ap bio <3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:43 PM on 10/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
1
New cards
unsaturated fatty acid
fatty acid w unsaturated carbon chain (double bond between carbons in the chain), usually liquid, plants and fish

2
New cards
saturated fatty acid
fatty acid w fully saturated carbon chain (no double bonds), solid at room temp, animals

3
New cards
glycerol
C3H8O3, lipid monomer that links other lipids, usually fatty acid chains

4
New cards
protein monomer
amino acids, have amino and carboxyl groups and R functional group (determines function)

5
New cards
carbohydrate monomer
monosaccharide

6
New cards
nucleic acid monomers
nucleotides, phosphate group, pentose sugar, and nitrogenous base

7
New cards
lipid functions
barriers (cell membranes), energy storage
8
New cards
carbohydrate basic formula
(CH2O)n
9
New cards
carbohydrate functions
energy storage, structural support
10
New cards
phospholipid
lipid monomer type, negative charged phosphate head, two nonpolar fatty acid chains, amphipathic (diff spots are polar vs nonpolar)

11
New cards
polarity of water =
unequal sharing of electrons, resulting in partial pos charge in hydrogens and partial neg in oxygen, hydrogen bonding with other charged molecules

12
New cards
cohesion
same types of molecules bind together (usually weaker bonds)

13
New cards
adhesion
different types of molecules bind (stick) together (usually weaker bonds)

14
New cards
surface tension
air is less dense and nonpolar, less binding to water molecules, more binding cohesion, water sticks together and resists force

15
New cards
capillary action
adhesion to the sides of the container and cohesion to adject water molecules allow water to climb against gravity, thinner tube goes higher (pressure differential encourages climb)

16
New cards
specific heat
amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1g of the substance to change temp by 1 deg C
17
New cards
specific heat of water is high bc...
hydrogen bonds between molecules take energy to break, in order to heat water (move molecules faster) those bonds need to be broken
18
New cards
bc specific heat of water is ..., it is good for...
high, cooling and regulating internal temps (resists temp change)
19
New cards
breaking hydrogen bonds ... energy
requires/absorbs (endo)
20
New cards
making hydrogen bonds... energy
gives off/releases (exo)
21
New cards
water ... when freezing bc...
expands, molecules orient themselves in matrix position that is more spread out to balance charges
22
New cards
hydration shells
water molecules gathered around a charged particles after dissolving it, all molecules should be oriented specifically
23
New cards
acids
increase H+ or H3O+ (hydronium) concentration
24
New cards
bases
increase OH- concentration (decrease H+)
25
New cards
bufferes
stabilize pH by minimizing effects of strong acids and bases
26
New cards
standard deviation
how much data points differ from the mean
27
New cards
x bar =
mean
28
New cards
n =
number of data points
29
New cards
higher standard deviation...
lower reliability
30
New cards
standard error
represents uncertainty, sample size and variability (smaller standard error, more likely mean is accurate generalization)
31
New cards
error bars
usually 2SEM, show the standard error, overlap = no statistical significance
32
New cards
hydroxyl
OH, polar, makes hydrophilic
33
New cards
amino
-NH2, often in bases, in amino acids with carboxyl
34
New cards
carboxyl
-COOH, carboxylic acid group (dissociates into acid in water), in amino acids with amino
35
New cards
methyl
-CH3, nonpolar, binds to cytosine to promote gene expression

36
New cards
euchromatin
open, methylated DNA
37
New cards
heterochromatin
closed, wrapped around histones, unmethylated
38
New cards
phosphate
-PO4 2-, negative charge = hydrophilic, in phospholipids and nucleotides
39
New cards
sulfhydryl
-SH, crosslinked molecules, when bound S-S
40
New cards
carbohydrate bond
glycosidic bond
41
New cards
disaccharides
2 bonded monosaccs, maltose, sucrose, lactose
42
New cards
polysaccharides
staches, glycogen, cellulose - long term energy storage and structure
43
New cards
cellulose
plant cell walls
44
New cards
peptidoglycan
bacterial cell walls
45
New cards
chitin
fungal cell walls, arthropod exoskeletons
46
New cards
lipid bond
ester bond
47
New cards
hydrogenation
artificially adding hydrogen to carbon chains in fats to saturate them
48
New cards
endomembrane system pathway
synthesize protein in ER, go inside ER, vesicle to golgi, absorbed thru cis face, packaging and tagging, exit thru trans face, vesicle to membrane (fuse w membranes along the way)

49
New cards
smooth ER
manufactures and replenishes the lipids (phospholipids mostly) consumed in the cell
50
New cards
cholesterol
animal sterol, produced in liver, stabilizes membrane
51
New cards
testosterone and estradiol
hormones (steroids), 4 ring structure
52
New cards
protein based hormones
bind to receptors on cell membrane, don't acc enter, trigger internal signalling
53
New cards
lipid based hormones
because membrane also lipid, can enter the cell itself, trigger signaling once inside of the cell
54
New cards
waxes
lipids, alcohol chain and fatty acid chain, insulate from water loss
55
New cards
protein functions
literally everything, cell functions, catalysts (enzymes), cell communication, structure (histones, cytoskeleton?), transport (motor proteins)
56
New cards
protein synthesis location
ribosomes, proteins the will be in the cytosol synthesized in free ribosomes, proteins secreted or in plasma membrane synthesized in bound ribosomes (er)
57
New cards
protein function determined by...
sequence of amino acids and R group interactions (20 diff R groups)
58
New cards
protein bond
peptide bonds
59
New cards
genetic code
triplet code of codons and which amino acids they relate to
60
New cards
primary protein structure
linear, chain of amino acids
61
New cards
secondary protein stucture
hydrogen bonding between near R groups, alpha helices and beta pleated sheets

62
New cards
tertiary protein structure
3D shape stabilized by R group interactions, hydrophobic, disulfide bridges, ionic bonds, folded into shape, for some proteins final

63
New cards
quaternary protein structure
association of multiple peptides (multiple subunits), usually weaker bonds, only some proteins

64
New cards
denaturation
protein unraveling (degrading) due to change of environment (temp, pH, etc)
65
New cards
2 types of nucleic acids
DNA (deoxy), RNA (ribo)
66
New cards
pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, uracil (t in rna), single rings

67
New cards
purines
adenine, guanine, double rings, larger

68
New cards
nucleic acid bonds across the helix
A - T (2 h bonds) G - C (3 h bonds)
69
New cards
nucleotide bonds
phosphodiester bonds

70
New cards
antiparallel orientation
sides of double helix run in opp directions, count from carbon bound to base clockwise
71
New cards
5 things all cells share
cell membrane, genetic material, ribosomes, cytoskeleton, cytosol
72
New cards
cytoskeleton
support and mobility, microtubules (thick) microfilaments (thin), cilia and flagella, motor protein highway
73
New cards
golgi apparatus
enter the cis face, out the trans face, transport vesicles and motor proteins carry, golgi gives chemical tags
74
New cards
free ribosome
makes proteins that stay in the cytosol
75
New cards
bound ribosomes
make proteins that go to plasma membrane and outside of cell
76
New cards
phagocytosis
lysosomes break down invasive particles, food vacuoles with hydrolytic enzymes
77
New cards
autophagy
lysosomes break down old parts from the cell itself
78
New cards
amphipathic
have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
79
New cards
functions of membrane proteins
transport, enzymatic activity, signal transduction, cell-cell recognition, intercellular joining, attachment to extracellular matrix

80
New cards
passive transport
transport across the cell membrane with the concentration gradient, no energy required (diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion)
81
New cards
active transport
transport across the cell membrane against the concentration gradient, requires cell energy as ATP (endocytosis, exocytosis, sodium-potassium pump)
82
New cards
dynamic equilibrium
the state in which a substance is evenly dispersed and movement is uniform
83
New cards
selective permeability in the cell membrane
smaller, nonpolar molecules diffuse through faster than larger, polar molecules; certain molecules can go thru and others can't
84
New cards
facilitated diffusion
passive transport with transport protein channel (bind loosely to molecule, carry it thu) (aquaporins)
85
New cards
sodium potassium pump
inside cell, 3 sodium ions bind to pump, shape change, ATP bind a phosphate (phosphorylation), shape change, sodium out, 2 potassium bind, shape change, dephosphorylation, shape change, potassium release, start over
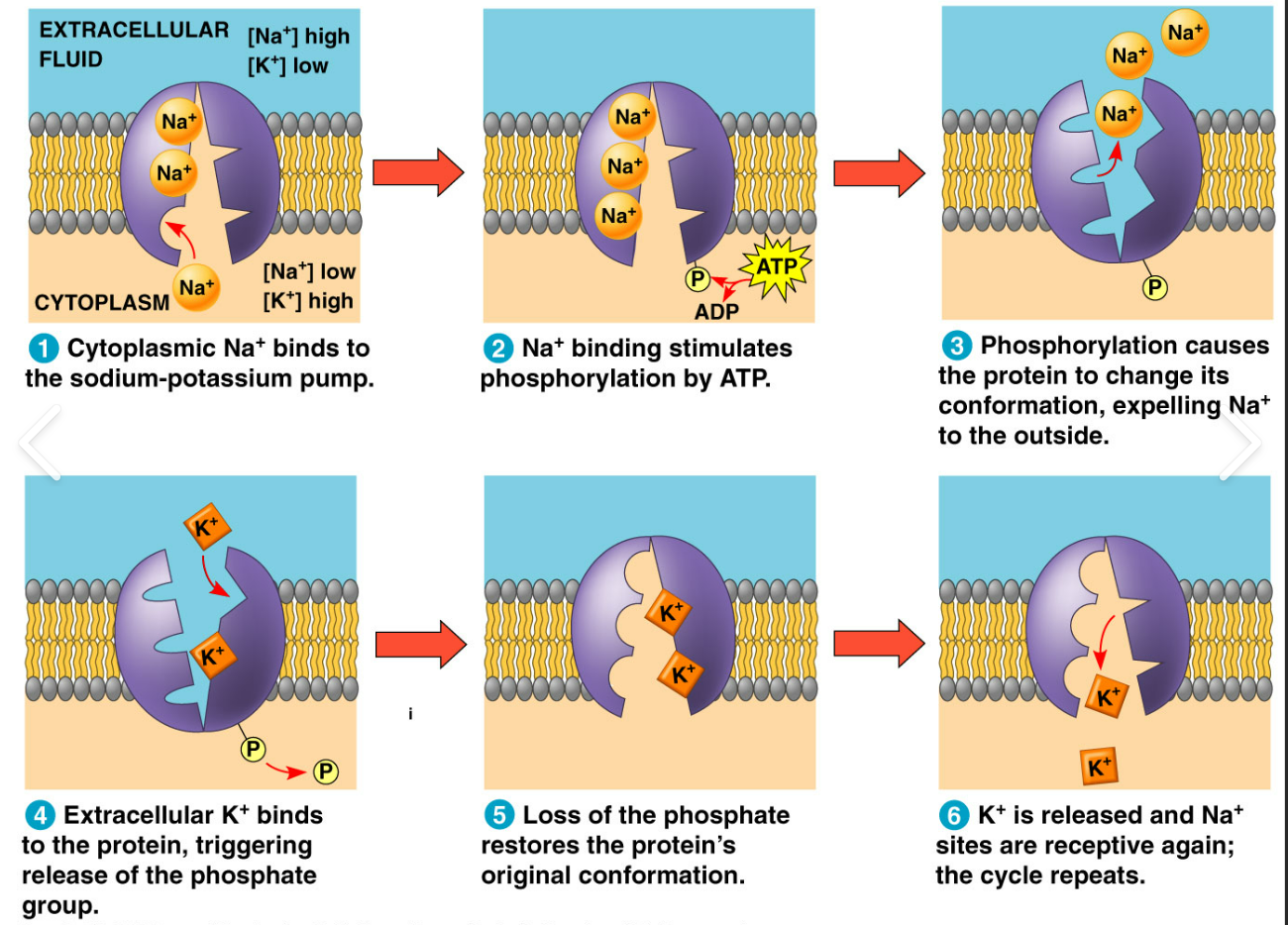
86
New cards
membrane potential
difference in electric charge across a membrane (inside usually more negative)
87
New cards
electrochemical gradient
chemical gradient - concentration of molecules, and voltage gradient - pos charged ions outside cells attracted to neg charge inside cell, when cell pos repel
88
New cards
endocytosis
invagination caused by membrane budding off to the inside of cell containing smth (usually large molecules or large numbers of molecules) as a vesicle (ex: phagocytosis, phagosome) - lots of atp (motor proteins)
89
New cards
exocytosis
vesicles from cell merge with membrane and push contents to outside of cell (ex: neurotransmitters into synapse) - lots of atp
90
New cards
cotransport
technically active transport, 2 molecules have to be present at a transport protein to diffuse thru the protein - active bc another pump moves co-molecule against concentration gradient (usually to outside) to be present at the protein - co-molecule often allows shape change, enables transport

91
New cards
antiport
2 molecules moving in opposite directions thru the same pump
92
New cards
symport
moving in same direction, move together
93
New cards
water potential
takes pressure and solute concentration to predict where water will travel (% = %p + %s)
94
New cards
metabolism
complete set of organic chemical reactions in the body
95
New cards
catabolism (catabolic reaction)
break down of large into smth smaller (ex: hydrolysis, proteases, nucleases, etc)
96
New cards
anabolism (anabolic reaction)
building large molecules from smaller (ex: kinases, dna polymerase, etc)
97
New cards
exergonic reactions
lower activation energy, high energy reactant w/ low energy products, releases energy into environment (ex: cellular respiration first steps, glucose + oxygen gas high energy -> co2 + H20 low energy, releases energy)
98
New cards
endergonic reactions
higher activation energy. low energy reactant w/ high energy products, need to take in energy for the bonds (ex: photosynthesis, co2 + h20 low energy, need sun to make glucose + o2)
99
New cards
enzymes lower...
activation energy
100
New cards
energy coupling
when the energy released from an exergonic reaction is used as the activation energy to fuel an endergonic reactions (es: breakdown of glucose to fuel atp production)