PSYCH CHAPTER 12 PERSONALITY
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is personality?
An individual’s characteristic pattern of:
• Thinking
• Feeling
• Acting
What are psychodynamic theories?
Theories that view personality with a focus on the unconscious and the
importance of childhood experiences
What is psychoanalysis?
Freud’s theory of personality, which attributes thoughts and actions to
unconscious motives and conflicts
techniques include: seeking to expose or intepret unconncious tensions
Q: What is the core focus of Freud’s psychoanalytic view of personality?
A: It focuses on the unconscious mind and the importance of childhood experiences in shaping personality.
Q: According to Freud, what does the mind contain that influences behavior?
A: A large unconscious region filled with hidden, repressed thoughts, feelings, and desires.
Q: What are “Freudian slips”?
A: Unintentional slips of speech or behavior that reveal unconscious thoughts or feelings.
What is the technique of free association for?
uncovering unconscious thoughts: patients say whatever comes to mind to reveal repressed material
Q: Why are childhood experiences important in Freud’s theory?
A: He believed early experiences shape the unconscious and have long-lasting effects on personality.
Q: According to Freud, what causes human personality to arise?
A: A conflict between our impulses and restraints
How do people develop restraints against their impulses, according to Freud?
A: Through socialization, where they internalize society’s rules and expectations.
Q: What part of the mind does the id correspond to in Freud’s iceberg model?
A: It lies completely below the water, fully in the unconscious.
Q: What principle does the id operate on?
A: The pleasure principle — seeking immediate gratification of needs and desires. (I WANT IT NOW)
Q: How does the id behave and when is it first present in someone’s life?
It’s present from birth and behaves like: I WANT IT NOW
Q: What part of the mind does the ego correspond to in Freud’s iceberg model?
A: The tip of the iceberg: conscious, logical and problem solving
What principle does the ego operate on?
A: The reality principle — satisfying the id’s desires in realistic, socially acceptable ways.
When does the ego develop and what is it’s main role?
develops in early childhood & its main role is to balance the needs id, superego, and real-world demands.
Q: Where is the superego located in the iceberg model?
A: In the middle — partly conscious, partly unconscious.
Q: What principle does the superego follow?
A: The morality principle — focusing on right, wrong, and ideal standards
What does the superego produce?
guilt and pride
Q: What is the Oral Stage (0–18 months) and its focus?
A: Pleasure centers on the mouth—sucking, biting, and chewing.
Q: What is the Anal Stage (18–36 months) and its focus?
A: Pleasure focuses on bowel and bladder elimination and coping with demands for control.
Q: What is the Phallic Stage (3–6 years) and its focus?
A: Pleasure centers on the genitals and involves coping with incestuous sexual feelings.
Q: What is the Latency Stage (6 years to puberty) and its focus?
A: A phase of dormant sexual feelings
Q: What is the Genital Stage (puberty on) and its focus?
A: Maturation of sexual interests and development of mature sexuality.
Q: What is the Oedipus Complex, and when does it occur?
A: During the Phallic stage (ages 3–6), a boy feels unconscious sexual desire for his mother and jealousy and rivalry toward his father.
Q: What is the Electra Complex, and when does it occur?
A: During the Phallic stage (ages 3–6), a girl feels unconscious sexual desire for her father and rivalry toward her mother.
Q: How are the Oedipus and Electra conflicts resolved?
A: By identifying with the same-sex parent rather than seeing them as a rival—leading to internalization of parental values and development of the superego.
Q: How are the Oedipus and Electra conflicts resolved?
A: By identifying with the same-sex parent rather than seeing them as a rival—leading to internalization of parental values and development of the superego.
Q: What is fixation in Freud’s psychosexual theory?.
A: A lingering focus of the id’s pleasure-seeking energies on an earlier psychosexual stage due to unresolved conflicts during that stage (over or under of one stage of id)
What personality characteristics may result from phallic fixation?
Overly flirtatious or seductive behavior
Excessive vanity
Need for attention
Ego problems
Confusion about sexual identity
Relationship difficulties later in lif
Q: What are defense mechanisms?
A: The ego’s unconscious strategies for reducing anxiety by distorting reality; they operate indirectly and unconsciously.
Q: What is regression?
A: Retreating to a younger, more infantile behavior pattern, such as a child beginning to thumb-suck on the first day of school or after a new sibling arrives.
Q: What is reaction formation?
A: Replacing an unacceptable impulse with its opposite, such as someone feeling anger but showing exaggerated friendliness instead.
Q: What is projection?
A: Attributing one’s own unacceptable impulses to others, such as accusing someone else of the anger or impulses you actually feel.
Q: What is rationalization?
A: Offering self-justifying explanations to hide the real, less acceptable motives—like a habitual drinker saying they drink “just to be sociable.”
Q: What is displacement?
A: Shifting impulses toward a safer or more acceptable target, such as a child who, after a time-out, kicks the family dog instead of expressing anger at the parent.
Q: What is denial?
A: Refusing to believe painful or threatening realities—such as a partner denying evidence of an affair
What are projective tests and give me an example?
They ask people to interpret ambiguous stimuli to assess unconscious processes, like the inkblot tests
Q: What is the central idea of Carl Rogers’ person-centered perspective?
A: Humans are naturally primed to grow and reach their potential when they are in a growth-promoting environment.
Q: According to Rogers, what three qualities in an environment promote human growth?
A: Acceptance (unconditional positive regard), genuineness, and empathy.
what is self concept
a person’s overall understanding of who they are
Q: What are traits in personality psychology?
A: Characteristic patterns of behavior or tendencies to feel and act in certain ways.
Q: What are “factors” in trait theories?
A: Clusters of behavior tendencies that occur together and reflect a basic personality factor.
example: someone is often talkative, sociable, and enjoys being around people. These behaviors cluster together and represent a factor called “extraversion.”
What are Hans & Sybil Esneck theory when it comes to trait theories?
restricted it only to extraversion-introversion, instability-stability
Q: What is a personality inventory?
A: A questionnaire that assesses a wide range of feelings and behaviors to assess personality traits.
Q: What is the MMPI?
The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory, the most widely researched and clinically used personality test (self-report & true/false questions)
What are the Big Five broad dimensions of personality? (OCEAN)
O - Openness
C -onscientousness
E -xtraversion
A - greeableness
N -euroticism (emotional instability-stability)
How do they test for the Big 5?
answer a series of statements, put 1-5
Q: What is the social-cognitive perspective?
A: A view of personality that emphasizes how a person’s traits and thoughts interact with their social situations
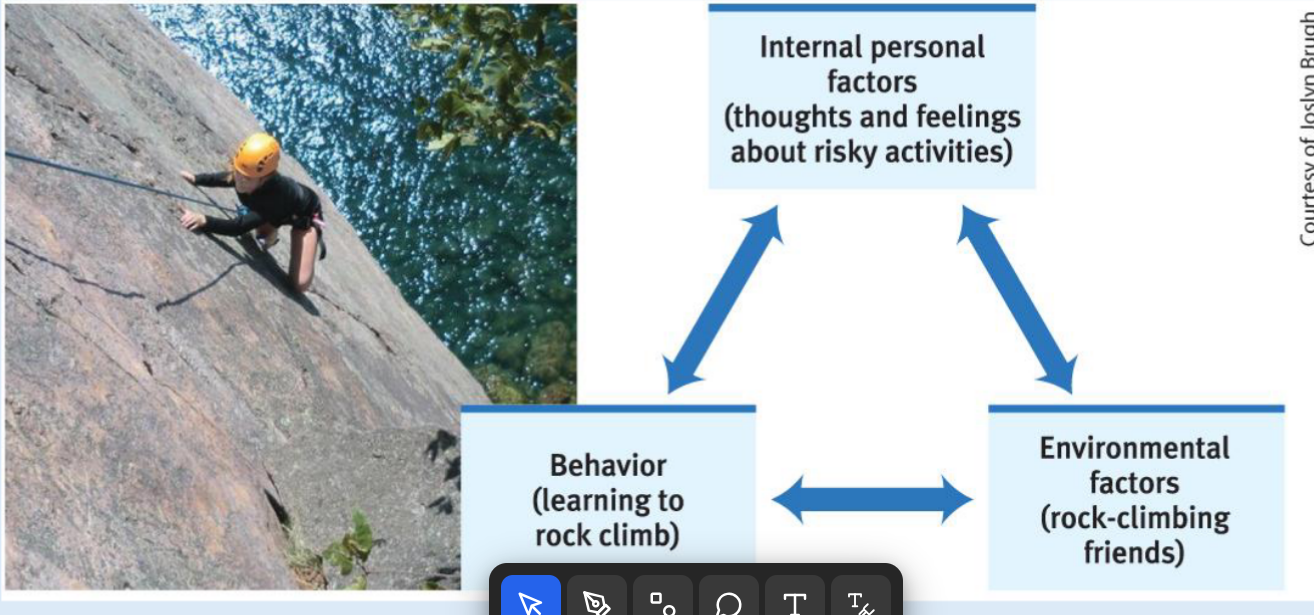
Q: What is reciprocal determinism?
A: Albert Bandura’s idea that behavior, personal factors, and the environment all influence each other.
personal factor
Q: What do people bring with them into social situations, according to Bandura?.
A: Their past learning, self-efficacy, and ways of thinking about the situation
Q: What is self-efficacy?
A: A person’s belief in their ability to succeed or handle a situation.
What is the criticism for social-cognitive theories?
focus more on situation than a person’s inner traits
What is the criticism for trait theories?