Introduction to Linear Algebra Module 1, lesson 4 Position vectors and components
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
there is also matrix question learn in paris through Elia's book
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What is a matrix
A matrix is a 2d array of numbers. Each element is identified by two indices
How we usually write a matrix?
We usually give matrices uppercase variable names with bold typeface
What denote Ai,:
All the Number with vertical coordinate i… this “:” refer to all numbers of that horizontal line.
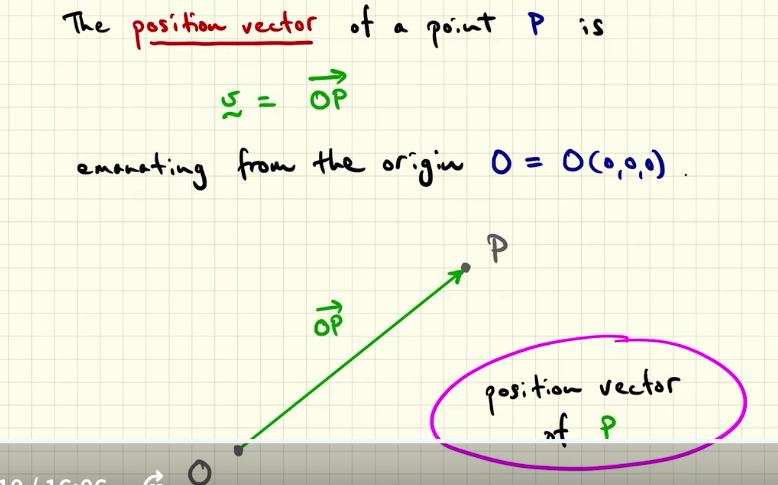
what is a position vector?
A position vector is a vector that represents the position of a point in space relative to a fixed origin. It has a specific starting point, the origin, and its endpoint is the point whose position it describes
quali sono i “building block” dei vettori geometrici? che in altri termini non sono altro che i vettori nello spazio per come li conosciamo (segmenti orientati sul piano cartesiano)
the building blocks of geometric vectors are i,j,k which are the unit vector pointing in the direction of x,y,z axes rispectively

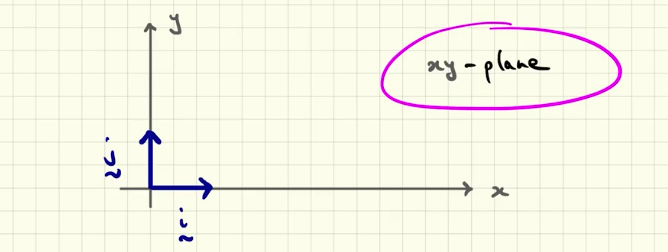
When we say “unit vector i and j” what unit vector are we referring to?
to the x and y axes unit vector. (questo per quanto riguardo un piano cartesiano 2d) As we can see y axis is usually though as “vertival” in this 2d representation (this change when we represent things on a 3d space)
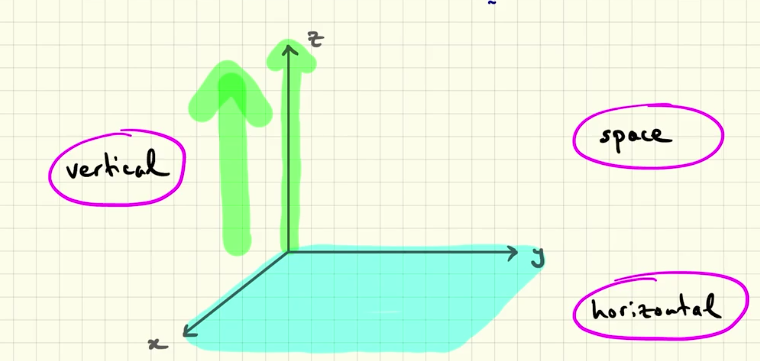
what is the unit vector’s names of x,y and z axes?
as we can see when we have a 3d space, the y axis is not anymore usually consider the "vertical axis” but the horizontal axis, while the “z” axis is considered in this context the vertical axis… this difference between what is usually represent as vertical in 2d or 3d space can be very usefull!
we said that a geometric vector has as its building block i,j,k; but what kind of combination of i, j, k define any possible geometric vector?
every geometric vector is a LINEAR COMBINATION of i,j,k… this mean that a geometric vector can be described by a sum! This it’s really important because means that now, we can convert a geometric problem into an arithmetic problem!

the fact that geometric vector can be described by a linear combination of numbers (unit vector i,j,k) which implications has?
the most important implication is that something that we see by a geometric prospective has now an arithmetic one!
A vector v in 3D space can be written as: v=ai^+bj^+ck^
Here, a, b, and c are the components of the vector, which are simply the coordinates of its endpoint if it starts at the origin.
what is the position vector of a point P?
First, a position vector is a directed line segment that start from origin and terminate in a specific point in the space.
The position vector of a point P is “v = OP” where OP is the segment that starts at the origin and terminate in P