Gram Positive and Negative Cocci
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards reviewing key concepts related to gram-positive and gram-negative cocci.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Staphylococcus
Genus of bacteria including important human pathogens S. aureus, S. epidermidis, and S. saprophyticus.
Staphylococcus aureus
Important human pathogen causing minor and serious diseases; can survive on dry surfaces and is heat-resistant. Gram positive and in grape clusters. Facultative anaerobic

Staphylococcus epidermidis
Present in normal flora, usually benign except when introduced via catheters, causing hospital-acquired infections.
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Causes urinary tract infections.
Capsule and slime layer: Virulence factor of S.aureus
Mediates attachment to medical devices and inhibits chemotaxis and phagocytosis.
Protein A: Virulence factor of S.aureus
Specific affinity for Fc of IgGs, avoiding antibody clearance.
Teichoic acids: Virulence factor of S.aureus
Mediate attachment to fibronectin on mucosal membranes.
Peptidoglycan: Virulence factor of S.aureus
Inhibits phagocytosis and confers osmotic resistance.
Coagulase: Virulence factor of S.aureus
Binds to fibrinogen, making insoluble fibrin, aggregating bacterial cells.
Fibrinolysin (staphylokinase): Virulence factor of S.aureus
Dissolves fibrin clots.
Hyaluronidase: Virulence factor of S.aureus
Degrades connective tissues, facilitating spread (present in 90% of S. aureus strains).
Lipases: Virulence factor of S.aureus
Required for invasion into cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues.
Nuclease: Virulence factor of S.aureus
Hydrolyzes viscous DNA.
Penicilase: Virulence factor of S.aureus
Breaks the β-lactamic ring, providing resistance to penicillin.
Cytolytic toxins: Virulence factor of S.aureus
Membrane-damaging toxins that cause lysis of neutrophils, leading to lysosomal enzyme secretion.
– Alpha, beta, delta, gamma, leukocidin
– All cause lysis of neutrophils leading to massive lysosomal enzyme
secretion. Aditionally:
– Alpha is also toxic for red blood cells, hepatocites and platelets
– Beta is toxic for rbc, fibroblasts, and macrophages
– Delta is toxic for rbc and many other cells
Exfoliative toxins (A and B): Virulence factor of S.aureus
Separates the epidermal layer from the dermis, causing blistering and peeling of the skin; also known as exfoliative or epidermolytic toxin.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1)
Ultra absorbing tampons bind mg2+. Low mg2+ triggers TSST-1. Stimulates IL-1 by macrophagesand promotes massive cytokine release, leading to severe systemic effects including fever and shock.
Enterotoxins (A-E, G-I): Virulence factor of S.aureus
Resistant to gastric and jejunal enzymes; stable to heating; stimulate intestinal peristalsis and cause intense vomiting.
Folliculitis
Inflammation of hair follicle.
Furuncle (boil)
Inflammation of hair follicle or sebaceous gland progressing into abscess or pustule.
Carbuncle
Larger and deeper lesion created by aggregation and interconnection of a cluster of furuncles.
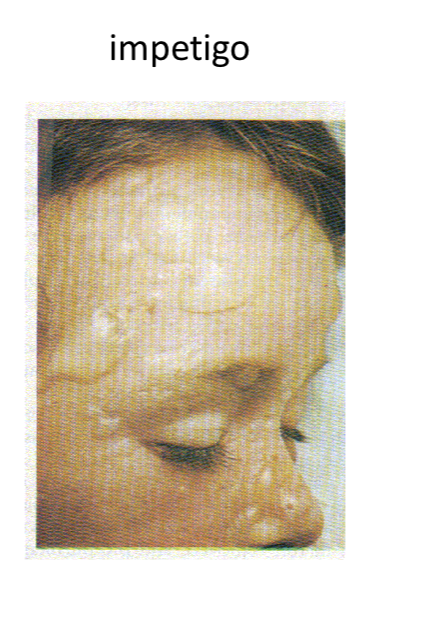
Impetigo
Bubble-like swellings that can break and peel away, commonly seen in newborns.
Food intoxication
Ingestion of heat-stable enterotoxins causing gastroenteritis.
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Toxin induces bright red flush, blisters, then desquamation of the epidermis.
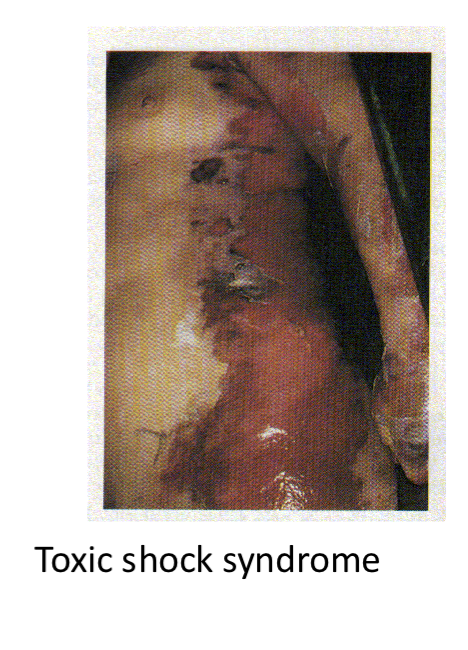
Toxic shock syndrome
Toxemia leading to shock and organ failure.
Osteomyelitis
Infection established in the metaphysis, forming an abscess.
Bacteremia
Bacteria arrive in the bloodstream from another infected site or medical devices, potentially leading to endocarditis.
Methicillin, oxacillin, nafcillin, dicloxacillin
Semisynthetic penicillins resistant to ß-lactam hydrolysis, used to treat S. aureus.
MRSA
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus; resistant to synthetic penicillin methicillin.
Vancomycin
Acts by interfering with cell wall construction; side effects include hearing loss and nephrotoxicity.
Linezolid
Protein synthesis inhibitor used against MRSA.
Daptomycin
Causes membrane depolarization in bacteria, interrupting membrane transport.
Oritavancin
New glycopeptide similar to vancomycin, approved by the FDA in 2014 with fewer secondary effects.
Tigecyclin
Glycylcycline not affected by efflux pump or ribosomal protection mechanisms of resistance.
Dalbavancin
Semisynthetic lipoglycopeptide designed to improve vancomycin's effect.
StaphVAX®
Polysaccharide conjugate vaccine against S. aureus infections, not yet FDA approved.
Streptococcus
Gram-positive cocci in chains, facultative anaerobic, sensitive to penicillin.
Lancefield antigens
Classification criteria based on antigens (A, B, C, F, G).
Alpha hemolysis
Iron in haemoglobin oxidised, greenish color.
Beta hemolysis
Complete disruption of red cells, clear zone around colonies.
Gamma hemolysis
Non-hemolytic streptococci.
Streptococcus pyogenes
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
Streptococcus agalactiae
Group B beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Alpha hemolytic streptococcus.
Virulence factors of Streptococcus pyogenes to avoid phagocytosis
Capsule, M protein, F protein, lipoteichoic acid.
Streptolysin O
O2-labile toxin that causes hemolysis.
Streptolysin S
O2-stable toxin that causes hemolysis and is produced in the presence of serum.
Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins (A, B, C, and F)
Also known as erythrogenic toxins; mediators of red rash in scarlet fever and shock.
Streptokinases (A and B)
Anticlotting properties by degrading plasminogen, fibrin, and fibrinogen.
DNases (A to D)
Depolymerize free DNA in pus abscesses, increasing microorganism dissemination.
Strep throat
Acute bacterial pharyngitis/tonsillitis.
Scarlet fever
Complication of pharyngitis causing rash on trunk and extremities, mediated by pyrogenic toxin.
Impetigo (pyoderma)
Superficial lesions that break and form highly contagious crust.
Erysipelas
Acute skin infection with localized pain, inflammation, lymph node enlargement, and fever.
Cellulitis
Pathogen enters through a break in the skin and spreads to the dermis and subcutaneous tissues.
Necrotizing fasciitis
Infection of deep areas of subcutaneous tissue, destroying muscle and adipose tissues.
Streptococcal toxic shock like syndrome (TSLS)
Initial infection may have been pharyngitis, cellulitis, or peritonitis; leads to rapid shock and organ failure.
Rheumatic fever
Nonsuppurative complication of pharyngeal infections causing inflammation of heart, joints, blood vessels, and subcutaneous tissues.
Acute glomerulonephritis (AGN)
Antigen-antibody complexes deposit in the glomerulus, causing kidney damage.
Penicillin
Drug of choice for S. pyogenes treatment; erythromycin if patient is allergic.
Streptococcus agalactiae
Colonizes the urogenital tract of pregnant women and can cause premature rupture of membranes and premature delivery.
Early-onset infection of S. agalactiae
Occurs in neonates younger than 7 days; vertical transmission from mother, manifests as pneumonia or meningitis with bacteremia.
Late-onset infection of S. agalactiae
Occurs between 1 week and 3 months after birth, usually in the form of meningitis.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Inhibits the nasopharyngeal areas of healthy individuals
Pneumonia
Most common cause of bacterial pneumonia.
Otitis media
Most common cause of otitis media in children < 3 years.
Enterococci
Gram-positive cocci in short chains, part of the normal bowel flora, common cause of nosocomial infections.
Associated infections of Enterococcus
Bacteremia, urinary tract infections, wound infections, nosocomial infections, and endocarditis.
Virulence factors of Enterococcus
Surface adhesins, cytolysin, pheromone, gelatinase, multiple plasmid and antibiotic resistance.
Genus Neisseria
Gram-negative cocci often arranged in pairs with adjacent sides flattened.
Growth conditions of N. gonorrhoeae
Requires complex media pre-warmed to 35-37C, soluble starch, and moist atmosphere with CO2.
Gonococcal virulence factor
Only fimbriated cells are virulent.
Por (porin protein)
Prevents phagolysosome fusion, promoting intracellular survival.
Opa (opacity protein)
Mediates firm attachment to epithelial cells and subsequent invasion.
Rmp (reduction-modifiable protein)
Protects other surface antigens from bactericidal antibodies.
Lipooligosaccharide (LOS)
Incomplete Lipopolysaccharide that still retains endotoxin activity.
Chromosomally-mediated changes in cellular permeability
Inhibits entry of penicillin, tetracycline, erythromycin, aminoglucosides.
Epidemiology of gonorrhea
Major reservoirs, lack of protective immunity, higher risk of disseminated disease with late complement deficiencies.
Pathogenesis of N. gonorrhoeae
Microorganism invades intact mucous membranes or skin with abrasions, penetrates, multiplies, and establishes infection in the sub-epithelial layer.
Gonorrhea in men
Urethritis, epididymitis.
Gonorrhea in women
Cervicitis, vaginitis, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Disseminated Gonococcal Infection (DGI)
Disseminated Gonococcal Infection (DGI)
Skin lesions, arthralgias, tenosynovitis, septic arthritis.
Opthalmia neonatorum
Chemoprophylaxis with silver nitrate, tetracycline, or erythromycin eye ointments; treatment with ceftriaxone.
Neisseria meningitidis virulence factor
Pili-mediated, receptor-specific colonization of nonciliated cells of nasopharynx.
Antiphagocytic polysaccharide capsule
Spreads in the absence of specific immunity.
Toxic effects of N. meningitidis
Effects mediated by hyperproduction of lipooligosaccharide.
Highest incidence for Neisseria meningitidis
Children younger than 5 years.
Treatment of N. meningitidis
Penicillin along with supportive therapy for meningeal symptoms; chloramphenicol or cephalosporins as alternatives.