NS 3410 CC1- Receptor Mediated Endocytosis
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Disorders of Fe homeostasis are among?
most common diseases in humans
Iron is highly reactive so needs to be transported bound to?
a carrier protein
Old (senescent) red blood cells (RBC”s) lose their flexibility, get trapped in the ____, are catabolized, the Fe is _____
spleen; reutilized
What are 4 key cells regulate Fe:
Macrophage
Enterocyte
Hepatocyte
Erythroid precursors
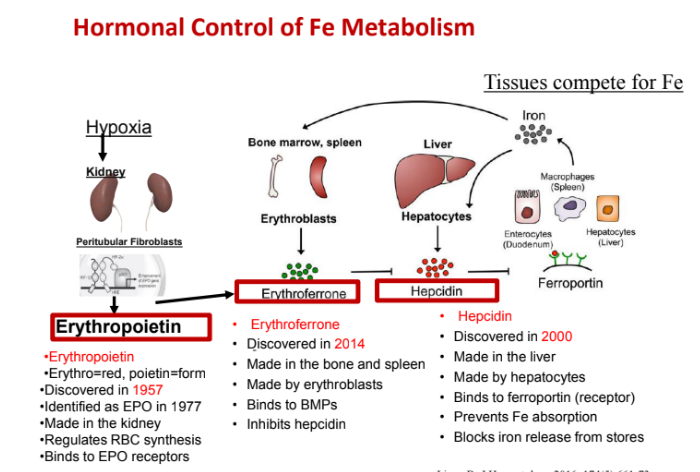
What stimulates Erythropoietin
hypoxia; inadequate supply of oxygen to the body's tissues
What does “erytho” mean?
red
What does “poietin” mean?
form
Where is erythropoietin made?
kidney
What does erythropoietin regulate? What does it Bind?
RBC synthesis; EPO receptors
Where is erythroferrone made in? What is made by? What does it bind to?
bone and spleen; erythroblast; binds to BMPs
What does Erythroferrone inhibit?
hepcidin
Where is hepcidin made in? What is it made by? What does it bind?
Made in the liver
Made by hepatocytes
Binds to ferroprotein (receptor)
Hepcidin prevents what? What does hepcidin block?
Prevents Fe absorption
Blocks iron release from stores
What unique aspect of Fe homeostasis predisposes humans to Fe overload?
there is no regulatable way to get rid of excess Fe that gets into the body; i.e no way to excrete excess Fe
Must balance the amount of iron absorbed as a function of body Fe demand
Iron must be in ______ to be absorbed but it ingested mainly as ______?
ferrous form (Fe2+); ferric (Fe3+)
In ENTEROCYTE Fe3+ reduced to Fe2+ by?
ferric reductase (Dcytb-duodenal cytochrome b)
Fe imported into cell by transmembrane protein ….?
DMT1; Divalent Metal Transporter
Once in the cell Fe enters the?
labile iron pool (LIP) and be stored as ferritin if not needed
If Fe is needed it is exported as Fe2+ by?
Ferroportin; ferroportin is the only iron export protein for non-heme Fe
Fe2+ (ferrous Fe) is oxidized to Fe3+ by?
Hephaestin (ferroxidase)
Fe must be in what form to bind to TfR?
Ferric 3+
Fe3_ binds to specific serum protein _____ to keep it in a non-reactive state
transferrin
What does “entero” mean
gut
What does “cyte”
cell
Iron uptake- Enterocyte

Iron uptake– Enterocyte Pt2

What unique property of enterocytes compared to the macrophage or hepatocyte makes this cell type effective at maintaining Fe balance?
Enterocyte physiology is unique compared to hepatocytes or macrophages. These cells turn over every 3 days and old cells are sloughed into GI lumen and lost in feces. Iron that stored as ferritin in the enterocyte would be lost from the body every 3 days. Liver cells must store iron indefinitely which can cause damage if too much is accumulated.
What does “em” mean?
blood
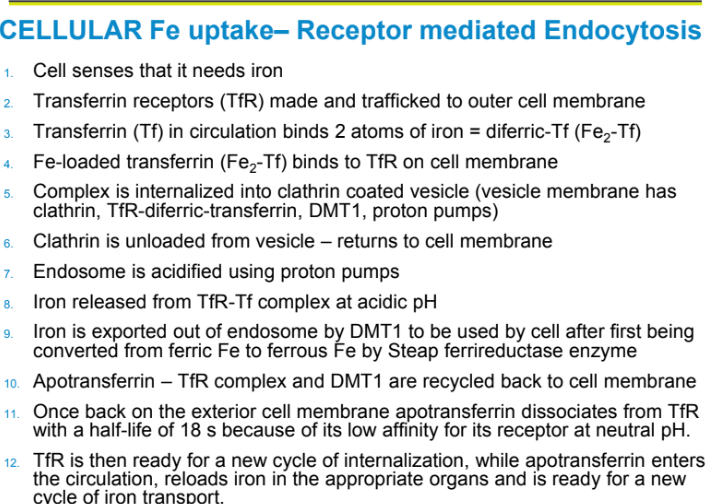
Once Fe is absorbed into the body what do target tissues need to express in order to capture Fe from the circulation?
Transferrin receptor to capture transferrin bound Fe by receptor mediated endocytosis cell must have receptor for Tf=TfR
What tissue likely has the highest expression of this?
Erythroid tissue- tissue that make RBC’s
Erythroid tissue is found in red bone marrow
Cellular Fe uptake- Receptor Mediated endocytosis: Iron is exported out of endosome by? Only after being converted from?
DMT1; converted from Ferric Fe to Ferrous Fe by Steap 3 ferrireductase enzyme
Summary
Transferrin is a very?
abundant plasma protein
Transferrin saturation normally about 30%; Transferrin bound Fe is the primary?
physiological source available to most cells under normal Fe status conditions
Cells regulate update of Tf-fe by altering the expression of?
TfR1
If too much Fe in circulation (Transferrin saturation excessive) some Fe can also bind to what 3 things?
Citrate
Albumin
Other low molecular weight compounds
non-transferrin bound Fe (NTBI)
NTBI in the plasma is taken up most avidly by the?
liver
to a lower extent by the pancreas and heart
Excess uptake of the NTBI form can cause?
oxidant mediated cellular injury
Laboratory Data: Microcytic, hypochromic anemia:

7. How can you have both anemia and tissue Fe overload?
Some cells (like erythroid tissue) rely only on TfR to take up Fe from the blood. Erythroid tissues have TfR but if there is no Tf-Fe in blood they can’t scavenge Fe from blood. This leads to low Hb concentrations (anemia) and high NTBI (the Fe must go somewhere since we can’t excrete it). Tissues like liver, heart pancreas, can take up NTBI so they develop Fe overload.
Different tissues express different proteins on their membranes giving specificity of functions in different tissues / organs in the body
Production of heme in erythroid tissue requires?
Tf-Fe
NTBI cannot be used by erythroid tissue to form?
heme
NTBI can’t upregulate?
hepcidin
Tf-Fe regulates hepcidin via?
TfR