Hearing Aids I
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Prep (BEFORE STARTING)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are the 4 main custom hearing aid styles?
BTE (Behind-the-Ear), RIC (Receiver-in-Canal), ITE (In-the-Ear), CIC (Completely-in-Canal)
Which HA style is best for severe-to-profound hearing loss?
Behind-the-Ear (BTE) — fits all HL types (mild to profound)
What is the occlusion effect?
A "plugged-up" feeling when natural sound can’t enter/exit the ear (common in BTEs)
What’s the difference between BTE and RIC styles?
BTE: Speaker/receiver is in the hearing aid body.
RIC: Receiver is in the ear canal (better for high-frequency HL, less visible than BTE, and offers a more natural sound experience.)
What is a BTE (Behind-the-Ear) hearing aid?
A style that sits behind the pinna, connected to tubing/earmold to route sound into the ear.
Pros of BTE?
Fits all HL types (mild to profound).
Durable; good for children (easy to adjust).
Offers directional mics for noise reduction.
easy to clean and maintain
Cons of BTE?
Visible (less cosmetic appeal).
Occlusion effect (plugged-ear feeling).
Who is BTE best for?
Severe/profound HL (e.g., "corner audiogram").
Those needing high power or durability.
What’s a "slim-tube" BTE?
A less visible BTE with thin tubing; reduces occlusion (good for high-frequency HL).
How does (Receiver-in-canal) RIC differ from BTE?
The receiver (speaker) is in the ear canal, connected to the BTE unit via thin wire.
Pros of RIC?
Less visible than BTE.
Reduces occlusion (open domes allow natural sound in).
Good for high-frequency HL.
Cons of RIC?
Less powerful than BTE (not ideal for profound HL).
Receiver can clog with earwax.
Who is RIC best for?
Mild to severe sensorineural HL (especially high-frequency loss).
What is an ITE (In-the-Ear) hearing aid?
A custom shell filling the outer ear bowl (full-shell or half-shell).
Pros of ITE?
Easier to handle (vs. smaller styles).
Fits mild to severe HL.
Can include telecoil and directional mics.
Cons of ITE?
Visible in the ear.
More feedback risk (due to mic/receiver proximity).
Who is ITE best for?
Those with dexterity issues (easier to insert than CIC).
What is a CIC (Completely-in-Canal) hearing aid?
A tiny, custom-molded aid that fits deep in the ear canal (nearly invisible).
Pros of CIC?
Cosmetically appealing (least visible).
Uses the ear’s natural acoustics.
Less wind noise (protected by canal).
Cons of CIC?
Short battery life (tiny battery).
Not for severe HL (limited power).
Hard to adjust (small size).
Who is CIC best for?
Mild to moderate HL; those prioritizing discretion.
Rank HA styles from most to least powerful
BTE > RIC > ITE > CIC.
Rank styles from most to least visible.
BTE > ITE > RIC > CIC
Which HA styles reduce occlusion best?
RIC (open domes) and slim-tube BTE.
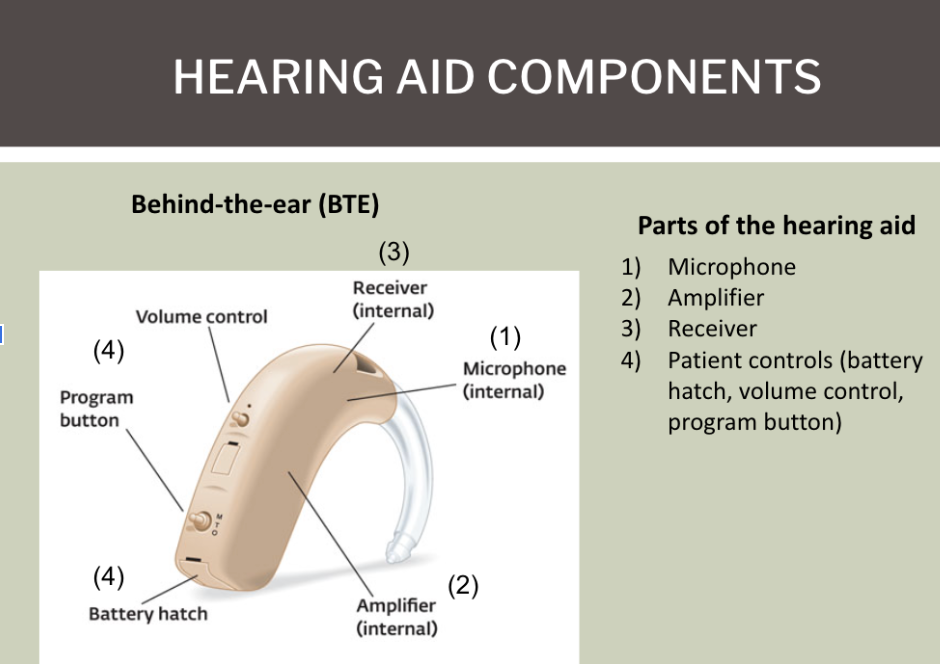
List the 4 main parts of a hearing aid
microphone, amplifier, receiver, battery
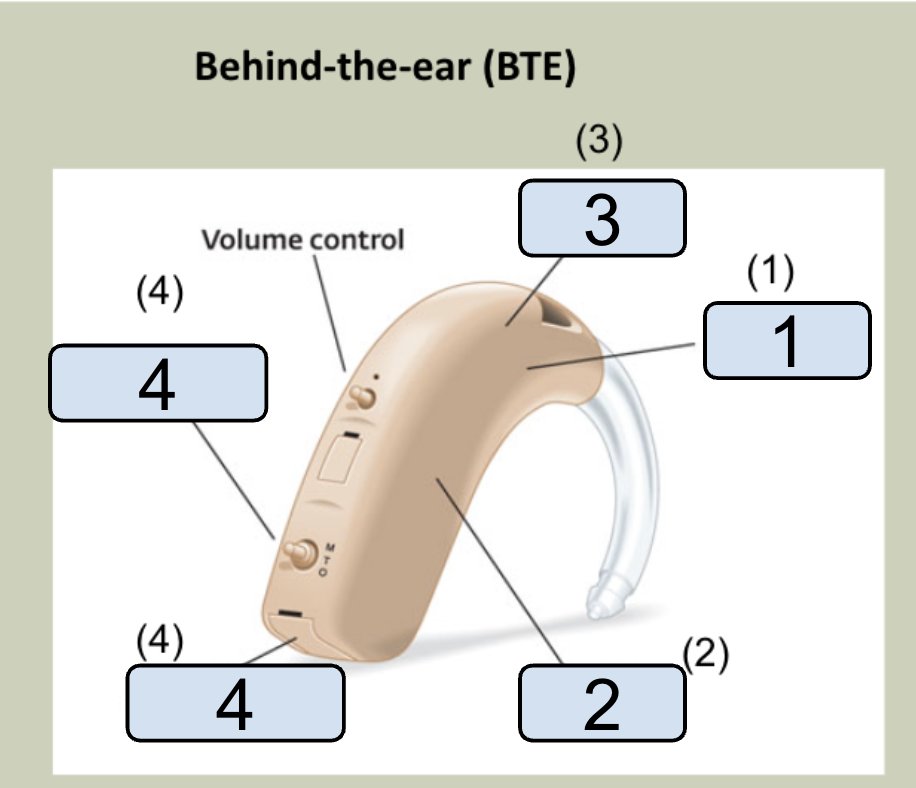
Identify the parts of the BTE HA
Look at image
What does the telecoil do?
Picks up magnetic signals (e.g., from phones/loop systems) for clearer sound.
What is venting?
Tiny air passages in earmolds that reduce occlusion/echo.
digital HAs
Converts sound to binary code; filters noise, customizable.
Analog HA
Amplifies all sounds equally; cheaper but less precise.
Why are digital HAs more common now?
Better noise filtering, feedback management, and customization.
How do directional microphones help?
Improve SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) by focusing on sounds in front of the user (e.g., speech in noise).
What is SNR (signal-to-noise) ratio?
the loudness of a signal, such as speech, compared to the loudness of any unwanted background noise.
The higher it is, the louder and easier to hear a signal is
The lower it is, the harder it is to understand the signal; noise is louder.
What is gain?
The amount of amplification a HA provides.
How does noise reduction work in digital HAs?
Detects modulated (speech) vs. unmodulated (noise) sounds and suppresses steady noise.
Which battery is smallest and lasts 2–3 days?
Size 10 (yellow tab).
Which battery is used for powerful BTEs?
Size 675 (blue tab; lasts 7–14 days).