Bio 006 - Photosynthesis II & Cell Communication
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Light Reactions
Initial phase of photosynthesis converting light energy. Absorbing and Storing it for later.
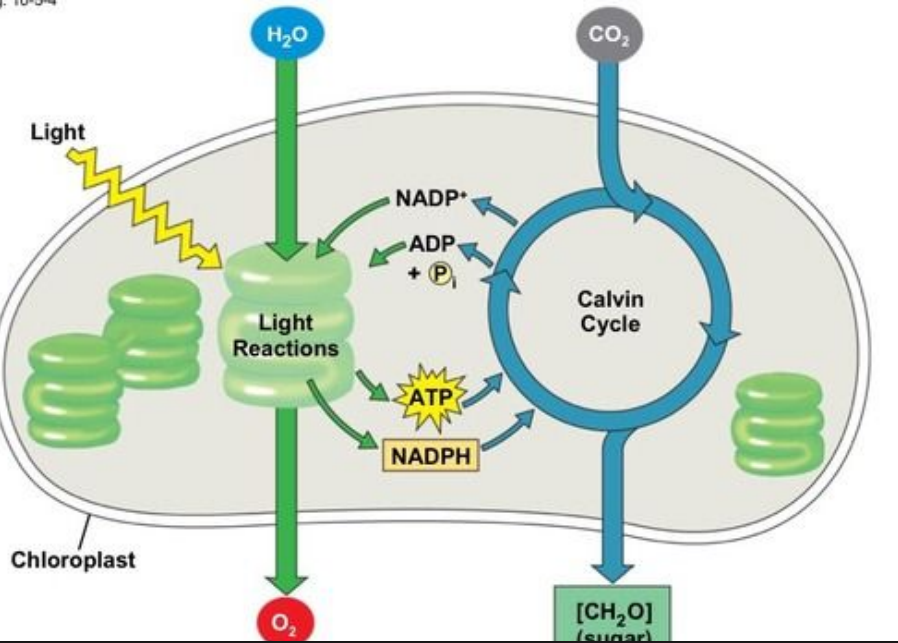
Photosystems
Light Reactions
Protein complexes that absorb light energy.
NADP Reductase
Light Reactions
Enzyme converting NADP+ to NADPH.
ATP Synthase
Light Reactions
Enzyme producing ATP from ADP.
Thylakoid Space
Light Reactions
Location where water splits into H+ and O2.
Calvin Cycle
Process converting CO2 into glucose.
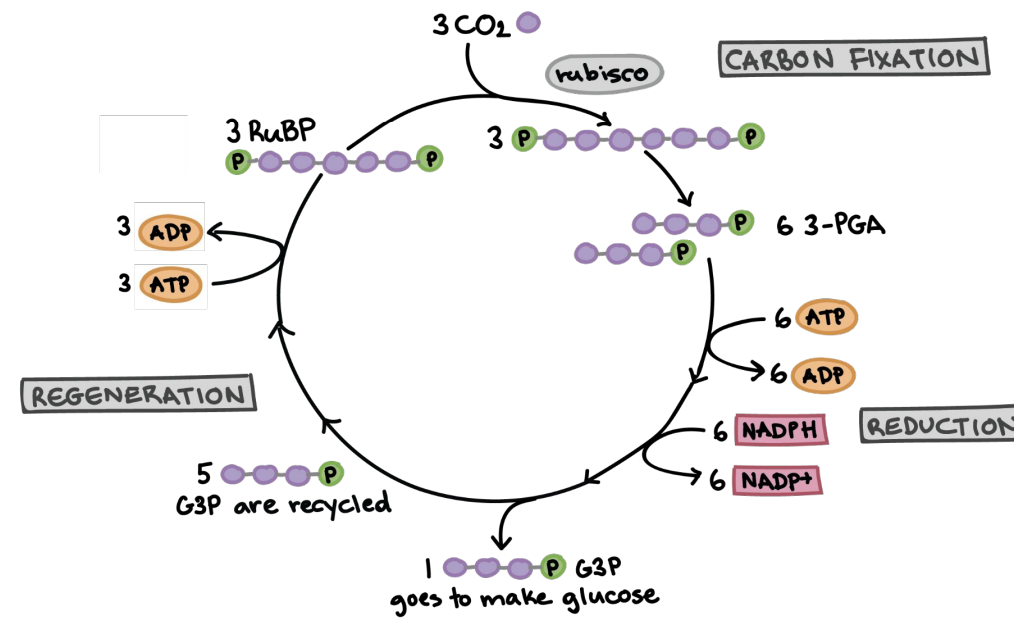
Stroma
Fluid surrounding thylakoids in chloroplasts.
Location of the Calvin cycle
G3P
Main Reaction of the Calvin cycle…
Intermediate product in glucose synthesis.
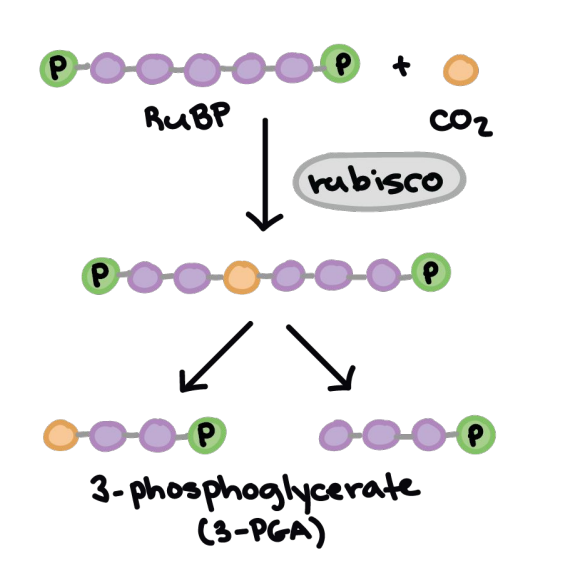
CO2 —>_____
Rubisco
Enzyme catalyzing CO2 fixation with RuBP.
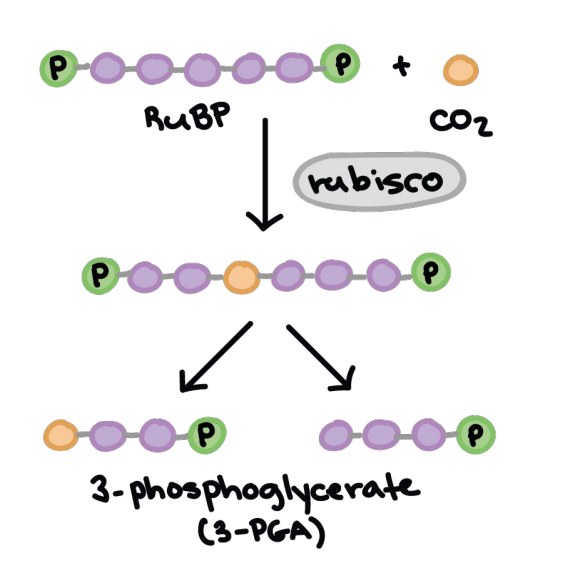
3-Phosphoglycerate
Product of CO2 fixation in Calvin Cycle.
Cell Membrane
Amphipathic barrier regulating substance passage.
Integral Proteins
Proteins embedded in cell membranes facilitating transport.
Ligands
Chemical signals used for cell communication.
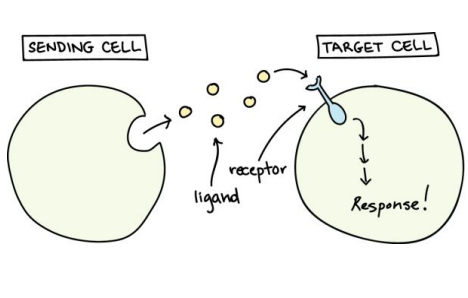
Receptors
Proteins that bind ligands and initiate responses.
Signal Reception
First step in cell communication where ligand binds to receptor.
Signal Transduction
Step 2 in cell communication.; process of relaying signals within the cell.
Cellular Response
Final outcome of signal transduction pathway.
Quorum Sensing
Bacterial communication to assess population density.
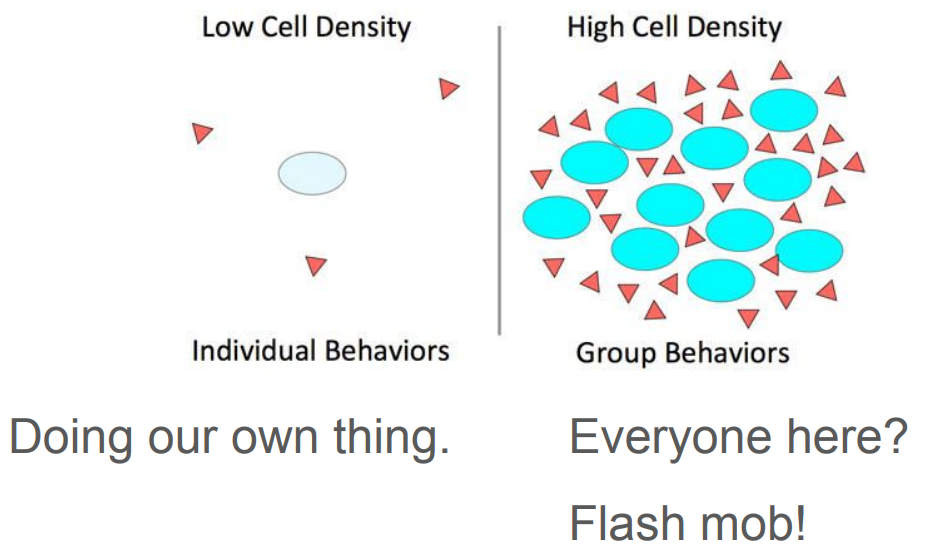
Biofilms
Communal structures formed by bacterial coordination.
G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Membrane receptors activating G proteins upon binding.
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
Receptors that dimerize and phosphorylate upon activation.
Ion Channel Receptors
Membrane proteins that allow ion passage when activated.
Cyclic AMP
Common second messenger in signal transduction.
Calcium Ions
Important signaling molecules in various cellular processes.
Transcription Regulation
Controlling gene expression by modifying transcription.
Cytoplasmic Activities
Modifying existing proteins' functions in response to signals.
Epinephrine
Hormone activating enzymes for immediate cellular response.
Response Variation Factors
Elements affecting how cells respond to signals.
sugar
The point of the Calvin cycle is to create ________
carbon fixation
Sub-steps of Calvin Cycle:
a) Rubisco (an enzyme) puts CO2 together with RuBP (a sugar) to form 3-phosphoglycerate (pre-G3P)
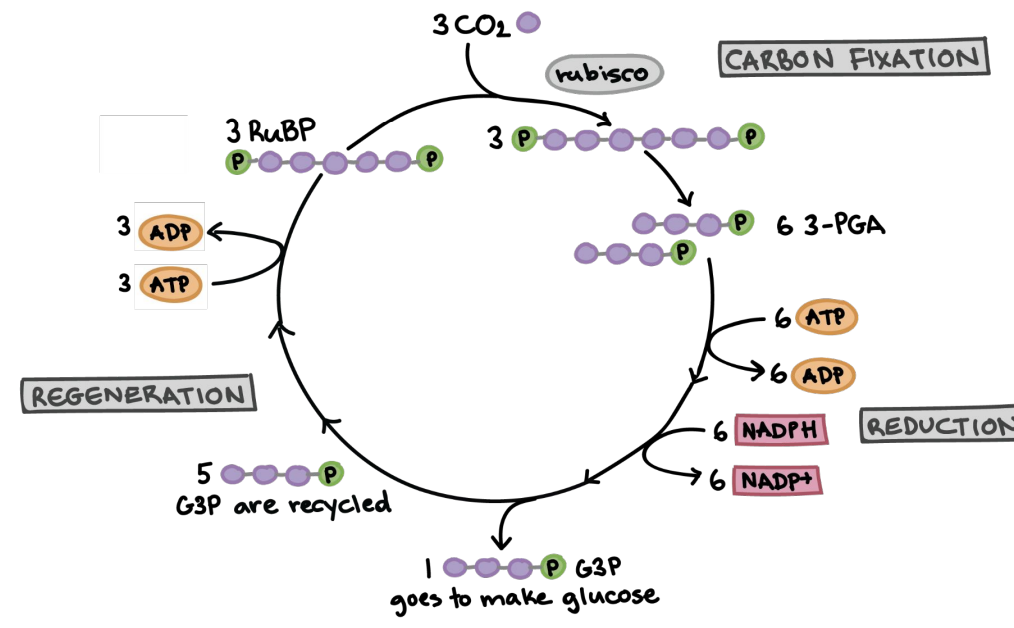
reduction
Sub-steps of Calvin Cycle:
b) Phosphate from ATP goes to 3-phosphoglycerate → G3P
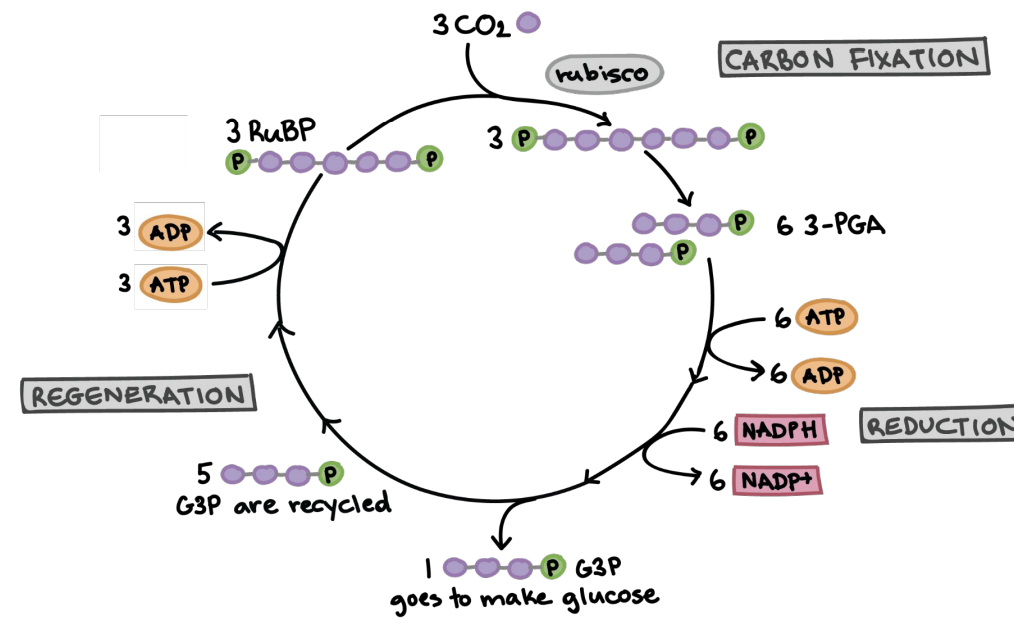
regeneration
Sub-steps of Calvin Cycle:
c) Remake RuBP for later
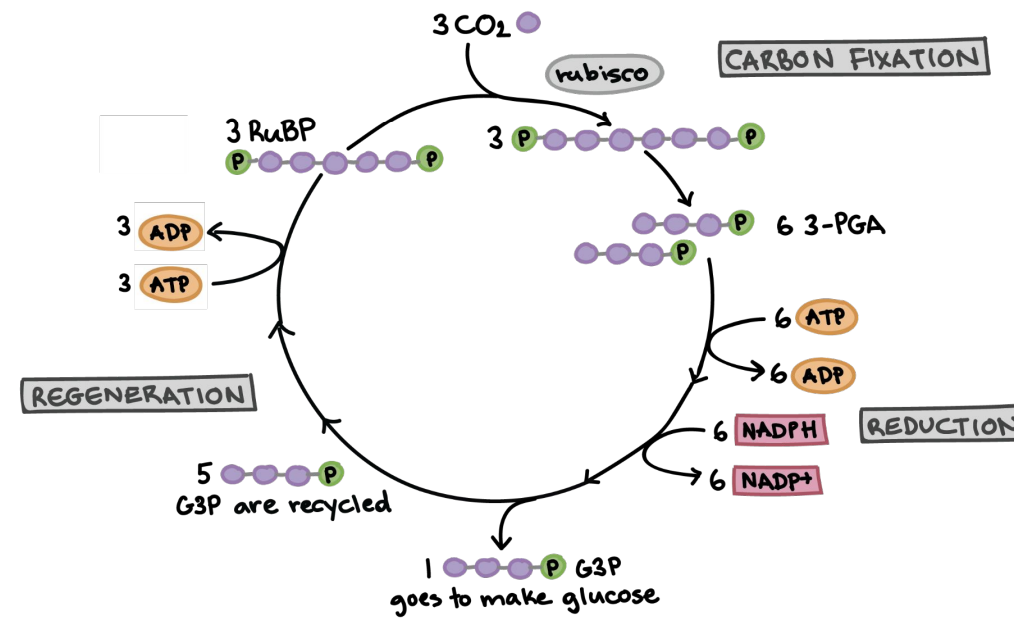
1
3 G3P make __ Glucose
after
Glucose is technically made right ________ the Calvin Cycle
sucrose
G3P is used to build other sugars, too, like ________
amphipathic
allows specific things to pass through
signal
Proteins in the cell membrane can also allow cells to _______ to one another
ATP
Powers reactions throughout the cell
call response
Step 3 in cell communication when something in cell is changed
cell communication
identify the picture
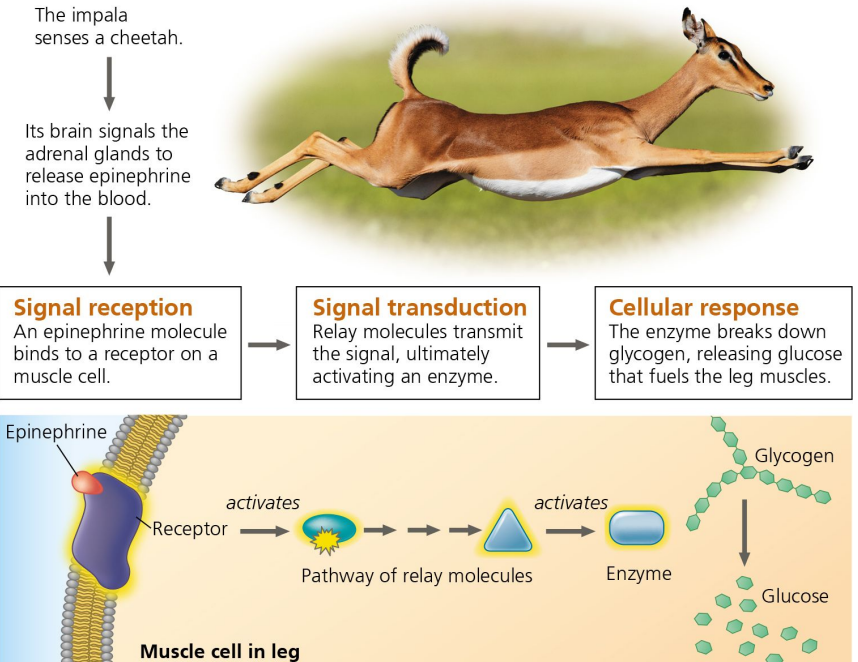
2
Yeast are single-celled fungi (Eukaryotic) with __ mating types:
𝛂 (alpha) and a
cell signaling
Yeast uses __________ to tell the difference between mating types
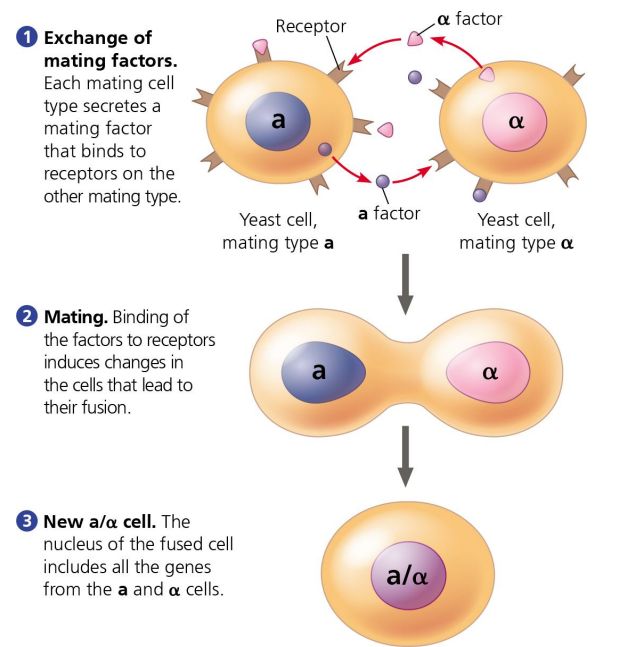
call junctions
signaling molecule
Receptor needs the ________ to begin breaking down glycogen in the cytoplasm