Michaelis - Menten Equation and Lineweaver derivation and Inhibition
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Steps to derive MM equation
1) k1 [E][S] = k-1[ES] + k2[ES]
2) [ET] = [E] + [ES], so —> [E] = [ET] - [ES]
3) Plug in [E] into 1)
4) k1([ET] - [ES])[S] = k-1[ES] + k2[ES]
5) Find KM= ([ET] - [ES])[S] / [ES]
6) Now solve for [ES]
7) [ES] = [ET][S] / KM + [S]
8) Incorporate in V0= k2[ES]
9) V0= k2[ET][S] / KM + [S]
10) Vmax= k2[ET] —> Substitute into previous
11) V0= Vmax[S] / KM + [S] —> MM Equation
What is Km
Vmax/2, when the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half maximal
Indicates Affinity
Lower Km = Higher Affinity
Vmax
Indicates Chemistry
The theoretical maximal velocity
Vmax is asymptotically approached
0th order: independent of [S]
Vmax / Km
1st order reaction
only depends on [S]
indicates Binding
kcat
Vmax/[ET]
1st order rate constant: only dependent on the Enzyme
The number of substrate molecules converted to product per enzyme per unit of time, when E is fully saturated
High kcat: high number of substrate to product
kcat/Km
The specificity constant
2nd order rate constant
measure of the specificity of the enzyme at low substrate concentrations
[S]«Km
How “perfect” and enzyme can be
Find S, bind S, ES —> P
High number = High productivity
Lineweaver - Burk plot
Vmax:
Km:
Vmax/Km:
Vmax: Chemistry
Km: Affinity
Vmax/Km: Binding
Lineweaver - Burk plot:
Slope:
y-int
x-int:
Km/Vmax
1/Vmax
1/Km
Km app means
the presence of an inhibitor, not the true Km
Inhibitors alter the activity of ___ by combining with it in a way that influences ______ and ______
enzymes
the binding of substrates
the turnover number
Irreversible inhibitor
substance that causes inhibition that cannot be reversed: Inactivators
Usually forming or breaking covalent bonds
Reversible Inhibitor
A substance that binds to an enzyme to inhibit it, but can be released
formation of non covalent bonds
Types of inhibition
Competitive
Uncompetitive
Mixed or Noncompetitive (same thing)
May bind at the active site or alternative binding sit e
Competitive Inhibition
Competes with substrate for binding site
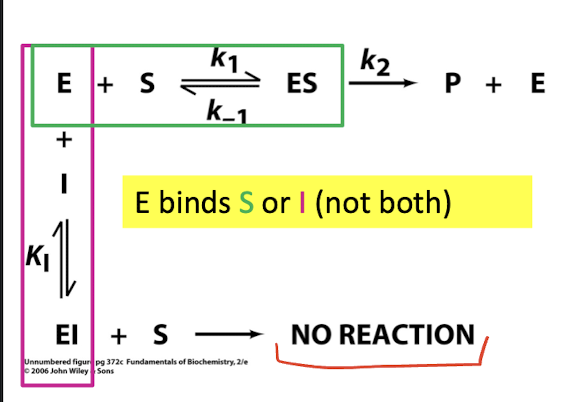
What does KI measure
The dissociation constant for enzyme inhibitor binding
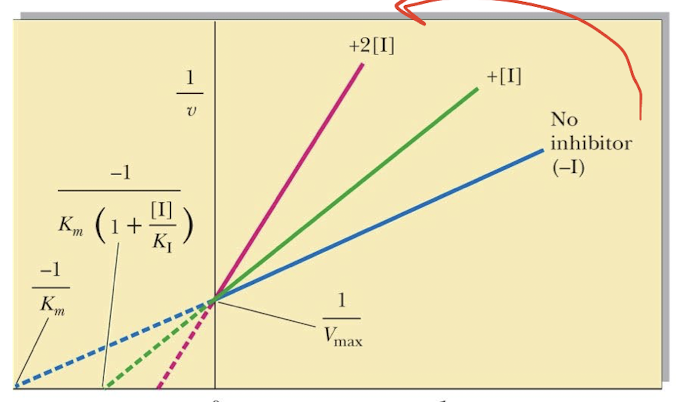
The presence of I make [S] appear to be _____ so Km appears _____ than normal. This “new” Km is called ____. This can also be known as ___Km
less
larger
KMapp
alpha
A competitive inhibitor _____ the amount of free enzyme available for substrate binding thus _____ the KM for the substrate
reduces
increasing
The effect of a competitive inhibitor can be overcome with ____ concentrations of _____
(alpha effect of inhibitor)
high
substrate
Competitive inhibitors _____ structure of substrates with ______ that prevent _____ from occurring
mimic
modifications
chemistry
Competitive inhibitors affect
KM—> affinity
Vmax/Km —> Binding
But not Vmax—> chemistry
Why does Competitive Inhibition not affect Vmax
Inhibitors do not effect E’s ability to catalyze a reaction