory nerves
Carry impulses from the sensory receptor to the central nervous system, located primarily on the skin, somatic and visceral, AFFERENT
10
New cards
Somatic sensory nerves
Sensory nerves that we consciously perceive - 5 senses and proprioception
11
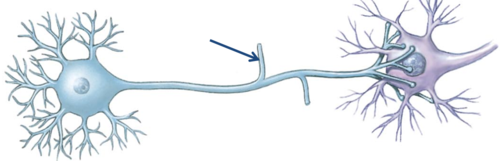
New cards
Visceral nerves
Detect stimuli that we do not consciously perceive, ie. blood pressure, blood glucose
12
New cards
Motor nerves
EFFERENT, carry information from CNS to effectors: muscles and glands
13
New cards
Somatic motor nerves
Transmit voluntary impulses to skeletal muscles (voluntary control)
14
New cards
Autonomic nerves
Involuntary control over cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glandular tissue
15
New cards
Parasympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
16
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Fight or Flight
Fight or Flight
17
New cards
Glial cells
6 different kinds (4 in CNS and 2 in PNS) of cells that play a supportive roll, mitotic
18
New cards
Excitability
Respond to stimuli, very sensitive
19
New cards
Conductivity
Respond to stimuli by producing electrical signals that are conducted to other cells
20
New cards
Secretion
Secrete neurotransmitters that communicate with other cells - trigger or stop response
21
New cards
Cell body
Part of neuron that contains the nucleus, transmits graded potentials
22
New cards
Perikaryon
Cytoplasm of the neuron
23
New cards
Nissl bodies
Clustered ribosomes and rough ER in neurons that produce tau proteins
24
New cards
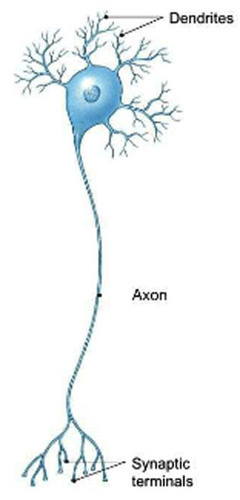
Dendrites
Receptive segment: short small projections that extend from the cell body, unmyelinated, receive input and transfer the information to the cell body
25
New cards
Axon
Conductive segment: long singular projection from the cell body, connects to other neurons of muscle/gland cells, extend from axon hillock
26
New cards
Axon hillock
Initial segment: cone-shaped structure that connects the axon to the cell body, initiates action potential
27
New cards
Axoplasm
Cytoplasm of axon; contains neurofibromas, neurotubules, enzymes, organelles
28
New cards
Axolemma
Cell membrane of axon
29
New cards
Axon collaterals
Side branches of the axon
30
New cards
Telodendria
Transmissible segment: distal ends of axon and collaterals that contain synaptic vesicles
31
New cards
Synaptic knob
Distal end of telodendria that contain vesicles with neurotransmitters
32
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Structural network that provides support to the axon of the neuron
33
New cards
Neurofilaments
Intermediate filaments that aggregate to form bundles called neurofibrils
34
New cards
Neurofibrils
Bundles of neurofilaments that provide support for dendrites and axon
35
New cards
Tau proteins
Proteins that stabilize microtubules of neuron
36
New cards
Microtubules
Move materials between the cell body and axon
37
New cards
Axonal transport
Movement of organelles, nutrients, vesicles, and other materials to and from the cell body via the axoplasm
38
New cards
Anterograde
Transport of materials from the cell body to the axon terminal, delivers required materials to the synaptic knob
39
New cards
Retrograde
Transport of materials from the synaptic knob to the cell body for recycling or exocytosis
40
New cards
Fast axonal transport
Bidirectional (anterograde and retrograde) active transportation of materials along microtubules, powered by ATP
41
New cards
Slow axonal transport
Unidirectional (anterograde), uses the flow of axoplasm to transport enzymes and cytoskeleton parts to the axon terminal, doesn’t require ATP (passive)
42
New cards
Multipolar
Most common type of neuron
* multiple dendrites and 1 axon extend from cell body
* multiple dendrites and 1 axon extend from cell body
43
New cards
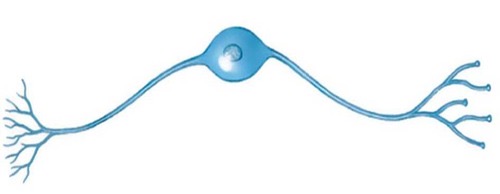
Bipolar
One axon and one dendrite are attached to the cell body, only sensory, limited locations
44
New cards
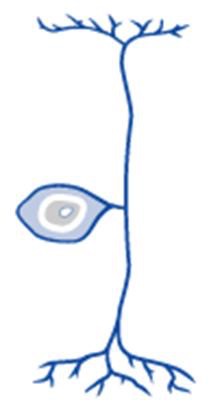
Unipolar
Singular long dendrite extends from the cell body and merges with the axon
45
New cards
Nerve
A bundle of parallel axons in the PNS
46
New cards
Epineurium
Surrounds the entire nerve providing protection and support
47
New cards
Perineurium
Surrounds each fascicle
48
New cards
Fascicle
Bundle of parallel axons, synonymous with nerve
49
New cards
Endoneurium
Surrounds the axon of a single neuron to insulate it from surrounding axons, if the axon is myelinated is external to the myelin sheath.
50
New cards
Mixed nerves
Nerves extending from cranial and spinal nerves that carry both sensory and motor fibers
51
New cards
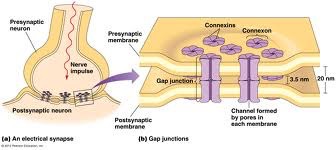
Electrical synapse
Uncommon form of synapse where ions flow through gap junction between the cells to transmit electricity, no delay therefore faster propagation and more difficult to modify
52
New cards
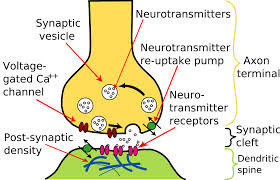
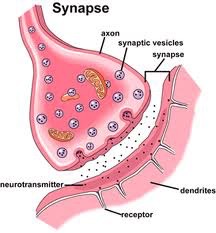
Synapse
Functional connection between a neuron and another neuron or an effector
53
New cards
Chemical synapse
Presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitter to postsynaptic cell, NT diffuses across synaptic cleft, delay allows for modification
54
New cards
Synaptic delay
Time it takes for NT to diffuse and bind to receptors in chemical synapses
55
New cards
Astrocytes
Most abundant type of glial cell in CNS, have podocytes that anchor neurons and blood vessels in place, repair damaged neurons (limited) and help form the blood-brain barrier
56
New cards
Blood brain barrier
Blood vessels that selectively let certain substance enter the brain tissue and keep other substances out (toxins). Formed by peri vascular feet of asrtocytes, endothelial cells, and thickened basement membrane
\-Cocaine and methamphetamines destroy the BBB
\-Cocaine and methamphetamines destroy the BBB
57
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
Produce myelin in the CNS
58
New cards
Microglia
Phagocytize infectious agents, cellular debris, and harmful substances in the CNS
59
New cards
Ependymal cell
Ciliated cells that line the ventricles of the brain, produce and circulate CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)
60
New cards
Schwann cells
Produce myelin in PNS, limited capacity repair damaged axons
61
New cards
Satellite cells
Surround cell bodies in PNS and provide protection and support
62
New cards
Myelin
White lipoprotein that surrounds axon of neuron insulating it from electrical insulation and speeding up the propagation of nerve impulses, produced by oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells
63
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
Unmyelinated sections of axon
\-Expose axolemma
\-Expose axolemma
64
New cards
Multiple sclerosis
Autoimmune disease that destroys myelin by attacking oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells
65
New cards
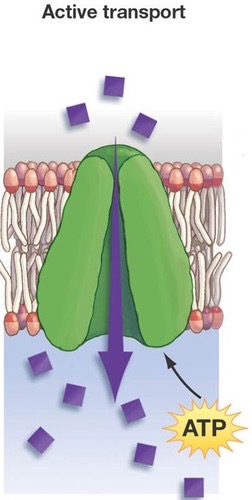
Pumps
Active transport: move ions against their gradient (low to high) using ATP ie. Na+/K+ pump and Ca2+ pump
66
New cards
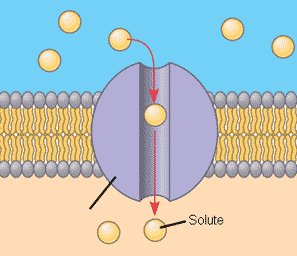
Channels
Passive transport: move ions down their gradient (high to low), do not require ATP
67
New cards
Leaky channels
Always open, allow for diffusion of K+ and Na+
68
New cards
Chemically-gated ion channels
Open when neurotransmitter binds to its receptor, allows for diffusion of K+, Na+, and Cl-
69
New cards
Voltage-gated ion channel
Open in response to change in electrical charge across membrane (voltage), K+ and Cl- are simple either open or closed, Na+ is more complex
70
New cards
Na+ voltage gated channel
Has 2 gates: inactivation and activation
Resting: inactivation gate is open and activation gate is closed
Activation: both gates are open
Inactivation: inactivation gate is closed and activation gate is opened
Resting: inactivation gate is open and activation gate is closed
Activation: both gates are open
Inactivation: inactivation gate is closed and activation gate is opened
71
New cards
modality gates
Open and close in response to sensory stimuli ie. Light, touch, and sound waves
72
New cards
Receptive segment
Contains chemically-gated ion channels: Na+, K+, Cl-
73
New cards
Initial segment
Voltage-gated Na+ channels and voltage-gated K+ channels
74
New cards
Conductive segment
Contains voltage-gated ion channels: Na+ and K+
75
New cards
Transmissive segment
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and Ca2+ pumps
76
New cards
Resting membrane potential (RMP)
Voltage that exists across the membrane when AP isn’t being produced, polarized at rest (extra cellular is relatively positive), -70mV
77
New cards
Graded potentials
IPSPs and EPSPs: short lived changes in RMP due to ion movement as a result of chemically gated ion channels, occur in receptive segment and move to the initial segment
78
New cards
Hyperpolarization
IPSPs: make the membrane potential more negative by opening chemically gated K+ and Cl- channels
79
New cards
Depolarization
EPSPs: makes the membrane potential more positive by opening chemically gated Na+ channels, rapid once threshold is met via voltage-gated Na+ channels —> +30mV
80
New cards
IPSP
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential, makes membrane potential more negative
81
New cards
EPSP
Excitatory postsynaptic potential, makes membrane potential more positive
82
New cards
Threshold stimulus
Minimal stimulus required to initiate an action potential: -55mV
83
New cards
Spatial summation
The adding together of EPSPs generated by multiple presynaptic neurons
84
New cards
Repolarization
Following depolarization (30mV) voltage gated K+ channels, K+ leak channels, and Na+/K+ pump restore the membrane potential to -70 mV or lower (hyperpolarization)
85
New cards
Refractory period
Period following depolarization and depolarization during hyperpolarization when the membrane has a limited capacity to respond to action potentials
\- ensures that the action potential is unidirectional
\- ensures that the action potential is unidirectional
86
New cards
Absolute refractory period
Time during an action potential in which a second stimulus cannot initiate another action potential regardless of strength of the stimulus.
87
New cards
Relative refractory period
Second refractory period when stimulus of above average intensity (above threshold0 can initiate a second action potential
88
New cards
Neurotransmitters
\- synthesized by presynaptic neurons
\- released via exocytosis as a result of voltage-gated Ca+ channels
\- bind to specific receptors on postsynaptic membrane
\- receptor type determines physiologic activity
\- released via exocytosis as a result of voltage-gated Ca+ channels
\- bind to specific receptors on postsynaptic membrane
\- receptor type determines physiologic activity
89
New cards
Acetylcholine
Widespread, can be excitatory or inhibitory depending on the receptor, broken down by acetylcholinesterase
90
New cards
Biogenic amines (monoamines)
Derived from amino acids with carboxyl group removed, catecholamines and indolamines
91
New cards
Catecholamines
Dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine synthesized from tyrosine
92
New cards
Epinephrine
Catacholamine: adrenaline, secreted by adrenal gland initiating a fight or flight response
93
New cards
Norepinephrine
Catecholamine: noradrenaline, responsible for arousal, wakening, dreaming, and mood regulation, controls heart rate during fight or flight response
94
New cards
Dopamine
Catecholamine: regulates pleasure and reward sensations (cocaine), effects skeletal muscle tone
95
New cards
Indolamines
Serotonin and histamine
96
New cards
Histamine
An indolamine - involved in sleep and memory
97
New cards
Serotonin
An indolamine - involved in sensory perception, thermoregulation, mood, appetite, and sleep, lower levels in those with depression
98
New cards
Glutamate
\- amino acid
\- the most common neurotransmitter in the brain; excitatory, excess is toxic, related to ALS
\- the most common neurotransmitter in the brain; excitatory, excess is toxic, related to ALS
99
New cards
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
\- amino acid
\- inhibitory: blocks Ca2+ channels; influences muscle tone; alcohol and anti-anxiety drugs increase levels
\- inhibitory: blocks Ca2+ channels; influences muscle tone; alcohol and anti-anxiety drugs increase levels
100
New cards
Enkephalins
\- neuropeptide
\- endogenous opioid
\- analgesic: blocks pain perception; associated with pleasure
\- endogenous opioid
\- analgesic: blocks pain perception; associated with pleasure