Physics vectors and projectiles
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
How are vectors defined?
magnitude (length)
direction (angle)
What are scalars?
defined by magnitude only (normal numbers)
What are examples of scalars?
speed (just how fast your going)
time
distance
mass
energy
What are examples of vectors?
velocity
acceleration
displacement
force
How do you add vectors?
align them from head to tail (arrow head to end of arrow)
then the resultant (the sum) is the line that connects them from the tail of the first to the head of the second vector
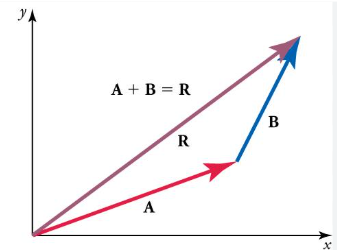
How do you subtract vectors?
A-B = A+ (-B)
(-B) is the inverse of B (flip the arrow head to the tail)
then draw the resultant
vector components
the x and y components of the vector
they go horizontally (x) and vertically (y)
What are the vector components equations?
these are the equations where you can find how much the vectors equal (usually a velocity)
equations on back of reference table
make sure calculator is in DEGREE mode
What is the key rule for motion?
x and y motion are completely INDEPENDENT
ex. how fast something is going in the x direction will not impact the distance it travels in the y direction
projectile motion
object moving in 2D or 3D dimensions affected only by gravity
What is important to remember in horizontal projectile problems?
the velocity in the x direction is constant (doesn’t change)
What table do you make at the start of every problem?
make a table with an x column and a y column
under both columns put distance, velocity, and acceleration
same time value is used for both (scalar)
For horizontal projectile motion what values can you immediately fill in?
a= 0 (because the velocity is constant (not accelerating))
ay= -9.81
viy= 0 (because the object is not initially moving in the y direction because it is a horizontal projectile) (not initially getting any y velocity)
What does time depend on/ is impacted by for horizontal projectiles?
the height it is dropped from only (dy)
time will only change if dropped from a different height compared to the orginal
What does range mean?
horizontal distance traveled
What equations do you use for the x and y side of the table?
use x separately and y separately
dx=vxt always for the x side
any kinematic equation for the y side
What does the horizontal velocity impact?
the horizontal distance (range)
the faster it goes the more ground it covers
What is a key thing to remember with horizontal projectiles?
especially when asking for a velocity, make sure you read the question
if it is asking for the vfy then solve normally same with vx
but if it is just asking for the velocity, then you have to figure out the slanted velocity (vfy and vx are the components so you have to find v) (use Pythagorean theorem)
What do you do when trying to find an angle?
do soh CAH toa
then you have to do the inverse (so 2nd tan, sin, or cos in you calculator)
projectiles fired at an angle
not starting at just a horizontal velocity
is still constant
the y velocity changes though (increases, then zero, then inreases in opposite direction)
What are usually your first steps for a projectiles fired at an angle problem?
create table
find Vx, and Vy
What is the key thing to remember about when the projectile reaches max height?
when the projectile reaches it maximum height the Vfy = 0
imagine the path of the projectile like the top of a parabola
Symmetric
projectiles are only symetric when it stops at the same dy as when it started
the time will be symmetric
What do you need to remember when you are solving for the time when you plug in vfy=0?
when vfy=0 that is the max height of the projectile not the full time that it traveled for the full range
double the time
What controls how long the projectile is in the air for?
y -velocity
projectile shot at 90 degrees will be in the air the longest
What angle does a projectile need to be launched from to the the greatest range?
45 degrees Wha
What drawing do you need to make sure to have for angle problems?
a triangle with the velocities and specify the angle