unit 6: economic geography
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
developed
improvement in tech/production
social+economic welfare of the people
developing
progress being made
measuring development
economic welfare
development in tech+production
development in social welfare
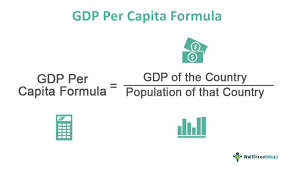
gross national product (GNP)
the total value of officially recorded goods + services by the people of a country during a year
gross domestic product (GDP)
total value of officially recorded goods + services within the country during a year
gross national income (GNI)
total income earned by a country’s residents and businesses
GNI per capita = ____
average salary
formal economy
legal economy that the gov taxes and moniters
informal economy
illegal and untracked economy
eg: illegal drug trade, cash under the table jobs
4 classes in measuring development
very high developed
high developing
medium developing
low developing
everyplace lies somewhere here; a continuous process
human development index (HDI)
used to measure development
highest score is: 1.0
3 factors
standard of living (avg salary per capita)
long + healthy life (life expectancy)
access to knowledge (avg # of years people are in school)
purchasing power parity (PPP)
adjustment made to GNI to account for difference among countries in cost of goods
inequality HDI
modifies the HDI to account for inequality within a country
gender in quality index (GII)
closest score to 0 is best
3 factors:
women’s empowerment (% women that are high school graduates, % women in political decision making)
labor/work force(% women that work + get paid)
reproductive health (% of teen pregnancies, maternal mortality rate)
rostow’s model
traditional
preconditions to take off
take off
drive to maturity
age of mass consumption
rostow’s model: traditional
society hasn’t started development yet
rostow’s model: preconditions to take off
progressive leaderships leads to the country’s greater productivity
rostow’s model: take off
country experiences a sort of industrial revolution
sustain growth takes hold
urbanization increases
rostow’s model: drive to maturity
technology diffuses
modernization is evident
rostow’s model: age of mass consumption
high income
widespread production
majority works in sector
dependency theory
countries are dependent on other countries
some will always be dependent on others
neocolonialism
world powers (core countries) control poorer (periphery) countries economies
fair trade
commerce in which products are made & traded according to standards to protect workers & small businesses.
micro finance
alternative source of loans
small loans + other financial services
aids in the development of small businesses
repayment of loans allows for future lending
comparative advantage
producing products cheaper than the competitor
barriers to development
lack of education
poor economy
lack of resources
conflict
isolation/bad location
cost of development: environment
pollution (air, soil, water)
exceed carrying capacity
destruction of ecosystem
cost of development: lack of regulations
encourages investment in development
creates exporting zones
exporting zone
areas in country that have less regulation + encourage development
during industrialization: location of factories
near coal (power source)
near ports (faster to transport)
when tech improved, didn’t need to be near the power source
modes of transportation
boat
trains
planes
truck
pipeline
alfred weber’s least cost theory
focuses on minimizing cost and multiple input points
looks at secondary economic activity
transportation is the #1 cost to think about
weber’s least cost theory: transportation
lowest cost of moving raw material to factory and finished product to market
weber’s least cost theory: labor
if it’s cheap to transport, company may locate farther away from raw materials+factory
weber’s least cost theory: agglomeration
locating your businesses next to others that will benefit your business
can produce high cost
eg: silicon valley (lots of tech companies)
deagglomeration
companies leaving an established agglomeration
one reason: costs are to high
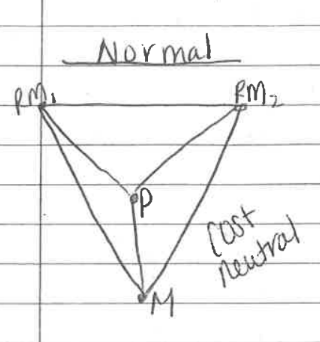
cost neutral
product in middle of raw materials and market
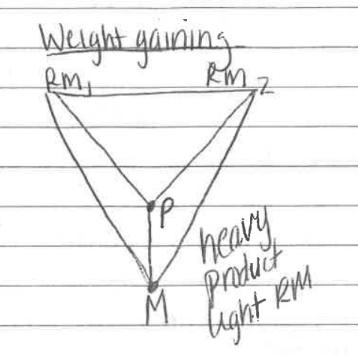
weight gaining
product closer to market
farther from raw material
final product is heavier than raw material
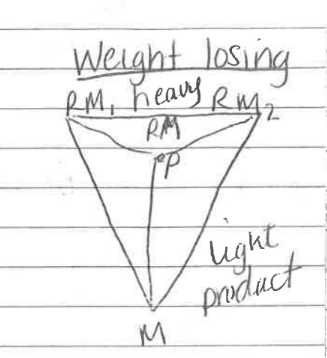
weight reducing/losing
product far from market
closer to raw materials
weight of final product is lighter than raw materials
eg: copper, steel
hotelling’s model (model of spatial competition)
in tertiary economic activity
put your location next to opponents; force people to choose you or opponent
location interdependence
how far are people willing to travel for your product
fordism (in the past)
mass production (standardization of the product)
assembly lines
special tools + machines
only one site to mass produce
corporations + countries help each other
eg: adopted the gold standard
financial orders
workers given higher wages so they can afford the product
post-fordism
goods aren’t mass produced in one place anymore
companies outsource so production passed is all around the world
global division of labor
produced + put together in different parts of the world
reasons:
less labor laws
cheaper
less environmental standards
commodity chain
entire process that a product goes through to become a product
complex commodity chain
commodity chain with lots of steps
eg: cars
just in time delivery
business strategy to reduce cost: companies only order what is needed instead of having extra inventory
break of bulk point
a location where the mode of transportation or handling of goods changes
vertical integration
own the commodity chain
horizontal integration
buying out competition
spatial disaggregation
parts for a product are produced in different factories around the world
rust belt
former industrial/manufacturing states in northern United States that lost their main job of manufacturing due to foreign competition
debt for nature swaps
some debt forgiven if a country is willing to invest in conservation
this tends to be for countries in the periphery or semi-periphery
economic complementaries
when places specialize in different things that each other demand
ecotourism
tourism that supports nature conservation, the environment, and benefits local communities
can lead to big corporations taking over which is bad
eg: national parks, costa rica
ethanol manufacturing
near corn producing areas
growth pole
specific area or sector that drives economic development in a region
idea is it can help spill over and create growth in surrounding region
brownfields
land within an urban area that was previously developed but now may contain hazardous materials and pollutants
cities will redevelop these areas into housing complexes, retail, etc
cities and developers clean it up and repurpose the area